Chronological, geochemical characteristics and tectonic evolution significance of the Sanyan eclogites in the Jinsha River suture zone, eastern Xizang
-
摘要: 金沙江−哀牢山缝合带作为东特提斯构造域的关键组成部分,被广泛认为是一条古特提斯造山带。然而,由于缺乏标志性高压/超高压岩石的变质作用研究,该区域洋壳俯冲闭合过程及后续碰撞造山演化一直未能得到有效约束。研究针对藏东金沙江缝合带“三岩地区”新发现的榴辉岩,开展了系统的野外调查、岩相学观察、锆石U-Pb测年及全岩主微量元素分析。根据退变质程度、主要矿物组合及结构特征,将“三岩地区”榴辉岩划分为石榴钠长阳起片岩、石榴阳起石岩、榴闪岩和榴辉岩4类。选取2件榴辉岩样品进行锆石U-Pb测年,获得206Pb/238U年龄分别为 247±2 Ma 和 246±1 Ma。锆石具有低 Th/U 比值、极低的Nb、Ta 和重稀土元素(HREE)含量,且无明显 Eu 负异常,表明其为榴辉岩相变质成因,~246 Ma 代表榴辉岩相变质时代。12 件样品的全岩主量元素分析显示原岩为苦橄质玄武岩−玄武岩,微量元素特征揭示原岩构造背景多样,包括洋岛玄武岩(OIB)、正常型洋中脊玄武岩(N-MORB)和富集型洋中脊玄武岩(E-MORB),表明“三岩地区”榴辉岩主要由古特提斯洋壳物质(洋岛及洋中脊玄武岩)经俯冲作用形成,属于洋壳型榴辉岩。结合前期研究获得的榴辉岩锆石U-Pb 年龄和多硅白云母 Ar-Ar 坪年龄,进一步限定金沙江古特提斯洋在中三叠世早期(T21)完全闭合。Abstract:
Objective As a key component of the eastern Tethys tectonic domain, the Jinsha River–Ailao Mountain suture zone is widely recognized as a Paleo-Tethys orogenic belt. However, due to the lack of metamorphic studies on high-pressure/ultra-high-pressure rocks, the subduction-to-closure process of the oceanic crust and the subsequent collisional orogenic evolution remain poorly constrained. Methods Systematic field surveys, petrographic observations, zircon U–Pb dating, and whole-rock major and trace element analyses were carried out on the newly discovered eclogites in the Sanyan area of the Jinsha River suture zone in eastern Xizang (Tibet). Based on the degree of retrogressive metamorphism, major mineral assemblages, and textural features, the Sanyan eclogites are classified into four types: garnet–albite–actinolite schist, garnet–actinolite, garnet–amphibolite, and eclogite. Results Zircon U–Pb dating of two eclogite samples yields 206Pb/238U ages of 247±2 Ma and 246±1 Ma, respectively. These zircons feature low Th/U ratios, extremely low content of Nb, Ta, and HREE, and no obvious negative Eu anomalies. Therefore, the genesis of the zircons should be eclogite-facies metamorphism, with the ~246 Ma age representing the timing of eclogite-facies metamorphism. Conclusion The whole-rock major element analysis of 12 samples shows that the protoliths are picritic basalt–basalt, and the trace element characteristics reveal diverse tectonic settings of the protoliths, including ocean island basalt (OIB), normal mid-ocean ridge basalt (N-MORB), and enriched mid-ocean ridge basalt (E-MORB), suggesting that the Sanyan eclogites were mainly formed by subduction of Paleo-Tethys oceanic crust materials (ocean islands and mid-ocean ridge basalts). Significance Combining the previously obtained zircon U–Pb ages of eclogites and the Ar–Ar plateau ages of phengites, the complete closure of the Jinsha River Paleo-Tethys Ocean in the early Middle Triassic (T21) is further constrained. -
Key words:
- Jinsha River suture zone /
- eclogite /
- subduction /
- Paleo-Tethys /
- Qinghai–Tibet Plateau /
- geochemistry
-
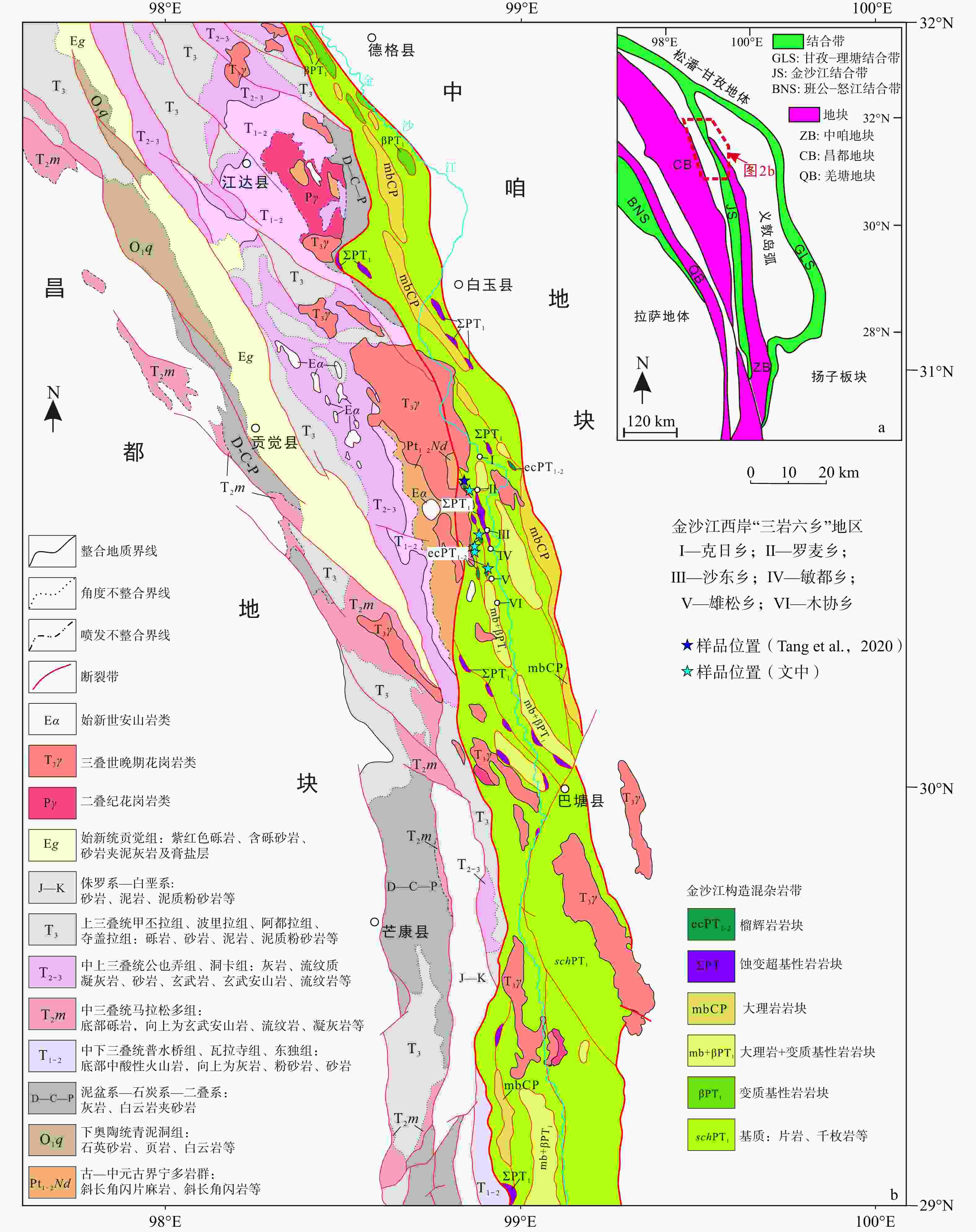
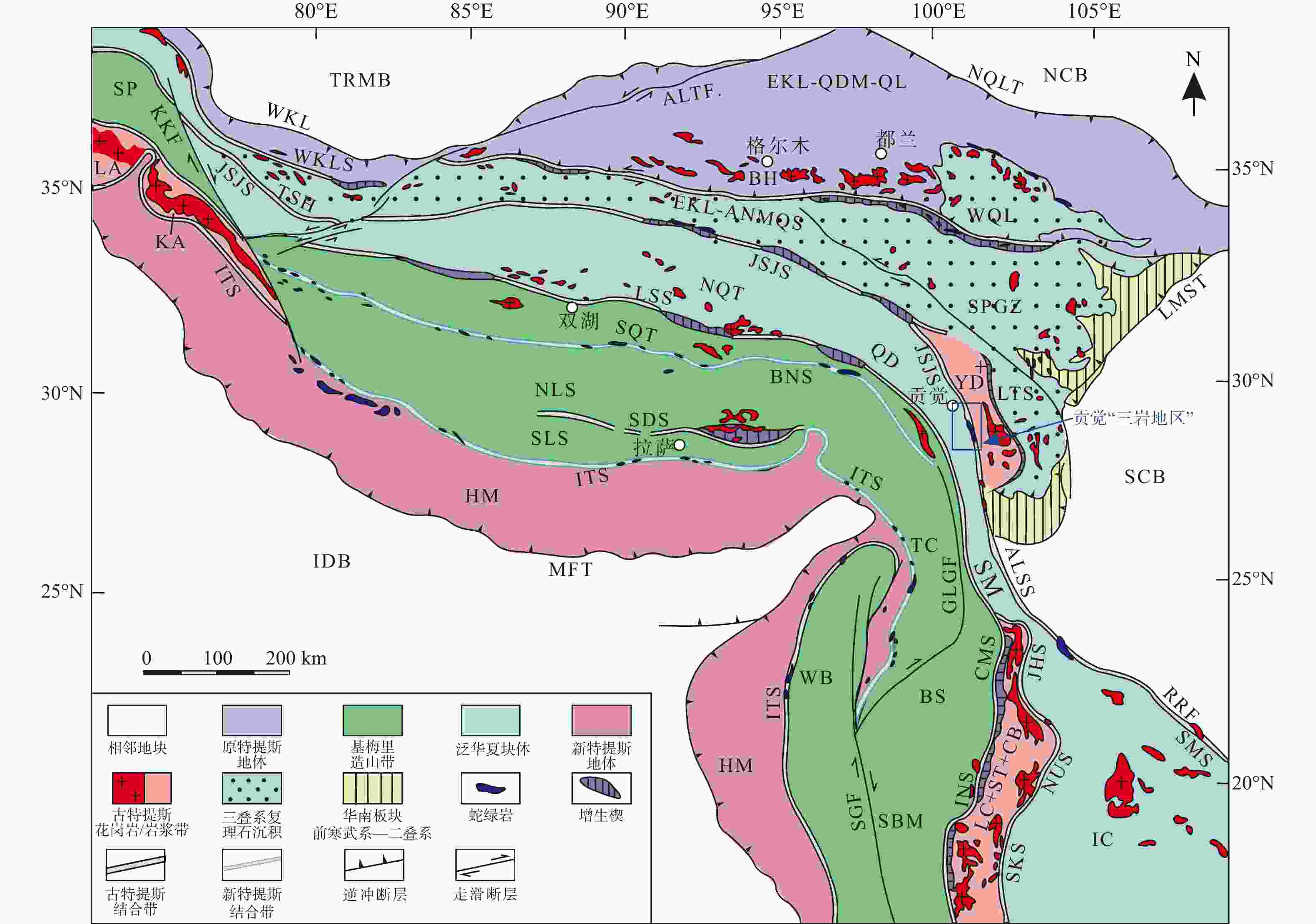
图 1 青藏高原及东南缘大地构造简图(据Xu et al.,2015修改)
板块或地块:NCB—华北板块;SCB—华南板块;TRMB—塔里木板块;IDB—印度板块;EKL–QDM–QL—东昆仑−柴达木−祁连地块;WKL—西昆仑地块;SPGZ—松潘−甘孜地块;NQT–QD–SM–IC—北羌塘−昌都−思茅−印支地块;SQT–BS–SBM—南羌塘−保山−Sibumasu 地块;NLS—北拉萨地块;SLS—南拉萨地块;TC—腾冲地块;TSH—甜水海地块;WB—西缅地块;WQL—西秦岭;SP—南帕米尔地块;HM—喜马拉雅地块结合带:EKL–ANMQS—东昆仑−阿尼玛卿结合带;WKLS—西昆仑结合带;LTS—理塘结合带;JSJS–ALSS–SMS—金沙江−哀牢山−马江结合带;LSS–CMS–INS—龙木措双湖−昌宁孟连−Inthanon 结合带;JHS–NUS–SKS—景洪−Nan Uttaradit−Sra Kaeo 结合带;BNS—班公湖−怒江结合带; SDS—松多结合带;ITS—雅鲁藏布江结合带岩浆弧:BH—布尔汉布达岩浆弧;YD—义敦岛弧;LC–ST–CB—临沧−Sukhothai−Chanthaburi 岩浆弧;KA—科希斯坦岩浆弧;LA—拉达克岩浆弧断层:ALTF—阿尔金断裂带;NQLT—北祁连逆冲推覆带;LMST—龙门山逆冲推覆带;RRF—红河断裂带;KKF—喀喇昆仑断裂带;MFT—主前锋逆冲断层;SGF—实皆断裂带;GLGF—高黎贡断裂带
Figure 1. Simplified tectonic map of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau and its southeastern margin (modified after Xu et al., 2015)
Blocks and Terranes: NCB−North China Block; SCB−South China Block; TRMB−Tarim Block; IDB−India Block; EKL−QDM−QL−East Kunlun−Qaidam−Qilian Terrane; WKL−West Kunlun Terrane; SPGZ−Songpan−Ganze Terrane; NQT−QD−SM−IC−North Qiangtang−Qamdo−Simao−Indochina Terrane; SQT−BS−SBM−South Qiangtang−Baoshan−Sibumasu Terrane; NLS−North Lhasa Terrane; SLS−South Lhasa Terrane; TC−Tengchong Terrane; TSH−Tianshuihai Terrane; WB−West Burma Terrane; WQL−West Qinling; SP−South Pamir Terrane; HM−Himalaya Block Suture Zones: EKL−ANMQS−East Kunlun−A’nyemaqen Suture; WKLS−West Kunlun Suture; LTS−Litang Suture; JSJS−ALSS−SMS−Jinshajiang−Ailaoshan−Song Ma Suture; LSS−CMS−INS− Longmu Tso Shuanghu− Changning Menglian−Inthanon Suture; JHS−NUS−SKS−Jinghong−Nan Uttaradit−Sra Kaeo Suture; BNS−Bangonghu−Nujiang Suture; SDS−Sumdo Suture; ITS−Indus−Tsangbo Suture Magmatic arc: BH−Bulhanbuda magmatic arc; YD−Yidun magmatic arc; LC−ST−CB−Lincang−Sukhothai−Chanthaburi magmatic arc; KA−Kohistan magmatic arc; LA−Ladakh magmatic arc Faults: ALTF−Altyn Tagh Fault; NQLT−North Qilian Thrust; LMST−Longmenshan Thrust; RRF−Red River Fault; KKF−Karakurum Fault; MFT−Main Frontal Thrust; SGF−Sagaing Fault; GLGF−Gaoligong Fault
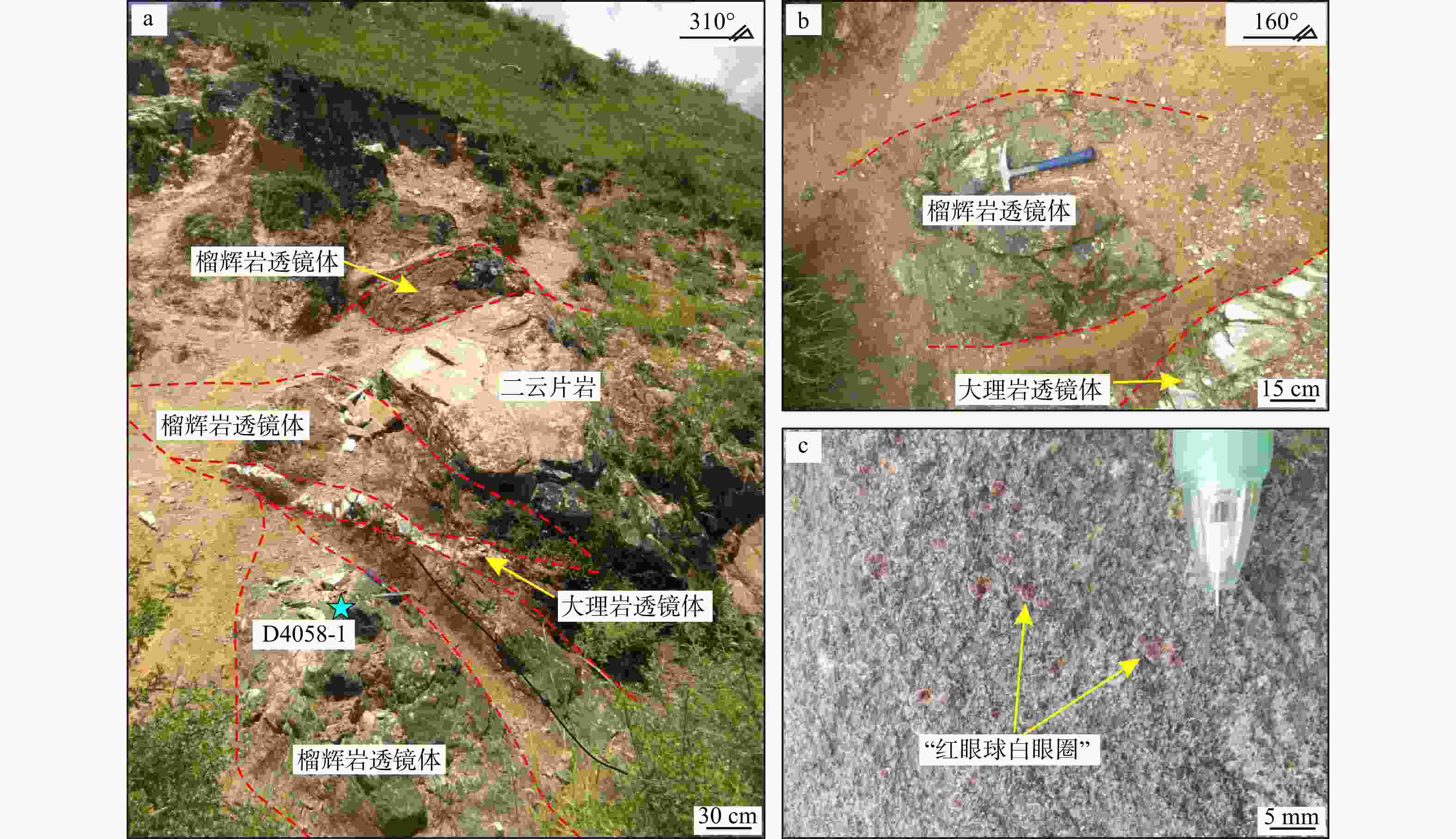
图 3 榴辉岩的野外产出特征
蓝色五角星为采样位置,D4058-1为文中样品代号a、b—呈透镜体状产出的榴辉岩;c—石榴石发育“红眼球白眼圈”构造
Figure 3. Field photographs of eclogites
(a, b) Eclogites occurring as lenticular bodies; (c) Garnet exhibiting "red-eye white-rim" texture (yellow arrows) The blue five-pointed star indicates the sampling location, and D4058-1 is the sample in the text.
图 4 不同退变程度榴辉岩的偏光显微镜和背散射电子显微特征
Omp—绿辉石;Grt—石榴石;Qz—石英;Phg—多硅白云母;Ab—钠长石;Act—阳起石;Pl—斜长石;Bt—黑云母;Spn—榍石;Ru—金红石;Cpx—单斜辉石;Brs—冻蓝闪岩;Amp—角闪石a—石榴阳起石岩在偏光显微镜下特征,显示主要矿物为阳起石和石榴石(单偏光);b—石榴阳起石岩在偏光显微镜下特征,显示主要矿物为阳起石和石榴石(正交偏光);c、d—石榴阳起石岩的背散射电子图像特征,可见绿辉石边缘发育单斜辉石+斜长石组成的蠕虫状细小颗粒;e—榴闪岩在偏光显微镜下特征,显示主要矿物为角闪石和石榴石(正交偏光);f—榴辉岩在偏光显微镜下特征,显示角闪石和绿辉石等矿物定向排列(正交偏光)
Figure 4. Microscopic characteristics of eclogites with different retrogradation degrees under polarized light microscopy and backscattered electron imaging
(a) Microscopic characteristics of garnet-actinolite under plane-polarized light, showing dominant minerals of actinolite and garnet; (b) Microscopic characteristics of garnet-actinolite under cross-polarized light, showing dominant minerals of actinolite and garnet; (c and d) Backscattered electron images of garnet-actinolitite, showing worm-like fine grains of clinopyroxene–plagioclase developed along the rim of omphacit; (e) Microscopic characteristics of garnet-amphibolite under cross-polarized light, showing dominant minerals of amphibole and garnet; (f) Microscopic characteristics of eclogite under cross-polarized light, showing amphibole and omphacite with oriented arrangement Omp−omphacite; Grt−garnet; Qz−quartz; Phg−phengite; Ab−albite; Act−actinolite; Pl−plagioclase; Bt−biotite; Spn−Sphene; Ru−rutile; Cpx−clinopyroxene; Brs−barroisite; Amp−amphibole
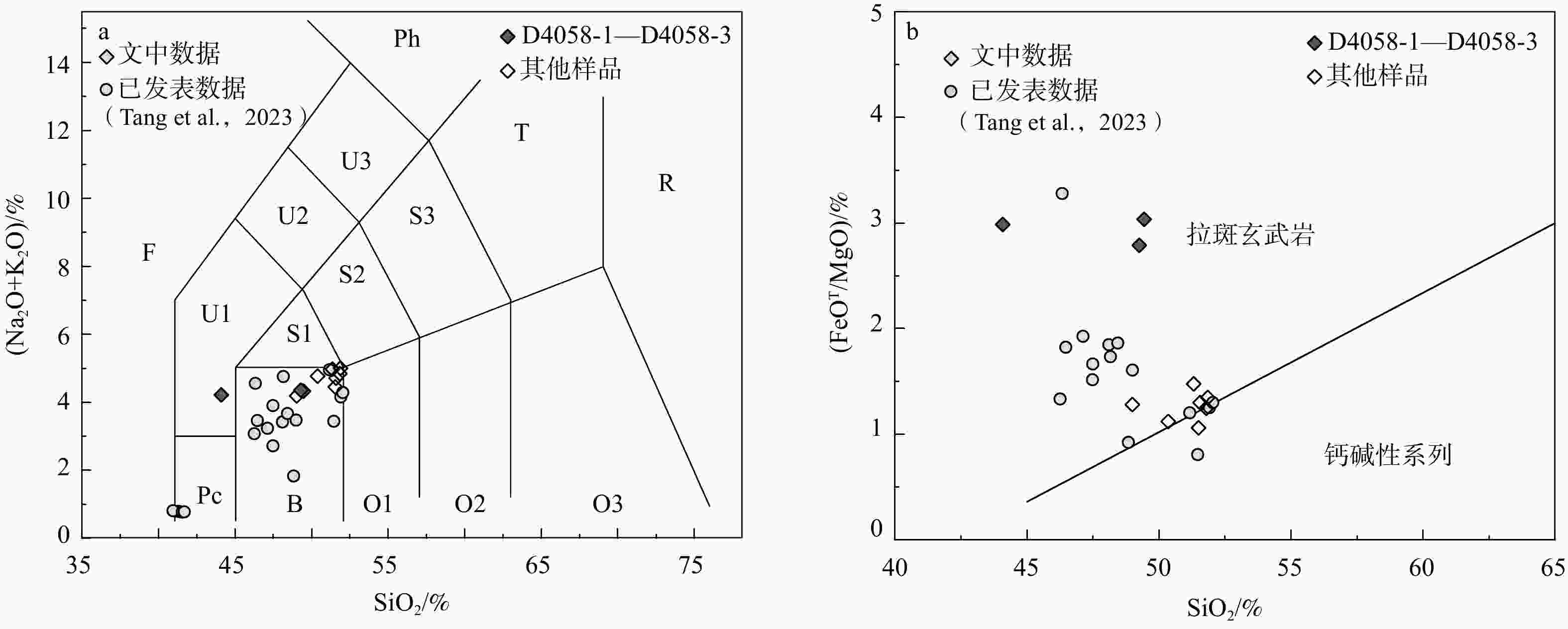
图 5 “三岩地区”榴辉岩的主量元素图解
Pc—苦橄玄武岩;B—玄武岩;O1—玄武安山岩;O2—安山岩;O3—英安岩;R—流纹岩;S1—粗面玄武岩;S2—玄武质粗面安山岩;S3—粗面安山岩;T—粗面岩、粗面英安岩;F—副长石岩;U1—碱玄岩、碧玄岩;U2—响岩质碱玄岩;U3—碱玄质响岩;Ph—响岩a—SiO2–(Na2O+K2O)分类图解(底图据Le Bas et al.,1986修改), b— SiO2–(FeOT/MgO) 分类图解(底图据Miyashiro,1974修改)
Figure 5. Major element diagrams of the Sanyan eclogites
(a) SiO2 vs. (Na2O+K2O) diagram of eclogite samples(base map modified from Le Bas et al., 1986); (b) SiO2 vs. (FeOt/MgO) diagram of eclogite samples (base map modified from Miyashiro, 1974) Pc–picritic basalt; B–basalt; O1–basaltic andesite; O2–andesite; O3–dacite; R–rhyolite; S1–trachybasalt; S2–basaltic trachyandesite; S3–trachyandesite; T–trachyte, trachydacite; F–foidite; U1–tephritebasanite; U2–phonotephrite; U3–tephriphonolite; Ph–phonolite
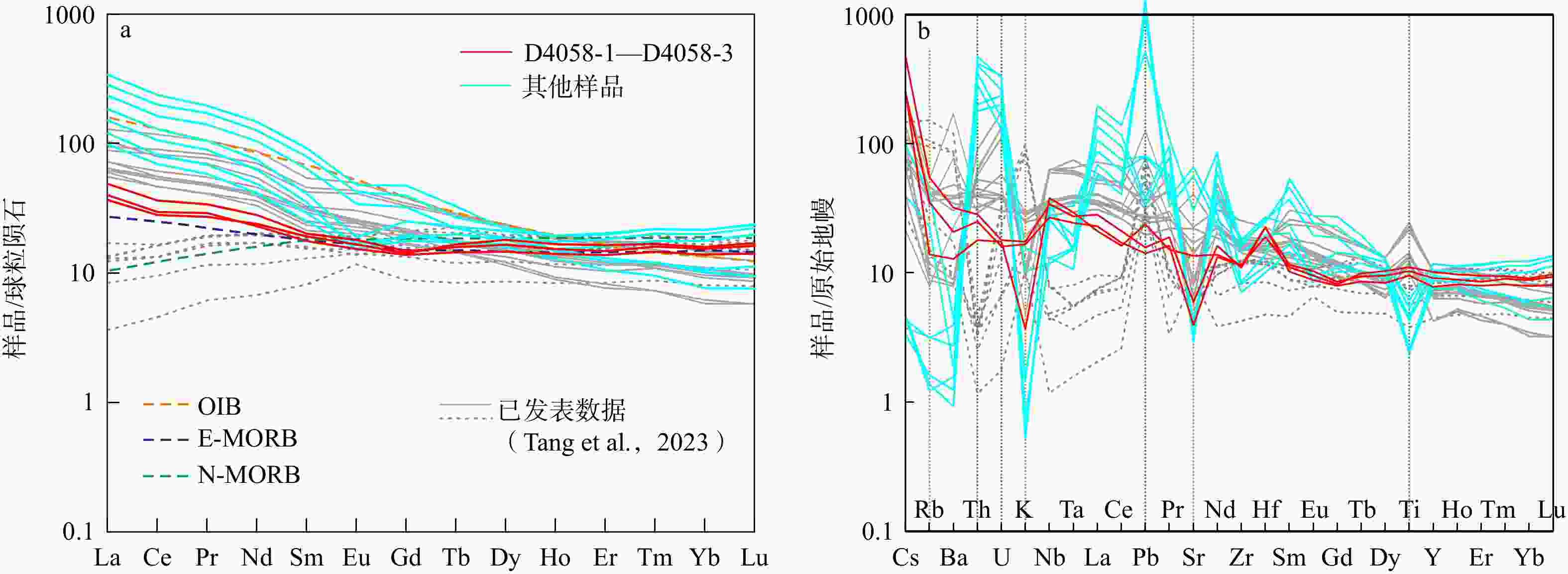
图 6 榴辉岩样品的球粒陨石标准化REE模式图和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(球粒陨石、原始地幔数据引自McDonough and Sun,1995)
a—球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线;b—微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图
Figure 6. The chondrite-normalized REE pattern diagram , and the primitive mantle-normalized trace-element spider diagram of eclogite samples (Values of chondrites and primitive mantle are cited from McDonough and Sun, 1995)
(a) Chondrite-normalized REE distribution pattern; (b) Primitive mantle-normalized trace element spidergram
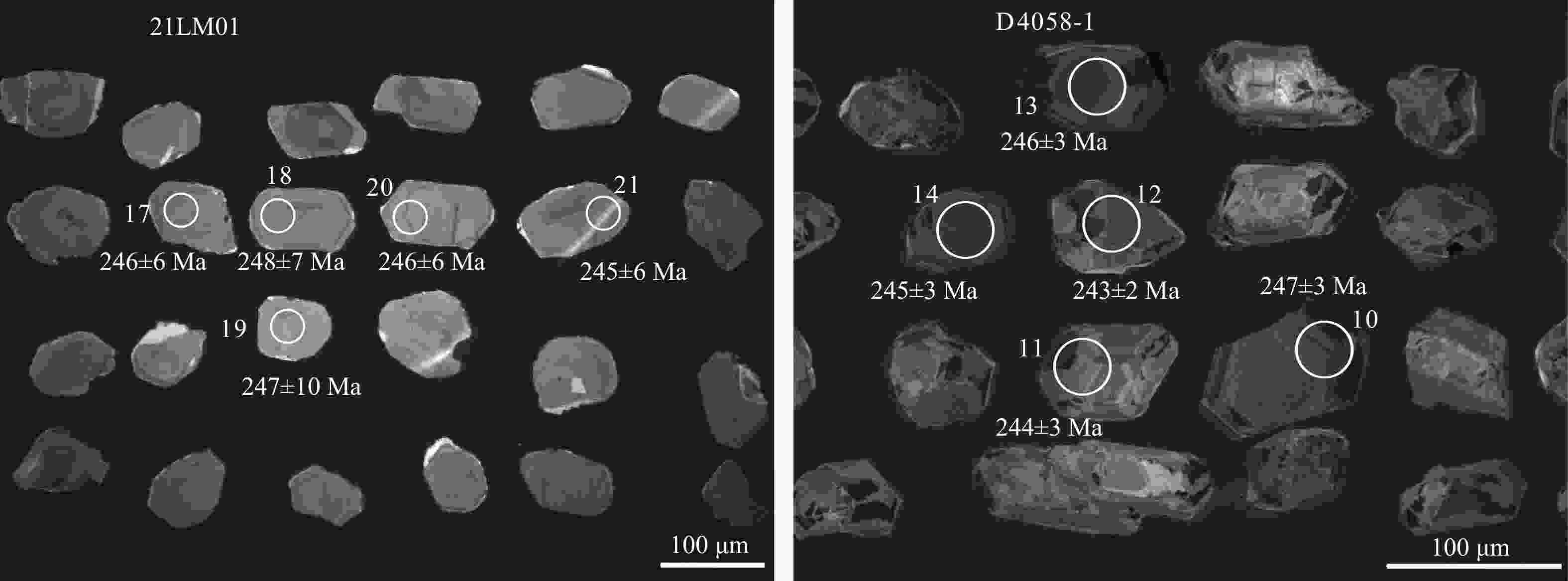
图 7 榴辉岩测年样品代表性锆石阴极发光图像(圆圈为测年打点位置,束斑直径为32 μm)
a—样品21LM01锆石阴极发光图像;b—样品D4058-1锆石阴极发光图
Figure 7. Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of representative zircons from the eclogite samples (Circles with data indicate spots and ages of U–Pb dating. The diameters of the circles are 32 μm.)
(a) CL image of zircons from sample 21LM01; (b) CL image of zircons from sample D4058-1
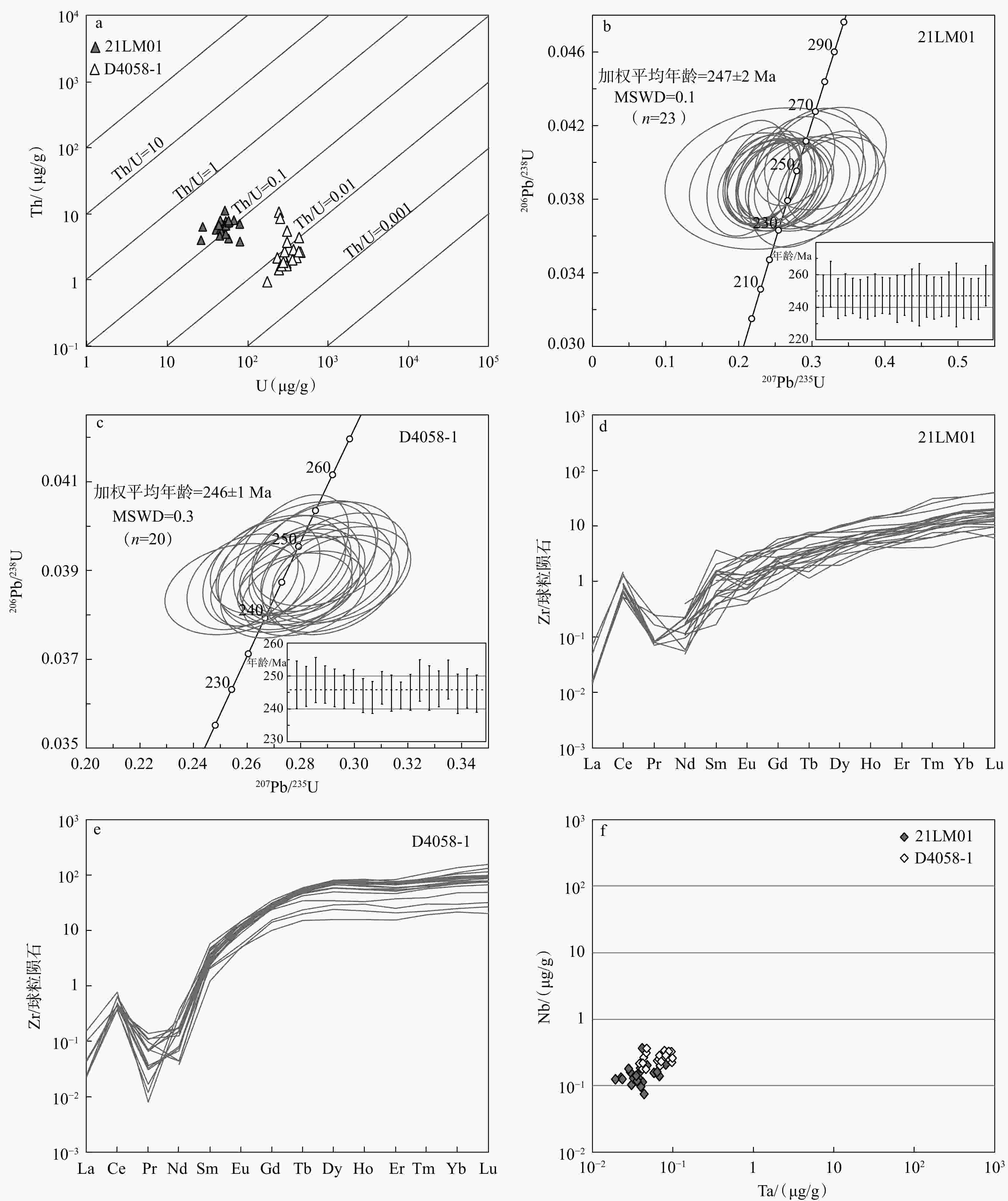
图 8 榴辉岩测年样品的锆石微量稀土元素特征及U-Pb年龄谐和图
a—样品21LM01和D4058-1的锆石Th、U含量和Th/U比值;b—样品21LM01的锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图;c—D4058-1的锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图;d—样品21LM01的锆石稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图;e—D4058-1的锆石稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图; f—样品21LM01和D4058-1的锆石Ta、Nb含量
Figure 8. Trace rare earth element characteristics and U−Pb concordia diagrams of zircons from eclogite dating samples
(a) Th and U contents and Th/U ratios in zircons from samples 21LM01 and D4058-1; (b) Concordia diagram of zircon U–Pb ages for sample 21LM01; (c) Concordia diagram of zircon U–Pb ages for sample D4058-1; (d) Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of zircons from sample 21LM01; (e) Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of zircons from sample D4058-1; (f) Ta and Nb contents in zircons from samples 21LM01 and D4058-1
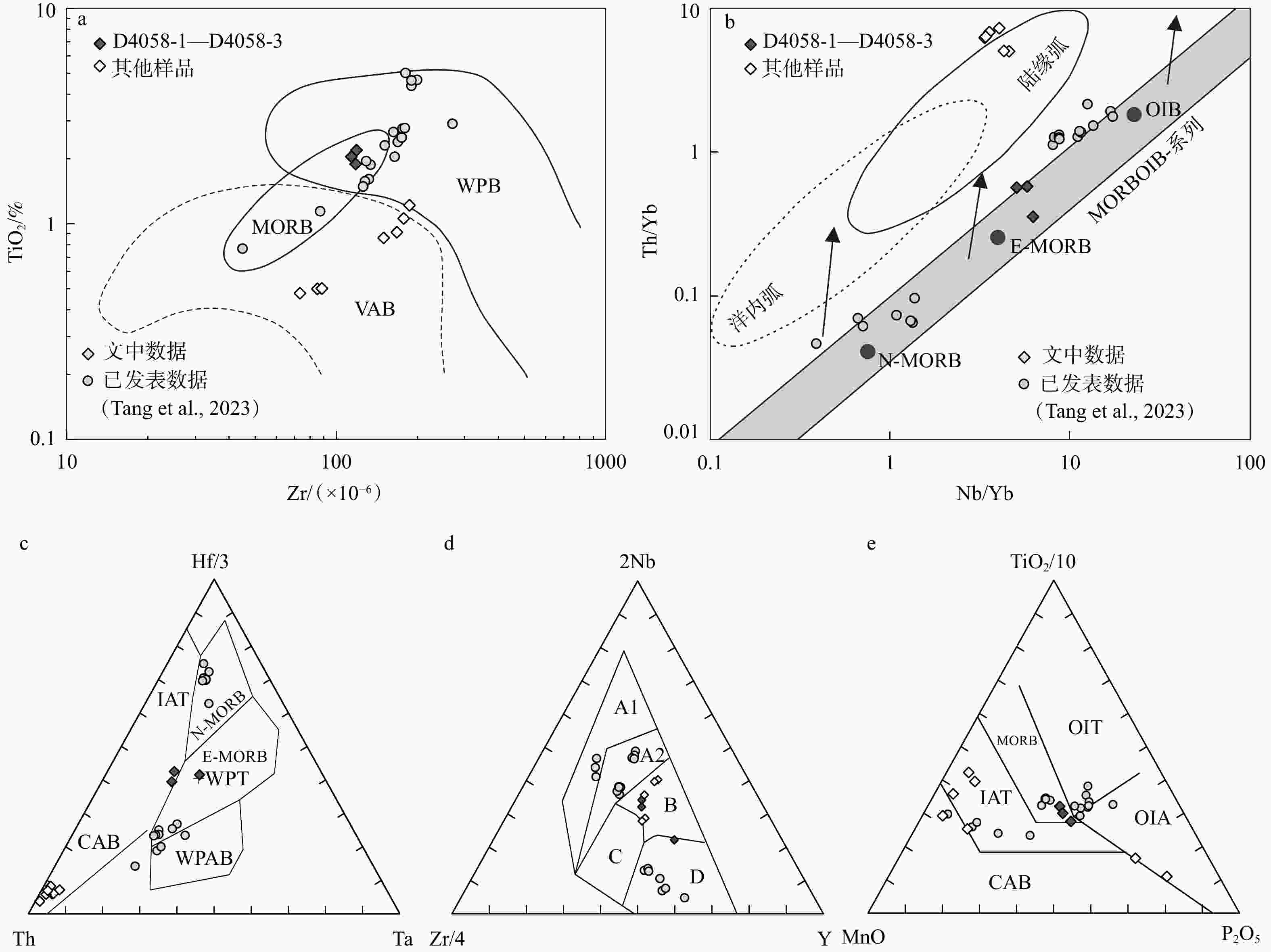
图 9 榴辉岩的构造背景判别图
MORB—洋中脊玄武岩;E-MORB—富集型洋中脊玄武岩;N-MORB—正常型洋中脊玄武岩;WPB—板内玄武岩;WPAB—板内碱性玄武岩;WPT—板内拉斑玄武岩;OIB—洋岛玄武岩;OIT—洋岛拉斑玄武岩;OIA—洋岛碱性玄武岩;VAB—火山弧玄武岩;IAT—岛弧拉斑玄武岩;CAB—钙碱性玄武岩;A1—板内碱性玄武岩;A2—板内碱性玄武岩和拉斑玄武岩;B—富集型洋中脊玄武岩;C—板内拉斑玄武岩和火山弧玄武岩;D—正常型洋中脊玄武岩和火山弧玄武岩a—Zr–TiO2 (底图据Pearce,1982);b—Nb/Yb–Th/Yb (底图据Pearce,2008);c—Hf/3–Th–Ta (底图据Wood,1980);d—2Nb–Zr/4–Y (底图据Meschede,1986);e—TiO2/10–MnO–P2O5 (底图据 Mullen,1983)
Figure 9. Discrimination diagrams for the eclogites
(a) Zr vs. TiO2 (adapted from Pearce, 1982); (b) Nb/Yb vs. Th/Yb (adapted from Pearce, 2008); (c) Hf/3–Th–Ta (adapted from Wood, 1980); (d) 2Nb–Zr⁄ 4–Y (adapted from Meschede, 1986); (e) TiO2/10–MnO–P2O5(adapted from Mullen, 1983) MORB−mid ocean ridge basalt; E-MORB−enriched MORB; N-MORB−normal MORB; WPB−within-plate basalts; WPAB−within plate alkaline basalt; WPT−within plate tholeiite; OIB−oceanic island basalt; OIT−oceanic island tholeiite; OIA−oceanic island alkaline basalt; VAB−volcanic arc basalt; IAT− island arc tholeiite; CAB− calc-alkaline basalt; A1−intraplate alkali basalt; A2−intraplate alkali basalt and tholeiite; B−E-MORB; C−intraplate tholeiite and volcanic arc basalt; D−N-MORB and volcanic arc basalt
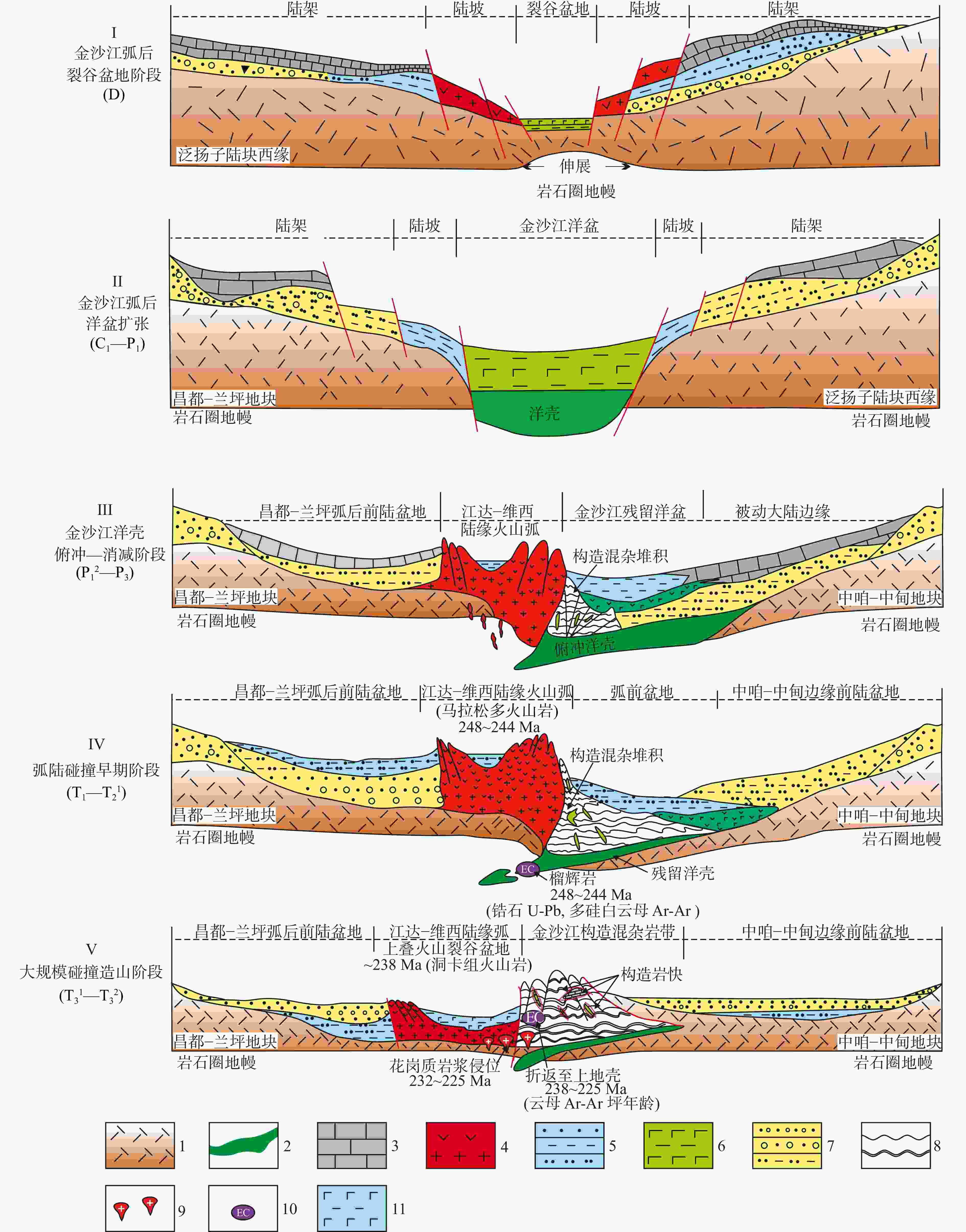
图 10 金沙江古特提斯缝合带构造演化模式图(据王立全等,1999修改)
1—陆壳基底;2—洋壳;3—碳酸盐岩; 4—陆缘火山弧;5— 浅海相/海相碎屑岩;6— 洋盆火山沉积岩;7—陆缘碎屑岩;8— 构造混杂岩;9— 花岗质岩浆;10— 榴辉岩;11—玄武质火山沉积岩
Figure 10. Schematic diagram of tectonic evolution of the Jinsha River Paleo-Tethys Suture Zone (modified after Wang et al., 1999)
表 1 榴辉岩样品的主量元素含量和稀土微量含量
Table 1. Major and trace element composition of eclogites
样品号 22SD01-1 22SD01-2 22SD02-1 22SD02-2 22SD02-3 22SD03-1 22SD03-2 D4058-1 D4058-2 D4058-3 岩性 石榴钠长阳起片岩 榴闪岩 石榴阳起石岩 SiO2 /% 47.94 49.59 51.13 50.77 51.25 51.54 52.02 41.88 47.73 47.72 TiO2 /% 0.49 0.47 0.85 1.21 0.50 1.06 0.92 2.09 1.98 1.84 Al2O3 /% 17.95 16.22 11.76 12.06 14.40 11.46 11.45 13.10 13.66 13.56 FeOT/% 5.84 5.94 9.67 10.23 6.99 9.74 9.51 15.98 15.88 16.40 MnO /% 0.06 0.06 0.19 0.20 0.12 0.13 0.12 0.24 0.20 0.20 MgO/% 4.56 5.30 7.17 6.93 6.59 7.50 7.64 5.35 5.23 5.88 CaO /% 16.72 15.88 12.88 12.60 15.20 13.80 13.88 12.04 7.46 6.82 Na2O/% 3.67 4.41 4.89 4.88 4.41 4.70 4.85 3.91 3.70 3.76 K2O/% 0.43 0.29 0.04 0.04 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.10 0.48 0.46 P2O5 /% 0.19 0.32 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.31 0.22 0.23 LOI /% 2.01 1.61 0.78 0.64 0.83 <0.01 0.10 5.98 3.48 2.96 Total/% 99.86 100.09 99.38 99.58 100.34 99.96 100.53 100.98 100.02 99.83 Mg# 58 62 57 55 63 58 59 38 37 39 Na2O+K2O/% 4.10 4.70 4.93 4.92 4.43 4.72 4.87 4.01 4.18 4.22 Na2O/K2O 8.5 15.2 111.1 116.2 191.7 313.3 269.4 39.1 7.7 8.2 Li/ (×10−6) 46.90 52.90 64.90 73.20 66.30 39.30 40.60 12.70 27.60 13.20 Be/(×10−6) 5.67 5.56 7.57 6.86 6.10 3.74 5.90 1.32 0.57 0.96 Sc/(×10−6) 5.67 5.56 7.57 6.86 6.10 3.74 5.90 1.32 0.57 0.96 V/(×10−6) 93.90 83.30 102.00 104.00 101.00 180.00 177.00 396.00 401.00 383.00 Cr/(×10−6) 72.60 67.20 114.00 142.00 126.00 168.00 163.00 163.00 215.00 156.00 Co/(×10−6) 9.83 13.70 19.10 18.00 13.80 23.90 24.80 35.80 44.90 36.20 Ni/(×10−6) 30.20 33.80 58.00 65.60 63.60 57.60 60.60 43.80 61.50 48.80 Cu/(×10−6) 13.20 8.14 20.90 7.39 8.14 10.90 11.30 20.60 75.40 21.70 Zn/(×10−6) 125.00 146.00 155.00 149.00 144.00 126.00 133.00 87.20 103.00 91.80 Ga/(×10−6) 39.10 34.80 19.70 20.00 35.40 22.20 20.60 21.40 23.30 17.80 Rb/(×10−6) 24.30 13.40 1.90 1.86 0.96 0.82 0.73 8.22 32.30 20.80 Sr/(×10−6) 1300.00 1100.00 83.80 75.20 600.00 63.50 57.80 267.00 117.00 77.60 Y/(×10−6) 40.70 32.60 40.30 50.00 37.30 49.90 45.00 43.20 38.70 33.20 Zr/(×10−6) 85.30 73.40 150.00 187.00 88.50 178.00 168.00 119.00 114.00 118.00 Nb/(×10−6) 8.44 7.66 20.20 22.90 8.49 19.00 16.80 24.60 22.10 17.40 Sn/(×10−6) 6.50 5.27 3.49 3.20 5.30 3.56 3.40 1.61 1.46 1.46 Cs/(×10−6) 2.01 0.82 0.08 0.09 0.07 0.10 0.09 5.23 9.73 5.14 Ba/(×10−6) 29.20 12.20 17.80 25.60 8.20 6.10 10.30 83.80 208.00 135.00 La/(×10−6) 44.30 36.20 55.60 68.00 126.00 105.00 86.60 13.50 18.00 14.70 Ce/(×10−6) 78.90 66.80 102.00 124.00 228.00 192.00 157.00 26.90 34.90 28.40 Pr/(×10−6) 9.41 8.02 12.30 14.40 27.00 23.60 19.30 3.74 4.66 4.00 Nd/(×10−6) 34.90 29.40 44.80 53.60 105.00 90.10 74.30 17.10 20.00 16.40 Sm/(×10−6) 6.68 5.82 8.15 9.46 21.30 18.40 14.80 4.45 4.66 4.10 Eu/(×10−6) 1.47 1.34 1.30 1.66 4.19 3.69 2.98 1.45 1.57 1.34 Gd/(×10−6) 5.80 5.44 6.09 7.70 14.50 12.20 9.94 4.36 4.55 4.25 Tb/(×10−6) 1.16 1.01 1.01 1.33 1.91 1.57 1.29 0.97 0.92 0.84 Dy/(×10−6) 6.91 6.04 6.38 8.06 8.32 8.55 7.11 6.89 6.34 5.58 Ho/(×10−6) 1.30 1.10 1.31 1.66 1.25 1.66 1.49 1.43 1.31 1.20 Er/(×10−6) 3.26 2.64 4.00 4.94 3.08 5.09 4.56 4.10 3.70 3.44 Tm/(×10−6) 0.43 0.34 0.63 0.78 0.43 0.78 0.72 0.60 0.57 0.52 Yb/(×10−6) 2.52 1.90 4.42 5.36 2.64 5.35 4.96 3.96 3.84 3.45 Lu/(×10−6) 0.36 0.29 0.76 0.90 0.43 0.91 0.85 0.65 0.62 0.54 Hf/(×10−6) 3.14 2.82 5.45 7.52 3.87 6.94 7.22 5.29 6.30 6.33 Ta/(×10−6) 0.57 0.56 1.20 0.54 0.39 0.70 0.57 1.07 1.00 0.89 Tl/(×10−6) 0.15 0.11 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.07 0.22 0.11 Pb/(×10−6) 187.00 150.00 11.80 11.80 76.20 5.54 4.94 3.52 2.34 2.10 Th/(×10−6) 15.80 13.90 22.30 27.20 32.60 36.70 31.60 1.41 2.22 1.96 U/(×10−6) 4.70 4.00 2.58 3.18 6.66 6.48 5.18 0.35 0.36 0.32 ΣREE/(×10−6) 197.40 166.34 248.75 301.85 544.05 468.90 385.90 90.10 105.64 88.76 LREE/HREE 8.08 7.87 9.11 8.82 15.71 11.99 11.48 2.92 3.83 3.48 δEu 0.72 0.73 0.56 0.59 0.73 0.75 0.75 1.01 1.04 0.98 LaN/YbN 12.61 13.67 9.02 9.10 34.23 14.08 12.52 2.45 3.36 3.06 表 2 榴辉岩样品的锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄
Table 2. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb data of zircons in eclogites
分析点 含量 /(×10−6) Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 21LM01 21LM01-01 7.84 54.3 0.14 0.0474 0.0060 0.2405 0.0243 0.0391 0.0010 219 20 247 6 21LM01-02 6.62 51.5 0.13 0.0632 0.0087 0.3185 0.0340 0.0402 0.0011 281 26 254 7 21LM01-03 11.20 52.9 0.21 0.0542 0.0059 0.2866 0.0267 0.0388 0.0010 256 21 245 6 21LM01-04 4.29 58.9 0.07 0.0627 0.0074 0.3261 0.0251 0.0392 0.0010 287 19 248 6 21LM01-05 8.07 68.6 0.12 0.0446 0.0050 0.2355 0.0210 0.0391 0.0009 215 17 247 5 21LM01-06 7.11 48.4 0.15 0.0502 0.0069 0.2527 0.0281 0.0388 0.0009 229 23 245 6 21LM01-07 6.93 49.3 0.14 0.0683 0.0085 0.3276 0.0299 0.0388 0.0010 288 23 246 6 21LM01-08 7.48 58.7 0.13 0.0484 0.0052 0.2502 0.0221 0.0391 0.0011 227 18 247 7 21LM01-09 7.12 81.2 0.09 0.0450 0.0043 0.2411 0.0182 0.0391 0.0009 219 15 247 6 21LM01-10 3.85 81.4 0.05 0.0484 0.0048 0.2554 0.0233 0.0390 0.0009 231 19 247 6 21LM01-11 5.81 41.1 0.14 0.0412 0.0071 0.2190 0.0353 0.0388 0.0012 201 29 245 7 21LM01-12 6.77 52.4 0.13 0.0491 0.0072 0.2309 0.0215 0.0391 0.0010 211 18 247 6 21LM01-13 5.93 46.9 0.13 0.0442 0.0067 0.2132 0.0232 0.0391 0.0013 196 19 248 8 21LM01-14 6.41 28.0 0.23 0.0622 0.0106 0.2916 0.0321 0.0392 0.0015 260 25 248 10 21LM01-15 5.39 47.9 0.11 0.0613 0.0081 0.3064 0.0273 0.0390 0.0010 271 21 247 6 21LM01-16 8.00 46.4 0.17 0.0570 0.0083 0.2869 0.0318 0.0388 0.0010 256 25 246 7 21LM01-17 4.69 45.7 0.10 0.0530 0.0069 0.2644 0.0267 0.0389 0.0010 238 21 246 6 21LM01-18 6.64 54.3 0.12 0.0455 0.0060 0.2334 0.0214 0.0393 0.0011 213 18 248 7 21LM01-19 4.04 26.8 0.15 0.0506 0.0130 0.2451 0.0596 0.0391 0.0016 223 49 247 10 21LM01-20 4.99 54.2 0.09 0.0517 0.0058 0.2627 0.0203 0.0388 0.0010 237 16 246 6 21LM01-21 7.44 59.2 0.13 0.0484 0.0055 0.2562 0.0243 0.0387 0.0010 232 20 245 6 21LM01-22 6.79 44.4 0.15 0.0508 0.0069 0.2494 0.0319 0.0388 0.0010 226 26 245 6 21LM01-23 7.99 58.7 0.14 0.0529 0.0056 0.2763 0.0225 0.0401 0.0010 248 18 253 6 D4058-1 D4058-1-01 0.95 178 0.01 0.0517 0.0022 0.2786 0.0120 0.0391 0.0006 250 10 247 4 D4058-1-02 10.70 249 0.04 0.0510 0.0020 0.2752 0.0109 0.0390 0.0005 247 9 247 3 D4058-1-03 2.65 463 0.01 0.0508 0.0015 0.2764 0.0088 0.0393 0.0006 248 7 249 3 D4058-1-06 1.84 309 0.01 0.0506 0.0020 0.2715 0.0103 0.0391 0.0005 244 8 247 3 D4058-1-07 2.03 296 0.01 0.0541 0.0019 0.2895 0.0100 0.0390 0.0005 258 8 246 3 D4058-1-09 2.19 238 0.01 0.0536 0.0023 0.2857 0.0116 0.0388 0.0004 255 9 245 3 D4058-1-10 2.22 414 0.01 0.0519 0.0014 0.2797 0.0078 0.0390 0.0004 250 6 247 3 D4058-1-11 1.69 263 0.01 0.0483 0.0021 0.2554 0.0106 0.0386 0.0004 231 9 244 3 D4058-1-12 1.67 311 0.01 0.0532 0.0019 0.2812 0.0094 0.0385 0.0004 252 7 243 2 D4058-1-13 2.91 378 0.01 0.0520 0.0017 0.2806 0.0096 0.0390 0.0004 251 8 246 2 D4058-1-14 1.45 249 0.01 0.0517 0.0022 0.2743 0.0114 0.0387 0.0004 246 9 245 3 D4058-1-15 2.72 439 0.01 0.0520 0.0016 0.2778 0.0088 0.0386 0.0003 249 7 244 2 D4058-1-16 2.73 292 0.01 0.0484 0.0016 0.2583 0.0085 0.0387 0.0004 233 7 245 3 D4058-1-18 4.43 443 0.01 0.0525 0.0018 0.2853 0.0096 0.0393 0.0005 255 8 249 3 D4058-1-19 8.65 259 0.03 0.0546 0.0021 0.2927 0.0111 0.0390 0.0005 261 9 246 3 D4058-1-20 2.04 367 0.01 0.0550 0.0020 0.2952 0.0106 0.0389 0.0004 263 8 246 3 D4058-1-21 1.67 268 0.01 0.0531 0.0020 0.2887 0.0110 0.0394 0.0005 258 9 249 3 D4058-1-22 3.78 315 0.01 0.0512 0.0018 0.2746 0.0100 0.0387 0.0005 246 8 245 3 D4058-1-23 5.57 314 0.02 0.0493 0.0016 0.2653 0.0089 0.0389 0.0005 239 7 246 3 D4058-1-24 1.88 282 0.01 0.0550 0.0019 0.2927 0.0098 0.0387 0.0005 261 8 245 3 表 3 榴辉岩样品的锆石稀土元素含量(μg/g)
Table 3. REE analytical data in situ single zircon of eclogites
点号 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu ∑REE *Eu *Ce Nb Ta 21LM01 21LM01-01 bd 0.88 bd 0.151 0.36 0.11 1.16 0.37 3.79 1.23 4.27 0.92 8.31 1.54 23.11 0.53 1.07 0.19 0.04 21LM01-02 bd 0.75 0.023 0.082 0.13 0.04 0.23 0.11 0.74 0.30 1.23 0.22 2.38 0.37 6.61 0.69 0.93 0.16 0.06 21LM01-03 bd 1.31 0.011 0.162 0.86 0.20 1.79 0.42 3.03 0.86 2.67 0.46 4.53 0.73 17.03 0.49 0.85 0.10 0.03 21LM01-04 0.0062 0.51 bd bd 0.32 0.06 0.57 0.087 1.46 0.49 1.78 0.32 2.83 0.48 8.91 0.46 0.69 0.14 0.07 21LM01-05 0.0177 1.44 bd 0.162 0.47 0.26 0.83 0.22 1.98 0.39 1.39 0.22 1.99 0.23 9.61 1.27 9.04 0.11 0.04 21LM01-06 bd 0.86 0.011 0.158 0.30 0.19 1.15 0.38 3.93 1.16 4.50 1.12 8.34 1.52 23.62 0.98 bd 0.13 0.04 21LM01-07 bd 0.78 bd 0.077 0.37 0.08 0.43 0.20 2.10 0.71 2.35 0.51 4.63 0.77 12.99 0.59 bd 0.17 0.04 21LM01-08 bd 0.86 bd 0.080 0.04 0.13 0.54 0.14 1.78 0.56 1.97 0.47 4.60 0.74 11.90 2.73 bd 0.37 0.04 21LM01-09 bd 0.89 0.013 bd 0.24 0.10 0.57 0.13 1.24 0.47 1.89 0.38 2.72 0.40 9.05 0.83 bd 0.21 0.08 21LM01-10 bd 0.87 0.011 0.040 0.34 0.29 1.28 0.38 2.39 0.65 2.01 0.38 2.98 0.51 12.13 1.37 bd 0.16 0.06 21LM01-11 bd 0.62 bd 0.126 0.31 0.12 0.74 0.27 2.27 0.67 2.41 0.50 4.30 0.77 13.09 0.73 bd 0.10 0.04 21LM01-12 0.0057 0.66 0.011 0.117 0.13 0.07 0.87 0.19 1.78 0.53 2.46 0.48 4.27 0.62 12.20 0.63 20.60 0.16 0.03 21LM01-13 bd 0.49 0.011 0.120 0.09 0.09 0.53 0.10 1.63 0.55 2.48 0.43 4.65 0.78 11.94 1.29 bd 0.13 0.02 21LM01-14 0.0059 0.70 bd 0.285 0.22 0.19 1.36 0.39 3.65 1.13 3.77 0.68 6.29 1.02 19.70 1.08 7.90 0.12 0.02 21LM01-15 bd 0.77 0.012 bd 0.09 0.05 0.71 0.07 0.90 0.36 1.01 0.15 1.43 0.28 5.83 0.64 bd 0.13 0.03 21LM01-16 0.0184 0.68 0.024 0.087 0.01 0.13 0.77 0.22 2.05 0.60 2.51 0.50 5.29 0.62 13.49 8.12 8.03 0.12 0.04 21LM01-17 0.0052 0.60 bd 0.035 0.15 0.25 1.15 0.24 1.90 0.43 1.25 0.27 1.96 0.37 8.60 1.80 12.70 0.13 0.02 21LM01-18 bd 0.82 bd 0.084 0.13 0.11 0.63 0.21 1.90 0.54 1.91 0.31 3.48 0.59 10.73 1.21 bd 0.07 0.04 21LM01-19 bd 0.50 0.035 0.042 0.09 0.05 0.34 0.12 1.17 0.33 1.41 0.34 3.06 0.57 8.06 0.90 bd 0.20 0.05 21LM01-20 bd 0.60 0.010 bd 0.16 0.06 0.65 0.16 1.57 0.43 1.47 0.32 2.68 0.46 8.57 0.61 bd 0.14 0.03 21LM01-21 bd 0.67 bd 0.124 0.13 0.09 0.79 0.18 1.62 0.64 2.04 0.42 3.66 0.69 11.06 0.87 bd 0.18 0.03 21LM01-22 bd 0.84 0.010 0.069 0.07 0.03 0.52 0.18 2.12 0.55 2.26 0.42 4.71 0.65 12.44 0.53 bd 0.19 0.04 21LM01-23 0.0253 1.21 0.034 0.160 0.36 0.23 1.51 0.45 2.95 0.69 2.24 0.39 3.39 0.61 14.24 0.96 10.20 0.09 bd D4058-1 D4058-1-01 bd 0.28 bd 0.058 0.72 0.98 8.86 3.44 30.8 7.16 19.19 3.06 23.70 3.77 102.04 1.19 0.93 0.22 0.04 D4058-1-02 0.0159 0.44 0.009 0.131 0.81 1.13 9.64 3.19 27.2 5.82 17.20 3.06 27.72 5.07 101.47 1.24 9.03 0.24 0.06 D4058-1-03 bd 0.61 0.005 bd 0.48 0.42 4.35 1.16 9.2 1.93 5.19 0.80 6.19 1.02 31.33 0.89 0.93 0.33 0.10 D4058-1-06 0.0168 0.36 0.002 0.260 0.87 1.29 9.21 2.82 22.7 4.65 13.46 2.13 17.32 2.90 77.97 1.39 16.93 0.18 0.04 D4058-1-07 bd 0.30 bd 0.099 0.67 0.78 7.61 2.91 25.4 5.56 14.92 2.28 17.56 2.90 80.98 1.05 0.69 0.31 0.08 D4058-1-09 0.0157 0.36 0.013 0.032 0.62 0.92 9.51 3.35 29.2 6.40 18.64 2.94 22.72 3.72 98.45 1.16 6.07 0.27 0.04 D4058-1-10 bd 0.63 bd 0.028 0.28 0.43 3.09 0.88 6.0 1.34 3.85 0.69 5.38 0.77 23.40 1.42 bd 0.25 0.07 D4058-1-11 bd 0.38 0.010 0.031 0.58 0.87 7.46 2.92 25.8 5.35 14.94 2.28 18.11 2.96 81.68 1.28 bd 0.34 0.08 D4058-1-12 bd 0.41 0.015 0.127 0.99 1.09 9.06 2.73 22.7 4.79 14.25 2.36 19.12 3.01 80.62 1.11 bd 0.22 0.40 D4058-1-13 0.0088 0.61 0.005 0.048 1.04 1.29 8.98 2.70 22.1 4.68 12.76 2.14 17.87 2.84 77.12 1.29 22.48 0.18 0.05 D4058-1-14 bd 0.41 0.010 0.109 0.71 0.98 9.13 3.21 29.0 6.35 17.05 2.80 21.76 3.45 94.96 1.18 bd 0.29 0.07 D4058-1-15 bd 0.60 bd 0.127 1.12 1.14 7.29 2.01 13.2 2.84 9.34 1.40 11.91 1.85 52.83 1.22 bd 0.22 0.10 D4058-1-16 0.0370 0.42 0.004 0.054 0.74 1.01 9.48 3.40 27.9 5.99 16.56 2.68 21.15 3.58 93.01 1.16 8.17 0.31 0.05 D4058-1-17 bd 0.63 0.010 0.183 0.84 0.87 7.80 2.46 19.0 4.08 11.63 2.02 15.70 2.56 67.78 1.04 bd 0.2 0.07 D4058-1-19 bd 0.35 0.002 0.115 0.86 0.99 9.62 3.34 30.2 6.77 20.78 3.85 33.91 5.95 116.69 1.06 bd 0.37 0.05 D4058-1-20 bd 0.48 0.005 0.058 0.51 0.50 4.75 1.38 11.1 2.56 6.27 1.07 7.42 1.22 37.30 0.98 bd 0.26 0.10 D4058-1-21 bd 0.40 bd 0.121 0.62 0.87 9.29 3.32 30.1 6.50 17.58 2.97 22.50 3.71 97.96 1.10 bd 0.23 0.07 D4058-1-23 0.0083 0.46 0.015 0.090 0.81 0.95 8.63 3.14 27.7 6.27 17.92 3.15 26.10 4.39 99.67 1.10 9.87 0.29 0.08 D4058-1-24 0.0563 0.75 0.001 0.203 1.35 1.27 10.60 3.43 28.3 6.06 16.88 2.77 21.22 3.46 96.36 1.03 23.23 0.22 0.04 注:*Ce=CeN/(LaN×PrN)1/2;*Eu=EuN/(SmN×GdN)1/2;bd—低于检测限 -
[1] BEBOUT G E, 2007. Metamorphic chemical geodynamics of subduction zones[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 260(3-4): 373-393. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2007.05.050 [2] CHUNG S L, LEE T Y, LO C H, et al., 1997. Intraplate extension prior to continental extrusion along the Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone[J]. Geology, 25(4): 311-314. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0311:IEPTCE>2.3.CO;2 [3] DAN W, ZHANG X Z, CHEN Y X, et al., 2025. Metamorphic evolution of Mesozoic microcontinent suture zones in the Tibet region[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 268: 105174. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2025.105174 [4] ERNST W G, LIOU J G, 1995. Contrasting plate-tectonic styles of the Qinling-Dabie-Sulu and Franciscan metamorphic belts[J]. Geology, 23(4): 353-356. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0353:CPTSOT>2.3.CO;2 [5] FAN W M, PENG T P, WANG Y J, 2009. Triassic magmatism in the southern Lancangjiang zone, southwestern China and its constraints on the tectonic evolution of Paleo-Tethys[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 16(6): 291-302. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] FAURE M, LEPVRIER C, VAN NGUYEN V, et al., 2014. The South China block-Indochina collision: where, when, and how?[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 79: 260-274. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.09.022 [7] FENG Q L, YE M, ZHANG Z J, 1997. Early carboniferous radiolarians from western Yunnan[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 14(1): 79-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] GONG X D, TANG Y, QIN Y D, et al., 2020. Late Triassic Collision of Jinshajiang Suture Belt: Geochronological, Geochemical and Hf Isotope Evidences from Quartz Monzonite in Gonjo Area[J]. Earth Science, 45(8): 2905-2919. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] GUAN C, YAN M D, ZHANG W L, et al., 2021. Paleomagnetic and chronologic data bearing on the Permian/Triassic boundary position of Qamdo in the eastern Qiantang Terrane: implications for the closure of the Paleo-Tethys[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 48(6): e2020GL092059. doi: 10.1029/2020GL092059 [10] HUANG F, XU J F, ZENG Y C, et al., 2017. Slab breakoff of the Neo‐Tethys Ocean in the Lhasa terrane inferred from contemporaneous melting of the mantle and crust[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 18(11): 4074-4095. doi: 10.1002/2017GC007039 [11] HUANG K N, OPDYKE N D, 2016. Paleomagnetism of the Upper Triassic rocks from south of the Ailaoshan Suture and the timing of the amalgamation between the South China and the Indochina Blocks[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 119: 118-127. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.12.005 [12] JIAN P, LIU D Y, SUN X M, 2008. SHRIMP dating of the permo-carboniferous Jinshajiang ophiolite, southwestern China: geochronological constraints for the evolution of Paleo-Tethys[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 32(5-6): 371-384. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.11.006 [13] JIAN P, LIU D Y, KRÖNER A, et al., 2009a. Devonian to Permian plate tectonic cycle of the Paleo-Tethys Orogen in southwest China (II): insights from zircon ages of ophiolites, arc/back-arc assemblages and within-plate igneous rocks and generation of the Emeishan CFB province[J]. Lithos, 113(3-4): 767-784. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.04.006 [14] JIAN P, LIU D Y, KRÖNER A, et al., 2009b. Devonian to Permian plate tectonic cycle of the Paleo-Tethys Orogen in southwest China (Ⅰ): Geochemistry of ophiolites, arc/back-arc assemblages and within-plate igneous rocks[J]. Lithos, 113(3-4): 748-766. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.04.004 [15] LE BAS M J, LE MAITRE R W, STRECKEISEN A, et al., 1986. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali-silica diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 27(3): 745-750. doi: 10.1093/petrology/27.3.745 [16] LI J L, 2020. Blueschist: a window into high-pressure/low-temperature metamorphism and subduction zone dynamics[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 63(12): 1852-1867. doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9630-2 [17] LIANG Q K, KANG H, CHEN Y L, et al., 2023. U-Pb-Hf Isotope compositions of detrital zircons from Tongtian River Sediments of Northern-Central Tibetan Plateau: implications for the closure of the Jinshajiang Ocean[J]. Geochemistry, 83(4): 126018. doi: 10.1016/j.chemer.2023.126018 [18] LIN W, WANG Y, LIU F, et al., 2025. Indochina orogenic belt and related geodynamics[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 68(6): 1691-1715. doi: 10.1007/s11430-024-1499-5 [19] LIU X C, HU J, CHEN L Y, et al., 2021. Oceanic-type high-temperature eclogites from Hainan Island, South China: General characteristics and unsolved problems[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 37(1): 143-161. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.01.10 [20] LIU Y S, HU Z C, GAO S, et al., 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 257(1-2): 34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004 [21] MARUYAMA S, LIOU J G, TERABAYASHI M, 1996. Blueschists and eclogites of the world and their exhumation[J]. International Geology Review, 38(6): 485-594. doi: 10.1080/00206819709465347 [22] MCDONOUGH W F, SUN S S, 1995. The composition of the Earth[J]. Chemical Geology, 120(3-4): 223-253. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)00140-4 [23] MESCHEDE M, 1986. A method of discriminating between different types of mid-ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites with the Nb 1bZr 1bY diagram[J]. Chemical Geology, 56(3-4): 207-218. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(86)90004-5 [24] MIYASHIRO A, 1974. Volcanic rock series in island arcs and active continental margins[J]. American Journal of Science, 274(4): 321-355. doi: 10.2475/ajs.274.4.321 [25] MULLEN E D, 1983. MnO/TiO2/P2O5: a minor element discriminant for basaltic rocks of oceanic environments and its implications for petrogenesis. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 62(1): 53-62. [26] NAKANO N, OSANAI Y, MINH N T, et al., 2008. Discovery of high-pressure granulite-facies metamorphism in Northern Vietnam: constraints on the Permo-Triassic indochinese continental collision tectonics[J]. Comptes Rendus Géoscience, 340(2-3): 127-138. [27] NAKANO N, OSANAI Y, SAJEEV K, et al., 2010. Triassic eclogite from northern Vietnam: inferences and geological significance[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 28(1): 59-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.2009.00853.x [28] NING W B, KUSKY T, WANG L, et al., 2022. Archean eclogite-facies oceanic crust indicates modern-style plate tectonics[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(15): e2117529119. [29] PEARCE J A, 1982. Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries[M]//THORPE R S. Orogenic andesites and related rocks. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons: 525-548. [30] PEARCE J A, 2008. Geochemical fingerprinting of oceanic basalts with applications to ophiolite classification and the search for Archean oceanic crust[J]. Lithos, 100(1-4): 14-48. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.06.016 [31] SONG P P, DING L, LI Z Y, et al., 2015. Late Triassic paleolatitude of the Qiangtang block: implications for the closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 424: 69-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2015.05.020 [32] SPANDLER C, HERMANN J, ARCULUS R, et al., 2004. Geochemical heterogeneity and element mobility in deeply subducted oceanic crust; insights from high-pressure mafic rocks from New Caledonia[J]. Chemical Geology, 206(1-2): 21-42. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.01.006 [33] SUN X M and JIAN P, 2004. The Wilson cycle of the Jinshajiang paleo-Tethys Ocean, in western Yunnan and western Sichuan provinces[J]. Geological Review, 50(4): 343-350. (in Chinese with English abstract) [34] TANG Y, QIN Y D, GONG X D, et al., 2020. Discovery of eclogites in Jinsha River suture zone, Gonjo County, eastern Tibet and its restriction on Paleo-Tethyan evolution[J]. China Geology, 3(1): 83-103. doi: 10.31035/cg2020003 [35] TANG Y, QIN Y D, GONG X D, et al., 2022. Determination of material composition of Jinshajiang tectonic mélange belt in Gonjo-Baiyu area, eastern Tibet[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 42(2): 260-278. (in Chinese with English abstract) [36] TANG Y, QIN Y D, GONG X D, et al., 2023. Petrology, geochemistry and Ar-Ar geochronology of eclogites in Jinshajiang orogenic belt, Gonjo area, eastern Tibet and restriction on Paleo-Tethyan evolution[J]. China Geology, 6(2): 285-302. [37] VOLANTE S, BLEREAU E, GUITREAU M, et al. , 2023. Current applications using key mineral phases in igneous and metamorphic geology: perspectives for the future[M]//VAN SCHIJNDEL V, CUTTS K, PEREIRA I, et al. Minor minerals, major implications: using key mineral phases to unravel the formation and evolution of earth’s crust. London: The Geological Society of London: 57-121. [38] WANG B D, WANG L Q, WANG D B, et al., 2018. Tectonic evolution of the Changning-Menglian Proto-Paleo Tethys Ocean in the Sanjiang area, southwestern China[J]. Earth Science, 43(8): 2527-2550. (in Chinese with English abstract) [39] WANG B D, WANG L Q, WANG D B, et al., 2021. The temporal and spatial framework and its tectonic evolution of the Jinsha River arc-basin system, southwest China[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 41(2): 246-264. (in Chinese with English abstract) [40] WANG D B, TANG Y, LUO L, et al., 2024. Timing of closure of the Jinshajiang Paleo-Tethys Ocean in eastern Tibet: Constraints from the Early - Middle Triassic unconformity and collision-related igneous rock in the eastern margin of Qamdo block[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 40(12): 3801-3816. (in Chinese with English abstract) [41] WANG H N, LIU F L, LI J, et al., 2019a. Petrology, geochemistry and P-T-t path of lawsonite-bearing retrograded eclogites in the Changning-Menglian orogenic belt, southeast Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 37(4): 439-478. doi: 10.1111/jmg.12462 [42] WANG H N, LIU F L, SUN Z B, et al. , 2021. Identification of continental-type eclogites in the Paleo-Tethyan Changning–Menglian orogenic belt, southeastern Tibetan Plateau: implications for the transition from oceanic to continental subduction[J]. Lithos, 396-397: 106215. [43] WANG H N, LIU F L, WANG F, et al., 2022a. Metamorphic evolution and orogenic process related to the Eastern Paleo-Tethyan warm subduction and Indochina-South China collision[J]. Journal of Petrology, 63(12): egac114. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egac114 [44] WANG L Q, PAN G T, LI D M, et al., 1999. The spatio-temporal framework and geological evolution of the Jinshajiang Arc-Basin systems[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 73(3): 206-218. (in Chinese with English abstract). [45] WANG Y, ZHANG L F, LI Z H, et al., 2019b. The exhumation of subducted oceanic‐derived eclogites: insights from phase equilibrium and thermomechanical modeling[J]. Tectonics, 38(5): 1764-1797. doi: 10.1029/2018TC005349 [46] WANG Y, LIN W, FAURE M, et al., 2022b. Correlation among the Ailaoshan–Song Ma–Song Chay orogenic belts and implications for the evolution of the eastern Paleo-Tethys Ocean[J]. Tectonophysics, 843: 229618. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2022.229618 [47] WEI B T, CHENG X, DOMEIER M, et al., 2025. A Cimmerian keystone: middle-late Triassic paleomagnetic and calcite geochronologic constraints on the South Qiangtang Block[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 664: 119442. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2025.119442 [48] WOOD D A, 1979. A variably veined suboceanic upper mantle-genetic significance for mid-ocean ridge basalts from geochemical evidence[J]. Geology, 7(10): 499-503. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1979)7<499:AVVSUM>2.0.CO;2 [49] WOOD D A, 1980. The application of a Th-Hf-Ta diagram to problems of tectonomagmatic classification and to establishing the nature of crustal contamination of basaltic lavas of the British Tertiary Volcanic Province[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 50(1): 11-30. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(80)90116-8 [50] WU F Y, WAN B, ZHAO L, et al., 2020. Tethyan geodynamics[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(6): 1627-1674. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.06.01 [51] WU Z, JI J P, WANG B D, et al. , 2021. Zircon U-Pb age, geochemical characteristics and constraints on the Jinshajiang Paleo-Tethys collision of Early-Middle Triassic Malasongduo Formation volcanic rocks from the Gongjue area, Eastern Tibet[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 40(11), 1877-1891 (in Chinese with English abstract) [52] XU W, LIU L S, KOHN M J, et al., 2025. Late Triassic continental eclogite in the central Tibetan Plateau reveals 2500-km-long Paleo-Tethys continental subduction[J]. Geology, 53(1): 23-28. doi: 10.1130/G52796.1 [53] XU Z Q, DILEK Y, CAO H, et al., 2015. Paleo-Tethyan evolution of Tibet as recorded in the East Cimmerides and West Cathaysides[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 105: 320-337. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.01.021 [54] YAN Y G, ZHAO Q, ZHANG Y P, et al., 2019. Direct Paleomagnetic constraint on the closure of Paleo‐Tethys and its implications for linking the Tibetan and southeast Asian blocks[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 46(24): 14368-14376. doi: 10.1029/2019GL085473 [55] YANG L C, TANG Y, ZHU X P, et al., 2025. Magmatism during collisional orogenic processes in Early–Middle Triassic Jinsha River suture zone[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 45(1): 168-186. (in Chinese with English abstract) [56] YU L, YAN M D, DOMEIER M, et al., 2022. New paleomagnetic and chronological constraints on the late triassic position of the eastern Qiangtang Terrane: implications for the closure of the Paleo-Jinshajiang Ocean[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 49: e2021GL096902. doi: 10.1029/2021GL096902 [57] YU L, YAN M D, DOMEIER M, et al., 2025. New paleomagnetic results from late triassic limestone of the Eastern Qiangtang Terrane: implications for the closure of the Paleo-Jinshajiang Ocean[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 657: 112610. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2024.112610 [58] YUMUL JR G P, ZHOU M F, WANG C Y, et al., 2008. Geology and geochemistry of the Shuanggou ophiolite (Ailao Shan ophiolitic belt), Yunnan Province, SW China: evidence for a slow-spreading oceanic basin origin[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 32(5-6): 385-395. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.11.007 [59] ZHANG L F, WANG Y, 2020. The exhumation of high- and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic terranes in subduction zone: Questions and discussions[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 63(12): 1884-1903. doi: 10.1007/s11430-020-9579-3 [60] ZHANG R Y, LO C H, CHUNG S L, et al., 2013. Origin and tectonic implication of ophiolite and eclogite in the Song Ma Suture Zone between the South China and Indochina Blocks[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 31(1): 49-62. doi: 10.1111/jmg.12012 [61] ZHANG R Y, LO C H, LI X H, et al., 2014. U-Pb dating and tectonic implication of ophiolite and metabasite from the Song Ma suture zone, Northern Vietnam[J]. American Journal of Science, 314(2): 649-678. doi: 10.2475/02.2014.07 [62] ZHENG Y F, 2012. Metamorphic chemical geodynamics in continental subduction zones[J]. Chemical Geology, 328: 5-48. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.02.005 [63] ZHENG Y F, CHEN R X, 2017. Regional metamorphism at extreme conditions: implications for orogeny at convergent plate margins[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 145: 46-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.03.009 [64] ZI J W, CAWOOD P A, FAN W M, et al. , 2012a. Triassic collision in the Paleo-Tethys Ocean constrained by volcanic activity in SW China[J]. Lithos, 144-145: 145-160. [65] ZI J W, CAWOOD P A, FAN W M, et al., 2012b. Contrasting rift and subduction-related plagiogranites in the Jinshajiang ophiolitic mélange, southwest China, and implications for the Paleo-Tethys[J]. Tectonics, 31(2): TC2012. [66] ZONG K Q, KLEMD R, YUAN Y, et al., 2017. The assembly of Rodinia: The correlation of early Neoproterozoic (ca. 900 Ma) high-grade metamorphism and continental arc formation in the southern Beishan Orogen, southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt (CAOB)[J]. Precambrian Research, 290: 32-48. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2016.12.010 [67] 范蔚茗, 彭头平, 王岳军, 2009. 滇西古特提斯俯冲-碰撞过程的岩浆作用记录[J]. 地学前缘, 16(6): 291-302. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.06.031 [68] 冯庆来, 叶玫, 章正军, 1997. 滇西早石炭世放射虫化石[J]. 微体古生物学报, 14(1): 79-92. [69] 巩小栋, 唐渊, 秦雅东, 等, 2020. 晚三叠世金沙江结合带碰撞作用: 贡觉石英二长岩年代学、地球化学及Hf同位素证据[J]. 地球科学, 45(8): 175-189. [70] 李继磊, 2020. 蓝片岩: 俯冲带高压低温变质作用和地球动力学过程的记录[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 50(12): 1692-1708. [71] 林伟, 王印, 刘飞, 等, 2025. 印支造山带及其地球动力学[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 55(6): 1737-1765. [72] 刘晓春, 胡娟, 陈龙耀, 等, 2021. 海南洋壳型高温榴辉岩: 基本特征及待解问题[J]. 岩石学报, 37(1): 143-161. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.01.10 [73] 孙晓猛, 简平, 2004. 滇川西部金沙江古特提斯洋的威尔逊旋回[J]. 地质论评, 50(4): 343-350. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2004.04.002 [74] 唐渊, 秦雅东, 巩小栋, 等, 2022. 藏东贡觉—白玉地区金沙江构造混杂岩带物质组成的厘定[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 42(2): 260-278. [75] 王保弟, 王立全, 王冬兵, 等, 2018. 三江昌宁-孟连带原-古特提斯构造演化[J]. 地球科学, 43(8): 2527-2550. [76] 王保弟, 王立全, 王冬兵, 等, 2021. 西南三江金沙江弧盆系时空结构及构造演化[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 41(2): 246-264. [77] 王冬兵, 唐渊, 罗亮, 等, 2024. 藏东金沙江古特提洋闭合时间: 来自昌都地块东缘早-中三叠世不整合及碰撞型岩浆岩的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 40(12): 3801-3816. [78] 王立全, 潘桂棠, 李定谋, 等, 1999. 金沙江弧-盆系时空结构及地史演化[J]. 地质学报, 73(3): 206-218. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1999.03.002 [79] 吴福元, 万博, 赵亮, 等, 2020. 特提斯地球动力学[J]. 岩石学报, 36(6): 1627-1674. [80] 吴喆, 冀建平, 王保弟, 等, 2021. 藏东贡觉地区早—中三叠世马拉松多组火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其对金沙江古特提斯碰撞时间的约束[J]. 地质通报, 40(11): 1877-1891. [81] 杨礼创, 唐渊, 祝向平, 等, 2025. 早中三叠世金沙江缝合带碰撞造山过程岩浆作用响应[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 45(1): 168-186. [82] 张立飞, 王杨, 2020. 俯冲带高压-超高压变质地体的抬升折返机制: 问题和探讨[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 50(12): 1727-1747. -




 下载:
下载: