| Citation: | Zhu Zhaoyu, 1997. TECTONIC ACTIVITY IN SEMI-ARID AREA OF NORTH CHINA DURING LATE QUATERNARY. Journal of Geomechanics, 3 (4): 13-19. |
近年来,随着我国经济建设的快速发展和西部开发战略的不断深入,滇西南地区成为当前重大工程建设的重要区域[1]。一系列大型-超大型生命线工程正在该区建设和规划[2-3],如大瑞(大理-瑞丽)铁路、中缅油气管道、中印公路等,以大瑞铁路为代表的西南泛亚铁路网已初步形成,为向西南入缅甸、向西经密支那入印度奠定了基础。大瑞铁路是我国首条穿越横断山脉的国家Ⅰ级干线铁路,该区的地质环境条件可以概括为“三高、四活跃”,即:高地热、高地应力、高地震烈度;活跃的新构造运动、活跃的地热水环境、活跃的外动力地质条件、活跃的岸坡浅表改造过程[1-3]。活跃的内外力地质作用导致该区成为环境工程地质条件极其复杂的地区,特殊的地质环境孕育了多种地质灾害和工程地质问题,并以类型全、数量多、规模大为特点。在众多地质灾害或不良地质现象中,除了活动断裂和地震外,以滑坡、崩塌和泥石流等浅表层地质灾害以及高地应力、高地热和深埋隧道岩爆等工程地质问题最为普遍[1, 4-6]。近年来该地区地质灾害发育强烈,单体规模大,如2007年腾冲7.19苏家河口水电站滑坡等[7],导致了大量的人员伤亡和财产损失,严重的地质灾害事件已成为影响大型工程规划建设和社会经济发展的主要工程地质问题之一[8-9]。
规划建设中的大瑞铁路高黎贡山越岭段位于横断山脉东南段瑞丽和保山之间(见图 1),线路长约110 km,西南地区极其复杂的地质条件在该区表现尤为突出,活动断裂、地震、浅表层地质灾害(崩塌、滑坡和泥石流等)、隧道塌方、岩爆、软岩大变形、突水、高地温等一系列复杂的地质问题严重制约着铁路规划建设。越岭段方案从2006年即开始研究,目前已进行了多条线路方案的比选,仍未确定。各比选方案[2, 10-11]都不可避免地涉及高黎贡山深埋隧道,而复杂的地质条件导致该隧道具有岩爆、软岩大变形、突水、高地温等不良工程地质问题[1-4, 9-15]。本文结合大瑞铁路高黎贡山越岭段综合地质勘查和专题地质研究工作,对该段的主要工程地质问题进行分析,确定了在复杂地质环境条件下铁路地质选线的技术原则,重点研究地下热水活动区的综合地质选线,选定了工程地质条件相对较好的隧道线路方案,并进行优化。本文的研究思路和研究方法,既可指导大瑞铁路高黎贡山越岭段的规划设计,为大瑞铁路的全线贯通提供技术支撑,又可为以后国家重大工程规划和布局提供参考。
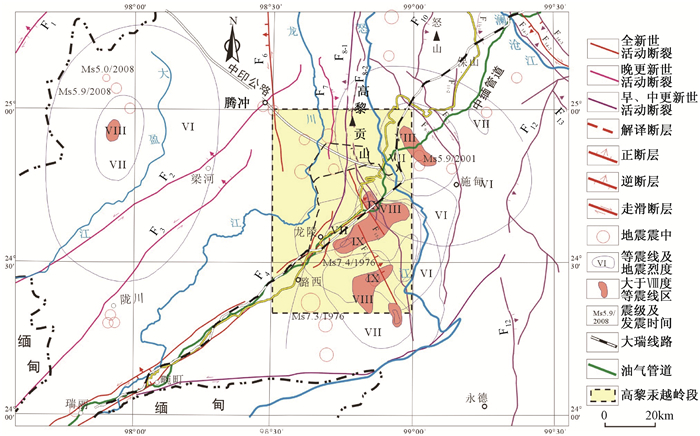
研究区地处印度板块与欧亚板块碰撞缝合带附近,横断山脉南段,铁路沿线山高谷深。线路横跨怒江后穿越高黎贡山,地形起伏度大。高黎贡山主峰高约3001.6 m,与怒江河面相对高差2140~2360 m。大地构造上属滇缅泰亚板块之保山地块和腾冲地块,两地块之间为挤压碰撞的怒江缝合带。研究区加里东和燕山末期发生褶皱变质,形成高黎贡山构造岩浆变质杂岩带;喜马拉雅运动以来,受印度板块向北(偏东)的强烈推挤和青藏高原向南南东强力楔入的叠加作用,地壳强烈抬升,加之川滇菱形块体向南南东滑移,导致区内新构造运动十分强烈,褶皱和断裂构造极其发育,表现为强烈的垂直差异运动和块体的侧向滑移及以近南北向断裂、北西向断裂右旋位移和北东向断裂左旋位移为代表的断裂活动(见图 1)。大瑞铁路高黎贡山越岭段内线路比选区大型断裂主要有(见图 1):怒江断裂带(F8-2)、龙陵-瑞丽断裂带(F4)、黄草坝断裂(F4-1),其中龙陵-瑞丽断裂、黄草坝断裂等为第四纪活动断裂。龙陵-瑞丽断裂全新世以来的走滑速率为0.81~1.35 mm/a[16];龙陵-澜沧断裂断错镇安盆地晚更新世砾石层。
研究区除白垩系缺失外,自寒武系至第四系均有出露,岩性复杂,既包括不同时代的碎屑岩、碳酸盐岩、变质岩,也包括不同时期的岩浆岩。新生界主要分布于河谷及断陷盆地,岩浆岩在区内广泛分布。区域活动断裂发育,新构造运动和水热活动强烈,强地震频发,岩体破碎,滑坡、错落、危岩落石、崩塌、岩堆、泥石流等斜坡不良地质体极为发育。
由于高黎贡山越岭段地形地貌和地质条件非常复杂,虽然经过多轮论证,线路方案仍很难确定。主要比选方案有CK、C1K、C4K、C10K、C12K、C22K和南绕方案(C5K)等(见图 2),各方案中除南绕方案外,铁路主要以隧道和桥梁两种形式通过,具有桥梁跨度大、隧道长且埋深大等特点。多条比选线路中高黎贡山隧道均较长,无论是39.6 km隧道方案(CK)、17 km隧道方案(C4K)、24‰大坡度方案(C9K、C10K),还是后期推荐的拉通方案(C12K)都不可避免地涉及高黎贡山深埋隧道,以CK线路方案为例,隧道全长39.6 km,最大埋深约1600 m(见图 3)。复杂的地质条件导致该隧道具有岩爆、高地温、地下热水、涌水突泥和断裂断错等工程地质问题[10-11, 12-15],且工程建设难度大。
活断层作用有时仅引起地震,有时仅造成地面错动,有时既引起地震,同时又产生地面错动,此即活断层的断错效应。高黎贡山地区近年来发生的多次强震与正在规划建设的高黎贡山深埋隧道相距较近,如:1976年龙陵Ms 7.4级地震,震中位于隧道东南,最近处仅相距4 km,隧道部分地段位于地震烈度Ⅶ度和Ⅷ度区内(见图 1);2001年施甸Ms 5.9级地震,震中与隧道怒江端入口相距11 km,隧道口位于地震烈度Ⅶ度区内(见图 1)。这些地震在造成地表变形破坏的同时,也导致断裂带附近深部岩体产生显著变形和位移。
高黎贡山深埋隧道越岭段的黄草坝断裂、龙陵-澜沧断裂带的镇安断裂和勐冒-平达断裂均为第四纪活动断裂,断裂活动性较强,历史地震较多。高黎贡山深埋隧道越岭段C12K方案与黄草坝断裂平行,地表平面上最近处相距约1.9 km,高黎贡山深埋隧道位于黄草坝断裂的下盘,在隧道埋深附近与断裂相距一般为1.9~3.0 km,高黎贡山深埋隧道与龙陵-澜沧断裂带的镇安断裂和勐冒-平达断裂近于直交。大量事实表明,发震断裂会在地表形成一定宽度的破裂影响带,影响带内既会出现新生破裂,也会使原有破裂发生错动或进一步扩展,从而影响布设其中的工程设施。因此,对于高黎贡山深埋隧道,存在活动断裂的断错效应问题,应采取有针对性的防治措施。
高黎贡山越岭段位于地中海-南亚地热异常带,为区域性高热流区,区内高温沸泉、热泉、温泉、硫磺喷气孔等数量多、密度大,除受构造控制外,还受地形地貌条件的制约。高地温对工程建设具有极大的影响,如:位于金沙江断裂带的娘拥水电站1#施工支洞在施工过程中即受到了高地温的影响,该支洞地面高程约3060 m,长295 m,出露花岗片麻岩和砂岩夹板岩,2008年4月24日进洞,岩体温度30~50 ℃,每进洞10 m,岩温增加1 ℃,最高达78 ℃。地温升高导致以下问题[12]:① 作业人员经常出现头晕、呕吐现象,作业期间开始加大通风;② 围岩表面产生潮解现象,遇水即成粉末,岩面喷射混凝土后立即脱落,无法粘结;③ 使用普通硝铵炸药开始产生膨胀甚至包装纸破裂,导爆管发生软化失去弹性,挤压后无法回复原状;④ 施作的砂浆锚杆强度抗拔力不能满足设计要求;⑤ 出碴设备每作业1 h左右,机体温度升高就要出洞冷却;⑥ 测量仪器测距失效。这些问题导致工程投资加大,并且会延误工期。目前国内外尚无成熟技术处理洞内温度大于72 ℃的高地温、高温热水(汽)的经验和措施。
调查表明,高黎贡山越岭段内出露温泉群123个,水温20~102 ℃,其中低温泉(20~40 ℃)85处,中温泉(40~60 ℃)25处,高温泉(60~95 ℃)12处,沸泉(>95 ℃)1处,主要集中分布在怒江河谷、高黎贡山转折端、苏帕河流域、潞西-遮放盆地及腾冲-梁河-攀枝花硝塘等五大区域,温度最高的为龙陵邦腊掌温泉(见图 4),泉口温度102 ℃。线路比选区穿越多个地温热泉发育区,在深埋长隧道施工过程中可能会遇到高温高压热水(汽)及高温岩体等热害问题。
复杂的地质构造演化过程和强烈的新构造活动导致本区地应力普遍很高,加之该区比选线路隧道埋深大,高地应力意味着深埋隧道开挖过程中,在硬岩(石灰岩、片麻岩、花岗岩、砂岩等)分布区将不可避免地出现岩爆灾害,而在泥质岩、断裂破碎带等软弱岩体分布区会出现围岩大变形等工程地质问题,给隧道工程建设带来很大安全隐患。为了进一步掌握隧道附近地应力状况,中铁二院在高黎贡山越岭段深埋隧道线路比选区采用钻孔水压致裂法进行了深孔地应力测试,地应力测试孔主要分布于CK线(39.6 km隧道方案)、C1K线(21 km隧道方案)以及C12K线(34.5 km隧道方案)等线路附近,地应力测试孔深度600~1200 m。
根据各方案钻孔内地应力测量结果(见图 5),CK方案钻孔洞身附近最大水平主应力(σH)值20~29 MPa,最小水平主应力(σh)值13~19 MPa,估算的垂直主应力(σv)取决于各孔洞身埋深,为17~23 MPa;C1K方案最大水平主应力值14.0~30.7 MPa,最小水平主应力值10~22 MPa,估算的垂直主应力值为16~21 MPa;C12K洞身附近的最大水平主应力值为15~24 MPa,最小水平主应力值11~17 MPa,垂直主应力17~23 MPa。从各方案实测地应力值可见,隧道埋深附近地应力最大值分布特征一般以σv≥σH>σh为主,部分为σH≥σv>σh,但此时σH与σv值相差不大,一般仅为1~2 MPa,从最大主应力值大小来看,隧道埋深附近岩体处于高地应力状态。
大瑞铁路高黎贡山深埋隧道具有埋深大、距离长的特征,复杂的高地应力条件和岩性条件,预示着在该隧道开挖过程中将不可避免地出现岩爆灾害。以CK方案为例,高黎贡山隧道长约39.6 km,一般埋深600~1000 m,最大埋深约1600 m。张永双等[14]对大瑞铁路高黎贡山越岭段勘察钻孔中的花岗岩、大理岩等典型岩体进行了岩石力学实验和岩爆模拟实验,岩爆模拟试验结果表明,高黎贡山深埋隧道围岩发生岩爆的可能性高,单纯卸载和卸载-加载方式都可以出现岩爆,但卸载-加载方式的岩爆明显比单一卸载方式的岩爆强烈,说明隧道开挖后二次应力分布引起的应力集中对岩爆的发生起着十分重要的作用。在复杂地质背景条件下,岩爆会成为制约高黎贡山深埋隧道工程规划建设的主要工程地质问题之一[1, 13-15]。
高地应力条件下,隧道工程建设过程中软岩段常易发生大变形。高黎贡山深埋隧道穿过中志留统(S2)泥岩和寒武系公养河群上段(Єgn2)泥岩、千枚岩段,这几种岩石强度均较低,发生大变形的可能性较大;断层破碎带在高地应力条件下也易发生大变形。此外,研究区构造岩浆活动强烈,热液成矿带分布较多,与此相关的蚀变岩出露较多,如在C12-G-01、C12-G-03、C12-G-06、CZ-G-14、C2-17km-01等钻孔中均揭露蚀变岩(见图 6),多为蚀变花岗岩,蚀变岩的分布和其工程地质性质对工程的规划设计具有重要的影响。总体上,蚀变岩在区内主要发育于花岗岩、玄武岩等岩浆岩的岩体内,或岩浆岩与其他岩性的交界处,与岩浆活动和地下热水活动关系密切。蚀变岩具有强度低、易膨胀等不良工程地质特性,在隧道掘进和边坡开挖过程中常出现岩体变形破坏问题。如:滇藏铁路大理-丽江段的禾洛山隧道,围岩为遭受热液蚀变的玄武岩,宏观上表现为相对较完整的玄武岩夹蒙脱石化蚀变岩组合。在工程施工过程中,自DK55+622至DK61+710约5 km的范围内,曾发生过5次与蒙脱石化蚀变岩有关的塌方问题[17],有时甚至不到100 m就会出现一次塌方,塌方体积一般20~30 m3,塌方的出现主要是由于蚀变岩富含蒙脱石且性质软弱,在干湿交替和松弛条件下极易发生膨胀变形,加上围岩节理发育、破碎程度高,开挖后自稳能力差,从而造成围岩坍塌。因此,在大瑞铁路高黎贡山越岭段内铁路规划要密切关注隧道塌方与软岩大变形问题。
大瑞铁路高黎贡山越岭段地形地貌复杂,大致以象达-黄草坝-镇安-邦迈-小地方为分水岭,以东地带属怒江流域,以西地带属瑞丽江流域。分水岭以东主要分布有岩溶断块山底、中山中切割陡坡、垄岗谷地及高中山深切割峡谷等地貌,近山脊部位可见陡崖分布,地形条件有利于地表水的排泄。地表水均向东或南东方向排泄于怒江河谷,但在斜坡中部及近河谷地带,由于岩溶断块山地及垄岗谷地形、地表溶蚀裂隙、落水洞、漏斗发育,利于地表水入渗,潜在的涌水威胁和危害较大。分水岭以西斜坡地带属瑞丽江流域,地形条件有利于地表水排泄,主要为低中山浅切割缓坡、岩溶断块山地及中山中切割陡坡地形,地表水均向西或南西方向排泄于龙川江及芒市河;龙陵县城南西侧多分布岩溶断块山地地形,地表溶蚀裂隙发育,地表水入渗条件较好,隧道在施工过程中存在较大的突涌水危害和威胁。
越岭段铁路沿线碳酸盐岩类主要分布于怒江左岸中侏罗统(J2),分布范围较广,岩性主要为石灰岩、白云质灰岩、白云岩等,另外在龙陵以南隧道出口附近,也分布有大套的泥盆系回贤组(D2h)白云岩、石灰岩。区内碳酸盐岩富水性中等-强,岩溶弱-中等发育。地表局部可见溶蚀孔洞,但未发现大规模的溶洞。在隧道岩溶地下水垂直渗流地段,施工中可能遇竖井状溶洞,雨季隧道易受涌水、突泥的危害;另外,地下水水平径流带内岩溶水量较大,隧道开挖揭露该地带时,常易形成大规模突水。
越岭段内地质构造发育,断层破碎带中断层角砾和构造裂隙发育,岩体破碎疏松,断裂和褶皱内有潜在充水现象,隧道施工中可能存在多处由断裂导水通道、裂隙型与岩溶型导水通道等带来的涌水突泥灾害风险,涌突水水源可能来自地下水及地表大气降水等。
此外,越岭隧道工程施工人为地破坏了地质与地下水系统的压力平衡状态,爆破过程中隧道围岩也遭到破坏,隧道顶板易形成冒落带、裂隙带及整体移动带,其中冒落带、裂隙带可成为隧道充水水源进入隧道的通道,从而改变含水系统地下水的补给、径流条件,使隧道采空区成为地下水的排水场所,从而引起涌水突泥及对隧道围岩稳定造成影响。
高黎贡山越岭段内地质灾害发育强烈,地质灾害类型主要有崩塌、滑坡和泥石流,区内发育有528个崩塌(含岩堆)、滑坡和泥石流等地质灾害点。在区域上,地质灾害多分布于怒江两岸及龙川江两岸,人类活动密集区也有较多分布。如C12K线怒江大桥两侧桥墩即受等子滑坡(见图 7)等的影响,C12K高黎贡山深埋隧道龙陵出口处分布有凹子地古滑坡体等,是隧道工程勘察设计和施工中应重点防护的部位。
所谓高温,是指建设工程的工作面气温超过28 ℃;所谓高湿,是指相对湿度超过80%[2]。根据工程施工及劳动防护要求,高黎贡山越岭段地温带可划分为常温带(T≤28 ℃)、低高温带(Ⅰ)(28<T≤37 ℃)、中高温带(Ⅱ)(37<T≤60 ℃)和超高温带(Ⅲ)(T>60 ℃)等4级(见表 1),中高温带进一步细分为中高温带Ⅱ1(37<T≤50 ℃)、中高温带Ⅱ2(50<T≤60 ℃);断裂导热水能力、热害分析评估标准、隧道施工处理措施也相应分为4级。
| 地温带 | 温度界限T/℃ | 热害分析评估标准 | |
| 常温带 | ≤28 | 无热害 | |
| 低高温带(Ⅰ) | 28<T≤37 | 热害轻微 | |
| 中高温带(Ⅱ) | 中高温带(Ⅱ1) | 37<T≤50 | 热害中等 |
| 中高温带(Ⅱ2) | 50<T≤60 | 热害较严重 | |
| 超高温带(Ⅲ) | >60 | 热害严重 | |
研究区位于印度板块与欧亚板块碰撞带东部,地质构造复杂,地热显示与地质构造密切相关,大部分温泉热源是较高大地热流背景下,大气降水沿断裂裂隙带下渗,经深循环加热形成带状分布的断裂深循环型中低温地热系统。研究区162组温泉水和地表水体同位素分析结果显示,地热水的δD均落在腾冲大气降水线上或附近,少数水热区的δ18O稍有漂移,证明区内地热水来源于大气降水,δ18O漂移量小,亦说明区内水热区多为中、低温水热系统(温度低于150 ℃)。
越岭段内断裂以南北向为主,次为北东向、北西向(见图 2)。在现代近南北向构造应力场的作用下,近南北向压扭性超壳断裂转化为张性或张扭性断裂,是地热水的主通道。北东向、北西向断裂与主应力交角大者主要以压扭性为主,对地热水径流起着阻隔作用;交角小者多为张扭性,起导水作用,即黄草坝断裂(F3-1,见图 2)多为阻水隔热断裂,F3-1-1(见图 2)多为导水导热断裂。黄草坝断裂(F3-1)是区内阻水隔热的主要断裂之一,直接控制了高黎贡山-三台山弧形构造水热活动带南北两侧朝阳-平达水热活动亚带、邦腊掌-黄草坝水热活动亚带地下热水的补给、径流、排泄条件。
研究区水热活动显现与岩浆长期大规模的持续侵入、变质岩带的分布和活动性断裂系统密切关联,其空间展布明显与区域构造带相一致。水热活动以怒江断裂、龙川江断裂为界,划为怒江南北向构造带(Ⅰ)、高黎贡山-三台山弧形构造带(Ⅱ)、腾冲-梁河弧形构造水热活动带(Ⅲ)等3个水热活动带(见图 8);高黎贡山-三台山弧形构造水热活动带(Ⅱ)以黄草坝断裂为界,进一步可分为邦腊掌-黄草坝水热活动亚带(Ⅱ-1) 和朝阳-平达水热活动亚带(Ⅱ-2)2个亚带。
根据研究区专题地质研究实施的55个深孔及20个浅孔钻探孔内测温测试分析结果,研究区地温场有以下特征:
① 除邦腊掌一个钻孔属对流热流外,其他钻孔温度类型均为传导热流。
② 地温变化总的趋势是:东西方向,高黎贡山东西侧相对较低,中部相对较高;南北方向,北部温度等值线较密,向南部撒开,与区内构造线相一致。
③ 研究区平均地温梯度为3.02 ℃/100 m。在新生代,盆地的地温梯度一般均高于基岩;地温梯度变化趋势是由东至西从低变高,由北向南则从低至高再变低。
根据上述划分标准,用区内施钻的55个钻孔资料及123处水热区泉水温度,在地热地质图上做出最高温度等值线,并结合地下水点、断流构造、地层岩性以及地形地貌圈定地温带。隧道埋深层面的地温研究采取拟选隧道底面做温度等值线,即把C12K、CK、C1K、C4K的隧道底面视为一个平面,没有钻孔控制的部位用区内平均地温梯度(3.02 ℃/100 m)算至底面温度;水热区用对流热流值计算底面温度,最终形成隧道底面温度等值线图(见图 9)。从图 9可见,隧道埋深层面地温变化值为20~100 ℃,主要分布在30~70 ℃之间,根据表 1的划分标准,隧道层面地温共划分出11个超高温带(Ⅲ),面积14.46 km2,占总面积的0.39%;中高温带18个,面积682.95 km2,占总面积的18.24%;低高温带11个,面积1008.96 km2,占总面积的26.95%;常温带3个,面积2037.06 km2,占总面积的54.42%。超高温带零星分布在中高温带中间,其中以龙陵邦腊掌温泉地区面积最大,其次为潞西澡堂头和象达乡一带。
常温带沿龙川江、怒江河谷沿岸及芒市盆地周边山麓分布,就工程而言,主要体现在越岭隧道进出口浅埋段、地热水补给区、径流区。
高温带(低高温带、中高温带、超高温带)分布主要受构造控制,占总面积的45.58%,分布广泛,严重制约了越岭线路方案、尤其是隧道工程的比选和工程可行性。
受黄草坝断裂阻水隔热作用,邦腊掌-黄草坝水热活动亚带地热水排泄区以南,朝阳-平达水热活动亚带地热水补给区一定范围内,存在一条相对低温区,为越岭长隧道的选址提供了通道。
影响高黎贡山越岭地区选线和重大工程设置的地质因素众多,地质选线原则的确定直接关系着选线质量和重大工程的可行性。选线原则需要在综合地质勘察的基础上,结合相关专题研究成果确定。
① 由于国内外尚无成熟技术处理洞内温度大于72 ℃的高地温、高温热水(汽)的经验和措施,隧道工程必须绕避可能大范围出现严重热害的高地温地区。
② 隧道工程必须通过高地温地区时,应尽量绕避或远离中高温带及高温带,选择在常温带和低高温带通过。
③ 线路通过高地温地区时,宜以桥与路基形式通过;当必须以隧道通过时,应尽可能减少隧道埋深。
④ 高烈度地震区选线,应尽量提高线路抵御地震次生地质灾害的能力,有条件时应优先选用隧道工程。
⑤ 应综合考虑地质、地震因素,重视地震放大效应、近场区的地震效应,线路应绕避既有的地震及地震次生灾害严重地段和重力不良地质集中发育地段。
⑥ 线路宜短距离、大角度通过深大断裂,应避免在深大断裂带内迂回展线;避免采用高墩大跨及特殊结构桥直接跨越全新世活动断裂。
⑦ 鉴于研究区特殊的地质、地震和地应力场环境,选线应尽量减少顺岩层走向隧道长度。
⑧ 隧道洞口、桥梁墩台和路基工程应避开斜坡不稳定、不良地质发育或可能发生重大地震次生灾害的地段或地貌部位。
随着重大工程建设的发展,在地质灾害和工程地质问题防治领域的技术也日益发展,包含深埋隧道岩爆防治与预测、涌水突泥、软岩大变形等方面,并且在施工过程中取得良好的效果[8, 11, 13],因而高地温、高地热是制约高黎贡山越岭段地质选线的关键问题。综合上述地质选线原则,在高黎贡山越岭地区是否能发现相对低温的通道就成了选线的重点;同时,考虑活动断裂和边坡稳定性,开展地质选线综合研究,从而有利于综合防灾减灾。
从图 8、图 9中可以看出,虽然常温带和低高温带占总面积的80%以上(地表为90.2%,隧道层面为81.37%),但有较多的中高温带和高温带穿插其间,对铁路线路,尤其是隧道工程影响较大。
根据CK、C1K、C4K、C5K、C10K、C12K和C22K等方案的工程地质条件和工程地质问题,从高地温、断裂构造及不良地质条件3方面进行综合对比(见表 2)。
| 比选内容 | C12K | CK | C4K | C1K | C10K | C5K | C22K | ||
| 地热地质条件 | 隧道路肩面温度所占比例/% | 常温带 | 63.90 | 36.90 | 39.60 | 27.60 | 近100 | - | 100 |
| 低高温带(Ⅰ) | 34.10 | 61.10 | 32.10 | 23.80 | 无 | - | 无 | ||
| 中高温带(Ⅱ1) | 2.0 | 2.0 | 20.45 | 39.02 | 无 | - | 无 | ||
| 中高温带(Ⅱ2) | 无 | 无 | 7.10 | 6.75 | 无 | - | 无 | ||
| 高温带(Ⅲ) | 无 | 无 | 0.75 | 2.83 | 无 | - | 无 | ||
| 地温梯度(℃/100 m) | 1.68 | 1.78 | 3.66 | 3.91 | - | - | - | ||
| 热流值/(mW·m-2) | 29.2~52.2 | 30.9~52.2 | 52.5~190 | 52.5~190 | - | - | - | ||
| 岩温产热率(10-2 J/m2·s) | 2.4~4.3 | 3.0~3.5 | 3.0~6.4 | 6.5~12.0 | - | - | - | ||
| 隧道地热地质条件 | 位于相对低温通道 | 位于相对低温通道 | 穿越高地温地区,龙陵隧道进口地段高温热害严重 | 穿越高地温地区,龙陵隧道进口地段高温热害严重 | 线路多以路基、桥通过,避免了隧道高地温危害 | 穿越高地温地区,隧道热害严重 | 线路多以路基、桥通过,避免了隧道高地温危害 | ||
| 断裂构造 | 线路大角度与断裂构造大角度相交 | 线路大角度与断裂构造大角度相交 | 高黎贡山隧道位于断裂构造蜂腰部位,引线段与构造线平行 | 高黎贡山隧道位于断裂构造蜂腰部位,引线段与构造线平行 | 在断裂构造密集地区迂回展线 | 引线段与断裂构造平行 | 在断裂构造密集地区迂回展线 | ||
| 不良地质 | 绕避 | 引线段不良地质发育 | 引线段不良地质发育 | 不良地质发育 | 不良地质发育 | 不良地质发育 | 不良地质发育 | ||
| 工程地质条件评价 | 较好 | 好 | 差 | 差 | 差 | ||||
综合分析表明,南绕方案(C5K)大范围穿越朝阳-平达水热活动亚带地热水排泄区,深埋长大隧道高温热害问题突出,引线段平行于构造线,不良地质构造发育,线路抵御自然灾害和地震次生灾害的能力低;C1K、C4K等线路不同程度通过中高温带,C10K、C22K在邦腊掌一带有约2.5 km左右通过高温带。相对比而言,C12K(34.5 km隧道方案)和CK(39.6 km隧道方案)位于黄草坝阻水隔热断层之南相对低温通道内,地热危害较轻,线路与断裂构造大角度相交,工程地质条件较好。C12K作为CK的优化方案,线路抬高了156 m,改善了隧道环境地温,绕避了引线段不良地质构造,线路抵御自然灾害的能力相对较强,工程地质条件相对较好。
经综合比选,推荐采用工程地质条件相对较好,位于黄草坝阻水隔热断层之南相对低温通道内的C12K(34.5 km隧道)方案。但越岭长隧道开挖后,会形成新的地下水排泄低势面,改变地下水径流、排泄条件,如果隧道开挖不限制地下水排放,仍会导致隧道区水文地质条件复杂化,在高水头渗流条件下致使黄草坝阻水隔热断层的隔水能力减弱,甚至可能袭夺邦腊掌-黄草坝水热活动亚带的地下热水。因此施工过程中需要及时进行地下水监测与分析,并根据监测结果及时控制地下水排放。
大瑞铁路高黎贡山越岭段主要工程地质问题有:高地温、高地应力、活动断裂断错、岩爆、涌水突泥、软岩大变形和边坡稳定性等,其中高地温、高地热是制约高黎贡山深埋隧道规划建设的关键问题。
高黎贡山越岭段的地热分布在平面上可以分为3个区,地下热水的分布和运移与断裂构造密切相关,黄草坝断层的阻水隔热断层特性和地热水的空间分布特征,使得该断层之南存在一个相对低温通道。
从高地温、断裂构造和不良地质条件3个方面的差异特征对比选方案进行综合比选表明,通过黄草坝阻水隔热断层之南相对低温通道内的C12K方案地热危害较轻,是相对较好的一条方案,并且受断裂活动和边坡地质灾害影响较小。
复杂地质构造条件下,越岭铁路的地质选线是一个复杂的工程地质问题,需要综合考虑多种不良工程地质条件,特别是在具有高地热、高地下热水发育区内进行具有深埋隧道的地质选线,目前国内外经验还不足,相关理论和方法需要结合实际工程经验进一步完善。
致谢: 云南地质工程第二勘察院腾冲地热队和勇高级工程师、余仕勇高级工程师,成都理工大学许模教授、杨艳娜博士,中国地震局地壳应力研究所郭啓良研究员、包林海博士等参加了野外调查、测试分析工作。中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所曲永新研究员对本文提出了修改建议,在此一并感谢。| 地温带 | 温度界限T/℃ | 热害分析评估标准 | |
| 常温带 | ≤28 | 无热害 | |
| 低高温带(Ⅰ) | 28<T≤37 | 热害轻微 | |
| 中高温带(Ⅱ) | 中高温带(Ⅱ1) | 37<T≤50 | 热害中等 |
| 中高温带(Ⅱ2) | 50<T≤60 | 热害较严重 | |
| 超高温带(Ⅲ) | >60 | 热害严重 | |
| 比选内容 | C12K | CK | C4K | C1K | C10K | C5K | C22K | ||
| 地热地质条件 | 隧道路肩面温度所占比例/% | 常温带 | 63.90 | 36.90 | 39.60 | 27.60 | 近100 | - | 100 |
| 低高温带(Ⅰ) | 34.10 | 61.10 | 32.10 | 23.80 | 无 | - | 无 | ||
| 中高温带(Ⅱ1) | 2.0 | 2.0 | 20.45 | 39.02 | 无 | - | 无 | ||
| 中高温带(Ⅱ2) | 无 | 无 | 7.10 | 6.75 | 无 | - | 无 | ||
| 高温带(Ⅲ) | 无 | 无 | 0.75 | 2.83 | 无 | - | 无 | ||
| 地温梯度(℃/100 m) | 1.68 | 1.78 | 3.66 | 3.91 | - | - | - | ||
| 热流值/(mW·m-2) | 29.2~52.2 | 30.9~52.2 | 52.5~190 | 52.5~190 | - | - | - | ||
| 岩温产热率(10-2 J/m2·s) | 2.4~4.3 | 3.0~3.5 | 3.0~6.4 | 6.5~12.0 | - | - | - | ||
| 隧道地热地质条件 | 位于相对低温通道 | 位于相对低温通道 | 穿越高地温地区,龙陵隧道进口地段高温热害严重 | 穿越高地温地区,龙陵隧道进口地段高温热害严重 | 线路多以路基、桥通过,避免了隧道高地温危害 | 穿越高地温地区,隧道热害严重 | 线路多以路基、桥通过,避免了隧道高地温危害 | ||
| 断裂构造 | 线路大角度与断裂构造大角度相交 | 线路大角度与断裂构造大角度相交 | 高黎贡山隧道位于断裂构造蜂腰部位,引线段与构造线平行 | 高黎贡山隧道位于断裂构造蜂腰部位,引线段与构造线平行 | 在断裂构造密集地区迂回展线 | 引线段与断裂构造平行 | 在断裂构造密集地区迂回展线 | ||
| 不良地质 | 绕避 | 引线段不良地质发育 | 引线段不良地质发育 | 不良地质发育 | 不良地质发育 | 不良地质发育 | 不良地质发育 | ||
| 工程地质条件评价 | 较好 | 好 | 差 | 差 | 差 | ||||
| 地温带 | 温度界限T/℃ | 热害分析评估标准 | |
| 常温带 | ≤28 | 无热害 | |
| 低高温带(Ⅰ) | 28<T≤37 | 热害轻微 | |
| 中高温带(Ⅱ) | 中高温带(Ⅱ1) | 37<T≤50 | 热害中等 |
| 中高温带(Ⅱ2) | 50<T≤60 | 热害较严重 | |
| 超高温带(Ⅲ) | >60 | 热害严重 | |
| 比选内容 | C12K | CK | C4K | C1K | C10K | C5K | C22K | ||
| 地热地质条件 | 隧道路肩面温度所占比例/% | 常温带 | 63.90 | 36.90 | 39.60 | 27.60 | 近100 | - | 100 |
| 低高温带(Ⅰ) | 34.10 | 61.10 | 32.10 | 23.80 | 无 | - | 无 | ||
| 中高温带(Ⅱ1) | 2.0 | 2.0 | 20.45 | 39.02 | 无 | - | 无 | ||
| 中高温带(Ⅱ2) | 无 | 无 | 7.10 | 6.75 | 无 | - | 无 | ||
| 高温带(Ⅲ) | 无 | 无 | 0.75 | 2.83 | 无 | - | 无 | ||
| 地温梯度(℃/100 m) | 1.68 | 1.78 | 3.66 | 3.91 | - | - | - | ||
| 热流值/(mW·m-2) | 29.2~52.2 | 30.9~52.2 | 52.5~190 | 52.5~190 | - | - | - | ||
| 岩温产热率(10-2 J/m2·s) | 2.4~4.3 | 3.0~3.5 | 3.0~6.4 | 6.5~12.0 | - | - | - | ||
| 隧道地热地质条件 | 位于相对低温通道 | 位于相对低温通道 | 穿越高地温地区,龙陵隧道进口地段高温热害严重 | 穿越高地温地区,龙陵隧道进口地段高温热害严重 | 线路多以路基、桥通过,避免了隧道高地温危害 | 穿越高地温地区,隧道热害严重 | 线路多以路基、桥通过,避免了隧道高地温危害 | ||
| 断裂构造 | 线路大角度与断裂构造大角度相交 | 线路大角度与断裂构造大角度相交 | 高黎贡山隧道位于断裂构造蜂腰部位,引线段与构造线平行 | 高黎贡山隧道位于断裂构造蜂腰部位,引线段与构造线平行 | 在断裂构造密集地区迂回展线 | 引线段与断裂构造平行 | 在断裂构造密集地区迂回展线 | ||
| 不良地质 | 绕避 | 引线段不良地质发育 | 引线段不良地质发育 | 不良地质发育 | 不良地质发育 | 不良地质发育 | 不良地质发育 | ||
| 工程地质条件评价 | 较好 | 好 | 差 | 差 | 差 | ||||