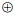MICRO-EARTHQUAKES IN THE SHIZIGOU OILFIELD, QINGHAI, AND THEIR GEOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE
-
摘要: 通过对柴达木盆地西部狮子沟地区一年多的微地震监测数据的分析处理, 发现该区微地震活动比较频繁, 总体走向北西, 且多集中在该区盆山过渡带北西走向的花土沟断裂北东侧2km深度附近。通过对地震与钻孔分布之间的关系和地震发生频次对数与震级线性关系的斜率b值的分析, 本文认为, 虽然油井注水等因素对研究区内微地震事件具有一定的诱发作用, 但大部分地震事件仍主要与断裂及其次级构造有关。Abstract: A large number of high-quality seismic data are recorded in the Shizigou oilfield of the western Qaidam basin by monitoring micro-earthquakes for more than one year.After processing and analyzing these data, the authors find that micro-earthquakes occur relatively frequently in the study area and are mainly concentrated at ~2 km depth on the NE side of the NW-trending Huatugou fault in the basinmountain transition zone of the area.Analyses of the relation between earthquakes and oil well distribution and the slope b in the linear relation between log frequency and magnitude show that microearthquakes in the study area are mainly related to the Huatugou fault and its secondary structures though fluid injection through the wells has a certain microearthquake-inducing effect in the area.
-
Key words:
- micro-earthquake /
- fault activity /
- Shizigou oilfield /
- western Qaidam basin
-
人工地震勘探是探测深部构造的常用方法, 但这种方法只能探测到两盘具有不同阻抗值的断层。而通过监测断层活动产生的微地震, 不但可以了解断层的空间位置, 还能够查明断层的活动规律。近年来在油田开发中广泛应用的微地震监测技术, 就是借助天然地震学方法和思路来监测微地震的空间和时间分布规律, 找出微地震与深部构造活动的关系, 并据此推断构造的活动情况。
当应力增大或屈服强度降低时, 构造薄弱面上一些局部部位会首先因材料失稳而产生裂缝及其微弱活动。水的注入等因素可以导致断层本身屈服强度降低。在裂缝活动过程中, 部分能量通过地震弹性波的方式释放, 并在之后达到新的平衡。当失稳范围和规模从小到大, 就可能发生地质灾害或较大的地震。利用观测到的裂缝微地震活动发出的高频波动信号可以获得发生破裂的位置和特征[1]。长期地震观测显示, 很多地震是由断裂活动引发的[2]。所以通过对微地震活动的监测, 可以得到断裂活动的有关信息。本文就是通过对微地震活动的分析来获得断裂活动信息的。
与人工地震勘探方法相比, 天然地震监测中的震源位置、发震时刻和震源强度都是未知的。与油田常用的微地震监测技术相比, 本文讨论的微地震主要是由布设在地表的地震台网来记录的, 而非像油田常用微震监测那样将探头置于井下[3~4]。
1. 技术方法
微地震监测研究主要包括两部分:①通过层析成像反演得到地下深部的波速结构; ②探知微地震发生的位置及性质。两者是相辅相成的。因为只有在可靠的深部波速结构的基础之上, 才能得到可靠的地震发生位置及性质。反之亦然。
地震层析成像是一种利用地震波对地球内部三维结构进行成像以发现地下波速异常的方法。自从30多年前Aki等[5]首次把天然地震层析成像技术应用于研究三维地球结构之后, 该技术在大尺度的地球深部结构研究中得到了广泛的应用。天然地震层析成像技术在矿产资源勘探领域的应用是近些年才兴起的。
按照地震波射线传播理论, 地震波沿着波的传播路径到达地震台站所需要的时间可以表示为对波的传播路径上的走时积分。为了计算上的简便, 通常需要把研究区划分为离散的网格, 并假设每个网格内的波速是均匀的。这样台站到震源的走时积分就可以简化为走时叠加。对于很多的震源和台站, 可以建立很多路径的走时叠加方程。而地震层析成像的目的正是要通过这些方程组中已知的其中两个量求第三个量。比如已知地震波走时和地震震源位置求速度分布, 或已知地震波走时和速度分布求地震震源位置。所以反演震源位置和波速结构这两个过程是相辅相成的, 实际上就是一个迭代反演解大型方程组的问题。
微地震层析成像[6~7]是利用密集地震台阵来监测岩层中微地震活动所产生的地震波, 然后运用地震学方法来反演微地震的活动特征和研究区三维横波、纵波波速分布的一种勘探方法。它主要利用被动震源, 也可以利用人工地震, 并适用于各种复杂的地区和环境。
本文所用的地震检波器的主要监测频率介于5~100Hz之间, 而油田监测的地震信号频率通常高达200~2000Hz。
2. 地震观测数据
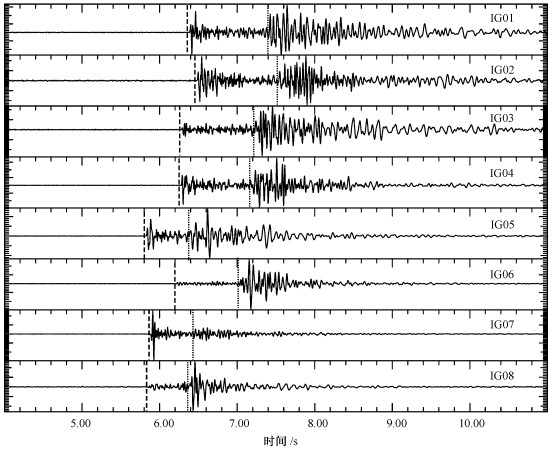
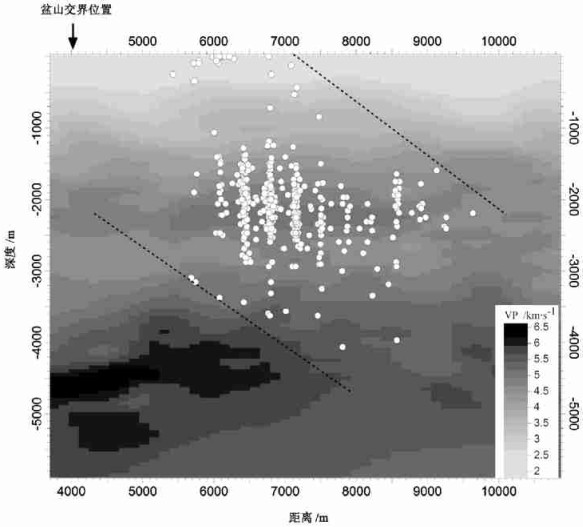
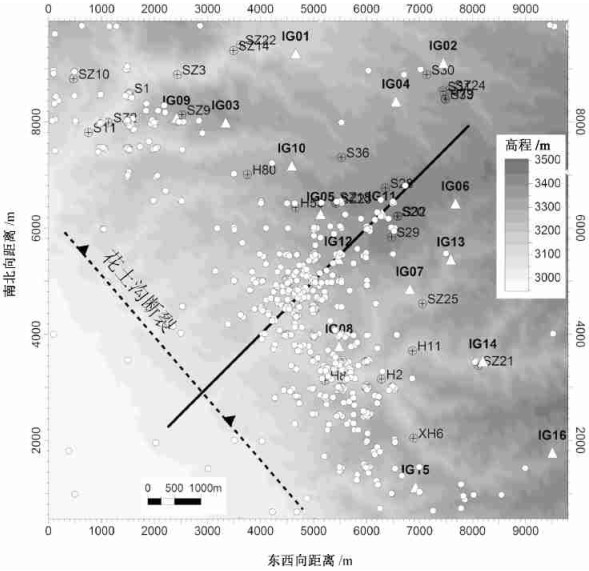
本文研究区(见图 1)是柴达木盆地西部狮子沟油田100km2的范围, 在该区布设的16个台站自2004年10月开始记录了大量连续的高质量的地震资料。地震波形实例见图 2, 地震台站位置见图 3。本文分析处理了2004年10月到2005年12月间共14个月的数据, 最终得到了研究区内952个微地震数据。
 图 3 研究区内微地震分布灰色影像表示高程(单位:m)。圆圈表示震中; 三角表示地震台站; 标注为
图 3 研究区内微地震分布灰色影像表示高程(单位:m)。圆圈表示震中; 三角表示地震台站; 标注为在数据处理过程中, 首先从连续地震记录中挑出研究区内信噪比高的地震事件波形, 然后对挑出的事件进行P波和S波震相到时拾取。图 2显示了8个地震台站记录到的同一个微地震的地震波, 数据信噪比高且震相到时清楚。图中标识为虚竖线的位置为首先到达的纵波P波震相, 标识为点竖线的位置为后到达的横波S波震相。
3. 结果及解释
研究区西南部分为地势平坦的盆地, 东北部地区海拔较高, 中部地形变化较大(图 3)。西南部存在一个走向近北西的明显的盆山边界, 被认为是花土沟断裂的地表出露位置(图 3中虚线标识其大概位置)。
图 3显示了14个月时间内记录到的大于-2级地震的二维分布。震中分布的一个明显特点是, 地震主要集中在研究区中部海拔变化较大(由海拔3100m迅速增加到3300m或更高)、地形复杂的部位。另外, 研究区西北角的地震也较多, 这里正是花土沟断裂和一条北东东走向大沟的交会区。由于盆山交界区域附近没有地震台站, 在该区域观测到的地震数量较少。多数地震呈带状集中在花土沟断裂带北东侧, 并且主体走向与花土沟断裂平行(图 3)。由于微地震通常沿着断层分布, 因此推断花土沟断裂为北东倾向。
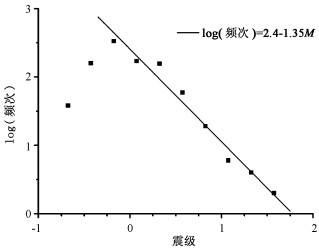
根据对较大地震(震级大于1级)的统计, 一般地, 一个地区一段时间内地震发生频次(N)的对数与地震震级(M)成近似线性关系(即log (N) =a-bM, 其中a和b为常数, b在地震学中称为b值)[8], 反映了该地区在一定时间段内的应力场特征。某个时期斜率常数b值发生的变化, 意味着区域应力场等性质发生变化, 因此, b值常常被用于地震预报中[9]。
图 4为观测到的微地震发生频次与地震震级关系分布图。本文-0.25到2级的微地震也表现出地震频次对数随震级增大而减小的线性关系, 但小于-0.25级的地震表现为频次随地震震级减小而减小的关系(图 4)。这说明, 现有设备可以记录所有震级大于-0.25的地震。但是, 可能由于设备及其部署等原因, 记录到的更小地震事件有所遗漏, 并随震级减小而遗漏增多。
均匀应力场下统计的b值通常小于1, 但构造应力场非常不均匀时可以产生很多地震群, 这时b值可以高达2.5[8]。研究显示[10~11], 钻孔注入流体或其他原因导致的孔隙压力变化同样可以触发局部微震。图 4数据显示的b值约为1.35, 略大于均匀应力场下的b值(< 1.0)。因此总体看来, 研究区应力场分布可能是均匀的。但是, 油田开采或钻孔注水等改变了孔隙压力, 从而触发了一些微震, 最终可能导致b值偏高。
油田生产或注水可以导致孔隙压力变化, 从而可能触发微震。如图 3左上角钻孔密度较大的地区(即钻孔SZ10, S11和S1等附近)的地震比周围偏多; 中部的S29和S28等钻孔较多的地区地震事件相对也较多。但是, 其他一些钻孔密集区域的地震事件并未明显增加。
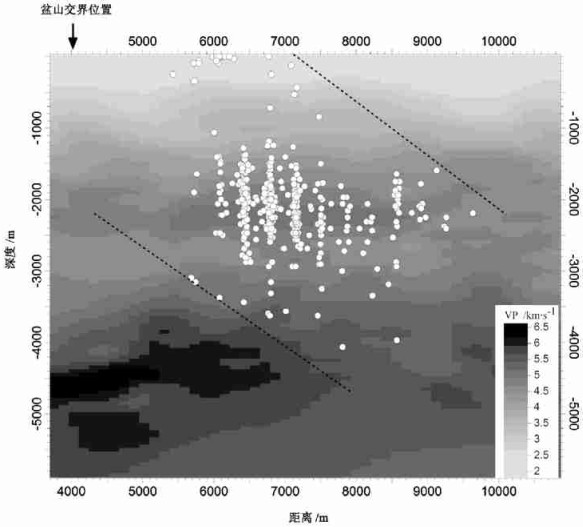
图 5为穿过研究区的一条北东向垂直剖面(剖面位置见图 3中黑实线)。由于盆山交界(花土沟断裂出露位置)附近没有布设地震台站, 所以该区基本没有检测到地震。另外, 图 5中的地震分布相对离散。虽然利用相对定位方法(如近年常用的双差分方法[12])可以使定位后的地震分布相对集中, 但由于没有证据表明微地震事件之间具有关联性, 因此这里没有采用。
图 5显示, 地震多集中在2km深度左右, 而且总体(图 5中虚线标出的范围)具有北东倾向。按照图中地震总体分布向左上方延伸, 就可以与花土沟断裂出露位置基本重合。考虑到图 3中地震带主体走向与花土沟断裂平行, 因此可以认为剖面显示的地震主要与以花土沟断裂为主的断裂带有关。
4. 结论
本文通过对柴达木盆地西部狮子沟地区密集高频地震台网一年多的微地震观测数据的分析, 检测到大量微地震, 可能与花土沟断裂的深部地震活动有关。该微地震活动带为北西走向, 北东倾向, 与前期地震观测结果[13]相吻合。
地震事件发生频次和震级之间关系的分析显示, 现有设备在现有布置格局下可以监测到研究区内所有震级大于-0.25的地震事件。因此, 虽然地震震级与频次对数的线性关系是在研究较大震级地震的过程中得到的, 但本文证实它同样适用于震级大于-0.25的微震。本区微震分布的b值约为1.35, 略大于均匀应力场下b值的范围。这可能与油田开采和钻孔注水等改变了孔隙压力而触发了一些微震有关。
-
图 3 研究区内微地震分布
灰色影像表示高程(单位:m)。圆圈表示震中; 三角表示地震台站; 标注为符号的表示钻孔。图中黑色虚线标识盆山交界, 为花土沟断裂在地表出露的大概位置, 标出的倾向为本文推测。黑实线为一条穿过研究区的垂直剖面的位置, 该剖面上的地震分布显示在图 2中。
Figure 3. Epicenter distribution for micro-earthquakes in the study region
-
[1] 安美建, 冯梅, 王小凤, 等. 被动地震勘探新方法在矿产勘探和地质灾害监测中的应用[M]以科学发展观促进科技创新(上). 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 2005: 384~388. [2] 薛霆, 傅容珊, 绍志刚.大尺度断层地震活动的数值模拟[J].中国地球物理2006年会会刊, 2006 :313. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HY000001787705 [3] 刘百红, 秦绪英, 郑四连, 等.微地震监测技术及其在油田中的应用现状[J].勘探地球物理进展, 2005, 28 (5): 325~329. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ktdqwljz200505005 [4] 董世泰, 高红霞.微地震监测技术及其在油田开发中的应用[J].石油仪器, 2004, 18 (5):5~8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9134.2004.05.002 [5] Aki K, Christoffersson A, Husebye E S, et al.Three-dimensional sei smi c-velocity anomalies in the crust and upper-mantle under the U.S.G.S.California seismic array (abstract)[J].EOS Trans.AGU, 1974, 56 :1145. [6] 王小凤, 冯梅, 史大年, 等.微地震台阵网天然地震层析成像技术在油田深层构造解析中的应用[J].地质通报, 2006, 25 (9 10):1028~1031. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz200609006 [7] Martakis N, Tselentis A, Kapotas S, et al., Passive seismic tomography a complementary geophysi cal method: successful case study, EAGE 65th Conference & Exhibition, Stavanger, Norway, 2003. [8] Lay Thorne, Wallace Terry C. Modern Global Seismology [M]. Academic Press, 1995. [9] 时振梁, 张少泉, 赵荣国, 等.地震工作手册[M].北京:地震出版社, 1990 :1~633. [10] Zoback M, Harjes H-P.Injection induced earthquakes and the crustal stress at 9 km depth at the KTB deep drilling site, Germany [J].J.Geophys.Res., 1997, 102:18477~18492. doi: 10.1029/96JB02814 [11] Shapiro SA, Kummerow J, Dinske C, et al.Fluid induced seismicity guided by a continental fault:Injection experiment of 2004 2005 at the German Deep Drilling Site (KTB)[J].Geophys.Res.Lett., 2006, 33 :L01309. doi: 10.1029-2005GL024659/ [12] Waldhauser Felix, Ellsworth William L.A double difference earthquake location algorithm:Method and application to the northern Hayward fault, California [J].Bull.Seism.Soc.Amer., 2000, 90 (6):1353~1368. doi: 10.1785/0120000006 [13] 马寅生, 史大年, 安美建, 等.苏门答腊地震对柴达木地方震的触发作用[J].地质力学学报, 2005, 11 (2):110~116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2005.02.002 -






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载: