ESR DATING OF THE PALAEOGENE IN MULI BASIN IN THE MIDDLE OF QILIAN MOUNTAINS AND ITS GEOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE
-
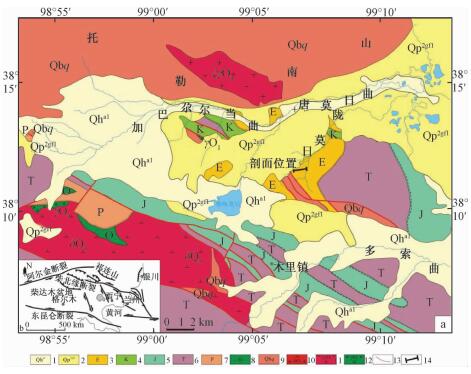
摘要: 对中祁连木里盆地新生代红层进行ESR测年,获得了祁连山地区新生代红层沉积时代及构造变形年代学数据。研究表明,中祁连木里盆地内沉积了巨厚的新生代红层,较好地记录了祁连山隆升历史。盆地最老的新生代地层为始新世由湖相沉积组成的火烧沟组,ESR年龄为40.2~35.3 Ma,与上覆沉积时代为32.6~24.3 Ma的渐新世河湖相沉积组成的白杨河组呈角度不整合接触。构造变形特征与沉积环境的变化说明始新世末与渐新世初木里地区发生了构造变形和山脉的隆升,与祁连山地区新生代早期的隆升有很好的对应关系。Abstract: The technique of ESR was applied to determine the Cenozoic red beds, Muli Basin, therefore, we can get the age of sedimentary and tectonic deformation. The results indicated there were huge thick Cenozoic Red Beds and tectonic deformation geochronological data, well recording the uplift of Qilian Mountains. Based on the ESR dating, the Tertiary sediments include the Eocene to Oligocene Huoshaogou Formation (40.2~35.3 Ma), which consists mainly of lacustrine facies and the Oligocene Baiyanghe Formation (32.6~24.3 Ma), which consists lacustrine and fluvial facies. From late Eocene to early Oligocene, an obvious angular unconformity exists between the upper and lower strata and it can be inferred that Qilian Mountains area has been a tectonic deformation and uplift, which has corresponding connection with the early Cenozoic uplift of Qilian Mountains.
-
Key words:
- Baiyanghe Formation /
- Huoshaogou Formation /
- ESR dating /
- the middle of Qilian Mountains
-
表 1 陇莫日曲剖面样品ESR测年结果
Table 1. ESR dating result of the Longmori profile in Muli Basin

表 2 青藏高原东北部始新世—渐新世岩石地层单位及沉积时代
Table 2. Eocene-Oligocene lithostratigraphic units in the northeast of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and their ages

-
[1] 潘保田, 李吉均, 陈发虎.青藏高原:全球气候变化的驱动机和放大器-Ⅰ:新生代气候变化的基本特征[J].兰州大学学报:自然科学版, 1995, 31(3):120~128.PAN Bao-tian, LI Ji-jun, CHEN Fa-hu. Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau:A driver and amplifier of global climatic changes-Ⅰ:Basic characteristics of climatic changes in Cenozoic Era[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University:Natural Sciences, 1995, 31(3):120~128. [2] 潘保田, 李吉均, 朱俊杰, 等.青藏高原:全球气候变化的驱动机和放大器-Ⅱ:青藏高原隆升的基本过程[J].兰州大学学报:自然科学版, 1995, 31(4):160~167. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10730-2008162364.htmPAN Bao-tian, LI Ji-jun, ZHU Jun-jie, et al. Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau:A driver and amplifier of global climatic changes-Ⅱ:Uplift processes of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University:Natural Sciences, 1995, 31(4):160~167. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10730-2008162364.htm [3] 潘保田, 李吉均.青藏高原:全球气候变化的驱动机和放大器-Ⅲ:青藏高原隆起对气候变化的影响[J].兰州大学学报:自然科学版, 1996, 32(1):108~115. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDZK601.023.htmPAN Bao-tian, LI Ji-jun. Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau:A driver and amplifier of global climatic changes-Ⅲ:The effects of the uplift of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau on climatic changes[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University:Natural Sciences, 1996, 32(1):108~115. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDZK601.023.htm [4] 李东旭.大陆边缘反S状造山带三维模式兼论青藏高原结构与隆升[J].地质力学学报, 2007, 13(1):31~41. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20070105&journal_id=dzlxxbLI Dong-xu. 3D model of reversed S-shaped orogenic belts on the continental margin:With a discussion of the internal structure and uplift of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2007, 13(1):31~41. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20070105&journal_id=dzlxxb [5] 朱大岗, 孟宪刚, 赵希涛, 等.西藏纳木错盆地116ka以来沉积演化与青藏高原隆升[J].地质力学学报, 2005, 11(2):172~180. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20050226&journal_id=dzlxxbZHU Da-gang, MENG Xian-gang, ZHAO Xi-tao, et al. Sedimentary evolution of the Namco Basin, Tibet, since 116ka BP and Qinghai-Tibet Plateau uplift[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2005, 11(2):172~180. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20050226&journal_id=dzlxxb [6] 李吉均, 文世宣, 张青松, 等.青藏高原隆升的时代、幅度和形式的探讨[J].中国科学, 1979, (6):608~616. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JAXK197906008.htmLI Ji-jun, WEN Shi-xuan, ZHANG Qing-song, et al. The age, range and forms of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau uplift[J]. Science in China, 1979, (6):608~616. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JAXK197906008.htm [7] 李吉均, 方小敏.青藏高原隆升与环境变化研究[J].科学通报, 1998, 43(15):1569~1574. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1998.15.001LI Ji-jun, FANG Xiao-min. The Qinghai-Tibet plateau uplift and environmental change research[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1998, 43(15):1569~1574. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1998.15.001 [8] 丁林, 钟大赉, 潘裕生, 等.东喜马拉雅构造结上新世以来快速抬升的裂变径迹证据[J].科学通报, 1995, 40(16):1479~1500. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199516017.htmDING Lin, ZHONG Da-lai, PAN Yu-sheng, et al. The fission track evidence about eastern Himalayan tectonic rapid uplift since Pliocene[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1995, 40(16):1479~1500. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199516017.htm [9] 钟大赉, 丁林.青藏高原的隆升过程及其机制探讨[J].中国科学:D辑, 1996, 26(4):289~295.ZHONG Da-lai, DING Lin. The Qinghai-Tibet plateau uplift process and its mechanism[J]. Science in China:Edition D, 1996, 26(4):289~295. [10] Harrison T M, Copeland P, Kidd W S F, et al. Activation of the Nyainqentanghla shear zone:Implications for uplift of the southern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonics, 1995, 14(3):658~676. doi: 10.1029/95TC00608 [11] Blisniuk M P, Hacker R B, Glodny J, et al. Normal faulting in central Tibet since at least 13.5 Ma ago[J]. Nature, 2001, 412:628~632. [12] Coleman M, Hodges K. Evidence for Tibetan Plateau uplifted before 14 Myr ago from a new minimal age for east-west extension[J]. Nature, 1995, 374:49~52. doi: 10.1038/374049a0 [13] Turner S, Arnaud N, Liu L, et al. Post-collision, shoshonitic volcanism on the Tibetan Plateau:Implications for convective thinning of the lithosphere and the source of ocean island basalts[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1996, 37:45~71. doi: 10.1093/petrology/37.1.45 [14] Rowley D B, Currie B S. Paleo-altimetry of the late Eocene to Miocene Lunpola Basin, central Tibet[J]. Nature, 2006, 439:677~681. doi: 10.1038/nature04506 [15] 吴珍汉, 吴中海, 胡道功, 等.青藏高原渐新世晚期隆升的地质证据[J].地质学报, 2007, 81(5):577~587. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200705000.htmWU Zhen-han, WU Zhong-hai, HU Dao-gong, et al. Geological evidences for the Tibetan Plateau uplifted in late Oligocene[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2007, 81(5):577~587. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200705000.htm [16] Tapponnier P, Xu Z Q, Francoise R, et al. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Science, 2001, 294:1671~1677. doi: 10.1126/science.105978 [17] Meyer B, Tapponnier P, Bourjot L, et al. Crustal thickening in Gansu-Qinghai, lithospheric mantle subduction, and oblique, strike-slip controlled growth of the Tibet plateau[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1998, 135(1):1~47. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.1998.00567.x [18] Yin A, Harrison T M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth Planet Science, 2000, 28:211~280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211 [19] Yin A, Rumelhrt P E, Bulter R, et al. Tectonic history of the Altyn Tagh fault system in northern Tibet inferred from Cenozoic sedimentation[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2002, 114(10):1257~1295. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2002)114<1257:THOTAT>2.0.CO;2 [20] 陆洁民, 郭召杰, 赵泽辉, 等.新生代酒西盆地沉积特征及其与祁连山隆升关系的研究[J].高校地质学报, 2004, 10(1):50~61. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200401003.htmLU Jie-min, GUO Zhao-jie, ZHAO Ze-hui, et al. Cenozoic sedimentary characteristics of Jiuxi Basin and its relationship with uplift of Qilian Mountains[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2004, 10(1):50~61. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200401003.htm [21] 戴霜, 方小敏, 宋春晖, 等.青藏高原北部的早期隆升[J].科学通报, 2005, 50(7):673~683. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200507011.htmDAI Shuang, FANG Xiao-min, SONG Chun-hui, et al. Northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau early uplift[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(7):673~683. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200507011.htm [22] Wang E Q. Displacement and timing along the northern strand of the Altyn Tagh fault zone, northern Tibet[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 150(1-2):55~64. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00085-X [23] 郑德文, 张培震, 万景林, 等.六盘山盆地热历史的裂变径迹证据[J].地球物理学报, 2005, 48(1):157~164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200501021.htmZHENG De-wen, ZHANG Pei-zhen, WAN Jing-lin, et al. Apatite fission track evidence for the thermal history of the Liupanshan Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2005, 48(1):157~164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200501021.htm [24] 张培震, 郑德文, 尹功明, 等.有关青藏高原东北缘晚新生代扩展与隆升的讨论[J].第四纪研究, 2006, 26(1):5~13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200601001.htmZHANG Pei-zhen, ZHENG De-wen, YIN Gong-ming, et al. Discussion on late Cenozoic growth and rise of northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26(1):5~13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200601001.htm [25] Meng Q R, Hu J M, Yang F Z. Timing and magnitude of displacement on the Altyn Tagh fault:Constraints from stratigraphic correlation of adjoining Tarim and Qaidam basins, NW China[J]. Terra Nova, 2001, 13(2):86~91. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3121.2001.00320.x [26] Gilder S, Chen Y, Sen S. Oligo-Miocene magnetostratigraphy and rock magnetism of the Xishuigou section, Subei (Gansu Province, western China) and implications on shallow inclinations in central Asia[J]. Journal of Geophysical Reasearch:Solid Earth, 2001, 106:30505~30521. doi: 10.1029/2001JB000325 [27] Wang X M, Wang B Y, Qiu Z X, et al. Danghe area (western Gansu, China) biostratigraphy and implications for depositional history and tectonics of northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 208(3/4):253~269. [28] 张雪亭, 杨生德, 杨站君, 等.青海省区域地质概论[M].北京:地质出版社, 2007:72~82.ZHANG Xue-ting, YANG Sheng-de, YANG Zhan-jun, et al. The regional geology of Qinghai Province[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2007:72~82. [29] 孙红波, 孙军飞, 张发德, 等.青海木里煤田构造格局与煤盆地构造演化[J].中国煤炭地质, 2009, 21(12):34~37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2009.12.010SUN Hong-bo, SUN Jun-fei, ZHANG Fa-de, et al. Structural framework and coal basin tectonic evolution in Muli Coalfield, Qinghai[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2009, 21(12):34~37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2009.12.010 [30] 张克信, 王国灿, 季军良, 等.青藏高原古近纪-新近纪地层分区与序列及其对隆升的响应[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2010, 40(12):1632~1654. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201012003.htmZHANG Ke-xin, WANG Guo-can, JI Jun-liang, et al. Paleogene-Neogene stratigraphic realm and sedimentary sequence of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and their response to uplift of the plateau[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences, 2010, 53:1271~1294. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201012003.htm [31] 宋春晖. 青藏高原北缘新生代沉积演化与高原构造隆升过程[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2006: 1~326. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1009009SONG Chun-hui. Teetonic uplift and Cenozoic sedimentary evolution in the northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[D]. Lanzhou:Lanzhou University, 2006:1~326. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1009009 [32] 岳乐平, Heller E, 邱占祥, 等.兰州盆地第三系磁性地层年代与古环境记录[J].科学通报, 2000, 45(18):1998~2003. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2000.18.019YUE Le-ping, Heller E, QIU Zhan-xiang, et al. Lanzhou basin, Tertiary magnetic formations and paleoenvironment records[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(18):1998~2003. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2000.18.019 [33] Williams M A J, Dunkerley D L, Deckker P D, 等.第四纪环境[M].刘东升, 编译.北京:科学出版社, 1997:190.Williams M A J, Dunkerley D L, Deckker P D, et al. Quaternary environment[M]. LIU Dong-sheng, ed. Beijing:Science Press, 1997:190. [34] 程强, 寇小兵, 黄绍槟, 等.中国红层的分布及地质环境特征[J].工程地质学报, 2004, 12(1):34~40. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200401006.htmCHENG Qiang, KOU Xiao-bing, HUANG Shao-bin, et al. The distributes and geologic environment characteristics of red beds in China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2004, 12(1):34~40. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200401006.htm [35] Lee T Y, Lawver L A. Cenozoic plate reconstruction of Southeast Asia[J]. Tectonophysics, 1995, 251(1-4):85~138. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(95)00023-2 [36] Patzelt A, Li H M, Wang J D, et al. Palaeomagnetism of Cretaceous to Tertiary sediments from southern Tibet:Evidence for the extent of the northern margin of India prior to the collision with Eurasia[J]. Tectonophysics, 1996, 259(4):259~284. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(95)00181-6 [37] Beck R A, Burbank D W, Sercombe W J, et al. Stratigraphic evidence for an early collision between northwest India and Asia[J]. Nature, 1995, 373:55~58. doi: 10.1038/373055a0 [38] Dewey J F, Shackleton R M, Chang C F, et al. The tectonic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Philosophical Transactions of Royal Society A:Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1988, 327(1594):379~413. doi: 10.1098/rsta.1988.0135 [39] Liu Z, Wang C S, Yi H S. Evolution and mass accumulation of the Cenozoic Hoh Xil Basin, northern Tibet[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2001, 71(6):971~984. doi: 10.1306/030901710971 [40] 刘志飞, 王成善, 伊海生, 等.可可西里盆地新生代沉积演化历史重建[J].地质学报, 2001, 75(2):250~258. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200102017.htmLIU Zhi-fei, WANG Cheng-shan, YI Hai-sheng, et al. Reconstruction of depositional history of the Cenozoic Hoh Xil Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2001, 75(2):250~258. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200102017.htm [41] 刘志飞, 王成善, 伊海生, 等. 青藏高原北部可可西里盆地早新生代沉降史及其高原隆升意义[C]//陈毓川. 中国地质学会80周年学术文集. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002: 111~119.LIU Zhi-fei, WANG Cheng-shan, YI Hai-sheng, et al. Early Cenozoic subsidence history of the Hoh Xil Basin in the northern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[C]//CHEN Yu-chuan. Academic papers of the 80th anniversary of the Geological Society of China. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2002:111~119. [42] 刘志飞, 王成善.青藏高原北部可可西里盆地第三纪风火山群沉积环境分析[J].沉积学报, 2001, 19(1):28~36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200101004.htmLIU Zhi-fei, WANG Cheng-shan. Depositional environment of the Tertiary Fenghuoshan Group in the Hoh Xil Basin, northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2001, 19(1):28~36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200101004.htm [43] 刘志飞, Stewart L K.图形显示和比较古水流数据的一种软件(PC99):以青藏高原北部可可西里盆地新生代古水流数据为例[J].沉积学报, 2002, 20(2):354~358. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200202027.htmLIU Zhi-fei, Stewart L K. A software tool for graphically displaying and comparing palaeocurrent data (PC99):An example utilizing palaeocurrent data of the Cenozoic Hoh Xil Basin, northern Tibet[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2002, 20(2):354~358. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200202027.htm [44] 刘志飞, 王成善, 金玮, 等.青藏高原沱沱河盆地渐新世-中新世沉积环境分析[J].沉积学报, 2005, 23(2):210~217. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200502004.htmLIU Zhi-fei, WANG Cheng-shan, JIN Wei, et al. Oligo-Miocene depositional environment of the Tuotuohe Basin, Central Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2005, 23(2):210~217. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200502004.htm -





 下载:
下载: