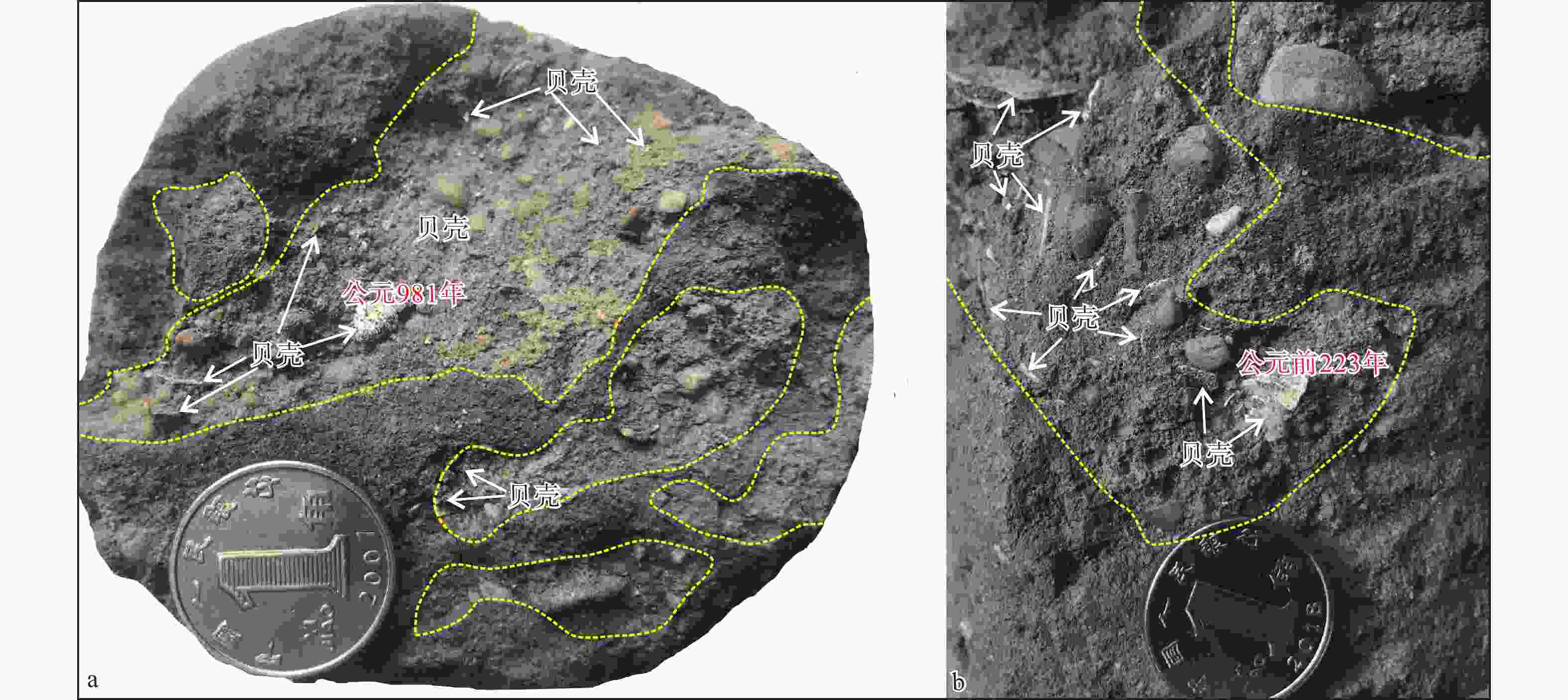
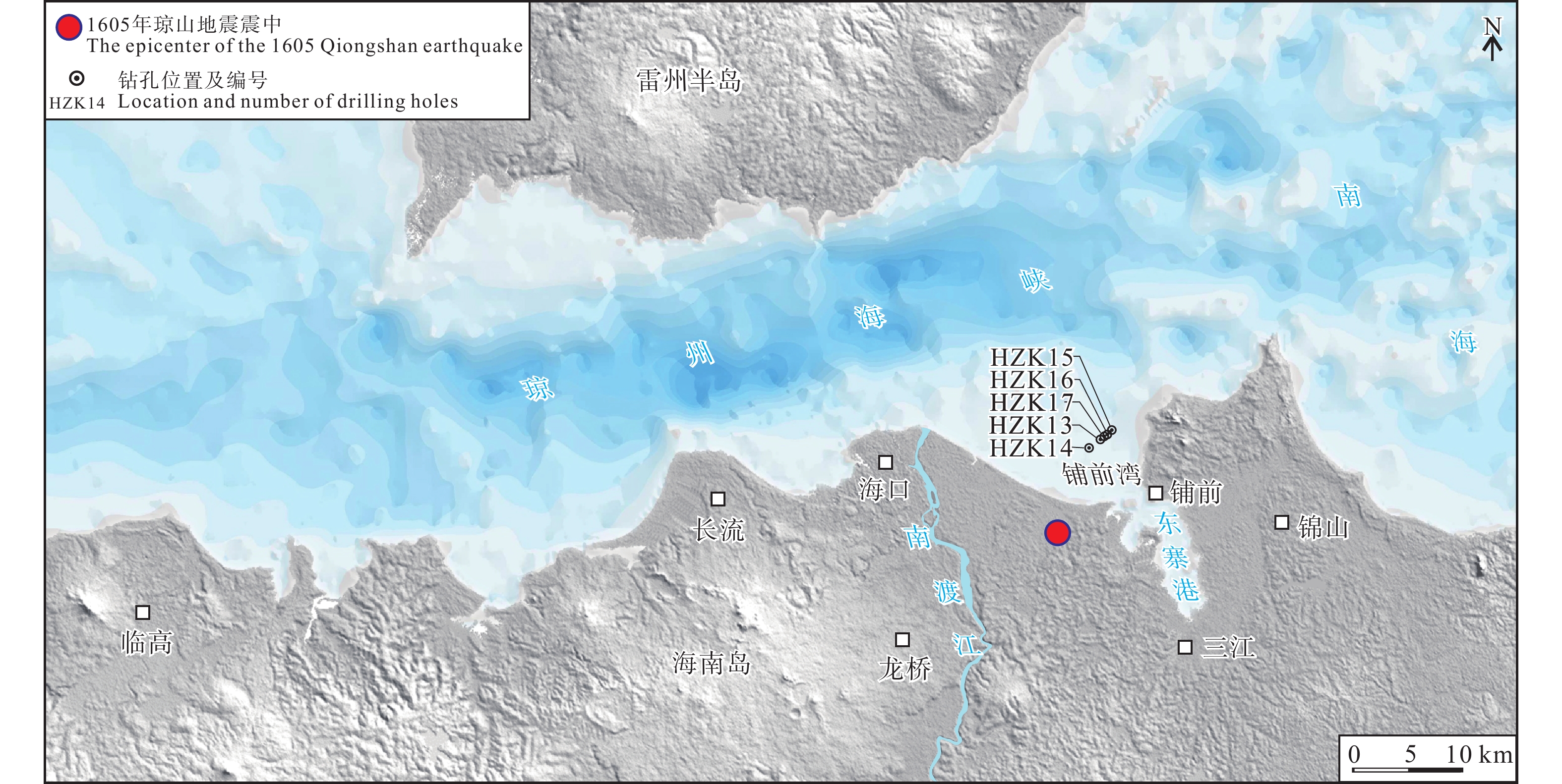
| [1] |
ATWATER B F, 1987. Evidence for great Holocene earthquakes along the outer coast of Washington State[J]. Science, 236(4804): 942-944. doi: 10.1126/science.236.4804.942
|
| [2] |
CHEN Y, CHEN Q F, ZHANG W, 2007. Tsunami disaster in China[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 16(2): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract
|
| [3] |
DAWSON A G, STEWART I, 2007. Tsunami deposits in the geological record[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 200(3-4): 166-183. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2007.01.002
|
| [4] |
ISHIZAWA T, GOTO K, YOKOYAMA Y, et al., 2020. Dating tsunami deposits: present knowledge and challenges[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 200: 102971. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102971
|
| [5] |
LI L L, QIU Q, LI Z G, et al., 2022. Tsunami hazard assessment in the South China Sea: a review of recent progress and research gaps[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 65(5): 783-809. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1007/s11430-021-9893-8
|
| [6] |
SUN L G, ZHOU X, HUANG W, et al., 2013. Preliminary evidence for a 1000-year-old tsunami in the South China Sea[J]. Scientific Reports, 3: 1655. doi: 10.1038/srep01655
|
| [7] |
WANG Y M, WANG Y K, LI L L, et al., 2023. Paleo-tsunami sedimentary records and potential triggering mechanism during the Earlier Song Dynasty at the northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 68(20): 2690-2708. (in Chinese with English abstract
|
| [8] |
YANG W Q, SUN L G, YANG Z K, et al., 2019. Nan’ao, an archaeological site of Song Dynasty destroyed by tsunami[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 64(1): 107-120. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1360/N972018-00740
|
| [9] |
陈颙,陈棋福,张尉,2007. 中国的海啸灾害[J]. 自然灾害学报,16(2):1-6.
|
| [10] |
李琳琳,邱强,李志刚,等,2022. 南海海啸灾害研究进展及展望[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,52(5):803-831.
|
| [11] |
王喻鸣,王玉琨,李琳琳,等,2023. 南海北部海域北宋年间的古海啸记录及其潜在触发机制[J]. 科学通报,68(20):2690-2708.
|
| [12] |
杨文卿,孙立广,杨仲康,等,2019. 南澳宋城:被海啸毁灭的古文明遗址[J]. 科学通报,64(1):107-120.
|




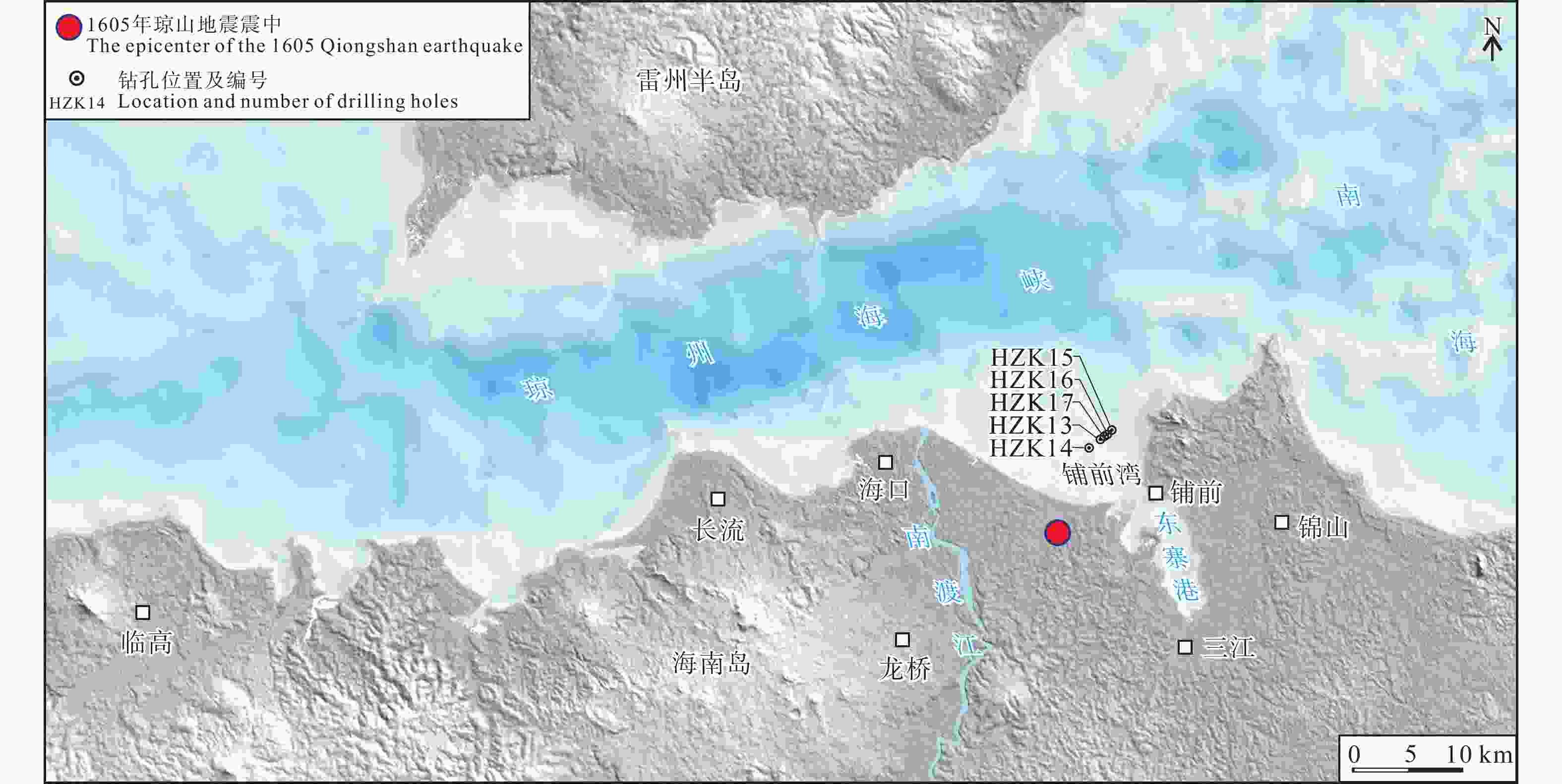
 下载:
下载: