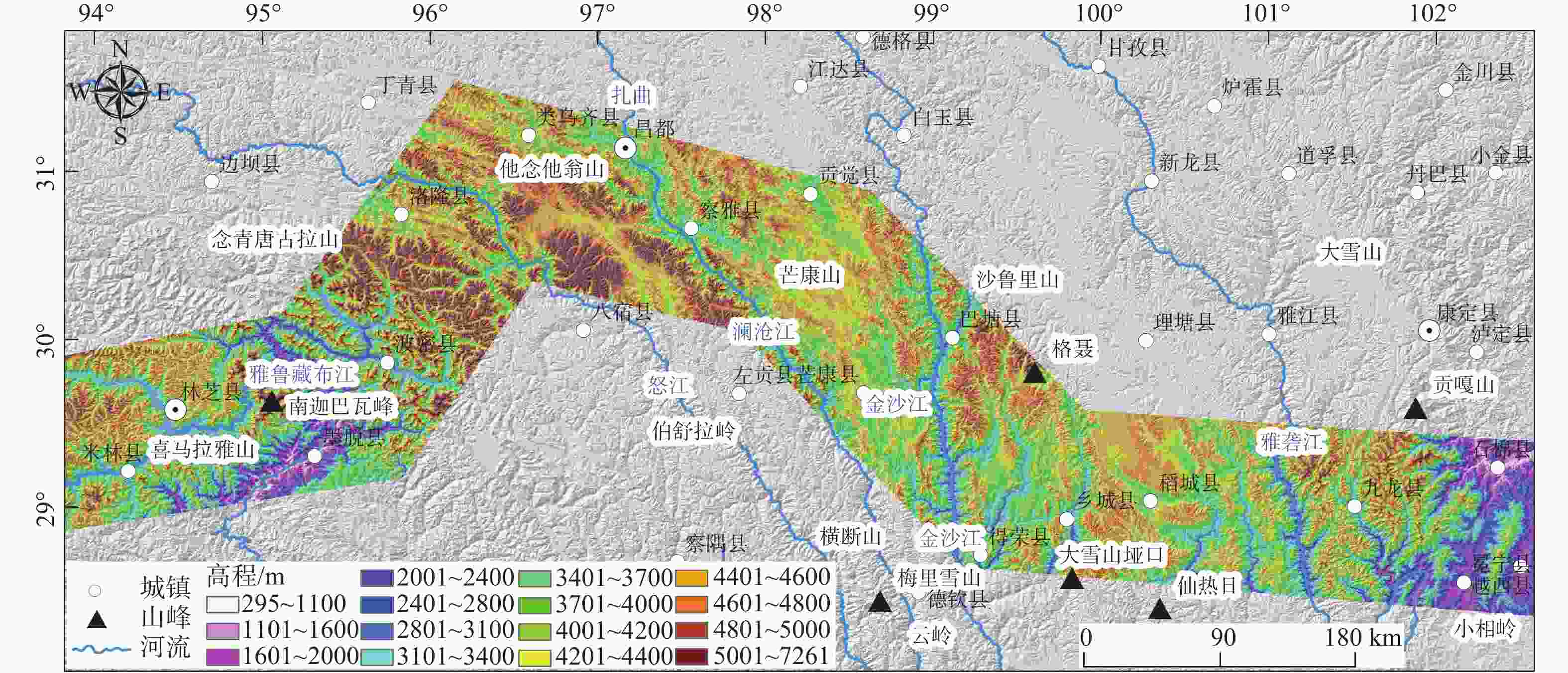
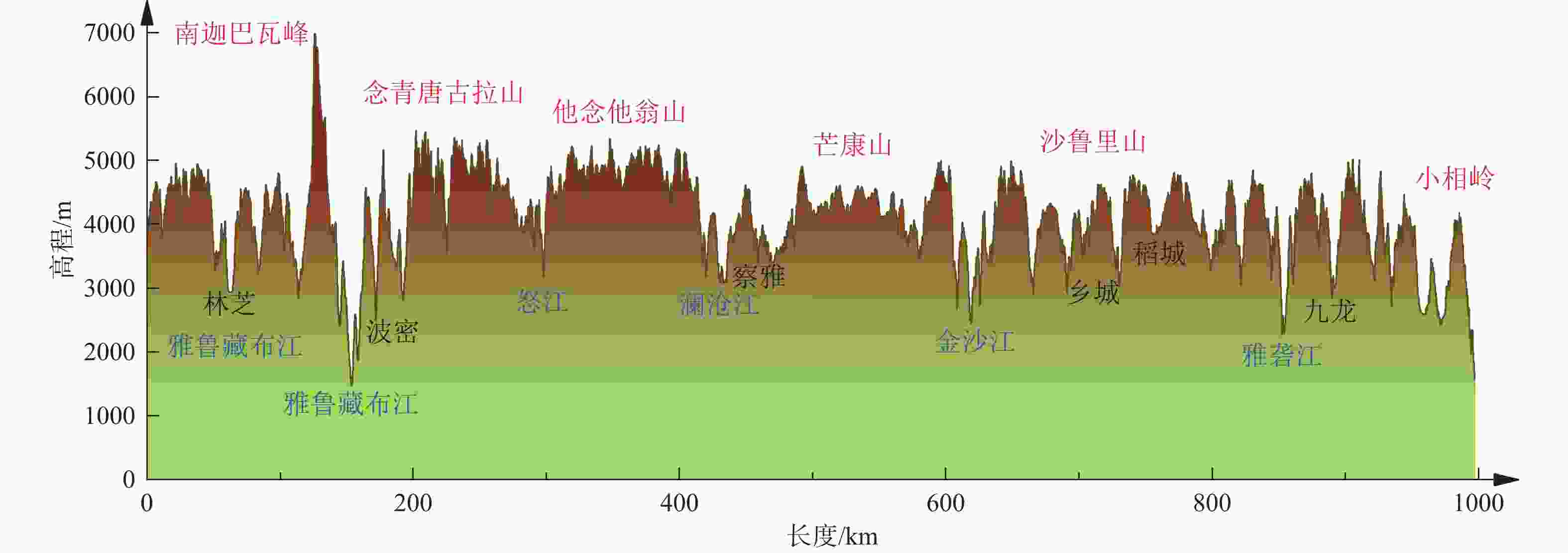
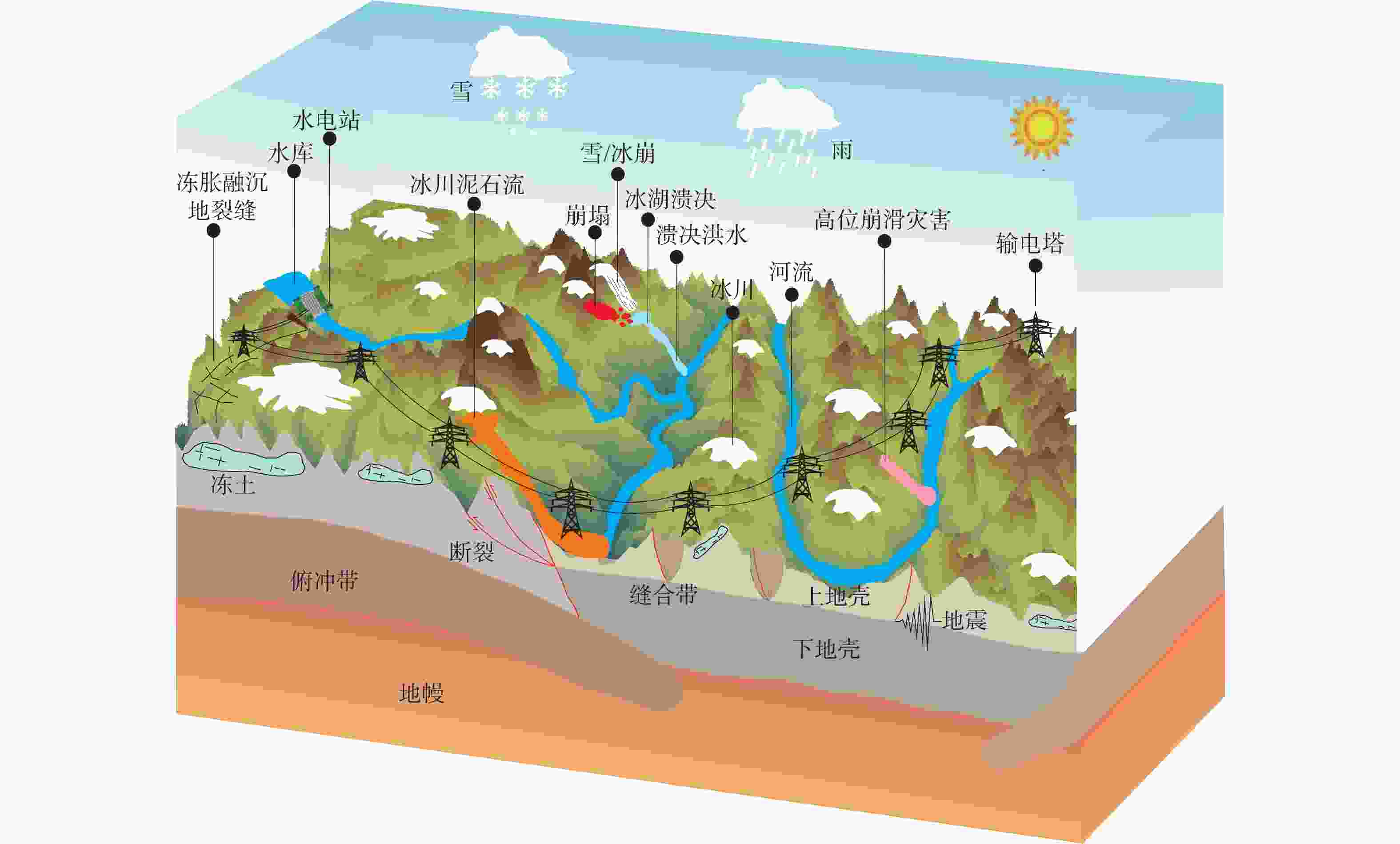
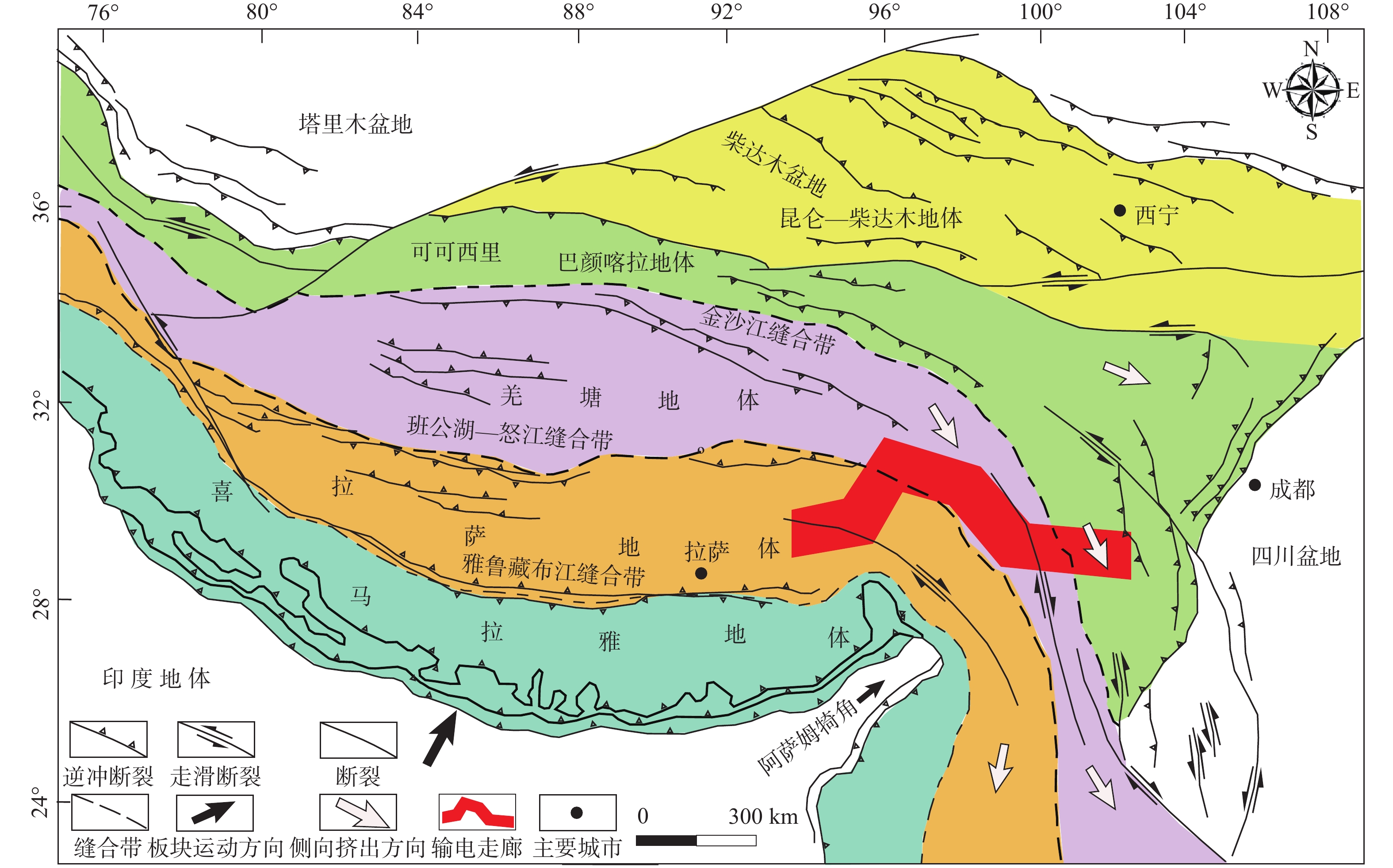
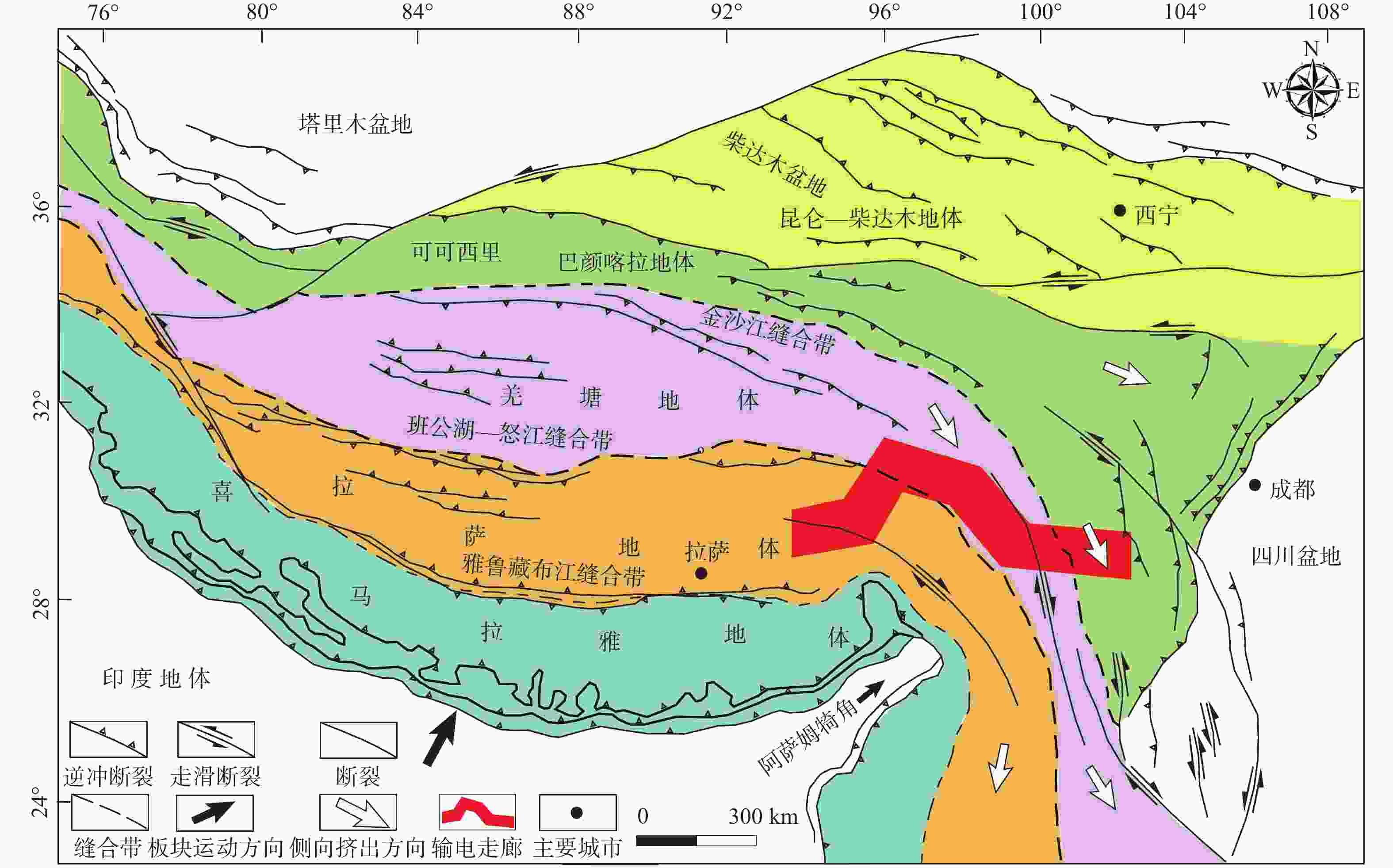
Geological environment and main geological safety challenges in the northern segment of the southeast Xizang (Tibet) power transmission corridor
-
摘要: 藏东南地区独特的地形地貌和气候条件特点,使之蕴藏着非常丰富的水电资源。为保障藏东南输电走廊北线的地质选线、建设和运营工作,文章通过归纳总结国内外文献资料,详细阐述了输电走廊北线沿线区域地质环境和主要地质安全隐患,并对藏东南输电走廊进一步灾害识别与监测工作提出了合理建议。结果表明:藏东南输电走廊沿线构造活动强烈、活动断裂发育、强震频发、地形地貌差异显著、岩土体结构损伤和劣化等独特的区域地质环境,极易诱发地质安全隐患;藏东南输电走廊北线的地质安全隐患主要包括滑坡、崩塌、泥石流、雪(冰)崩、冰湖溃决和冻胀融沉等;沿线地质安全隐患的发育受控于极高陡的地形和复杂的地貌条件、升温融雪气候变化、强烈的断裂活动与频发的地震、内外动力耦合诱发的高位远程灾害链等因素;深入融合InSAR技术、光学遥感、无人机摄影测量、机载LiDAR技术和在线实地监测等软防控手段的优势,可以有效打破藏东南输电走廊沿线灾害隐患错判、漏判、少判、智能化程度低和精准性差等困局。研究结果将为藏东南地区水电开发项目规划建设中的地质安全风险防控工作提供理论依据,也对藏东南地区可持续发展具有重要的现实意义。Abstract:
Objective Southeast Xizang(Tibet) boasts a wealth of hydroelectric resources, attributed to its distinctive topography, geomorphology, and climatic conditions. This study aims to safeguard the geological route selection, construction, and operation of the northern segment of the southeast Xizang(Tibet) power transmission corridor. Methods We conduct a comprehensive review of literature from both domestic and international sources, and elaborate extensively the regional geological conditions and significant geological safety challenges encountered along the corridor. Furthermore, this study presents sound recommendations for the further disaster identification and monitoring of the southeast Xizang(Tibet) power transmission corridor. Results The results are: (1)The transmission corridor in southeast Xizang(Tibet) exhibits pronounced structural activity, well-developed active faults, frequent strong seismic events, notable variations in topography and geomorphology, and distinctive regional geological conditions characterized by structural degradation of rock and soil; all of which have the potential to cause geological safety challenges. (2)The primary geological safety challenges in the northern section of the southeast Xizang(Tibet) power transmission corridor include landslides, collapses, debris flows, snow (ice) avalanches, glacial lake outburst floods, and frost heave settlements. (3)The development of geological safety issues along the route is controlled by extremely steep topography, complex geomorphological conditions, warming and snowmelt due to climate change, intense fault activity, frequent earthquakes, as well as the coupling of internal and external dynamics that induce high-altitude and long-distance disaster chains. Conclusion By deeply integrating the advantages of soft measures including InSAR technology, optical remote sensing, UAV photogrammetry, airborne LiDAR technology, and online field monitoring the issues of misinterpretation, oversight, and imprecision in hazard assessment for the southeast Xizang(Tibet) power transmission corridor can be effectively overcome. Significance The research establishes a theoretical foundation for the prevention and control of geological safety risks in the planning and implementation of hydroelectric projects in southeast Xizang(Tibet), holding substantial practical value for the sustainable development of the region. -
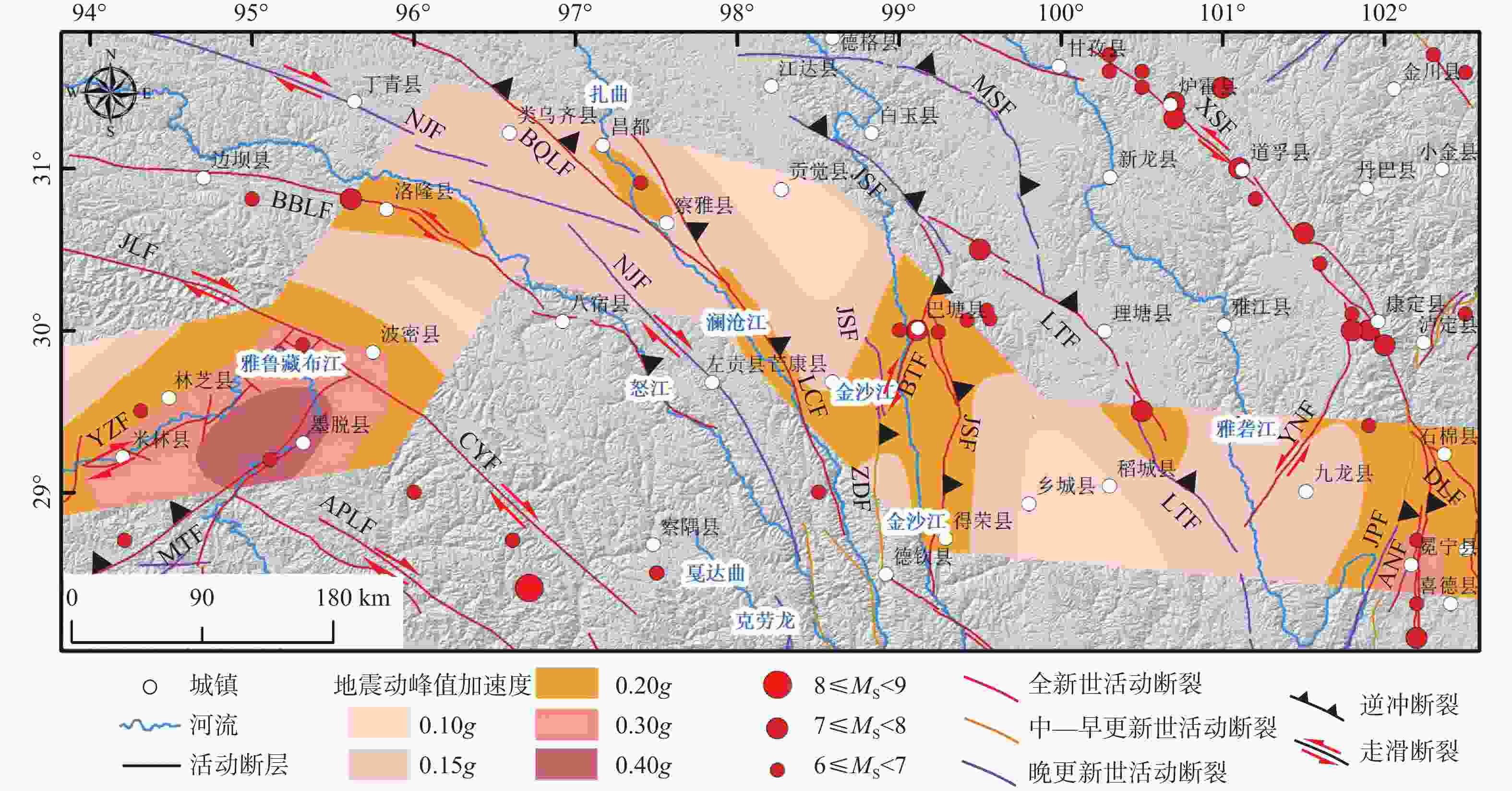
图 2 藏东南输电走廊沿线主要活动断裂与历史地震(MS≥6.0)分布
MTF—墨脱断裂;APLF—阿帕龙断裂;YZF—雅鲁藏布江断裂;CYF—察隅断裂;JLF—嘉黎断裂;BBLF—边坝−洛隆断裂;NJF—怒江断裂;LCF—澜沧江断裂;JSF—金沙江断裂;MSF—麦宿断裂;BQLF—巴青−类乌齐断裂;XSF—鲜水河断裂;LTF—理塘断裂;YNF—玉农希断裂;ANF—安宁河断裂;DLF—大凉山断裂;JPF—锦屏山断裂;ZDF—字嘎寺−德钦断裂
Figure 2. Distribution of major active faults and historical earthquakes (MS≥6.0) along the southeast Xizang (Tibet) power transmission corridor
MTF—Muotuo Fault; APLF—Apalong Fault; YZF—Yarlung Zangbo Jiang Fault; CYF—Chayu Fault; JLF—Jiali Fault; BLF—Bianba-Luolong Fault; NJF—Nujiang Fault; LCF—Lancang River Fault; JSF—Jinsha River Fault; MSF—Maisu Fault; BLF—Baqing-Leiwuqi Fault; XSF—Xianshuihe Fault; LTF—Litang Fault; YNF—Yunongxi Fault; ANF—Anninghe Fault; DLF—Daliangshan Fault; JPF—Jinpingshan Fault; ZDF—Zigasi-Deqin Fault
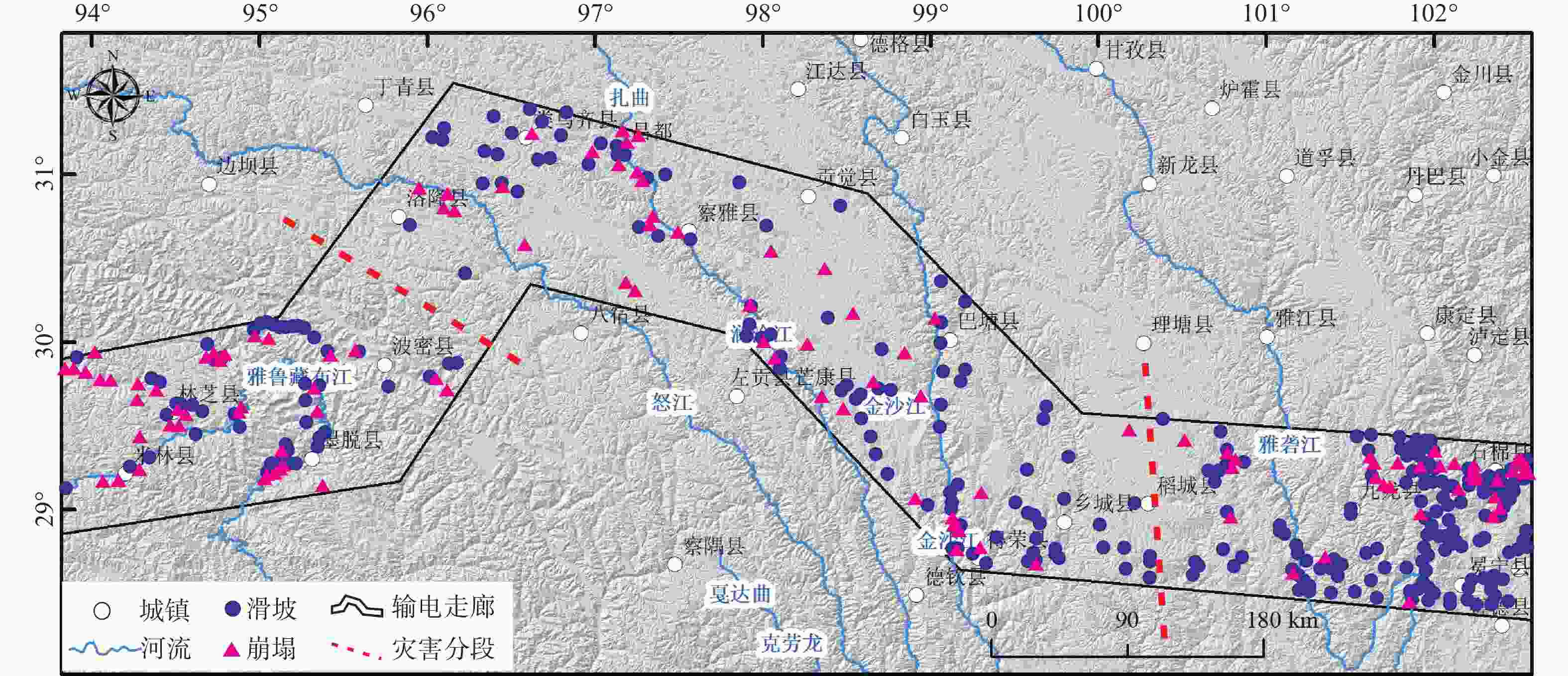
图 6 藏东南输电走廊沿线滑坡和崩塌灾害的分布(滑坡和崩塌的分布数据来源于王盈等,2019)
Figure 6. Distribution of landslide and collapse hazards along the power transmission corridor in southeast Xizang(Tibet) (the source of the landslide and collapse distribution data is Wang et al., 2019)
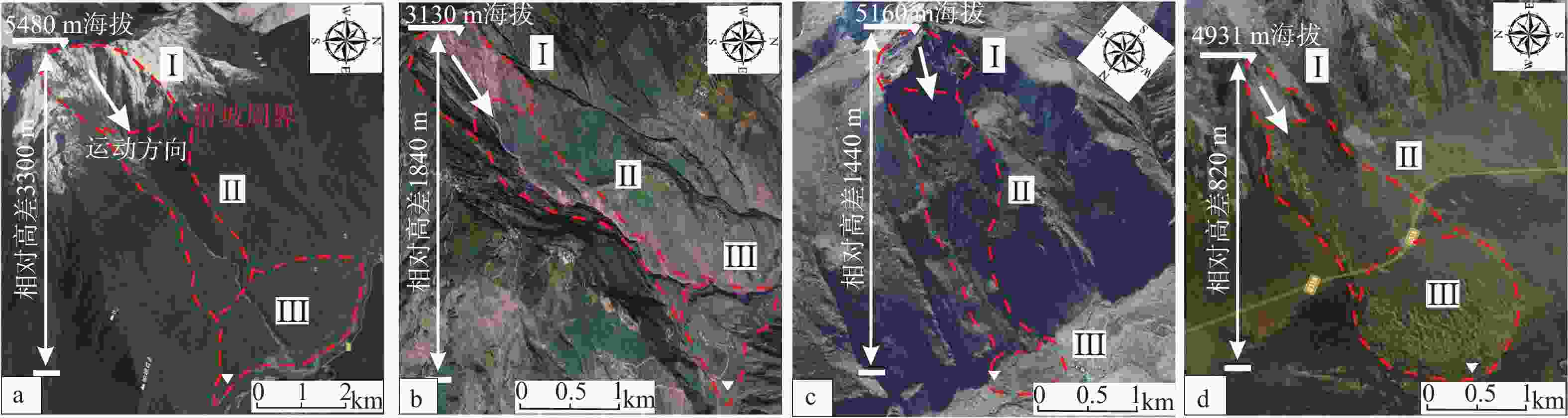
图 7 藏东南输电走廊沿线典型高位远程滑坡
Ⅰ—高位起滑区;Ⅱ—高速流通区;Ⅲ—堆积区a—易贡滑坡;b—烂泥沟滑坡;c—察达滑坡;d—乱石包滑坡
Figure 7. Typical long run-out landslides along the power transmission corridor in southeast Xizang(Tibet)
(a) Yigong landslide; (b) Lannigou landslide; (c) Chada landslide; (d) Luanshibao landslideⅠ—High-altitude uplift area; Ⅱ—High-speed movement area; Ⅲ—Accumulation area
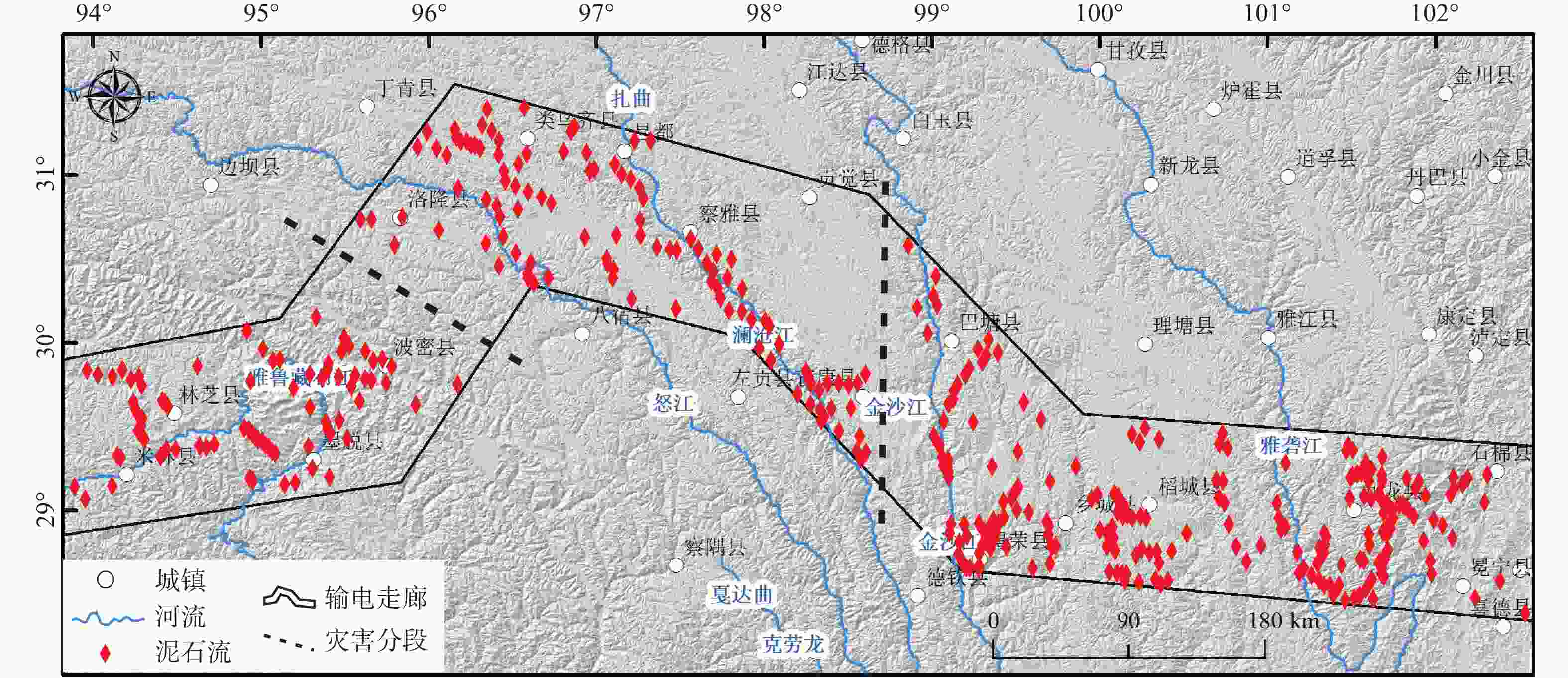
图 8 藏东南输电走廊沿线泥石流灾害的分布(泥石流分布数据来源于王盈等,2019)
Figure 8. Distribution of debris flow hazard along the power transmission corridor in southeast Xizang(Tibet) (the source of the debris flow distribution data is Wang et al., 2019)
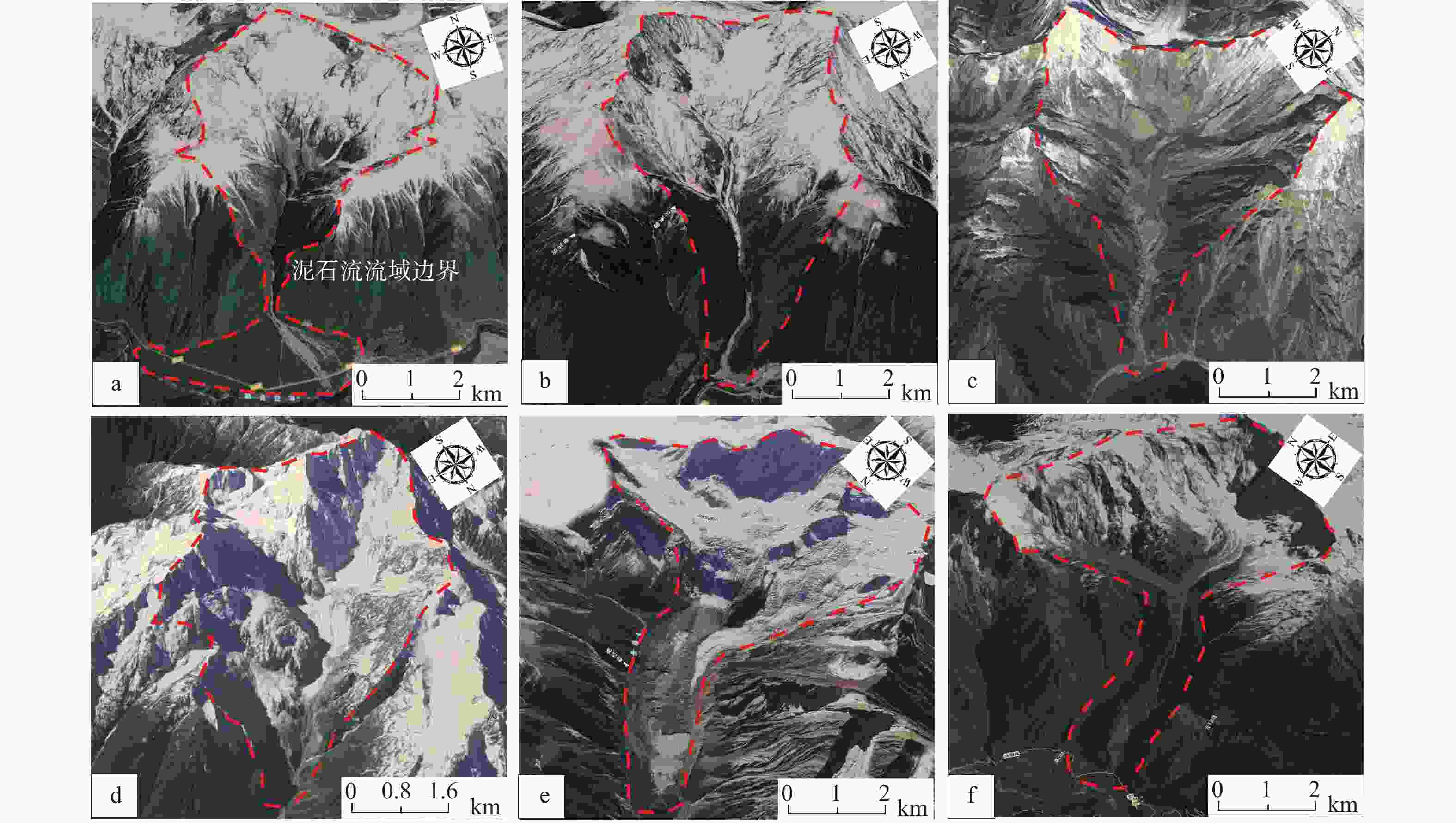
图 9 藏东南输电走廊沿线典型泥石流的光学影像
a—古乡沟泥石流;b—天摩沟泥石流;c—色东普泥石流;d—培龙沟泥石流;e—米堆沟泥石流;f—直白沟泥石流
Figure 9. Optical images of typical debris flows along the power transmission corridor in southeast Xizang(Tibet)
(a) Guxiang gully debris flow; (b) Tianmo gully debris flow; (c) Sedongpu debris flow; (d) Peilong gully debris flow; (e) Midui gully debris flow; (f) Zhibai gully debris flow
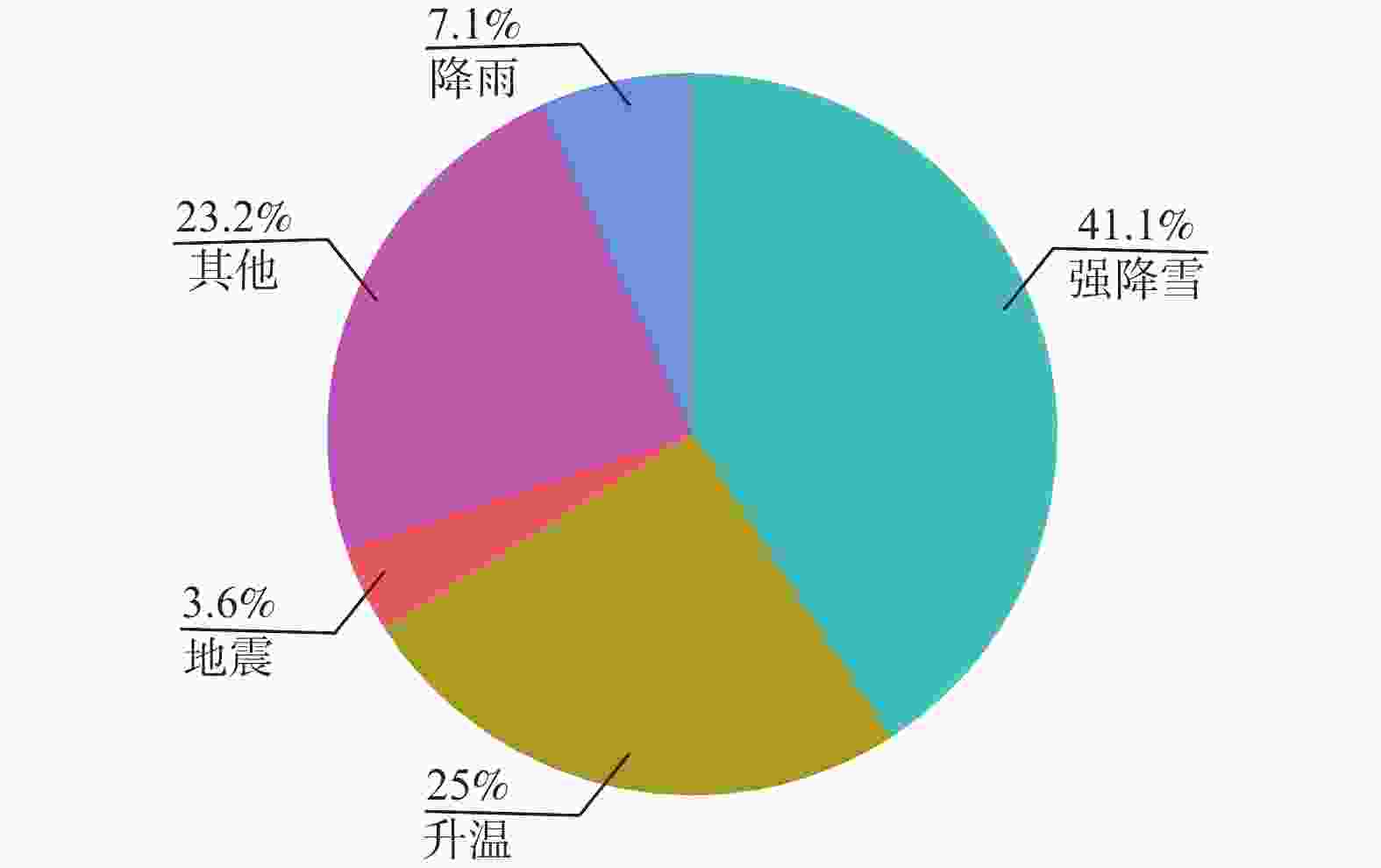
图 10 青藏高原高山区不同因素诱发雪崩的占比(据郝建盛等,2021修改)
Figure 10. Percentage of avalanches induced by different factors in the high mountainous areas of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (modified from Hao et al., 2021)
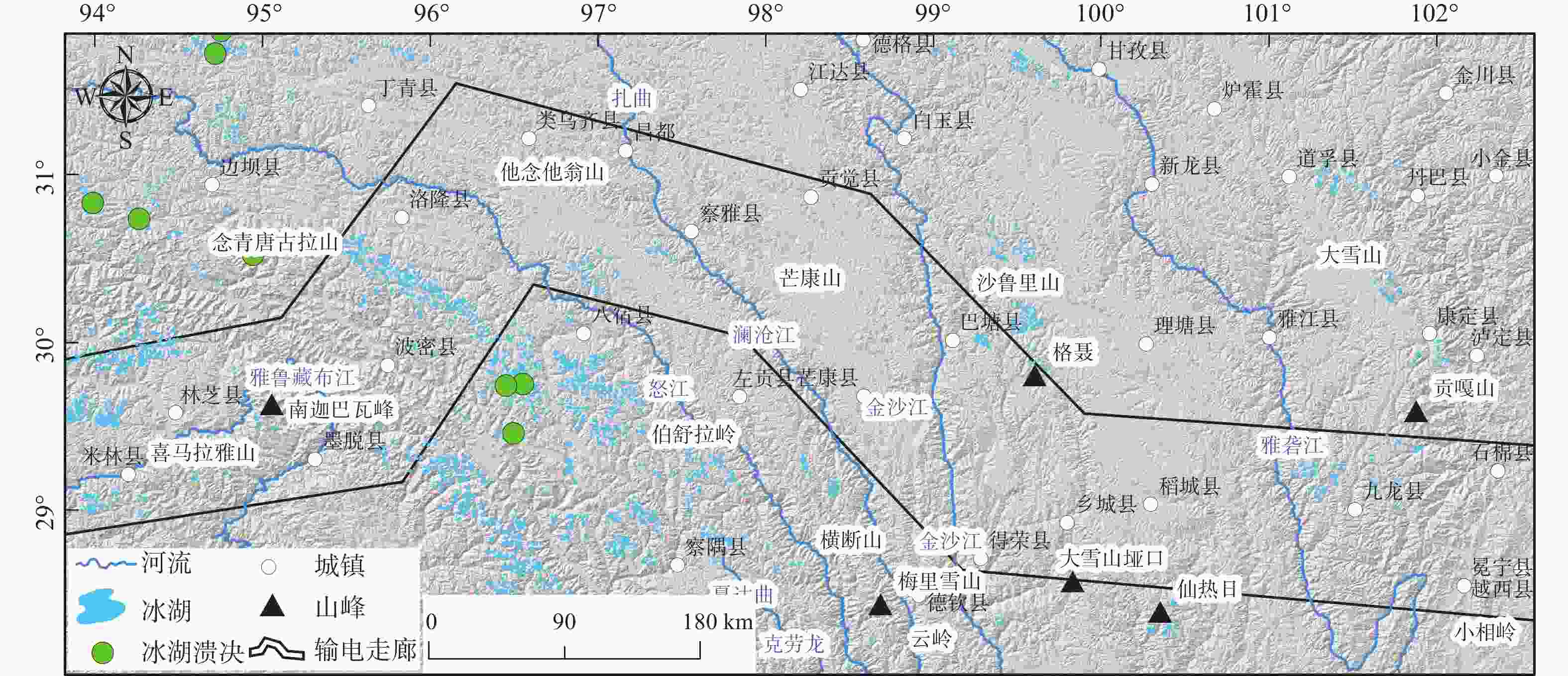
图 11 藏东南输电走廊沿线及邻区冰湖和冰湖溃决分布(冰湖分布数据来源于陈宁生等,2019)
Figure 11. Distribution of glacial lakes and glacial lake outbursts along the southeast Xizang(Tibet) power transmission corridor and neighboring areas (the glacial lake distribution data are from Chen et al., 2019)
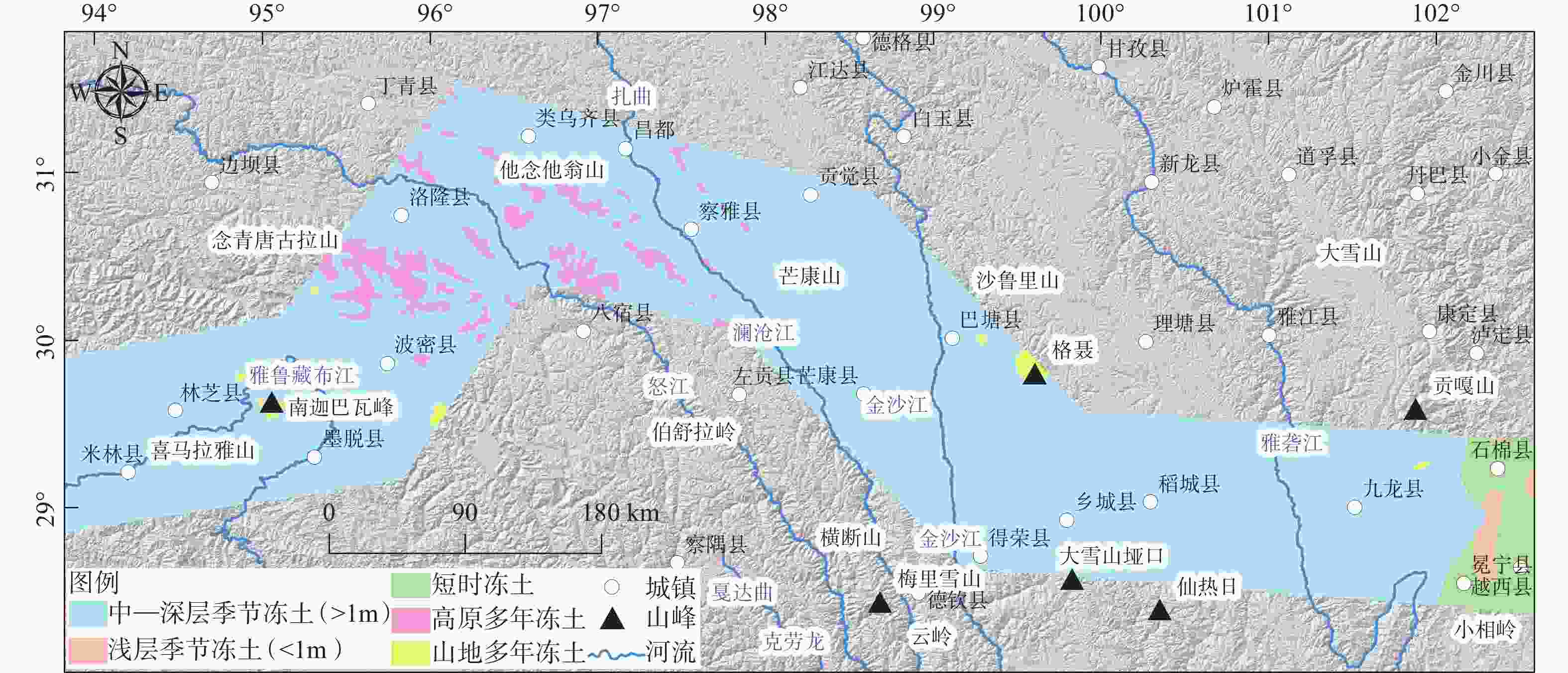
图 12 藏东南输电走廊沿线冻土分布(冻土分布数据来源于冉有华和李新,2018)
Figure 12. Distribution of frozen soil along the southeast Xizang(Tibet) power transmission corridor (the frozen soil distribution data are from Ran and Li, 2018)
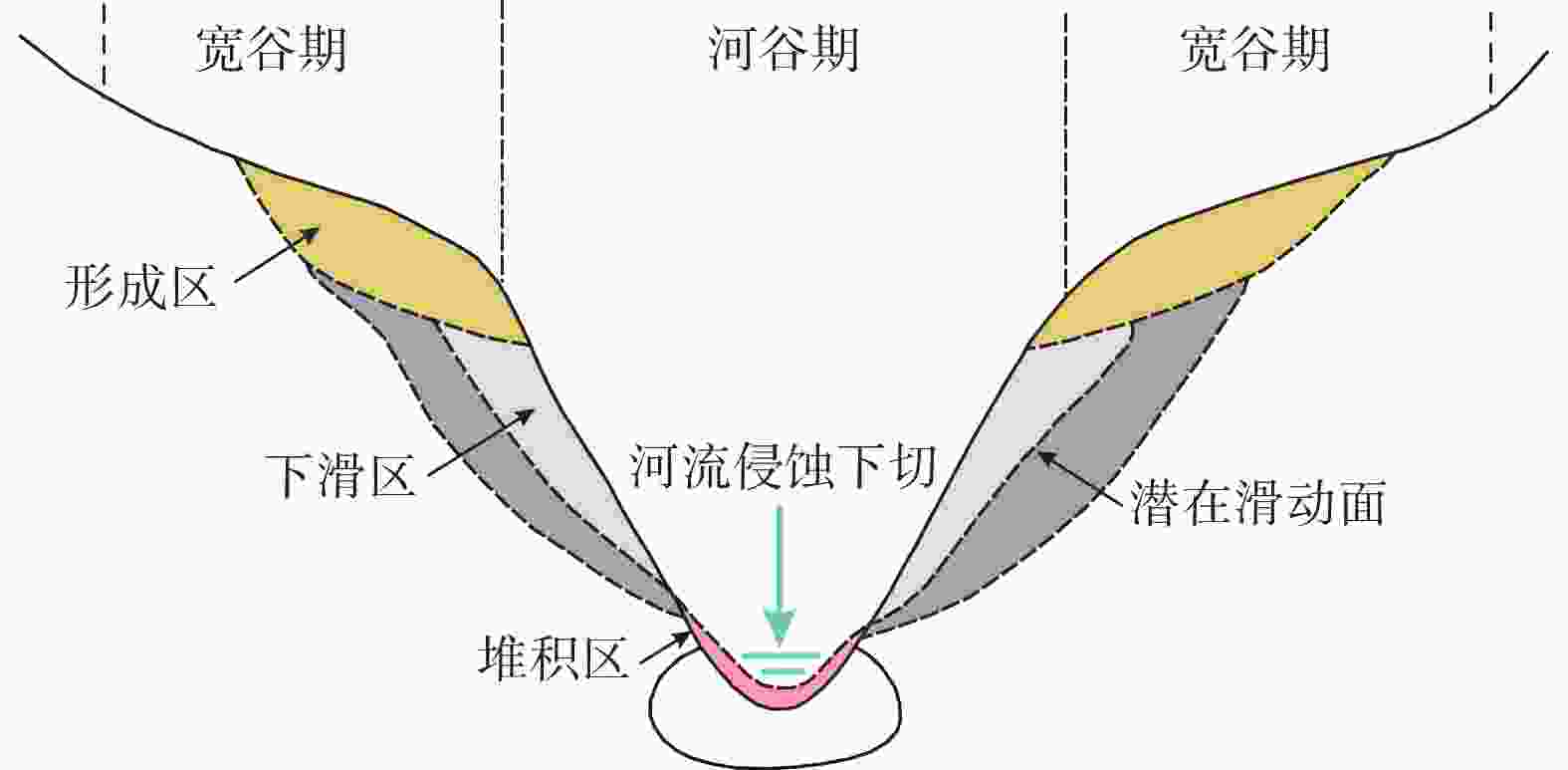
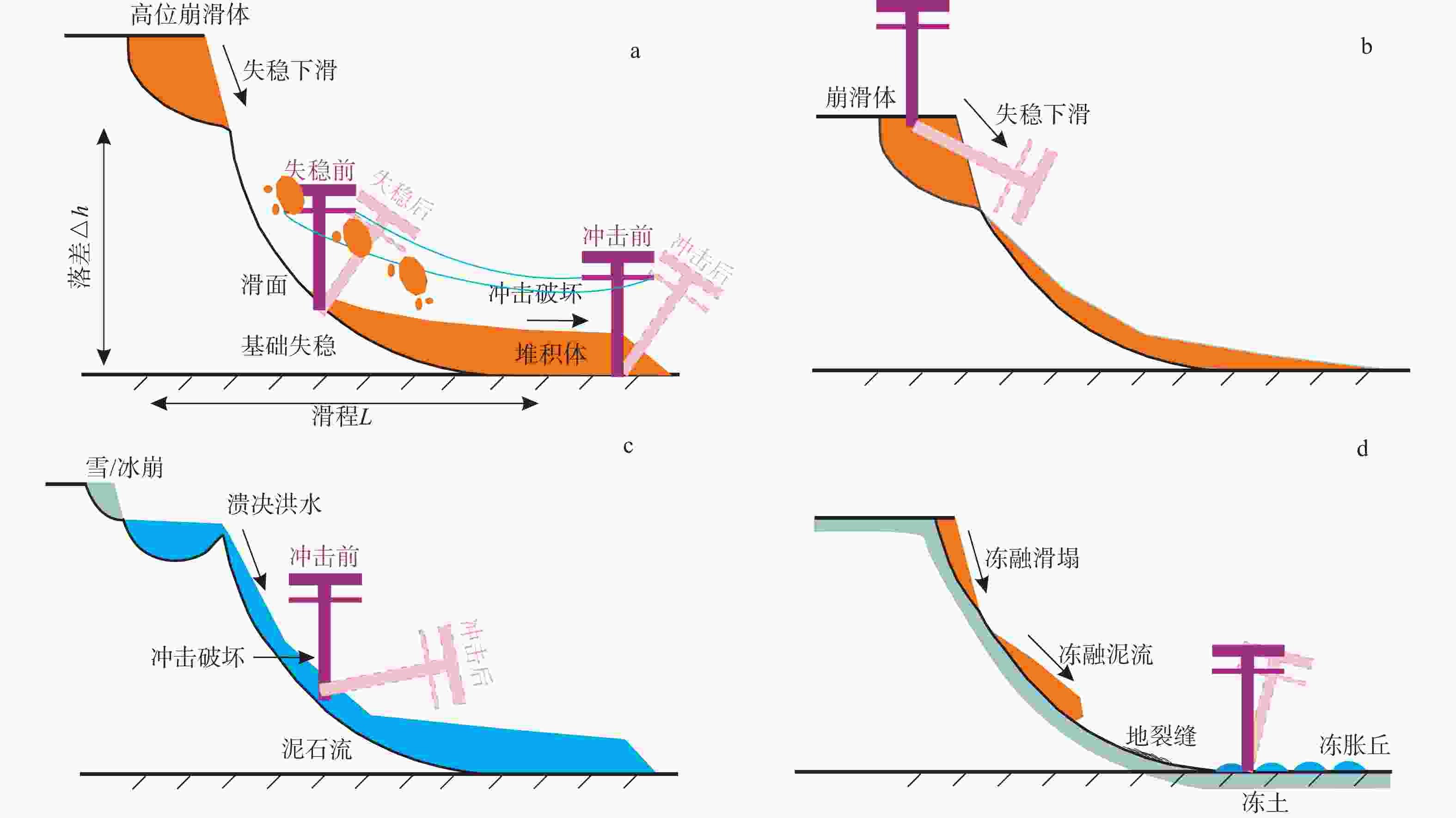
图 13 高山峡谷地貌中滑坡、崩塌和泥石流等灾害的演化机制(据Zhao et al.,2023修改)
Figure 13. Evolution mechanisms of disasters such as landslides, collapses, and debris flows in alpine canyon landforms (modified from Zhao et al., 2023)
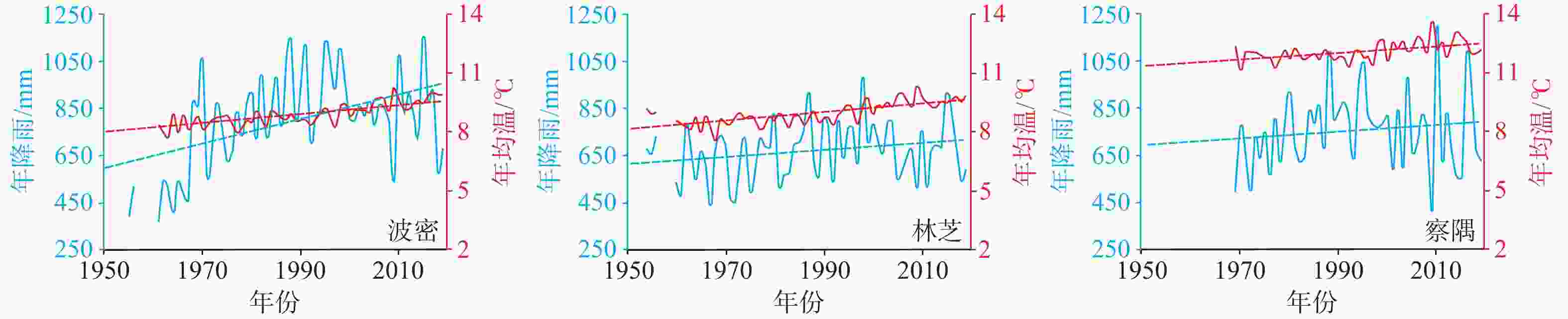
图 14 近60年藏东南地区典型气象站点年降雨/年均温变化(气象数据来源于余国安等,2024)
Figure 14. Variations in annual precipitation and mean annual air temperature over the past six decades at typical meteorological stations in southeast Xizang(Tibet) (the meteorological data are from Yu et al., 2024)
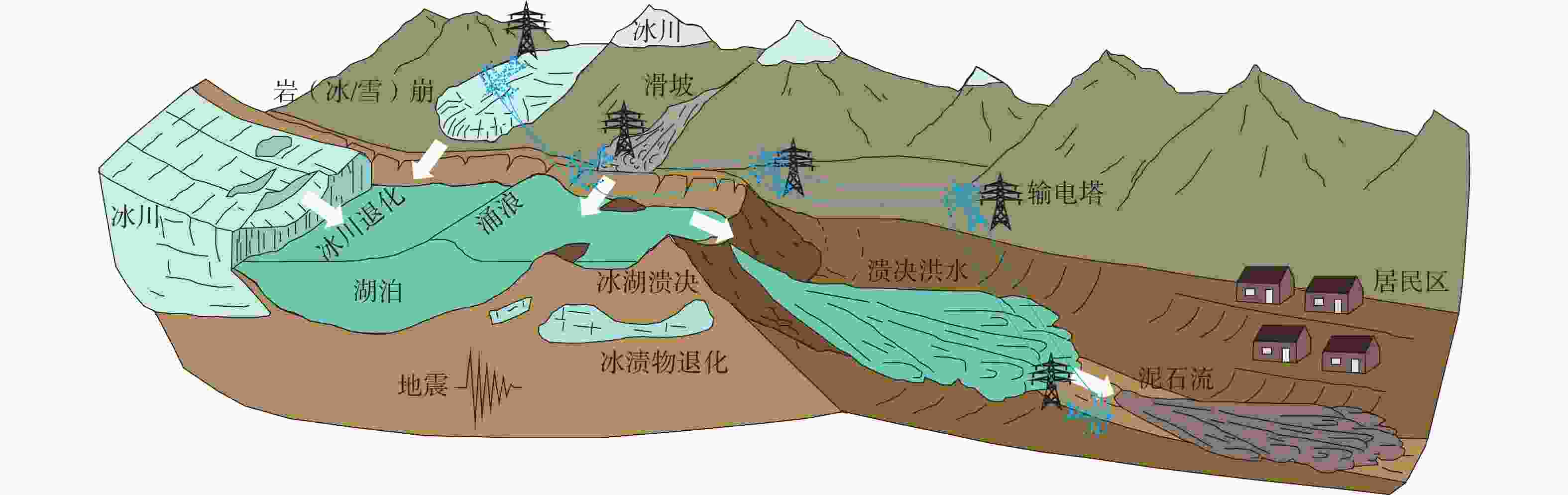
图 15 岩(冰/雪)崩−滑坡−碎屑流−冰湖溃决−洪水−泥石流灾害链演化过程(据Westoby et al.,2014修改)
Figure 15. Evolution of the rock (ice/snow)-landslide-debris flow-glacial lake outburst-flood-mudslide hazard chain (modified from Westoby et al., 2014)
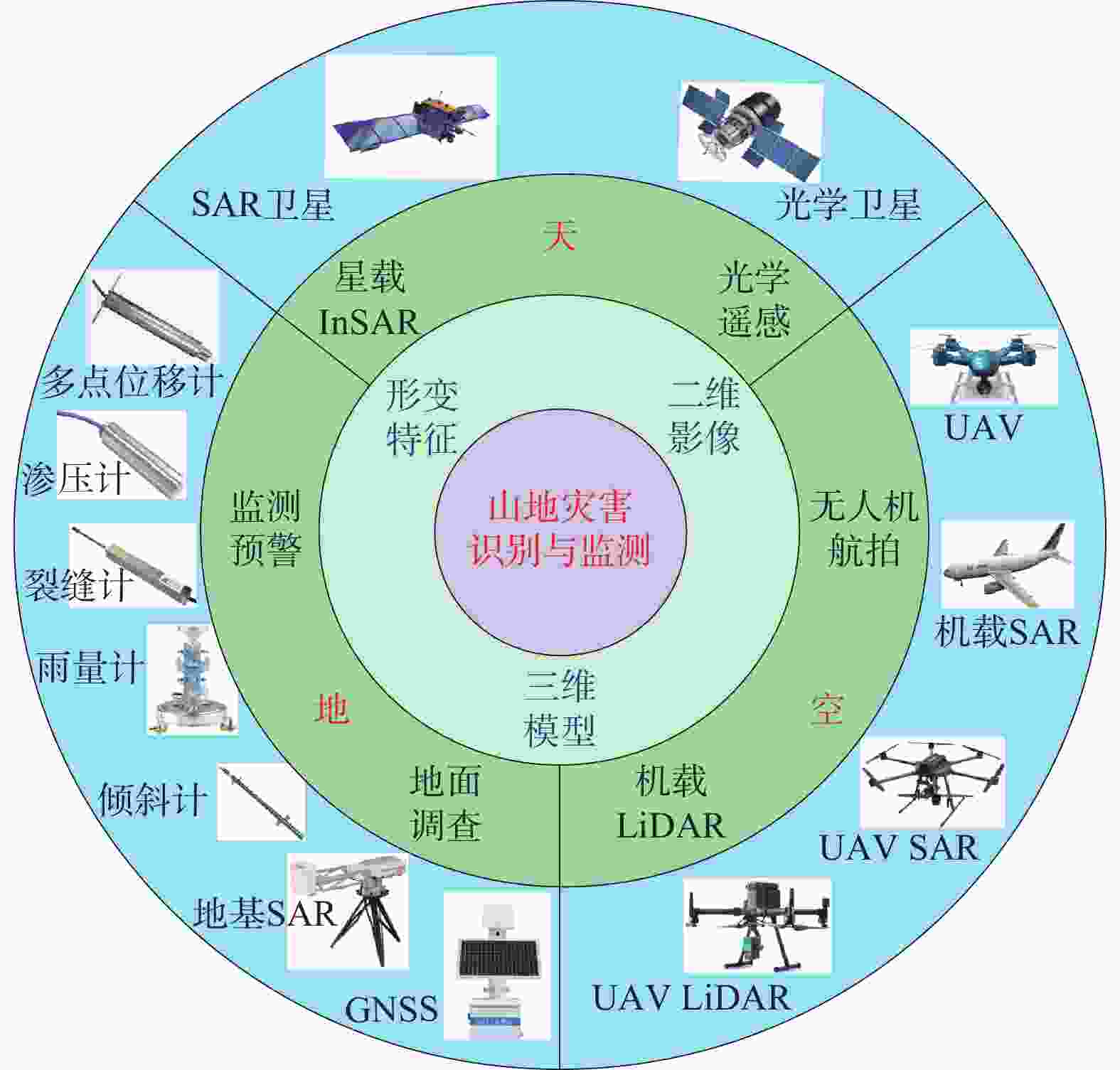
图 17 天−空−地一体化灾害识别、监测与预警技术体系(据许强等,2019修改)
Figure 17. Integrated sky-space-earth hazard identification, monitoring, and early warning technology system (modified from Xu et al., 2019)
表 1 藏东南输电走廊主要活动断裂一览表
Table 1. List of major active faults in the southeast Xizang(Tibet) power transmission corridor
序号 断裂名称 断裂性质 活动时代 与地震的关系 水平速度/
(mm/a)垂直速度/
(mm/a)参考资料 1 雅鲁藏布江断裂东段 右旋走滑 全新世 引起墨脱及邻区多次发生强震 6.0~7.0 1.0~4.0 唐方头等,2010 2 墨脱断裂 右旋走滑/逆冲 全新世 1950年察隅8.6级地震 — — 王晓楠等,2018 3 嘉黎断裂东段 右旋走滑 全新世 2017年米林6.9级地震 1.3 2.9 李鸿儒等,2021;赵远方等,2021 4 察隅断裂 左旋走滑 全新世 第四纪晚期至少发生了5次古地震事件 2.0~4.0 5.1~6.2 钟宁等,2021 5 边坝−洛隆断裂 左旋走滑 全新世 1642年洛隆7.0级地震和1791年边坝 63/4级地震 — — 韩明明等,2022 6 怒江断裂 右旋走滑 晚更新世 1930年腾冲6.0级地震;1950年益庆5.5级地震 3.2~6.4 3.9~5.7 钟宁等,2022 7 巴青−类乌齐断裂 走滑/逆冲推覆 全新世 2020年丁青5.1级地震 0.9~1.7 1.0~1.6 Ren et al., 2022 8 澜沧江断裂 逆断 全新世 尚无6级以上的地震记录 2.7~4.6 1.7~2.0 Ren et al., 2022 9 金沙江断裂 右旋走滑/逆倾滑 晚更新世 1950年扎西8.6级地震;1976年陆良7.2级地震 3.3~4.1 0.2 Ren et al., 2022 10 巴塘断裂 右旋走滑 全新世 1870年巴塘71/4级地震 3.0~4.0 — 徐正宣等,2021;杨志华等,2021 11 理塘断裂德巫段 左旋走滑兼逆冲 全新世 1948年理塘7.3级地震 3.2~4.4 0.1 徐锡伟等,2005 12 安宁河断裂北段 左旋走滑兼逆断 全新世 1952年冕宁石龙6.8级地震 3.1~3.3 1.5~1.7 周荣军等,2001 13 大凉山断裂 左旋走滑 全新世 1944年昭觉51/4级地震 3.0~4.0 — 孙浩越等,2015 14 玉农希断裂 左旋走滑 全新世 1975年康定6.2级地震 1.0~2.0 <1.0 马超,2013 15 锦屏山断裂 逆断 晚更新世 历史上无6.0级以上地震 — <1.0 吴俊杰,2022 -
[1] BAI Y J, NI H Y, GE H, 2019. Advances in research on the geohazard effect of active faults on the southeastern margin of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(6): 1116-1128. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] BHARDWAJ A, SAM L, 2022. Reconstruction and characterisation of past and the most recent slope failure events at the 2021 rock-ice avalanche site in Chamoli, Indian Himalaya[J]. Remote Sensing, 14(4): 949. doi: 10.3390/rs14040949 [3] CHEN N S, DING H T, DENG M F, 2019. 2014-2016 Ice lake observation data of Midui glacier in Southeast Tibet[R]. Lanzhou: National Cryosphere Desert Data Center. (in Chinese) [4] CHEN X F, ZHU C B, QI W F, et al., 2015. Formation conditions, development tendency and preventive measures of Pufu landslide in Luquan of Yunnan[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 29(3): 395-401. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] CUI P, MA D T, CHEN N S, et al., 2003. The initiation, motion and mitigation of debris flow caused by glacial lake outburst[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 23(6): 621-628. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] CUI P, GE Y G, LI S J, et al., 2022. Scientific challenges in disaster risk reduction for the Sichuan-Tibet Railway[J]. Engineering Geology, 309: 106837. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106837 [7] DAI L X, XU Q, FAN X M, et al., 2017. A preliminary study on spatial distribution patterns of landslides triggered by Jiuzhaigou earthquake in Sichuan on August 8th, 2017 and their susceptibility assessment[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 25(4): 1151-1164. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] DAI X R, ZHAO J J, LAI Q Y, et al., 2022. Movement process and formation mechanism of rock avalanche in Chada, Tibet Plateau[J]. Earth Science, 47(6): 1932-1944. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] DING L, KAPP P, CAI F L, et al., 2022. Timing and mechanisms of Tibetan Plateau uplift[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 3(10): 652-667. [10] DU R H, ZHANG S C, 1981. Characteristics of glacial mud-flows in south-eastern Qinghai-Xizang plateau[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology(3): 10-16. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] FAN J H, WU C Y, CHENG G W, 2006. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of geological hazards in Tibet[J]. Wuhan University Journal of Natural Sciences, 11(4): 806-812. doi: 10.1007/BF02830168 [12] FAN X M, SCARINGI G, KORUP O, et al., 2019. Earthquake-induced chains of geologic hazards: patterns, mechanisms, and impacts[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 57(2): 421-503. doi: 10.1029/2018RG000626 [13] FRIGO B, BARTELT P, CHIAIA B, et al., 2021. A reverse dynamical investigation of the catastrophic wood-snow avalanche of 18 January 2017 at Rigopiano, Gran Sasso National Park, Italy[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Science, 12: 40-55. doi: 10.1007/s13753-020-00306-6 [14] GE D Q, DAI K R, GUO Z C, et al., 2019. Early identification of serious geological hazards with integrated remote sensing technologies: thoughts and recommendations[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 44(7): 949-956. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] GOSWAMI U P, GOYAL M K, 2021. Assessment of glacial lake development and downstream flood impacts of critical glacial lake[J]. Natural Hazards, 109(1): 1027-1046. doi: 10.1007/s11069-021-04866-8 [16] GUO C B, DU Y B, ZHANG Y S, et al., 2015. Geohazard effects of the Xianshuihe fault and characteristics of typical landslides in western Sichuan[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(1): 121-134. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] GUO C B, DU Y B, TONG Y Q, et al., 2016. Huge long-runout landslide characteristics and formation mechanism: a case study of the Luanshibao landslide, Litang County, Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 35(8): 1332-1345. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] GUO D L, YANG M X, WANG H J, 2011. Characteristics of land surface heat and water exchange under different soil freeze/thaw conditions over the central Tibetan Plateau[J]. Hydrological Processes, 25(16): 2531-2541. doi: 10.1002/hyp.8025 [19] HAN M M, CHEN L C, LI Y B, et al., 2022. Geological and geomorphic evidence for Late Quaternary activity of the Bianba-Luolong Fault on the western boundary of the Bangong-Nujiang suture[J]. Earth Science, 47(3): 757-765. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] HAO J S, HUANG F R, FENG T, et al., 2021. Analysis of spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of snow avalanche disaster and its triggering factors in the high mountain Asia[J]. Mountain Research, 39(2): 304-312. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] HUANG R Q, LI W L, 2008. Research on development and distribution rules of geohazards induced by Wenchuan earthquake on 12th May, 2008[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 27(12): 2585-2592. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] LI B, YIN Y P, TAN C X, et al., 2022. Geo-safety challenges against the site selection of engineering projects in the eastern Himalayan syntaxis area[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(6): 907-918. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] LI H B, PAN J W, SUN Z M, et al., 2021. Continental tectonic deformation and seismic activity: a case study from the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(1): 194-213. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] LI H R, BAI L, ZHAN H L, 2021. Research progress of Jiali Fault activity[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, 52(2): 182-193. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] LI L J, WEN B P, YAO X, et al., 2023. InSAR-based method for monitoring the long-time evolutions and spatial-temporal distributions of unstable slopes with the impact of water-level fluctuation: a case study in the Xiluodu reservoir[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 295: 113686. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2023.113686 [26] LI T D, PAN G T, XIAO X C, et al. , 2013. Geological records and mechanism of the uplift of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau[M]. Guangzhou: Guangdong Science & Technology Press. (in Chinese) [27] LI Y, CUI Y F, LI Z H, et al., 2022. Evolution of glacier debris flow and its monitoring system along sichuan-tibet traffic corridor[J]. Earth Science, 47(6): 1969-1984. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] LI Y L, LIU J K, ZHANG J J, et al., 2021. Characteristics and potential hazard of the Chada collapse in eastern Tibet[J]. Geoscience, 35(1): 74-82. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] LI Y Y, FENG X Y, YAO A J, et al., 2022. Progressive evolution and failure behavior of a Holocene river-damming landslide in the SE Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Landslides, 19(5): 1069-1086. doi: 10.1007/s10346-021-01835-x [30] LI Z Z, YANG W C, ZHANG P, et al., 2023. In-situ stress measurement and inversion analysis of a large hydropower project in southeast Tibet[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 29(3): 442-452. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] LIN D M, BAO W X, REN Y H, et al. , 2020. Stereoscopic monitoring and integrated risk management of geohazards along highways in the central asian alpine region[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) [32] LIU J K, CHENG Z L, GUO F F, et al., 2011. Analysis on risk of glacier-lake outburst in southeastern Tibet[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 26(2): 45-49. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] LIU J K, ZHANG J J, GAO B, et al., 2019. An overview of glacial lake outburst flood in Tibet, China[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 41(6): 1335-1347. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] LU A X, DENG X F, ZHAO S X, et al., 2006. Cause of debris flow in Guxiang valley in Bomi, Tibet autonomous region, 2005[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 28(6): 956-960. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] LU X, QI S W, ZHENG B W, et al., 2023. Distribution and hazard assessment of collapses and landslides in Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 31(3): 718-735. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] LUCIEER A, JONG S M D, TURNER D, 2014. Mapping landslide displacements using Structure from Motion (SfM) and image correlation of multi-temporal UAV photography[J]. Progress in Physical Geography: Earth and Environment, 38(1): 97-116. doi: 10.1177/0309133313515293 [37] MA C, 2013. A study of fault activity and microtopography within the Chuandian active blocks's major fault[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] MOLNAR P, ENGLAND P, MARTINOD J, 1993. Mantle dynamics, uplift of the Tibetan Plateau, and the Indian Monsoon[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 31(4): 357-396. doi: 10.1029/93RG02030 [39] NIE Y, DENG Q, PRITCHARD H D, et al., 2023. Glacial lake outburst floods threaten Asia’s infrastructure[J]. Science Bulletin, 68(13): 1361-1365. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2023.05.035 [40] PENG D L, ZHANG L M, JIANG R C, et al., 2022. Initiation mechanisms and dynamics of a debris flow originated from debris-ice mixture slope failure in southeast Tibet, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 307: 106783. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106783 [41] PENG J B, CUI P, ZHUANG J Q, 2020. Challenges to engineering geology of Sichuan—Tibet railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 39(12): 2377-2389. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] PENG J B, XU N X, ZHANG Y S, et al., 2022. The framework system for geosafety research[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 30(6): 1798-1810. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] QI W W, ZHANG B P, PANG Y, et al., 2013. TRMM-data-based spatial and seasonal patterns of precipitation in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 33(8): 999-1005. (in Chinese with English abstract [44] QIN C Y, FU B, ZHU X K, et al., 2023. Spatial and temporal patterns of hydropower development on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau[J]. Sustainability, 15(8): 6688. doi: 10.3390/su15086688 [45] RAN Y H, LI X, 2018. Frozen soil map of China (2000)[R]. Beijing: National Qinghai Tibet Plateau Science Data Center. (in Chinese) [46] REN J J, XU X W, LV Y W, et al., 2022. Late Quaternary slip rate of the northern Lancangjiang fault zone in eastern Tibet: Seismic hazards for the Sichuan-Tibet Railway and regional tectonic implications[J]. Engineering Geology, 306: 106748. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106748 [47] SCHNEIDER D, HUGGEL C, HAEBERLI W, et al., 2011. Unraveling driving factors for large rock–ice avalanche mobility[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 36(14): 1948-1966. doi: 10.1002/esp.2218 [48] SHUGAR D H, BURR A, HARITASHYA U K, et al., 2020. Rapid worldwide growth of glacial lakes since 1990[J]. Nature Climate Change, 10(10): 939-945. doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-0855-4 [49] SONG Z, ZHANG G Z, JIANG L W, et al., 2016. Analysis of the characteristics of major geological disasters and geological alignment of Sichuan-Tibet Railway[J]. Railway Standard Design, 60(1): 14-19. (in Chinese with English abstract [50] STUART-SMITH R F, ROE G H, LI S, et al., 2021. Increased outburst flood hazard from Lake Palcacocha due to human-induced glacier retreat[J]. Nature Geoscience, 14(2): 85-90. doi: 10.1038/s41561-021-00686-4 [51] SUN D, YANG T, CAO N, et al., 2023. Characteristics and mitigation of coseismic geohazards associated with the Luding Ms6.8 earthquake[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 30(3): 476-493. (in Chinese with English abstract [52] SUN H Y, HE H L, WEI Z Y, et al., 2015. Late Quaternary activity of Zhuma fault on the north segment of Daliangshan fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 37(2): 440-454. (in Chinese with English abstract [53] SUN Y Q, GE Y G, CHEN X Z, et al., 2024. Analysis of the trigger conditions and activity trend in debris flow along Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor (Xinduqiao-Changdu section) under environmental changes[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 83(5): 189. doi: 10.1007/s10064-024-03689-8 [54] TANG C, VAN ASCH T W J, CHANG M, et al., 2012. Catastrophic debris flows on 13 August 2010 in the Qingping area, southwestern China: the combined effects of a strong earthquake and subsequent rainstorms[J]. Geomorphology, 139-140: 559-576. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.12.021 [55] TANG F T, SONG J, CAO Z Q, et al., 2010. The movement characters of main faults around Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis revealed by the latest GPS data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(9): 2119-2128. (in Chinese with English abstract [56] TIAN X W, 2023. Experimental study on nonlinear creep characteristics and long-term strength of microbially improved expansive soil[D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry and Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract [57] VALKANIOTIS S, PAPATHANASSIOU G, GANAS A, 2018. Mapping an earthquake-induced landslide based on UAV imagery; case study of the 2015 Okeanos landslide, Lefkada, Greece[J]. Engineering Geology, 245: 141-152. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.08.010 [58] WANG F W, CHEN Y, LIU W C, et al., 2022. Characteristics and challenges to dynamics of long-runout landslides with high-altitude in southeast Tibet[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 30(6): 1831-1841. (in Chinese with English abstract [59] WANG S J, REN J W, 2012. A review of the progresses of avalanche hazards research[J]. Progress in Geography, 31(11): 1529-1536. (in Chinese with English abstract [60] WANG X N, TANG F T, SHAO C R, 2018. The current movement characters of main faults surrounding the Namcha Barwa Syntaxis[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 13(2): 267-275. (in Chinese with English abstract [61] WANG Y, JIN J L, YUAN R M, 2019. Analysis on spatial distribution and influencing factors of geological disasters in southeast Tibet[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 42(3): 428-437. (in Chinese with English abstract [62] WESTOBY M J, GLASSER N F, BRASINGTON J, et al., 2014. Modelling outburst floods from moraine-dammed glacial lakes[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 134: 137-159. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.03.009 [63] WU G Q, XIE Y L, WEI J, et al., 2022. Water migration in subgrade soil under seasonal freeze-thaw cycles in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 19(6): 1767-1781. doi: 10.1007/s11629-021-7270-9 [64] WU J J, 2022. Study on the activity of the Jinpingshan-Xiaojinhe fault zone in Late Quaternary[D]. Guilin: Guilin University of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract [65] WU Y, WANG Y X, HAIM W, et al., 2020. Fracture of rocks in the mountains of Southeast Tibet under hydrothermal conditions at different elevations[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 79(8): 4291-4308. doi: 10.1007/s10064-020-01806-x [66] XIN P, WANG T, LIU J M, et al., 2022. The geological structure and sliding mode of the slopes in the Yigong landslide source area, Tibet[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(6): 1012-1023. (in Chinese with English abstract [67] XU L F, MENG X W, XU X G, 2014. Natural hazard chain research in China: a review[J]. Natural Hazards, 70(2): 1631-1659. doi: 10.1007/s11069-013-0881-x [68] XU Q, SHANG Y J, VAN ASCH T, et al., 2012. Observations from the large, rapid Yigong rock slide-debris avalanche, Southeast Tibet[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 49(5): 589-606. doi: 10.1139/t2012-021 [69] XU Q, DONG X J, LI W L, 2019. Integrated space-air-ground early detection, monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 44(7): 957-966. (in Chinese with English abstract [70] XU X W, WEN X Z, YU G H, et al., 2005. Average slip rate, earthquake rupturing segmentation and recurrence behavior on the Litang fault zone, western Sichuan Province, China[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 48(8): 1183-1196. doi: 10.1360/04yd0072 [71] XU Z Q, LI H B, YANG J S, 2006. An orogenic plateau: the orogenic collage and orogenic types of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(4): 54-58. (in Chinese with English abstract [72] XU Z Q, YANG J S, LI H B, et al. , 2007. Orogenic plateaux: terrane amalgamation, collision and uplift in the Qinghai-Tibet plateau[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. (in Chinese) [73] XU Z X, ZHANG L G, JIANG L W, et al., 2021. Engineering geological environment and main engineering geological problems of Ya'an—Linzhi Section of the Sichuan—Tibet Railway[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 53(3): 29-42. (in Chinese with English abstract [74] YANG Z H, GUO C B, WU R A, et al., 2021. Predicting seismic landslide hazard in the Batang fault zone of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 48(5): 91-101. (in Chinese with English abstract [75] YANG Z J, DONG W F, LIU J F, et al., 2021. Genetic types and distribution of glacial lakes in western Sichuan and eastern Tibet[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 40(12): 2071-2079. (in Chinese with English abstract [76] YAO J M, YAO X, LIU X H, 2022. Landslide detection and mapping based on SBAS-InSAR and PS-InSAR: a case study in Gongjue County, Tibet, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 14(19): 4728. doi: 10.3390/rs14194728 [77] YAO X, LI L J, ZHANG Y S, et al., 2017. Types and characteristics of slow-moving slope geo-hazards recognized by TS-InSAR along Xianshuihe active fault in the eastern Tibet Plateau[J]. Natural Hazards, 88(3): 1727-1740. doi: 10.1007/s11069-017-2943-y [78] YAO X, DENG J H, LIU X H, et al., 2020. Primary recognition of active landslides and development rule analysis for pan Three-river-parallel Territory of Tibet Plateau[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 52(5): 16-37. (in Chinese with English abstract [79] YAO X, CHEN Y P, LIU D L, et al., 2021. Average-DInSAR method for unstable escarpments detection induced by underground coal mining[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 103: 102489. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2021.102489 [80] YIN Y P, XING A G, 2012. Aerodynamic modeling of the Yigong gigantic rock slide-debris avalanche, Tibet, China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 71(1): 149-160. doi: 10.1007/s10064-011-0348-9 [81] YIN Z Q, XU Y Q, CHEN H Q, et al., 2016. The development and distribution characteristics of geohazards induced by August 3, 2014 Ludian earthquake and comparison with Jinggu and Yingjiang earthquakes[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(6): 1086-1097. (in Chinese with English abstract [82] YU G A, LU J Y, LI Z W, et al., 2022. Geomorphic effects of debris flows in high mountain areas of the Parlung Zangbo Basin, Southeast Tibet under the influence of climate change[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 77(3): 619-634. (in Chinese with English abstract [83] YU G A, YUE P S, ZHANG C D, et al., 2024. River hydrology studies in Southeast Xizang: progress and challenges[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 69(3): 394-413. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1360/TB-2023-0075 [84] YUAN H, GUO C B, WU R A, et al., 2023. Research progress and prospects of the giant Yigong long run-out landslide, Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 42(10): 1757-1773. (in Chinese with English abstract [85] ZHANG L X, PANG M Y, BAHAJ A S, et al., 2021. Small hydropower development in China: growing challenges and transition strategy[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 137: 110653. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2020.110653 [86] ZHANG P Z, WANG W T, GAN W J, et al., 2022. Present-day deformation and Geodynamic processes of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96(10): 3297-3313. (in Chinese with English abstract [87] ZHANG Y H, LIU C M, LIANG K, et al., 2022. Spatio-temporal variation of precipitation in the Yarlung Zangbo river basin[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 77(3): 603-618. (in Chinese with English abstract [88] ZHANG Y S, GUO C B, YAO X, et al., 2016. Research on the geohazard effect of active fault on the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 37(3): 277-286. (in Chinese with English abstract [89] ZHANG Y S, WU R A, GUO C B, et al., 2022. Geological safety evaluation of railway engineering construction in plateau mountainous region: ideas and methods[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96(5): 1736-1751. (in Chinese with English abstract [90] ZHAO B, SU L J, WANG Y S, et al., 2023. Insights into some large-scale landslides in southeastern margin of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 15(8): 1960-1985. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.09.005 [91] ZHAO Y F, GONG W B, JIANG W, et al., 2021. Multi-stage characteristics and tectonic significance of the Jiali fault in Guxiang-Tongmai section, South Tibet[J]. Geoscience, 35(1): 220-233. (in Chinese with English abstract [92] ZHONG N, GUO C B, HUANG X L, et al., 2021. Late Quaternary activity and paleoseismic records of the middle south section of the Jiali-Chayu fault[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(12): 3642-3659. (in Chinese with English abstract [93] ZHONG N, YANG Z, ZHANG X B, et al., 2022. Evidence of Holocene activity and paleoseismic records in the central section of Bangda fault in Nujiang fault zone[J]. Geological Review, 68(6): 2021-2032. (in Chinese with English abstract [94] ZHOU R J, HE Y L, YANG T, et al., 2001. Slip rate and strong earthquake rupture on the Moxi-Mianning segment along the Xianshuihe-Anninghe fault zone[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 17(3): 253-262. (in Chinese with English abstract [95] ZHOU Y Q, SHENG Q, CHEN J, et al., 2022. The failure mode of transmission tower foundation on the landslide under heavy rainfall: a case study on a 500-kV transmission tower foundation on the Yanzi landslide in Badong, China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 81(3): 125. doi: 10.1007/s10064-022-02628-9 [96] ZHOU Z K, YAO X, LIU H Y, et al., 2020. Accurate identification of active landslides in region composed with glacier, forest, steep valley: a case study in the Lantsang Meili snow mountain section[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 52(6): 61-74. (in Chinese with English abstract [97] ZHU Y F, YAO X, YAO L H, et al., 2022. Detection and characterization of active landslides with multisource SAR data and remote sensing in western Guizhou, China[J]. Natural Hazards, 111(1): 973-994. doi: 10.1007/s11069-021-05087-9 [98] 白永健,倪化勇,葛华,2019. 青藏高原东南缘活动断裂地质灾害效应研究现状[J]. 地质力学学报,25(6):1116-1128. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.06.095 [99] 陈宁生,丁海涛,邓明枫,2019. 2014-2016年藏东南米堆冰川冰湖观测数据[R]. 兰州:国家冰川冻土沙漠科学数据中心. [100] 程先锋,祝传兵,齐武福,等,2015. 云南省禄劝县普福滑坡形成条件、发展趋势与防治对策[J]. 矿产与地质,29(3):395-401. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2015.03.021 [101] 崔鹏,马东涛,陈宁生,等,2003. 冰湖溃决泥石流的形成、演化与减灾对策[J]. 第四纪研究,23(6):621-628. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2003.06.005 [102] 戴岚欣,许强,范宣梅,等,2017. 2017年8月8日四川九寨沟地震诱发地质灾害空间分布规律及易发性评价初步研究[J]. 工程地质学报,25(4):1151-1164. [103] 代欣然,赵建军,赖琪毅,等,2022. 青藏高原察达高速远程滑坡运动过程与形成机理[J]. 地球科学,47(6):1932-1944. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.6.dqkx202206003 [104] 杜榕桓,章书成,1981. 西藏高原东南部冰川泥石流的特征[J]. 冰川冻土(3):10-16. [105] 葛大庆,戴可人,郭兆成,等,2019. 重大地质灾害隐患早期识别中综合遥感应用的思考与建议[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),44(7):949-956. [106] 郭长宝,杜宇本,张永双,等,2015. 川西鲜水河断裂带地质灾害发育特征与典型滑坡形成机理[J]. 地质通报,34(1):121-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.01.010 [107] 郭长宝,杜宇本,佟元清,等,2016. 青藏高原东缘理塘乱石包高速远程滑坡发育特征与形成机理[J]. 地质通报,35(8):1332-1345. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.08.014 [108] 韩明明,陈立春,李彦宝,等,2022. 班公湖-怒江缝合带西界边坝-洛隆断裂全新世活动的地质地貌证据[J]. 地球科学,47(3):757-765. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.3.dqkx202203001 [109] 郝建盛,黄法融,冯挺,等,2021. 亚洲高山区雪崩灾害时空分布特点及其诱发因素分析[J]. 山地学报,39(2):304-312. [110] 黄润秋,李为乐,2008. “5.12”汶川大地震触发地质灾害的发育分布规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,27(12):2585-2592. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.12.028 [111] 李滨,殷跃平,谭成轩,等,2022. 喜马拉雅东构造结工程选址面临的地质安全挑战[J]. 地质力学学报,28(6):907-918. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222819 [112] 李海兵,潘家伟,孙知明,等,2021. 大陆构造变形与地震活动:以青藏高原为例[J]. 地质学报,95(1):194-213. [113] 李鸿儒,白玲,詹慧丽,2021. 嘉黎断裂带活动性研究进展[J]. 地球与行星物理论评,52(2):182-193. [114] 李廷栋,潘桂棠,肖序常,等,2013. 青藏高原隆升的地质记录及机制[M]. 广州:广东科技出版社. [115] 李尧,崔一飞,李振洪,等,2022. 川藏交通廊道林波段冰川泥石流发育动态演化分析及监测预警方案[J]. 地球科学,47(6):1969-1984. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.6.dqkx202206006 [116] 李元灵,刘建康,张佳佳,等,2021. 藏东察达高位崩塌发育特征及潜在危险[J]. 现代地质,35(1):74-82. [117] 李征征,杨文超,张鹏,等,2023. 藏东南某大型水电站工程区地应力状态及反演分析[J]. 地质力学学报,29(3):442-452. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20232912 [118] 林达明,包卫星,任玉环,等,2020. 中亚高寒山区公路地质灾害立体监测与综合防控技术[M]. 北京:科学出版社. [119] 刘建康,程尊兰,郭芬芬,等,2011. 藏东南典型冰湖溃决危险性分析[J]. 灾害学,26(2):45-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2011.02.009 [120] 刘建康,张佳佳,高波,等,2019. 我国西藏地区冰湖溃决灾害综述[J]. 冰川冻土,41(6):1335-1347. [121] 鲁安新,邓晓峰,赵尚学,等,2006. 2005年西藏波密古乡沟泥石流暴发成因分析[J]. 冰川冻土,28(6):956-960. [122] 鲁晓,祁生文,郑博文,等,2023. 川藏交通廊道崩滑灾害分布及其危险性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,31(3):718-735. [123] 马超,2013. 川滇块体内主干断裂活动性及微地貌研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学. [124] 彭建兵,崔鹏,庄建琦,2020. 川藏铁路对工程地质提出的挑战[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,39(12):2377-2389. [125] 彭建兵,徐能雄,张永双,等,2022. 论地质安全研究的框架体系[J]. 工程地质学报,30(6):1798-1810. [126] 齐文文,张百平,庞宇,等,2013. 基于TRMM数据的青藏高原降水的空间和季节分布特征[J]. 地理科学,33(8):999-1005. [127] 冉有华,李新,2018. 中国冻土分布图(2000)[R]. 北京:国家青藏高原科学数据中心. [128] 宋章,张广泽,蒋良文,等,2016. 川藏铁路主要地质灾害特征及地质选线探析[J]. 铁道标准设计,60(1):14-19. [129] 孙东,杨涛,曹楠,等,2023. 泸定MS6. 8地震同震地质灾害特点及防控建议[J]. 地学前缘,30(3):476-493. [130] 孙浩越,何宏林,魏占玉,等,2015. 大凉山断裂带北段东支:竹马断裂晚第四纪活动性[J]. 地震地质,37(2):440-454. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.02.008 [131] 唐方头,宋键,曹忠权,等,2010. 最新GPS数据揭示的东构造结周边主要断裂带的运动特征[J]. 地球物理学报,53(9):2119-2128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.09.012 [132] 田旭文,2023. 微生物改良膨胀土的非线性蠕变特性及长期强度研究[D]. 长沙:中南林业科技大学. [133] 汪发武,陈也,刘伟超,等,2022. 藏东南高位远程滑坡动力学特征及研究难点[J]. 工程地质学报,30(6):1831-1841. [134] 王世金,任贾文,2012. 国内外雪崩灾害研究综述[J]. 地理科学进展,31(11):1529-1536. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2012.11.014 [135] 王晓楠,唐方头,邵翠茹,2018. 南迦巴瓦构造结周边地区主要断裂现今运动特征[J]. 震灾防御技术,13(2):267-275. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20180202 [136] 王盈,金家梁,袁仁茂,2019. 藏东南地区地质灾害空间分布及影响因素分析[J]. 地震研究,42(3):428-437. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2019.03.017 [137] 吴俊杰,2022. 锦屏山-小金河断裂带晚第四纪活动性研究[D]. 桂林:桂林理工大学. [138] 辛鹏,王涛,刘甲美,等,2022. 西藏易贡滑坡源区坡体赋存的地质结构及其滑动模式[J]. 地质力学学报,28(6):1012-1023. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2022072 [139] 许强,董秀军,李为乐,2019. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),44(7):957-966. [140] 徐锡伟,闻学泽,于贵华,等,2005. 川西理塘断裂带平均滑动速率、地震破裂分段与复发特征[J]. 中国科学 D辑 地球科学,35(6):540-551. [141] 许志琴,李海兵,杨经绥,2006. 造山的高原:青藏高原巨型造山拼贴体和造山类型[J]. 地学前缘,13(4):1-17. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.04.002 [142] 许志琴,杨经绥,李海兵,等,2007. 造山的高原:青藏高原的地体拼合、碰撞造山及隆升机制[M]. 北京:地质出版社. [143] 徐正宣,张利国,蒋良文,等,2021. 川藏铁路雅安至林芝段工程地质环境及主要工程地质问题[J]. 工程科学与技术,53(3):29-42. [144] 杨志华,郭长宝,吴瑞安,等,2021. 青藏高原巴塘断裂带地震滑坡危险性预测研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,48(5):91-101. [145] 杨宗佶,董悟凡,柳金峰,等,2021. 川西藏东地区冰湖主要成因类型与分布规律[J]. 地质通报,40(12):2071-2079. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2021.12.010 [146] 姚鑫,邓建辉,刘星洪,等,2020. 青藏高原泛三江并流区活动性滑坡InSAR初步识别与发育规律分析[J]. 工程科学与技术,52(5):16-37. [147] 殷志强,徐永强,陈红旗,等,2016. 2014年云南鲁甸地震触发地质灾害发育分布规律及与景谷、盈江地震对比研究[J]. 地质学报,90(6):1086-1097. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.06.003 [148] 余国安,鲁建莹,李志威,等,2022. 气候变化影响下藏东南帕隆藏布流域高山区泥石流的地貌效应[J]. 地理学报,77(3):619-634. doi: 10.11821/dlxb202203009 [149] 余国安,岳蓬胜,张晨笛,等,2024. 藏东南地区的河流水文研究:进展与挑战[J]. 科学通报,69(3):394-413. [150] 袁浩,郭长宝,吴瑞安,等,2023. 西藏易贡高位远程滑坡研究进展与展望[J]. 地质通报,42(10):1757-1773. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2023.10.012 [151] 张培震,王伟涛,甘卫军,等,2022. 青藏高原的现今构造变形与地球动力过程[J]. 地质学报,96(10):3297-3313. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.10.003 [152] 张仪辉,刘昌明,梁康,等,2022. 雅鲁藏布江流域降水时空变化特征[J]. 地理学报,77(3):603-618. [153] 张永双,郭长宝,姚鑫,等,2016. 青藏高原东缘活动断裂地质灾害效应研究[J]. 地球学报,37(3):277-286. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2016.03.03 [154] 张永双,吴瑞安,郭长宝,等,2022. 高原山区铁路工程建设地质安全评价:思路与方法[J]. 地质学报,96(5):1736-1751. [155] 赵远方,公王斌,江万,等,2021. 藏南嘉黎断裂古乡—通麦段多期活动特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质,35(1):220-233. [156] 钟宁,郭长宝,黄小龙,等,2021. 嘉黎-察隅断裂带中南段晚第四纪活动性及其古地震记录[J]. 地质学报,95(12):3642-3659. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.12.005 [157] 钟宁,杨镇,张献兵,等,2022. 怒江断裂带邦达断裂中段全新世活动证据及其古地震记录[J]. 地质论评,68(6):2021-2032. [158] 周荣军,何玉林,杨涛,等,2001. 鲜水河-安宁河断裂带磨西-冕宁段的滑动速率与强震位错[J]. 中国地震,17(3):253-262. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2001.03.003 [159] 周振凯,姚鑫,刘红岩,等,2020. 冰川密林陡谷区活动性滑坡InSAR精细识别:以澜沧江梅里雪山段为例[J]. 工程科学与技术,52(6):61-74. -




 下载:
下载: