REGIONAL CRUSTAL STABILITY EVALUATION IN BEIJING-ZHANGJIAKOU AREA
-
摘要: 在野外调查和广泛收集资料的基础上,分析了控制和影响京张地区区域地壳稳定性的主要因素及内外动力地质的耦合作用。选取活动断裂、地震活动性和深部地球物理等因素,同时选取工程岩组、地形地貌与地表地质灾害等11个因素作为评价因子,并对评价因子进行了分类赋值。采用多因素加权叠加分析方法,建立了区域地壳稳定性评价模型,基于GIS平台对京张地区的区域地壳稳定性进行了定量化评价,将研究区划分为稳定区、次稳定区、次不稳定区和不稳定区4个等级。依据区域地壳稳定性评价结果,为京张高速铁路、云顶滑雪场、石京龙滑雪场的建设和运营提出相关建议,为京张地区国土规划提供了基础依据。Abstract: On the basis of field investigation and extensive collection of information, the main factors of controlling and influencing regional crustal stability and the coupling action of internal and external dynamic geology are analyzed. Active fracture, seismicity and deep geophysics are selected as the main influencing factors of regional stability. At the same time, 11 factors, including engineering rock group, topography and surface geological hazards, are selected as evaluation factors and assigned according to category. The regional crustal stability evaluation model is established by multi-factors weighted superposition analysis method. Based on the GIS platform, the regional crust stability in Beijing-Zhangjiakou area is quantitatively evaluated, in which the research region are divided into 4 grades, including stable region, substable region, subunstable region and unstable region. According to the evaluation results of regional crustal stability, relevant suggestions are put forward for the construction and operation of the Beijing-Zhangjiakou high-railway, Yun Ding Shan Ski Slope and Shi Jing Long Ski Slope, which provides the basis for territorial planning of Beijing-Zhangjiakou area.
-
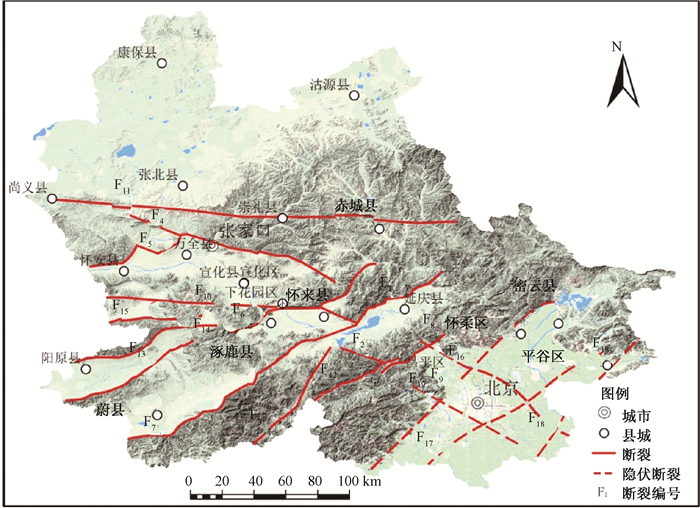
图 1 京张地区区域构造略图
F1—延矾盆地北缘断裂;F2—施庄断裂;F3—孙庄子-乌龙沟断裂;F4—张家口断裂;F5—怀安-万全盆地北缘断裂;F6—怀涿盆地北缘断裂;F7—蔚县盆地南缘断裂;F8—南口山前断裂;F9—黄庄-高丽营断裂;F10—宣化盆地南缘断裂;F11—崇礼-尚义断裂;F12—沿河城-紫荆关断裂;F13—六棱山南麓断裂;F14—阳原盆地北缘断裂;F15—六棱山北麓断裂;F16—南口-孙河断裂;F17—通县-南苑断裂;F18—夏垫-马坊断裂;F19—门头沟-大兴断裂
Figure 1. Regional tectonic sketch in Beijing-Zhangjiakou area
表 1 稳定性评价因素分类赋值标准及权重表
Table 1. Classification valuation criteria and weight of stability evaluation factors
稳定性分级 极高 高 中 低 极低 权值 代码 活动断裂(垂距/m) >4000 2000~4000 1000~2000 500~1000 <500 0.15 fault 地震动峰值加速度/(g/m·s-2) <0.05 0.05~0.10 0.10~0.15 0.15~0.20 0.20~0.30 0.13 dizhen 工程岩组 坚硬块状侵入岩、
深变质岩岩组坚硬火山碎屑岩、
坚硬碳酸盐岩岩组软硬相间碎屑岩、
软硬相间碳酸盐岩、
软硬相间变质岩组软弱层状碎屑
岩岩组松散冲洪
积物岩组0.11 yanzu 布格重力/10-5m·s-2 10~-10 -10~-30 -30~-60 -60~-100 -100~-175 0.10 zhongli 地形变/(mm/a) -2~2 -2~-4,2~4 -4~-7,4~7 -7~-10,7~10 -10~-25,10~12 0.08 xingbian 水系(垂距/m) >4000 2000~4000 1000~2000 500~1000 <500 0.06 shuixi 斜坡坡度/° 0~5 5~10 10~15 15~20 20~32.43 0.07 eleve-s 斜坡高差/m 0~200 200~400 400~800 800~1600 1600~3000 0.05 eleve-h 崩滑流灾点密度/(处/km2) <0.03 0.03~0.09 0.09~0.18 0.18~0.31 0.31~0.7 0.08 bhlt 采空塌陷点密度/(处/km2) <0.02 0.02~0.07 0.07~0.16 0.16~0.26 0.26~0.38 0.04 caikong 地裂缝点密度/(处/km2) <0.04 0.04~0.19 0.19~0.42 0.42~0.76 0.76~1.23 0.05 dlf 赋值 1 2 4 7 10 表 2 京张地区区域地壳稳定性定量评价分区表
Table 2. Regional crustal stability quantitative evaluation zoning description in Beijing-Zhangjiakou area
稳定程度 面积/km2 占全区面积比/% 稳定区 9482 18.02 基本稳定区 24369 46.32 次不稳定区 14596.5 27.75 不稳定区 4161 7.91 合计 52608.5 100.00 -
[1] 胡海涛.区域地壳稳定性评价的"安全岛"理论及方法[J].地质力学学报, 2001, 7(2):97~103. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20010215&flag=1HU Haitao. The theory and method of evaluation of regional crustal stability based on concept of "Safe Island"[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2001, 7(2):97~103. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20010215&flag=1 [2] 胡海涛. "安全岛"-相对稳定地(岩)块在广东核电站选址中的初步应用[J].工程勘察, 1983, (4):25~29. http://www.docin.com/p-301350335.htmlHU Haitao. Preliminary application of a relatively stable (rock) block in site selection of Guangdongnuclear power station[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 1983, (4):25~29. (in Chinese) http://www.docin.com/p-301350335.html [3] 杜东菊.中国区域稳定工程地质学产生与发展[J].工程地质学报, 1994, 2(3):21~26. http://www.bookask.com/book/107451.htmlDU Dongju. Establishment and development of regional stability engineering geology in Chinese[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 1994, 2(3):21~26. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.bookask.com/book/107451.html [4] 谷德振.岩体工程地质力学基础[M].北京:科学出版社, 1979.GU Dezhen. Fundamentals of geology and mechanics in rock engineering[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1979. (in Chinese) [5] 陈庆宣, 戴广秀, 杨超群, 等.深圳市地壳稳定性评价研究[J].中国地质科学院院报, 1990, 11(1):134. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB199001036.htmCHEN Qingxuan, DAI Guangxiu, YANG Chaoqun, et al. Assessment of the crustal stability of the Shenzhen city, Guangdong province, China[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Geological Science, 1990, 11(1):134. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB199001036.htm [6] 殷跃平.区域地壳稳定性的模糊综合评判——以广东核电站选址为例[J].工程勘察, 1985, (5):31~34. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/magadetail/GCKC198505.htmYIN Yueping. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of regional crustal stability-taking the site of Guangdong nuclear power station as an example[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 1985, (5):31~34. (in Chinese) http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/magadetail/GCKC198505.htm [7] 殷跃平, 胡海涛, 康宏达.区域地壳稳定性评价专家系统研究[J].地质论评, 1996, 42(2):174~186.YIN Yueping, HU Haitao, KANG Hongda. An expert system of regional crustal stability evaluation of the siting of key engineering works[J]. Geological Review, 1996, 42(2):174~186. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 刘传正, 胡海涛.工程选址的"安全岛"多级逼近与优选理论[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 1993, 4(1):28~37, 62. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82501-2007213412.htmLIU Chuanzheng, HU Haitao. The "Safety Island" theory by multi-scale approaching and optimum seeking in engineering site selection[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1993, 4(1):28~37, 62. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82501-2007213412.htm [9] 杨建军, 谢振乾, 郑宁平.模糊聚类分析在西安市区域地壳稳定性评价中的应用[J].地质力学学报, 2004, 10(1):57~64. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20040109&flag=1YANG Jianjun, XIE Zhenqian, ZHENG Ningping. Application of the fuzzy clustering analysis in the evaluation of regional crustal stability in Xi'an city[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2004, 10(1):57~64. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20040109&flag=1 [10] 杨勤业, 马欣, 李志忠, 等.黄河下游地区地壳稳定性评价[J].科学通报, 2006, 51(S1):140~147. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.z2.019YANG Qinye, MA Xin, LI Zhizhong, et al. Evaluation of crustal stability in the lower Yellow River region[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(B11):168~177. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.z2.019 [11] 相建华. GIS在中国区域地壳稳定性评价中的应用[J].山西建筑, 2006, 32(4):116~117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2006.04.076XIANG Jianhua. The application of GIS in regional crustal stability assessment in China[J]. Shanxi Architecture, 2006, 32(4):116~117. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2006.04.076 [12] 谭成轩, 丰成君, 张鹏, 等.北京地区主要活动断裂研究与地壳稳定性评价[M].北京:地质出版社, 2014.TAN Chengxuan, FENG Chengjun, ZHANG Peng, et al. Major active fracture research and regional crustal stability assessment in Beijing municipality[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2014. (in Chinese) [13] 杜建军, 马寅生, 谭成轩, 等.京津地区区域地壳稳定性评价[J].地球学报, 2008, 29(4):502~509. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/e3c81dc349649b6648d74765.htmlDU Jianjun, MA Yinsheng, Tan Chengxuan, et al. The evaluation of regional crustal stability in Beijing and Tianjin area[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2008, 29(4):502~509. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/e3c81dc349649b6648d74765.html [14] 谢富仁, 张红艳, 崔效锋, 等.延怀盆地活动断裂运动与现代构造应力场[J].地震地质, 2007, 29(4):693~705. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdz200704001XIE Furen, ZHANG Hongyan, CUI Xiaofeng, et al. Active fault movement and recent tectonic stress field in Yanhuai basin[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2007, 29(4):693~705. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdz200704001 [15] 徐锡伟, 邓起东.晋北张性区盆岭构造及其形成的力学机制[J].中国地震, 1988, 4(2):19~27. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD198802002.htmXU Xiwei, DENG Qidong. The basin-range structure in the tensile area at the Northern part of Shanxi province and its mechanism of formation[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 1988, 4(2):19~27. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD198802002.htm [16] 王磊, 张春山, 杨为民, 等.基于GIS的甘肃省甘谷县地质灾害危险性评价[J].地质力学学报, 2011, 17(4):388~401. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110409&flag=1WANG Lei, ZHANG Chunshan, YANG Weimin, et al. Risk assessment of geohazards by using GIS in Gangu county, Gangu province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2011, 17(4):388~401. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110409&flag=1 [17] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB 18306~2015中国地震动参数区划图[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB 18306~2015 Seismic ground motion parameters zonation map of China[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: