Zircon U-Pb dating of the Dizhuanggou Formation, Changjiaoba Group in the South Qinling Belt and its tectonic significance
-
摘要: 长角坝群出露于南秦岭佛坪地区,是该构造带内残留的少数研究程度较低的地层之一,其物质组成、形成时代一直缺乏准确的限定,进而制约了对南秦岭的构造归属和构造演化的深入研究。文章对长角坝群内低庄沟组变质沉积岩开展了岩石学和锆石U-Pb年代学研究,结果显示所取2个样品的碎屑锆石年龄主要峰值为810~835 Ma, 最年轻的年龄区间为600~700 Ma,最大沉积时代为新元古代。这与同为长角坝群、出露最广泛的泥盆纪黑龙潭组具有明显的时代差异,显示了长角坝群物质组成的复杂性。此外,低庄沟组的碎屑锆石年龄谱系特征与用于对比测试的另一个碎屑锆石最小年龄峰值为718 Ma、主要峰值为810 Ma的佛坪群样品高度相似,结合二者的岩石学及野外地质特征,认为二者共同构成了南秦岭西部的过渡性基底,与南秦岭带内宁陕断裂以东的过渡性基底−武当群、耀岭河群具有明显的可对比性。长角坝群新元古代物质的识别还为佛坪地区变质单元的划分提供了新的依据,进而梳理出成层性、变质程度不同的3个单元,为南秦岭中生代造山演化过程的恢复提供了佐证 。Abstract:
Objective The Changjiaoba Group, located in the Foping area of the South Qinling Belt, is one of the few poorly-studied strata in the belt. The lack of an accurate composition and formation age of these strata has restricted research on the tectonic affinity and evolution of the South Qinling Belt. Method This paper investigates the petrological characteristics and zircon U-Pb chronology of two metasedimentary rocks from the Dizhuanggou Formation of the Changjiaoba Group. Results The results show that the dominant peak detrital zircon dates of the two samples were approximately 810–835 Ma, with the youngest date range being approximately 600–700 Ma, indicating that the maximum depositional age was Neoproterozoic. This age spectrum differs significantly from that of the most exposed Devonian Heilongtan Formation of the Changjiaoba Group, but is highly similar to that of another sample from the Foping Group, which has a minimum age peak of 718 Ma and a major peak at 810 Ma. In addition, metamorphic zircons from the Dizhuanggou Formation and the Foping Group yielded ages of 207 Ma and 193 Ma, respectively. Conclusion The distinct depositional age of the Changjiaoba Group indicate the complexity of its composition. Combined with the petrological and field geological features, the Dizhuanggou Formation and a Neoproterozoic strata of the Foping Group are considered to form the transitional basement of the western South Qinling Belt. This is comparable to the transitional basement of the Wudang and Yaolinghe Groups east of the Ningshan Fault in the South Qinling Belt. Significance The identification of Neoproterozoic and Mesozoic materials in the Changjiaoba Group provides a new basis for the division of metamorphic units in the Foping area, identifying three units with different degrees of layering and metamorphism, which, in turn, facilitates understanding of the Mesozoic orogenic process in the South Qinling Belt. -
Key words:
- South Qinling Belt /
- Changjiaoba Group /
- detrital zircon /
- Neoproterozoic /
- unit division
-
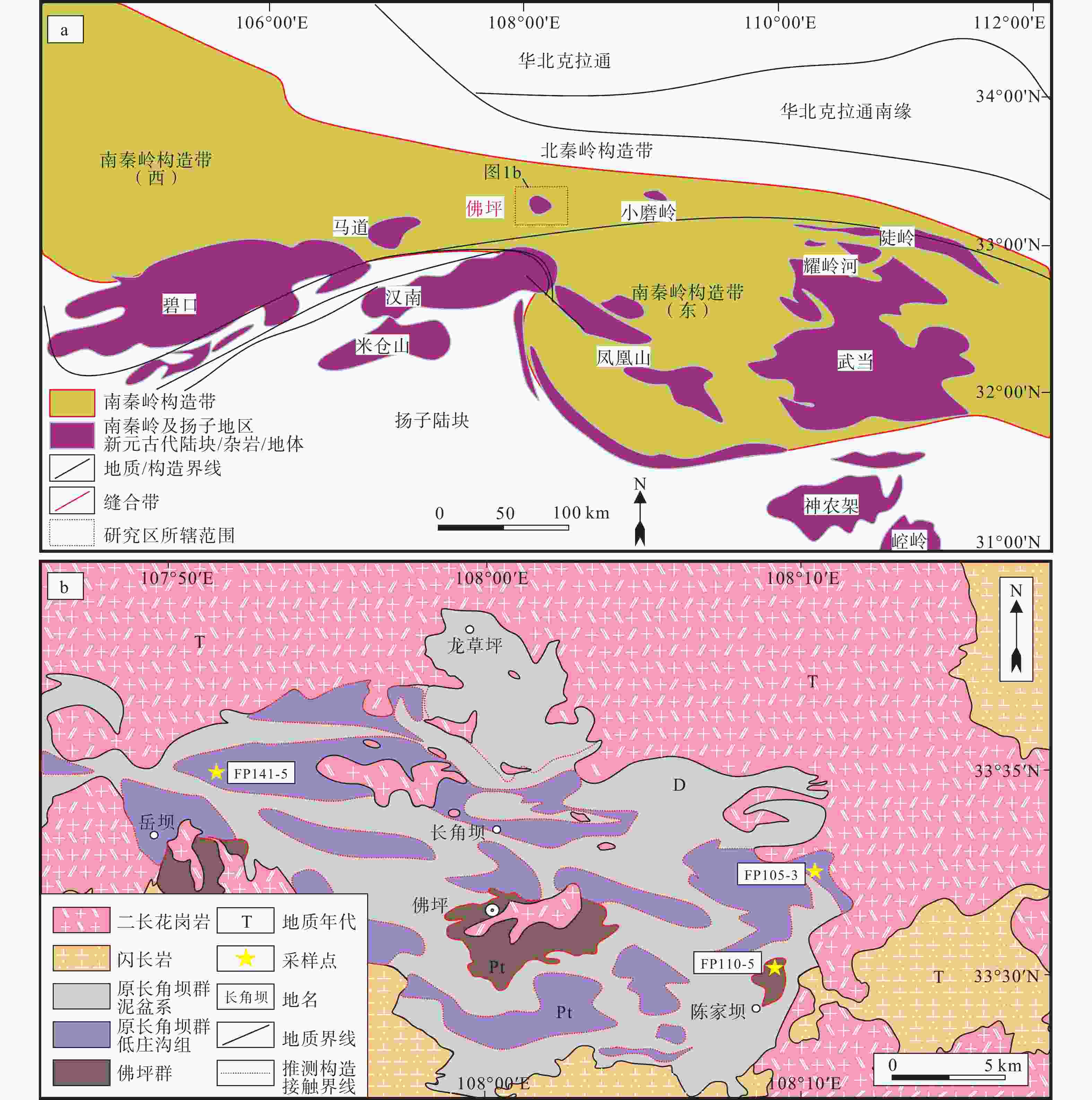
图 1 研究区位置图
T—三叠纪;D—泥盆纪;Pt—元古宙a— 秦岭造山带大地构造略图(据张国伟等,2001;李三忠等,2003;Dong et al.,2011;Zhao and Cawood,2012;Hu et al.,2016修改); b— 佛坪地区地质简图 (据陕西省地质矿产局,1999修改)
Figure 1. Location of the study area
(a) Simplified tectonic map of the Qinling orogenic belt (modified after Zhang et al., 2001; Li et al., 2003; Dong et al., 2011; Zhao and Cawood, 2012; Hu et al., 2016); (b) Geological sketch map of the Foping area (modified after Brueau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Shaanxi Province, 1999)T—Triassic; D—Devonian; Pt—Proterozoic
图 2 佛坪地区新元古代岩石样品野外露头照片及显微镜单偏光照片
Grt—石榴石;Bt—黑云母;Sill—矽线石;Pl—斜长石;Q—石英a— 长角坝群低庄沟组样品FP105-3野外照片;b— FP105-3单偏光照片;c—长角坝群低庄沟组样品FP141-5野外照片;d— FP141-5单偏光照片;e— 佛坪群样品FP110-5野外照片;f— FP110-5单偏光照片
Figure 2. Photographs and photomicrographs of the Neoproterozoic samples in the Foping area
(a) Outcrop of sample FP105-3 from the Dizhuanggou Formation; (b) Photomicrograph of sample FP105-3; (c) Outcrop of sample FP141-5 from the Dizhuanggou Formation; (d) Photomicrograph of sample FP141-5; (e) Outcrop of sample FP110-5 from the Foping Group; (f) Photomicrograph of sample FP110-5 Grt—garnet; Bt—biotite; Sill—sillimanite; Pl—plagioclase; Q—quartz
图 3 佛坪地区新元古代样品碎屑锆石的阴极发光(CL)图像
红色圆圈为锆石测点位置,黄色年龄数据来自岩浆锆石,蓝色年龄数据来自变质锆石a— 长角坝群低庄沟组样品FP105-3的碎屑锆石特征;b— 长角坝群低庄沟组样品FP141-5的碎屑锆石特征;c—佛坪群样品FP110-5的碎屑锆石特征
Figure 3. Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of detrital zircons from the Neoproterozoic samples
(a) FP105-3 from the Dizhuanggou Formation, Changjiaoba Group; (b) FP141-5 from the Dizhuanggou Formation, Changjiaoba Group; (c) FP110-5 from the Foping Group Red circles are analytical spots, yellow dates numbers are from magmatic zircons, while blue dates numbers are from metamorphic zircons.
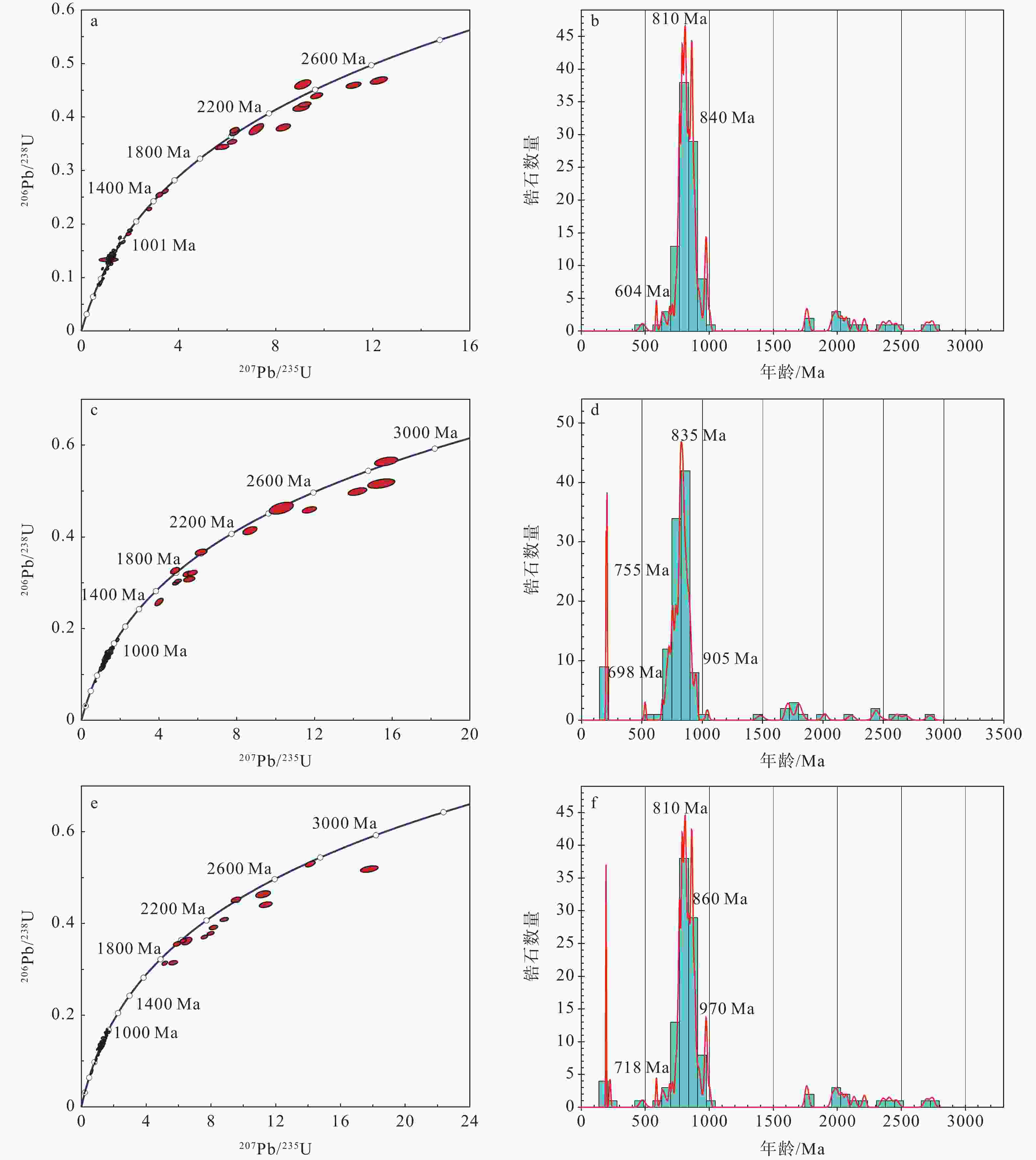
图 4 佛坪地区新元古代样品碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图与频率分布直方图
a—样品FP105-3的碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图;b—样品FP105-3的碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄频率分布直方图;c—样品FP141-5的碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图;d—样品FP141-5的碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄频率分布直方图;e—样品FP110-5的碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图;f—样品FP110-5的碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄频率分布直方图
Figure 4. U-Pb concordia and age probability density diagrams of detrital zircons from the Neoproterozoic rock samples in the Foping area
(a) Zircon U-Pb concordia diagrams of sample FP105-3; (b) Zircon U-Pb age histogram probability density diagrams of sample FP105-3; (c) Zircon U-Pb concordia diagrams of sample FP141-5; (d) Zircon U-Pb age histogram probability density diagrams of sample FP141-5; (e) Zircon U-Pb concordia diagrams of sample FP110-5; (f) Zircon U-Pb age histogram probability density diagrams of sample FP110-5
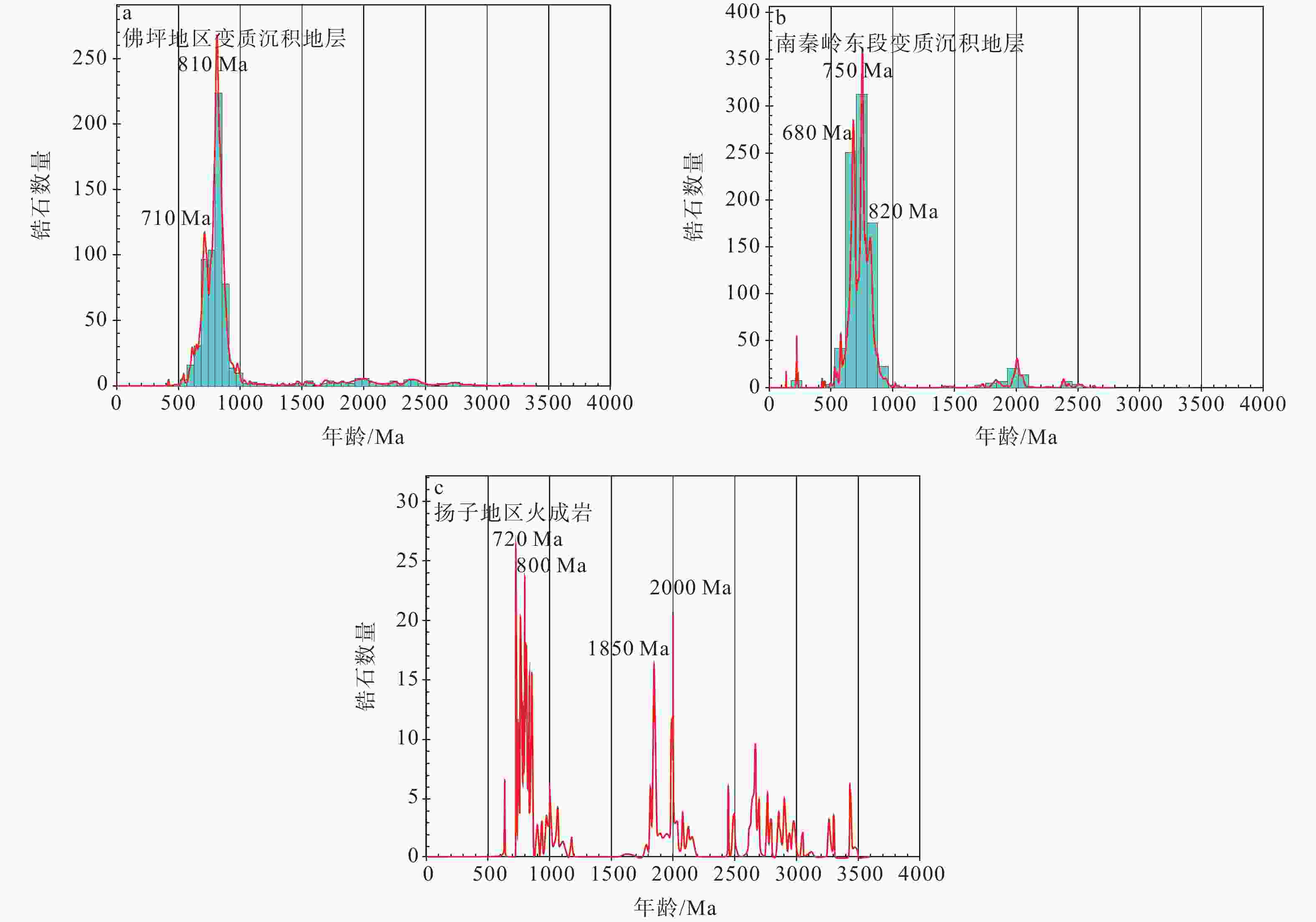
图 5 研究区及其相邻区域年代学数据频谱对比图
a—佛坪地区新元古代地层变质沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄频率分布直方图(数据来源于刘志慧等,2018及文中);b— 南秦岭东段新元古代地体变质沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄频率分布直方图(数据来源于李怀坤等,2003、 凌文黎等,2007,2010; 祝禧艳等,2008; 张永清等,2013;王嘉玮等,2021);c— 扬子地区火成岩结晶年龄(频率直方图及数据引自Zhang et al.,2023a)
Figure 5. Age probability density diagrams of the samples from the study area and its adjacent regions
(a) Ages of detrital zircons from the Neoproterozoic metasedimentary rocks in the Foping area (data are from this paper and Liu et al., 2018); (b) Ages of detrital zircons from the Neoproterozoic metasedimentary rocks in the eastern South Qinling area (data are from Li et al., 2003; Ling et al., 2007, 2010; Zhu et al., 2008 and Zhang et al., 2013); (c) Igneous ages from Yangtze block (diagram and data quoted from Zhang et al., 2023a)
-
[1] BADER T, RATSCHBACHER L, FRANZ L, et al., 2013. The heart of China revisited, I. Proterozoic tectonics of the Qin mountains in the core of supercontinent Rodinia[J]. Tectonics, 32(3): 661-687. doi: 10.1002/tect.20024 [2] Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Shaanxi Province, 1989. Regional geology of Shaanxi province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. (in Chinese) [3] Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Shaanxi Province, 1999. The People’s Republic of China regional geological survey report of Foping (I48E015024), 1: 50000[R]. National Geological Archives. (in Chinese) [4] CAI Z Y, XIONG X L, LUO H, et al., 2007. Forming age of the volcanic rocks of the Yaolinghe group from Wudang block, southern Qinling mountain: constraint from Grain-Zircon U-Pb dating[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(5): 620-625. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] CHANG H, WANG X L, XIONG W, 1998. The composition of the basement of the Foping vault of South Qinling[J]. Northwestern Geology, 19(3): 6-11. (in Chinese) [6] CHEN H, HU J M, WU G L, et al., 2010. Study on the intracontinental deformation of the Mian-Lue suture belt, western Qinling[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(4): 1277-1288. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] CHEN L G, DAI X Y, LI N, et al., 1999. The geological characteristic of bedded metamorphite series in middle Proterozoic in Foping area[J]. Journal of Xi’an Engineering University, 21(2): 19-23. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] CHEN L Y, LIU Z H, LIU X C, et al., 2019. Metamorphism and its relation of Magmatism of the Foping gneiss dome in the South Qinling tectonic belt[J]. Earth Science, 44(12): 4178-4185. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] CHEN L Y, LIU X C, QU W, et al., 2020. Metamorphic evolution and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the Wuguan complex, eastern Qinling area, China: implications for the late Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen[J]. Lithos, 358-359: 105415. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105415 [10] DENG H, PENG S B, POLAT A., et al., 2017. Neoproterozoic IAT intrusion into Mesoproterozoic MOR Miaowan Ophiolite, Yangtze Craton: Evidence for evolving tectonic settings[J]. Precambrian Research, 289: 75-94. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2016.12.003 [11] DENG Q Z, YANG Q X, MAO X W, et al., 2016. Study of Lithostratigraphic sequences and chronology of Middle-late Nanhua in Wudang-Suizhou area[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 30(2): 132-142. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] DONG Y P, ZHANG G W, FRANZ N, LIU X M, JOHANN G, CHRISTOPH H, 2011. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, China: Review and synthesis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(3): 213-237. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.03.002 [13] DONG Y P, LIU X M, ZHANG G W, et al., 2012. Triassic diorites and granitoids in the Foping area: Constraints on the conversion from subduction to collision in the Qinling orogen, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 47: 123-142. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.06.005 [14] DONG Y P, SANTOSH M, 2016. Tectonic architecture and multiple orogeny of the Qinling Orogenic Belt, Central China[J]. Gondwana Research, 29(1): 1-40. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.009 [15] DONG Y P, SUN S S, YANG Z, et al., 2017. Neoproterozoic subduction-accretionary tectonics of the South Qinling Belt, China[J]. Precambrian Research, 293: 73-90. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.02.015 [16] DONG Y P, SUN S S, SANTOSH M, et al., 2021. Central China Orogenic belt and amalgamation of East Asian continents[J]. Gondwana Research, 100: 131-194. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2021.03.006 [17] HAN Q S, PENG S B, POLAT A, et al., 2019. Petrogenesis and geochronology of Paleoproterozoic magmatic rocks in the Kongling complex: Evidence for a collisional orogenic event in the Yangtze craton[J]. Lithos, 342-343: 513-529. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2019.05.015 [18] HAN Q S, PENG S B, JIAO S J, 2020. Discovery and tectonic implications of Paleoproterozoic cold Subduction low-temperature/high-pressure Eclogitic Metapelites, Yangtze Craton[J]. Earth Science, 45(6): 1986-1998. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] HSÜ K J, WANG Q C, LI J L, et al., 1987. Tectonic evolution of Qinling Mountains, China[J]. Eclogae Geologicae Helvetiae, 80: 735-752. [20] HU Z C, GAO S, LIU Y S, et al., 2008. Signal enhancement in laser ablation ICP-MS by addition of nitrogen in the central channel gas[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 23(8): 1093-1101. doi: 10.1039/b804760j [21] HU F Y, LIU S W, SANTOSH M, et al, 2016. Chronology and tectonic implications of Neoproterozoic blocks in the south Qinling Orogenic Belt, central China[J]. Gondwana Research, 30: 24-47. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.01.006 [22] HU F Y, LIU S W, DUCEA M N, et al, 2017. The geochemical evolution of the granitoid rocks in the South Qinling Belt: insights from the Dongjiangkou and Zhashui intrusions, central China[J]. Lithos, 278-281: 195-214. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.01.021 [23] HU F Y, LIU S W, DUCEA M N, et al, 2018. Interaction among magmas from various sources and crustal melting processes during continental collision: insights from the Huayang intrusive complex of the South Qinling Belt, China[J]. Journal of Petrology, 59(4): 735-770. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egy042 [24] HU F Y, LIU S W, DUCEA M N, et al, 2020. Early Mesozoic magmatism and tectonic evolution of the Qinling Orogen: implications for oblique continental collision[J]. Gondwana Research, 88: 296-332. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2020.07.006 [25] HU J, LIU X C, CHEN L Y, et al., 2013. A~2.5 Ga magmatic event at the northern margin of the Yangtze craton: Evidence from U-Pb dating and Hf isotope analysis of zircons from the Douling Complex in the South Qinling orogen[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58(28): 3564-3579. [26] HU J, LIU X C, QU W, et al., 2019. Mid-neoproterozoic amphibolite facies metamorphism at the northern margin of the Yangtze craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 326: 333-343. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.10.010 [27] HU J M, MENG Q R, CHEN H, et al., 2011. Tectonic evolution and implication of Ningshan Fault in the central part of Qinling Orogen[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(3): 657-671. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] HU Z C, ZHANG W, LIU Y S, et al., 2015. “Wave” signal-smoothing and mercury-removing device for laser ablation Quadrupole and multiple collector ICPMS analysis: application to lead isotope analysis[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 87(2): 1152-1157. doi: 10.1021/ac503749k [29] JIANG X F, PENG S B, POLAT A, et al., 2016. Geochemistry and geochronology of mylonitic metasedimentary rocks associated with the Proterozoic Miaowan ophiolite complex, Yangtze craton, China: Implications for geodynamic events[J]. Precambrian Research, 279: 37-56. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2016.04.004 [30] JIANG Y Y, XIANG H, ZHANG Z M, 2017. Metamorphic P-T path and tectonic implication of garnet-biotite schist of the Wuguan complex, Qinling orogen[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(8): 2563-2574. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] LI H P, 1998. Discovery of Archean crystal complex in the Foping, Shaanxi Province[J]. Regional Geology of China, 17(3): 329-330. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] LI H K, LU S N, CHEN Z H, et al., 2003. Zircon U-Pb geochronology of rift-type volcanic rocks of the Yaolinghe Group in th South Qinling orogen[J]. , Geological Bulletin of China, 22(10): 755-781. [33] LI H Q, ZHOU W X, WEI Y X, et al., 2020. Two extensional events in the early evolution of the Yangtze Block, South China: Geochemical and isotopic evidence from two sets of Paleoproterozoic alkali porphyry in the northern Kongling Terrane[J]. Geological Journal, 55(9): 6296-6324. doi: 10.1002/gj.3802 [34] LI L M, LIN S F, DAVIS D W, et al., 2014. Geochronology and geochemistry of igneous rocks from the Kongling terrane: implications for Mesoarchean to Paleoproterozoic crustal evolution of the Yangtze Block[J]. Precambrian Research, 255: 30-47. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2014.09.009 [35] LI N, CHEN Y J, SANTOSH M, et al., 2015. Compositional polarity of Triassic granitoids in the Qinling Orogen, China: implication for termination of the northernmost paleo-Tethys[J]. Gondwana Research, 27(1): 244-257. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.09.017 [36] LI Q W, ZHAO J H, 2016. Petrogenesis of the Wudang mafic dikes: implications of changing tectonic settings in South China during the Neoproterozoic[J]. Precambrian Research, 272: 101-114. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2015.10.019 [37] LI S K, ZHANG Y Q, JI J Q, et al, 2022. Orogen-parallel mid-lower crustal ductile flow during the late Triassic Qinling orogeny: structural geology and geochronology[J]. International Geology Review, 64(11): 1611-1634. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2021.1949639 [38] LI S Z, ZHANG G W, LI Y L, YANG Y Y, 2000. Discovery of granulite in the Mianxian-Lueyang suture zone, Mianxian area and its tectonic significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 16(2): 220-226 (in Chinese with English abstract). [39] LI S Z, LAI S C, ZHANG G W, et al., 2003. Metamorphic dynamics of the Mian-Lüe suture zone of Qinling Orogenic belt and the southern Qinling Block[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 38(2): 137-154. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] LI X H, LI X W, HE B, 2012. Building of the South China block and its relevance to assembly and breakup of Rodinia supercontinent: observations, interpretations and tests[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 31(6): 543-559. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] LI Y L, WANG G B, WANG C S, et al., 2000. Zircon U-Pb isotopic geochronology of the Longcaoping crystal complex in Southern Qinling[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 20(1): 50-54. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] LIANG S, LIU L, ZHANG C L, et al., 2013. Metamorphism and zircon U-Pb age of high-pressure mafic granulites in in Mian-Lüe suture zone, South Qinling orogen[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(5): 1657-1674. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] LIAO X Y, LIU L, ZHAI M G, et al., 2021. Metamorphic evolution and Petrogenesis of garnet-corundum silica-undersaturated metapelitic granulites: A new case study from the Mianlüe Tectonic Zone of South Qinling, Central China[J]. Lithos, 392-393: 106154. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2021.106154 [44] LING W L, GAO S, ZHANG B R, et al., 2001. The recognizing of ca. 1.95 Ga tectono-thermal eventin Kongling nucleus and its significance for the evolution of Yangtze Block, South China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 46(4): 326-329. doi: 10.1007/BF03187196 [45] LING W L, REN B F, DUAN R C, et al., 2007. Zircon U-Pb isotopic geochronology of Wudangshan Group, Yaolinghe Group and basic intrusions and its geological significance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(12): 1445-1456(in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/csb2007-52-12-1445 [46] LING W L, REN B F, DUAN R C, et al., 2008. Timing of the Wudangshan, Yaolinghe volcanic sequences and mafic sills in South Qinling: U-Pb zircon geochronology and tectonic implication[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53(14): 2192-2199. doi: 10.1007/s11434-008-0269-6 [47] LING W L, DUAN R C, LIU X M, et al., 2010. U-Pb dating of detrital zircons from the Wudangshan Group in the South Qinling and its geological significance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(22): 2440-2448. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3095-6 [48] LIU J B, ZHANG L M, 2013. Neoproterozoic low to negative δ18O volcanic and intrusive rocks in the Qinling Mountains and their geological significance[J]. Precambrian Research, 230: 138-167. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2013.02.006 [49] LIU R Y, NIU B G, HE Z J, et al., 2011. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology of the eastern part of the Xiaomaoling composite intrusives in Zhashui area, Shaanxi, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(2-3): 448-460. (in Chinese with English abstract [50] LIU S W, YANG P T, LI Q G, et al., 2011. Indosinian granitoids and orogenic processes in the middle segment of the Qinling Orogen, China[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 41(6): 1928-1943. (in Chinese with English abstract [51] LIU Y S, HU Z C, GAO S, et al., 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 257(1-2): 34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004 [52] LIU Y S, HU Z C, ZONG K Q, et al., 2010. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(15): 1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4 [53] LIU Z H, LUO M, CHEN L Y, et al., 2018. Stratigraphic framework and provenance analysis in the Foping area, the South Qinling tectonic belt: Constraints from LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of detrital zircons from the metasedimentary rocks[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(5): 1484-1502. (in Chinese with English abstract [54] LIU Z H, CHEN L Y, QU W, et al., 2019. Early mesozoic metamorphism, Anataxis and deformation of Foping area in South Qinling belt: constrains from U-Pb Zircon dating[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 40(4): 545-562. (in Chinese with English abstract [55] LIU Z H, CHEN L Y, LIU X C, et al, 2025. Petrological and geochronological constraints on the genesis of the Foping gneiss dome, South Qinling Belt, central China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 277: 106406. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2024.106406 [56] LU K, LI X H, ZHOU J L, et al., 2020. Early Neoproterozoic assembly of the Yangtze Block decoded from metasedimentary rocks of the Miaowan Complex[J]. Precambrian Research, 346: 105787. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2020.105787 [57] LUDWIG K R, 2003. User's manual for ISOPLOT 3.00: a geochronological toolkit for Microsoft excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center. [58] MATTAUER M, MATTE P, MALAVIEILLE J, et al., 1985. Tectonics of the Qinling belt: build-up and evolution of eastern Asia[J]. Nature, 317(6037): 496-500. doi: 10.1038/317496a0 [59] MENG E, LIU F L, DU L L, et al., 2015. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the Baoxing granitic and mafic intrusions, southwestern China: evidence from zircon U-Pb dating and Lu-Hf isotopes, and whole-rock geochemistry[J]. Gondwana Research, 28(2): 800-815. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.07.003 [60] MENG Q R, 2017. Origin of the Qinling mountains[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 47(4): 412-420. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/N072016-00422 [61] NIE H, YAO J, WAN X, et al., 2016. Precambrian tectonothermal evolution of South Qinling and its affinity to the Yangtze Block: evidence from zircon ages and Hf-Nd isotopic compositions of basement rocks[J]. Precambrian Research, 286: 167-179. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2016.10.005 [62] PENG M, WU Y B, GAO S, et al., 2012a. Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope compositions of Paleoproterozoic aluminous A-type granites from the Kongling terrain, Yangtze Block: constraints on petrogenesis and geologic implications[J]. Gondwana Research, 22(1): 140-151. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.08.012 [63] PENG S B, KUSKY T M, JIANG X F, et al., 2012b. Geology, geochemistry, and geochronology of the Miaowan ophiolite, Yangtze craton: Implications for South China’s amalgamation history with the Rodinian supercontinent[J]. Gondwana Research, 21(2-3): 577-594. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.07.010 [64] QIN K L, SONG S S, HE S P, 1992. The geological characteristics of the Yudongzi granite-greenstone terrain and its gold-bearing property in Mianluening area Shaanxi[J]. Northwest Geoscience, 13(1): 65-74. (in Chinese with English abstract [65] QIU X F, ZHAO X M, YANG H M, et al., 2018. Geochemical and Nd isotopic compositions of the Palaeoproterozoic metasedimentary rocks in the Kongling complex, nucleus of Yangtze craton, South China block: implications for provenance and tectonic evolution[J]. Geological Magazine, 155(6): 1263-1276. doi: 10.1017/S0016756817000048 [66] RATSCHBACHER L, HACKER B R, CALVERT A, et al, 2003. Tectonics of the Qinling (Central China): tectonostratigraphy, geochronology, and deformation history[J]. Tectonophysics, 366(1-2): 1-53. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(03)00053-2 [67] Shaanxi Institute of Geological Survey, 2017. The regional geology of China, Shaanxi province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-1120. (in Chinese) [68] SHI Y, YU J H, SANTOSH M, 2013. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogenic belt, Central China: new evidence from geochemical, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes[J]. Precambrian Research, 231: 19-60. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2013.03.001 [69] WANG D S, WANG Z Q, ZHANG Y L, et al., 2014. Deformation structures of the Madao gneiss in South Qinling: structural analysis, geochronological constraints, and tectonic implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 88(4): 1102-1119. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12276 [70] WANG D S, WANG Z Q, ZHANG Y L, et al., 2016. Metamorphism of Metasedimentary rocks in Madao area, South Qinling Accretionary complex belt[J]. Geoscience, 30(6): 1254-1266. (in Chinese with English abstract [71] WANG D S, WANG Z Q, WANG T, et al., 2024. Unraveling the early Paleozoic tectonic history of the South Qinling Belt: evidence from geochronology, geochemistry, and Sm-Nd isotopes of meta-sedimentary rocks[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 257: 107362. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2023.107362 [72] WANG G B, 1997. Isotope chronology and its significances of Foping Gneiss System, South Qinling[J]. Northwest Geoscience, 18(2): 21-25. (in Chinese with English abstract [73] WANG J W, WANG G, WANG Z Q, et al., 2021. Genesis and tectonic significance of Mesozoic mafic rocks in the Wudang Mountain-Shiyan Belt, South Qinling Orogen: Constraints from geochemistry and zircon U-Pb, Hf isotopes[J]. Geological Review, 67(4): 869-885. (in Chinese with English abstract [74] WANG Q C, SUN S, LI J L, et al., 1989. The tectonic evolution of the Qinling Mountain Belt[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica), 24(2): 129-142. (in Chinese with English abstract [75] WANG R R, XU Z Q, SANTOSH M, et al., 2016. Late Neoproterozoic magmatism in South Qinling, Central China: geochemistry, zircon U-Pb-Lu-Hf isotopes and tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 683: 43-61. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.05.050 [76] WANG X C, LI X H, LI W X, et al., 2009. Variable involvements of mantle plumes in the genesis of mid-Neoproterozoic basaltic rocks in South China: a review[J]. Gondwana Research, 15(3-4): 381-395. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2008.08.003 [77] WANG X X, WANG T, ZHANG, C. L. , 2013. Neoproterozoic, Paleozoic, and Mesozoic granitoid magmatism in the Qinling Orogen, China: Constraints on orogenic process[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 72, 129-151. [78] WANG X X, WANG T, ZHANG C L, 2015. Granitoid Magmatism in the Qinling Orogen, central China and its bearing on orogenic evolution[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 58(9): 1497-1512. doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5150-2 [79] WANG Z Q, YAN Q R, YAN Z, et al., 2009. New division of the main tectonic units of the Qinling Orogenic Belt, central China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(11): 1527-1546. (in Chinese with English abstract [80] WEI C J, YANG C H, ZHANG S G, 1999. Metamorphism of the east sector of the southern Qinling orogenic belt and its geological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica‐English Edition, 73(1): 65-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.1999.tb00812.x [81] WEI C J, ZHANG C G. 2002. PT path of medium-pressure metamorphism of continental collision orogenic belt-Exemplified by the southern Qinling orogenic belt[J]. Acta Petrol Mineral, 21: 356-362. (in Chinese with English abstract [82] WU Y B, GAO S, GONG H J, et al., 2009. Zircon U-Pb age, trace element and Hf isotope composition of Kongling terrane in the Yangtze Craton: refining the timing of Palaeoproterozoic high-grade metamorphism[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 27(6): 461-477. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.2009.00826.x [83] WU Y B, ZHOU G Y, GAO S, et al., 2014. Petrogenesis of Neoarchean TTG rocks in the Yangtze Craton and its implication for the formation of Archean TTGs[J]. Precambrian Research, 254: 73-86. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2014.08.004 [84] XIA L Q, XIA Z C, LI X M, et al., 2008. Petrogenesis of the Yaolinghe Group, Yunxi Group, Wudangshan Group volcanic rocks and basic dyke swarms from eastern part of the South Qinling Mountains[J]. Northwestern Geology, 41(3): 1-29. (in Chinese with English abstract [85] XIONG Q, ZHENG J P, YU C M, et al., 2009. Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope of Quanyishang A-type granite in Yichang: signification for the Yangtze continental cratonization in Paleoproterozoic[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(3): 436-446. doi: 10.1007/s11434-008-0401-7 [86] XU Z Q, LU Y L, TANG Y Q, et al. , 1988. The Formation of the East Qinling Moutian Chain—deformation, evolution and plate dynamics[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 1-193. (in Chinese) [87] YAN Z, WANG Z Q, YAN Q R, et al., 2006. Devonian sedimentary environments and provenance of the Qinling orogen: constraints on late Paleozoic southward accretionary tectonics of the north China craton[J]. International Geology Review, 48(7): 585-618. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.48.7.585 [88] YAN Z, WANG Z Q, YAN Q R, et al., 2012. Geochemical constraints on the provenance and depositional setting of the Devonian Liuling Group, East Qinling Mountains, central China: implications for the Tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogenic belt[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 82(1): 9-20. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2012.4 [89] YANG C H, WEI C J, ZHANG S G, et al., 1999. U-Pb zircon dating of granulite facies rocks from the Foping area in the southern Qinling Mountains[J]. Geological Review, 45(2): 173-179. (in Chinese with English abstract [90] YANG Z B, PEI X Z, LI R B, et al., 2023. Provenance tracing of Detrital zircons from Nanhua system in Bikou Microblock, northwestern margin of Yangtze and its geological significance[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 43(1): 226-248. (in Chinese with English abstract [91] YIN C Q, LIN S F, DAVIS D W, et al., 2013. 2.1-1.85 Ga tectonic events in the Yangtze Block, South China: petrological and geochronological evidence from the Kongling Complex and implications for the reconstruction of supercontinent Columbia[J]. Lithos, 182-183: 200-210. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.10.012 [92] ZHA X F, DONG Y P, LI W, et al., 2010. Uplifting process of Foping dome in southern Qinling: constrained by structural analysis[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 34(3): 331-339. (in Chinese with English abstract [93] ZHANG G W, ZHANG B R, YUAN X C, et al. , 2001. Qinling Orogenic belt and continental dynamics[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 1-885. (in Chinese) [94] ZHANG G W, et al. , 2015. The Mianlue tectonic zone of the Qinling orogen and China continental tectonics[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) [95] ZHANG G W, GUO A L, DONG Y P, et al., 2019. Rethinking of the Qinling orogen[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(5): 746-768. (in Chinese with English abstract [96] ZHANG H, YE R S, LIU B X, et al., 2016a. Partial melting of the South Qinling orogenic crust, China: evidence from Triassic migmatites and diorites of the Foping dome[J]. Lithos, 260: 44-57. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.05.007 [97] ZHANG H, LI S Q, FANG B W, et al., 2018. Zircon U-Pb ages and geochemistry of migmatites and granites in the Foping dome: evidence for Late Triassic crustal evolution in South Qinling, China[J]. Lithos, 296-299: 129-141. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.10.024 [98] ZHANG H, HE J, LI Y C, et al., 2023a. Neoproterozoic crustal growth and reworking in South Qinling, central China: Evidence from zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotopic composition of paragneiss in the Foping dome[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 256: 105784. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2023.105784 [99] ZHANG R Y, AO W H, SUN Y, 2013. The formation age, material composition and geological significance of intrusive rocks in the western part of South Qinling (Foping-Liuba area)[C]//National Symposium on Petrology and Geodynamics (Abstract). Guangzhou: Geological Society of China. (in Chinese) [100] ZHANG R Y, SUN Y, ZHANG X, et al., 2016b. Neoproterozoic magmatic events in the South Qinling Belt, China: implications for amalgamation and breakup of the Rodinia supercontinent[J]. Gondwana Research, 30: 6-23. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.015 [101] ZHANG R Y, AO W H, ZHAO Y, 2023b. U-Pb zircon ages and geochemistry of the Metasedimentary rocks from the Foping area in the South Qinling belt: evidence for early Devonian amalgamation between North China and South China blocks[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 34(4): 1112-1127. doi: 10.1007/s12583-022-1608-2 [102] ZHANG S, LIU J X, ZUO M, et al., 2022. Analysis on geological characteristics and metallogenic conditions of Yuanjiazhuang crystalline graphite deposit in the Foping area[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 34(4): 137-141. (in Chinese with English abstract [103] ZHANG X, XU X Y, SONG G S, et al., 2010. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating and significance of Yudongzi Group deformation granite from Lueyang area, western Qinling, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 29(4): 510-517. (in Chinese with English abstract [104] ZHANG Y Q, ZHANG J, LI H K, et al., 2013. Zircon U-Pb geochronology of the meta-acidic volcanic rocks from the Wudangshan Group, southern Qinling mountains, central China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(7): 922-930. (in Chinese with English abstract [105] ZHANG Z Q, ZHANG G W, TANG S H, et al., 2001. On the age of metamorphic rocks of the Yudongzi group and the Archean crystalline basement of the Qinling Orogen[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 75(2): 198-204. (in Chinese with English abstract [106] ZHANG Z Q, SONG B, TANG S H, et al., 2004. Age and material composition of the Foping metamorphic crystalline complex in the Qinling Mountians: SHRIMP zircon U-Pb and whole-rock Sm-Nd geochronology[J]. Geology in China, 31(2): 161-168. (in Chinese with English abstract [107] ZHAO G C, CAWOOD P A, 2012. Precambrian geology of China[J]. Precambrian Research, 222-223: 13-54. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.09.017 [108] ZHAO J H, ZHOU M F, ZHENG J P, 2010. Metasomatic mantle source and crustal contamination for the formation of the Neoproterozoic mafic dike swarm in the northern Yangtze Block, South China[J]. Lithos, 115(1-4): 177-189. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.12.001 [109] ZHAO J H, ASIMOW P D, ZHOU M F, et al., 2017. An Andean-type arc system in Rodinia constrained by the Neoproterozoic Shimian ophiolite in South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 296: 93-111. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.04.017 [110] ZHENG Y F, ZHANG S B, ZHAO Z F, et al., 2007. Contrasting zircon Hf and O isotopes in the two episodes of Neoproterozoic granitoids in South China: implications for growth and reworking of continental crust[J]. Lithos, 96(1-2): 127-150. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.10.003 [111] ZHENG Y F, WU R X, WU Y B, et al., 2008. Rift melting of juvenile arc-derived crust: geochemical evidence from Neoproterozoic volcanic and granitic rocks in the Jiangnan Orogen, South China[J]. Precambrian Research, 163(3-4): 351-383. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2008.01.004 [112] ZHOU D W, ZHANG C L, HUA H, et al., 1998. New knowledge about division and correlation of the Mid-and Neo-Proterozoic strata in the South Qinling[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 4(3): 350-357. (in Chinese with English abstract [113] ZHOU D W, ZHANG C L, ZHOU X H, et al., 1999. 40Ar-39Ar dating of basic dykes from Wudang block and their geology significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 15(1): 14-20. (in Chinese with English abstract [114] ZHU X Y, CHEN F K, WANG W, et al., 2008. Zircon U-Pb ages of volcanic and sedimentary rocks of the Wudang group in the Qinling Orogenic belt within western Henan province[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 29(6): 817-829. [115] ZHU X Y, CHEN F K, NIE H, et al., 2014. Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution of South Qinling, China: evidence from zircon ages and geochemistry of the Yaolinghe volcanic rocks[J]. Precambrian Research, 245: 115-130. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2014.02.005 [116] 蔡志勇,熊小林,罗洪,等,2007. 武当地块耀岭河群火山岩的时代归属:单锆石U-Pb年龄的制约[J]. 地质学报,81(5):620-625. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.05.005 [117] 常宏,王向利,熊伟,1998. 南秦岭佛坪穹窿基底组成[J]. 西北地质,19(3):6-11. [118] 陈虹,胡健民,武国利,等,2010. 西秦岭勉略带陆内构造变形研究[J]. 岩石学报,26(4):1277-1288. [119] 陈陇刚,代新宇,李宁,等,1999. 佛坪地区中元古代孔兹岩系地质特征[J]. 西安工程学院学报,21(2):19-23. [120] 陈龙耀,刘志慧,刘晓春,等,2019. 南秦岭佛坪片麻岩穹隆变质作用及与岩浆作用的关系[J]. 地球科学,44(12):4178-4185. [121] 邓乾忠,杨青雄,毛新武,等,2016. 湖北武当—随枣地区中—晚南华世岩石地层序列与年代学研究[J]. 资源环境与工程,30(2):132-142. [122] 韩庆森,彭松柏,焦淑娟,2020. 扬子克拉通古元古代冷俯冲低温-高压榴辉岩相变泥质岩的发现及其大地构造意义[J]. 地球科学,45(6):1986-1998. [123] 胡健民,孟庆任,陈虹,等,2011. 秦岭造山带内宁陕断裂带构造演化及其意义[J]. 岩石学报,27(3):657-671. [124] 江媛媛,向华,张泽明,2017. 秦岭造山带武关杂岩石榴黑云片岩的变质作用P-T轨迹与构造意义[J]. 岩石学报,33(8):2563-2574. [125] 李海平,1998. 陕西省佛坪发现太古宇结晶杂岩[J]. 中国区域地质,17(3):329-330. [126] 李怀坤,陆松年,陈志宏,等,2003. 南秦岭耀岭河群裂谷型火山岩锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 地质通报,22(10):775-781. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2003.10.005 [127] 李三忠,张国伟,李亚林,等,2000. 勉县地区勉略带内麻粒岩的发现及构造意义[J]. 岩石学报,16(2):220-226. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2000.02.011 [128] 李三忠,赖绍聪,张国伟,等,2003. 秦岭勉(县-)略(阳)缝合带及南秦岭地块的变质动力学研究[J]. 地质科学,38(2):137-154. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2003.02.001 [129] 李献华,李武显,何斌,2012. 华南陆块的形成与Rodinia超大陆聚合-裂解:观察、解释与检验[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,31(6):543-559. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2012.06.002 [130] 李亚林,王根宝,王成善,等,2000. 南秦岭龙草坪结晶杂岩锆石U-Pb同位素地质年代学研究[J]. 矿物学报,20(1):50-54. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2000.01.009 [131] 梁莎,刘良,张成立,等,2013. 南秦岭勉略构造带高压基性麻粒岩变质作用及其锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 岩石学报,29(5):1657-1674. [132] 凌文黎,任邦方,段瑞春,等,2007. 南秦岭武当山群、耀岭河群及基性侵入岩群锆石U-Pb同位素年代学及其地质意义[J]. 科学通报,52(12):1445-1456. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.12.015 [133] 凌文黎,段瑞春,柳小明,等,2010. 南秦岭武当山群碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学及其地质意义[J]. 科学通报,55(12):1153-1161. [134] 刘仁燕,牛宝贵,和政军,等,2011. 陕西柞水地区小茅岭复式岩体东段LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年[J]. 地质通报,30(2-3):448-460. [135] 刘树文,杨朋涛,李秋根,等,2011. 秦岭中段印支期花岗质岩浆作用与造山过程[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),41(6):1928-1943. [136] 刘志慧,罗敏,陈龙耀,等,2018. 南秦岭佛坪地区地层格架与物源分析:变质沉积岩中碎屑锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年提供的制约[J]. 岩石学报,34(5):1484-1502. [137] 刘志慧,陈龙耀,曲玮,等,2019. 南秦岭佛坪地区早中生代变质-深熔-变形作用的锆石U-Pb年代学制约[J]. 地球学报,40(4):545-562. [138] 孟庆任,2017. 秦岭的由来[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,47(4):412-420. [139] 秦克令,宋述光,何世平,1992. 陕西勉略宁区鱼洞子花岗岩-绿岩地体地质特征及其含金性[J]. 西北地质科学,13(1):65-74. [140] 陕西省地质调查院,2017. 中国区域地质志-陕西志[M]. 北京:地质出版社:1-1120. [141] 陕西省地质矿产局,1989. 陕西省区域地质志[M]. 北京:地质出版社. [142] 陕西省地质矿产局,1999. 中华人民共和国区域地质调查报告:1:50000 佛坪县幅(I48E015024)[R]. 全国地质资料馆. [143] 王东升,王宗起,张英利,等,2016. 南秦岭增生杂岩带马道地区变泥质岩的变质作用[J]. 现代地质,30(6):1254-1266. [144] 王根宝,1997. 南秦岭佛坪片麻岩系同位素年代学及其地质意义[J]. 西北地质科学,18(2):21-25. [145] 王嘉玮,王刚,王宗起,等,2021. 南秦岭武当山十堰地区中生代镁铁质岩石成因与构造意义:岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素制约[J]. 地质论评,67(4):869-885. [146] 王清晨,孙枢,李继亮,等,1989. 秦岭的大地构造演化[J]. 地质科学,24(2):129-142. [147] 王宗起,闫全人,闫臻,等,2009. 秦岭造山带主要大地构造单元的新划分[J]. 地质学报,83(11):1527-1546. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.11.001 [148] 魏春景,张翠光,2002. 陆-陆碰撞造山带中压型变质作用的pT轨迹:以南秦岭佛坪地区为例[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,21(4):356-362. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2002.04.007 [149] 夏林圻,夏祖春,李向民,等,2008. 南秦岭东段耀岭河群、陨西群、武当山群火山岩和基性岩墙群岩石成因[J]. 西北地质,41(3):1-29. [150] 许志琴,卢一伦,汤耀庆,等,1988. 东秦岭复合山链的形成-变形、演化及板块动力学[M]. 北京:中国环境科学出版社:1-193. [151] 杨崇辉,魏春景,张寿广,等,1999. 南秦岭佛坪地区麻粒岩相岩石锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 地质论评,45(2):173-179. [152] 杨再兵,裴先治,李瑞保,等,2023. 扬子西北缘碧口微地块南华系碎屑锆石物源示踪及其地质意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,43(1):226-248. [153] 查显锋,董云鹏,李玮,等,2010. 南秦岭佛坪隆起的成因探讨:构造解析的证据[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,34(3):331-339. [154] 张国伟,张本仁,袁学诚,等,2001. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M]. 北京:科学出版社:1-885. [155] 张国伟,等,2015. 秦岭勉略构造带与中国大陆构造[M]. 北京:科学出版社. [156] 张国伟,郭安林,董云鹏,等,2019. 关于秦岭造山带[J]. 地质力学学报,25(5):746-768. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.05.064 [157] 张瑞英,敖文昊,孙勇,2013. 南秦岭西段(佛坪-留坝地区)侵入岩系的形成时代、物质组成及其地质意义[C]//全国岩石学与地球动力学研讨会论文集. 广州:中国地质学会. [158] 张诜,刘锦兴,左猫,等,2022. 佛坪袁家庄晶质石墨矿区地质特征及成矿条件浅析[J]. 西部探矿工程,34(4):137-141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2022.04.049 [159] 张欣,徐学义,宋公社,等,2010. 西秦岭略阳地区鱼洞子杂岩变形花岗岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年及地质意义[J]. 地质通报,29(4):510-517. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.04.004 [160] 张永清,张健,李怀坤,等,2013. 南秦岭武当山群变质酸性火山岩锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 地质学报,87(7):922-930. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2013.07.002 [161] 张宗清,张国伟,唐索寒,等,2001. 鱼洞子群变质岩年龄及秦岭造山带太古宙基底[J]. 地质学报,75(2):198-204. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2001.02.008 [162] 张宗清,宋彪,唐索寒,等,2004. 秦岭佛坪变质结晶岩系年龄和物质组成特征-SHRIMP锆英石U-Pb年代学和全岩Sm-Nd年代学数据[J]. 中国地质,31(2):161-168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2004.02.007 [163] 周鼎武,张成立,华洪,等,1998. 南秦岭中、新元古代地层划分对比新认识[J]. 高校地质学报,4(3):350-357. [164] 周鼎武,张成立,周小虎,等,1999. 武当地块基性岩墙群40Ar-39Ar定年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报,15(1):14-20. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1999.01.002 [165] 祝禧艳,陈福坤,王伟,等,2008. 豫西地区秦岭造山带武当群火山岩和沉积岩锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 地球学报,29(6):817-829. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.06.025 -




 下载:
下载: