DYNAMIC MECHANISM OF RIFT SYSTEMS IN WEST AND CENTRAL AFRICA
-
摘要: 中西非裂谷系是沿中非剪切带及邻区发育的一系列中新生代裂谷盆地,其成因机理一直存在争议。中西非裂谷系的构造演化主要经历了三个演化阶段,其中在早白垩世进入强烈断陷期,是盆地形成的重要阶段。以早白垩世中西非裂谷系的地质背景为基础,运用弹性力学有限元数值模拟方法,通过应力场和应变场的分析,为中西非裂谷系形成的力学机制提供依据。模拟结果表明,早白垩世非洲大陆内部走滑和伸展作用并存,中非剪切带不是所谓的"转换断层",而是与中西非裂谷系同时形成和发育的构造。中西非裂谷系是在中新生代泛大陆裂解时期,非洲板块绕西北非地块逆时针旋转,非洲内部不同地块在统一构造应力场作用下,由于伸展和走滑的差异作用形成和发育的。Abstract: The rift systems in West and Central Africa that developed along the shear zone in Central Africa is a series of Mesozoic-Cenozoic rift basins, and their formation mechanism is still a matter of debate. The evolution of those rift systems has three stages, and Early Cretaceous is the most important one for the basin formation, in which the rifts and major fault zones were strongly active. Based on the geological setting of rift systems in West and Central Africa in Early Cretaceous, using linear elastic theory with two dimensional finite element numerical simulation, through the analysis of the stress field and the strain field, reliable evidence to the mechanical mechanism of rift systems are produced. The simulation results suggest that strike-slipping and extensional process coexist in African continent in Early Cetaceous, and the shear zone in Central Africa is not a "transform fault" but a structure that formed and developed simultaneously with the rift systems in West and Central Africa. In Mesozoic-Cenozoic Pangea disintegration period, due to the different motion rates of the three blocks along parallel slip vectors under the unified tectonic stress field and the counterclockwise rotation around WB by African plate, rift systems were formed and developed.
-
图 1 非洲北部裂谷分布图[2]
WB—西北非地块;ANB—东北非地块;AB—中南非地块;CASZ—中非剪切带
Figure 1. Distribution map of the rifts in North Africa
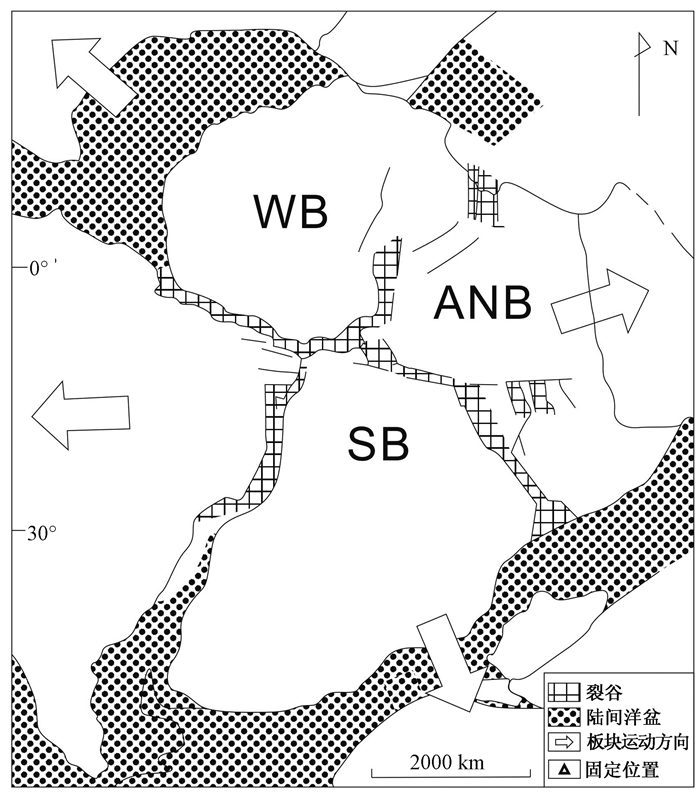
图 2 早白垩世泛大陆裂解时期非洲裂谷系分布图[15]
WB—西北非地块;ANB—东北非地块;SB—中南非地块
Figure 2. Distribution of the rife systems in Africa in Early Cetaceous Pangea distintegration period
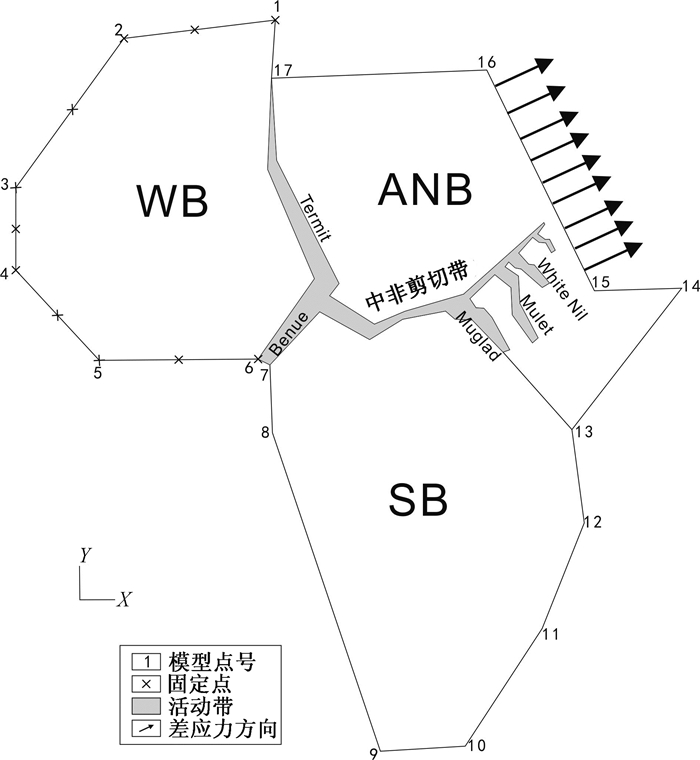
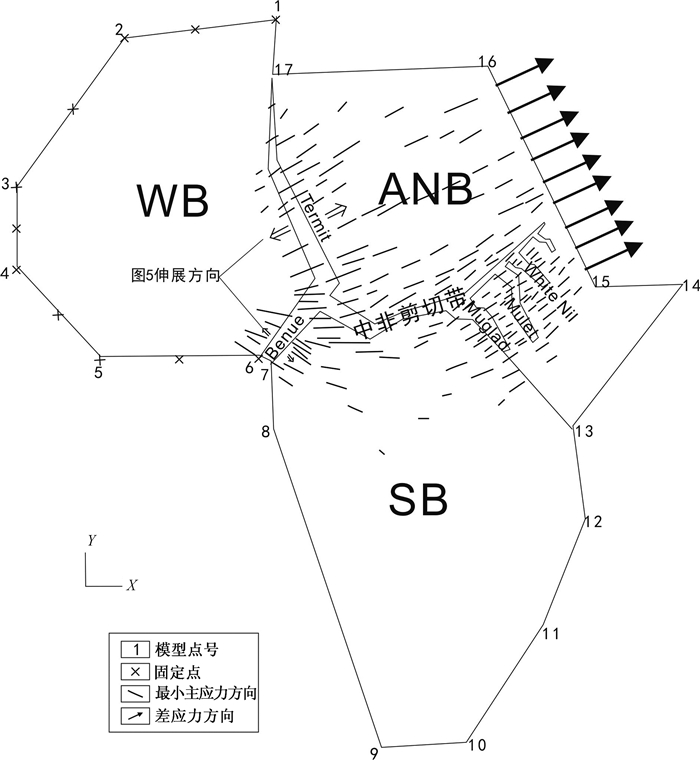
图 5 非洲裂谷系白垩纪伸展量或滑移量图[14]
WB—西北非地块;ANB—东北非地块;SB—中南非地块
Figure 5. Extension and slip map of African rift systems in Cretaceous
表 1 各构造分区的岩石力学参数表
Table 1. Rock mechanics parameters in different structural area
构造分区 岩性 杨氏模量/
×109 Pa泊松比 西北非 花岗岩 100 0.25 中南非 花岗岩 100 0.25 东北非 花岗岩 100 0.25 活动带(剪切带及裂谷系) 断层岩 15 0.14 注:岩石力学参数根据Hou et al.[45]的数据取平均值得出 -
[1] Genik G J. Regional framework, structural and petroleum aspects of rift basins in Niger, Chad and the Central African Republic (C.A.R.)[J]. Tectonophysics, 1992, 213(1/2):169~185. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780444899125500363 [2] Mohamed A Y, Pearson M J, Ashcroft W A, et al. Modeling petroleum generation in the Southern Muglad rift basin, Sudan[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1999, 83(12):1943~1964. doi: 10.1306/E4FD464D-1732-11D7-8645000102C1865D [3] Guiraud R, Mbaigane J C D, Carretier S, et al. Evidence for a 6000 km length NW-SE-striking lineament in northern Africa:the Tibesti Lineament[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2000, 157(5):897~900. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Stephane_Dominguez/publication/232562536_Evidence_for_a_6000_km_length_NW-SE-striking_lineament_in_northern_Africa_The_TIbesti_lineament/links/09e41508668e33cd2d000000/Evidence-for-a-6000-km-length-NW-SE-striking-lineament-in-northern-Africa-The-TIbesti-lineament.pdf [4] Guiraud R, Maurin J C. Early cretaceous rifts of Western and Central Africa:an overview[J]. Tectonophysics, 1992, 213(1/2):153~168. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0040195192902566 [5] Guiraud R, Bellion Y, Benkhelil J, et al. Post-Hercynian tectonics in Northern and Western Africa[J]. Geological Journal, 1987, 22(S2):433~466. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/229920933_PostHercynian_tectonics_in_Northern_and_Western_Africa [6] Pindell J, Dewey J F. Permo-Triassic reconstruction of western Pangea and the evolution of the Gulf of Mexico & sol; Caribbean region[J]. Tectonics, 1982, 1(2):179~211. doi: 10.1029/TC001i002p00179/full [7] Pavoni N. Pattern of mantle convection and Pangaea break-up, as revealed by the evolution of the African plate[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1993, 150(5):953~964. http://jgs.lyellcollection.org/content/150/5/953 [8] 张庆莲, 侯贵廷, 潘校华, 等. Termit盆地构造变形的力学机制[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2013, 37(3):377~383. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_ddgzyckx201303003.aspxZHANG Qinglian, HOU Guiting, PAN Xiaohua, et al. Mechanics of Termit basin in Central Africa rift systems[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2013, 37(3):377~383. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_ddgzyckx201303003.aspx [9] 张庆莲, 侯贵廷, 潘校华, 等. Muglad盆地形成力学机制的有限元数值模拟[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 49(6):981~985. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201306006.htmZHANG Qinglian, HOU Guiting, PAN Xiaohua, et al. Mechanics of Muglad basin in Central Africa Rift systems:a Paleostress field modeling[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2013, 49(6):981~985. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201306006.htm [10] Binks R M, Fairhead J D. A plate tectonic setting for Mesozoic rifts of West and Central Africa[J]. Tectonophysics, 1992, 213(1/2):141~151. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0040195192902555 [11] Ziegler P A. Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic intra-plate compressional deformations in the Alpine foreland-a geodynamic model[J]. Tectonophysics, 1987, 137(1/4):389~420. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0040195187903301 [12] Ziegler P A. Evolution of Laurussia:a study in late Palaeozoic plate tectonics[M]. Dordrecht, The Netherlands:Kluwer Academic, 1989. [13] Ziegler P A. Plate tectonics, plate moving mechanisms and rifting[J]. Tectonophysics, 1992, 215(1/2):9~34. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/004019519290072E [14] Moulin M, Aslanian D, Unternehr P. A new starting point for the South and Equatorial Atlantic Ocean[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2010, 98(1/2):1~37. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012825209001172 [15] Schettino A, Scotese C R. Apparent polar wander paths for the major continents (200 Ma to the present day):a palaeomagnetic reference frame for global plate tectonic reconstructions[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2005, 163(2):727~759. doi: 10.1111/gji.2005.163.issue-2 [16] Jacques J M. A tectonostratigraphic synthesis of the Sub-Andean basins:inferences on the position of South American intraplate accommodation zones and their control on South Atlantic opening[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2003, 160(5):703~717. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/jgs/article-abstract/160/5/703/94272/a-tectonostratigraphic-synthesis-of-the-sub-andean [17] 刘剑平, 潘校华, 马君, 等.西部非洲地区油气地质特征及资源概述[J].石油勘探与开发, 2008, 35(3):378~384. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=skyk200803021&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQLIU Jianping, PAN Xiaohua, MA Jun, et al. Petroleum geology and resources in West Africa:an overview[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2008, 35(3):378~384. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=skyk200803021&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [18] 江文荣, 李允, 蔡东升, 等.非洲油气勘探区战略选择建议[J].石油勘探与开发, 2006, 33(3):388~392. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=skyk200603029&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQJIANG Wenrong, LI Yun, CAI Dongsheng, et al. Recommendations on strategic selection of exploration areas in Africa[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2006, 33(3):388~392. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=skyk200603029&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [19] Genik G J. Petroleum geology of cretaceous-tertiary rift basins in Niger, chad, and central African Republic[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1993, 77(8):1405~1434. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/236357679_petroleum_geology_of_rift_basins_in_niger_chad_and_central_african_republic [20] Morley C K. Patterns of displacement along large normal faults:implications for basin evolution and fault propagation, based on examples from East Africa[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1999, 83(4):613~634. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/249897220_Patterns_of_Displacement_Along_Large_Normal_Faults_Implications_for_Basin_Evolution_and_Fault_Propagation_Based_on_Examples_from_East_Africa [21] 童晓光, 窦立荣, 田作基, 等.苏丹穆格莱特盆地的地质模式和成藏模式[J].石油学报, 2004, 25(1):19~24. doi: 10.7623/syxb200401004TONG Xiaoguang, DOU Lirong, TIAN Zuoji, et al. Geological mode and hydrocarbon accumulation mode in Muglad passive rift basin of Sudan[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2004, 25(1):19~24. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7623/syxb200401004 [22] Eagles G, König M. A model of plate kinematics in Gondwana breakup[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2008, 173(2):703~717. doi: 10.1111/gji.2008.173.issue-2 [23] Bumby A J, Guiraud R. The geodynamic setting of the Phanerozoic basins of Africa[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2005, 43(1/3):1~12. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1464343X05001111 [24] Janssen M E, Stephenson R A, Cloetingh S. Temporal and spatial correlations between changes in plate motions and the evolution of rifted basins in Africa[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1995, 107(11):1317~1332. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1995)107<1317:TASCBC>2.3.CO;2 [25] 窦立荣.苏丹迈努特盆地油气成藏机理和成藏模式[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2005, 24(1):50~57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2005.01.007DOU Lirong. Formation Mechanism and model of oil and gas accumulations in the Melut basin, Sudan[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2005, 24(1):50~57. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2005.01.007 [26] Turner J P, Rosendahl B R, Wilson P G. Structure and evolution of an obliquely sheared continental margin:Rio Muni, West Africa[J]. Tectonophysics, 2003, 374(1/2):41~55. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195103003251 [27] Dickson W G, Fryklund R E, Odegard M E, et al. Constraints for plate reconstruction using gravity data-implications for source and reservoir distribution in Brazilian and West African margin basins[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2003, 20(3/4):309~322. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817203000394 [28] Contrucci I, Matias L, Moulin M, et al. Deep structure of the West African continental margin (Congo, Zaïre, Angola), between 5 S and 8 S, from reflection/refraction seismics and gravity data[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2004, 158(2):529~553. doi: 10.1111/gji.2004.158.issue-2 [29] Aslanian D, Moulin M, Olivet J L, et al. Brazilian and African passive margins of the central Segment of the South Atlantic Ocean:kinematic constraints[J]. Tectonophysics, 2009, 468(1/4):98~112. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195108006252 [30] 窦立荣, 肖坤叶, 胡勇, 等.乍得Bongor盆地石油地质特征及成藏模式[J].石油学报, 2011, 32(3):379~386. doi: 10.7623/syxb201103002DOU Lirong, XIAO Kunye, HU Yong, et al. Petroleum geology and a model of hydrocarbon accumulations in the Bongor Basin, the Republic of Chad[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(3):379~386. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7623/syxb201103002 [31] Fairhead J D, Green C M. Controls on rifting in Africa and the regional tectonic model for the Nigeria and East Niger rift basins[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences (and the Middle East), 1989, 8(2/4):231~249. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0899536289800272 [32] Macdonald D, Gomez-Perez L, Franzese J, et al. Mesozoic break-up of SW Gondwana:implications for regional hydrocarbon potential of the southern south Atlantic[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2003, 20(3/4):287~308. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S026481720300045X [33] Karner G D, Driscoll N W. Tectonic and stratigraphic development of the West African and eastern Brazilian Margins:insights from quantitative basin modelling[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1999, 153(1):11~40. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1999.153.01.02 [34] Eagles G. New angles on South Atlantic opening[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2007, 168(1):353~361, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03206.x. [35] Fairhead J D. Mesozoic plate tectonic reconstructions of the central south Atlantic Ocean:the role of the west and central African rift system[J]. Tectonophysics, 1988, 155(1/4):181~191. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/004019518890265X [36] Fairhead J D, Binks R M. Differential opening of the central and south Atlantic oceans and the opening of the west African rift system[J]. Tectonophysics, 1991, 187(1/3):191~203. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/004019519190419S [37] Fairhead J D. The structure of the lithosphere beneath the Eastern Rift, East Africa, deduced from gravity studies[J]. Tectonophysics, 1976, 30(3/4):269~298. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0040195176901906 [38] Fairhead J D. Geophysical controls on sedimentation within the African Rift Systems[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1986, 25(1):19~27. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1986.025.01.03 [39] Fairhead J D, Henderson N B. The seismicity of southern Africa and incipient rifting[J]. Tectonophysics, 1977, 41(4):T19~T26. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(77)90133-0 [40] Fairhead J D, Okereke C S. Depths to major density contrats beneath the West African Rift System in Nigeria and Cameroon based on the spectral analysis of gravity data[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences (and the Middle East), 1988, 7(5/6):769~777. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0899536288900188 [41] Wilson M, Guiraud R. Magmatism and rifting in Western and Central Africa, from Late Jurassic to Recent times[J]. Tectonophysics, 1992, 213(1/2):203~225. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780444899125500387 [42] Lambiase J J. The framework of African rifting during the Phanerozoic[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences (and the Middle East), 1989, 8(2/4):183~190. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0899536289800235 [43] Cai Y E, Wang C Y. Fast finite-element calculation of gravity anomaly in complex geological regions[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2005, 162(3):696~708. doi: 10.1111/gji.2005.162.issue-3 [44] He J K, Xia W H, Lu S J, et al. Three-dimensional finite element modeling of stress evolution around the Xiaojiang fault system in the southeastern Tibetan plateau during the past -500 years[J]. Tectonophysics, 2011, 507(1/4):70~85. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195111001983 [45] Hou G T, Kusky T M, Wang C C, et al. Mechanics of the giant radiating Mackenzie dyke swarm:a paleostress field modeling[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2010, 115(B2):B02402, doi: 10.1029/2007JB005475. [46] Hou G T, Wang C C, Li J H, et al. Late Paleoproterozoic extension and a paleostress field reconstruction of the North China Craton[J]. Tectonophysics, 2006, 422(1/4):89~98. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195106002952 -






 下载:
下载: