|
| Citation: | LI Xiaoyue, XU Yongfu, 2018. THE CALCULATION METHOD FOR OSMOTIC SUCTION OF SALINE SOLUTION. Journal of Geomechanics, 24 (5): 723-729. DOI: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2018.24.05.074 |
陕西省宝鸡市是中国地质灾害较为严重的地区之一,每年汛期都有不同类型的地质灾害发生,对社会经济发展造成了严重危害。据不完全统计,截止2012年全市地质灾害已造成230多人死亡,直接经济损失超过2×108元。特别是近10年来,地质灾害的发生呈逐年增加的趋势[1~3],制约了宝鸡城市建设和大规模经济建设的快速发展。因此,开展宝鸡地区地质灾害系统调查和综合研究,探明区域地质灾害主要类型和发育特征,对于减灾防灾和促进地方经济发展具有重要意义。本文在持续7年的宝鸡市地质灾害详细调查、编录、数据库整理和综合研究[4~16]的基础上,总结分析宝鸡市地质灾害主要类型、分布规律和发育特征,重点剖析滑坡、崩塌、泥石流和不稳定斜坡的发育特征,为宝鸡市地质灾害危险性区划、监测预警和防治区划提供基础资料和信息。
宝鸡市地处黄土高原南缘、渭河流域河谷盆地、秦岭及陇山山地等多地貌类型复合交汇部位,地质灾害类型及发育特征兼具黄土地区和基岩山区两种鲜明特色,例如滑坡,既发育有典型的黄土滑坡特征,也发育典型基岩滑坡特征,更有两者组合特征。
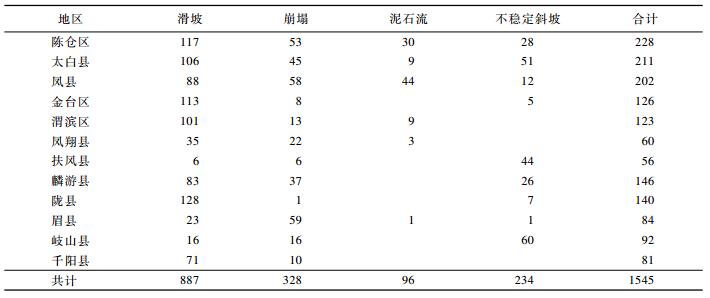
宝鸡市最具代表性的地质灾害类型包括滑坡、崩塌、泥石流及不稳定斜坡等4类,依据宝鸡市12区县地质灾害调查、编录和数据库资料统计分析,截止2012年,共计发生地质灾害点1545处(见表 1)。其中,滑坡887处,在各类灾害中数量最多,占灾点总数的57.41%;其次为崩塌328处,占灾点总数的21.23%;再次为不稳定斜坡234处,占灾点总数的15.15%;泥石流数量最少,为96处,占灾点总数的6.21%。地质灾害发育最多的3个区县分别是陈仓区、太白县和凤县;滑坡发育最多的3个区县分别是陇县、陈仓区和金台区;崩塌发育最多的3个区县分别是眉县、凤县和陈仓区;泥石流发育最多的3个区县分别是凤县、陈仓区和渭滨区;不稳定斜坡发育最多的3个区县分别是岐山县、太白县和扶风县(见表 1)。

|
根据地质灾害的形成条件及原始斜坡岩性组合关系,可将4种基本灾害类型进一步细分为12个亚类。其中,滑坡灾害包括6个亚类,分别为黄土滑坡、黄土-硬土软岩滑坡、黄土-基岩滑坡、残坡积层滑坡、阶地滑坡和基岩滑坡;崩塌包括2个亚类,分别是黄土崩塌和基岩崩塌;泥石流包括3个亚类,分别为沟谷型泥石流、坡面型泥石流和采矿弃渣潜在泥石流;不稳定斜坡则主要为人类工程切坡形成的危岩体1类。
宝鸡地区地质灾害主要在河流两岸、活动构造密集部位、地貌分区边界或转换地带以及人类工程扰动强烈地区相对集中分布,尤其在渭河两岸人类密集居住区和工程活动频繁主干道路切坡沿线分布密集(见图 1)。其中滑坡主要沿渭河谷地、东北部黄土丘陵区、南部和西部山区中人类工程活动频繁的山间盆地以及主干道路切坡沿线密集分布;崩塌和不稳定斜坡主要分布于渭河盆地周边的塬边和丘陵斜坡带、东北部典型黄土丘陵区高陡斜坡带和基岩山区交通干线道路沿线的切坡地段;泥石流灾害集中分布在西南部陇山和秦岭山区沟谷及黄土丘陵区的沟壑中。
以强降雨和强震为代表的极端异常天气和地质事件,是两种典型的区域崩塌、滑坡、泥石流灾害诱发因素。极端异常降雨是区内集中诱发区域崩塌、滑坡、泥石流灾害的最重要因素,自1949年建国以来至2010年间,有记载的降雨诱发地质灾害事件至少125次,且这种群发性并不局限于特定的地段或地质背景,无论基岩山区还是黄土地区均有体现,如地处秦岭山区的太白县和凤县,史载强降雨导致群发地质灾害事件14次,而地处黄土梁峁区的麟游县发生此类事件18次。
从地震诱发地质灾害角度分析,宝鸡市地处汾渭地震带与六盘山地震带交汇部位,具有强震活动背景,自古以来就有地震诱发区域地质灾害的记载。公元前780年岐山7级地震诱发大量滑坡,堵塞泾河、渭河以及洛河流域形成堰塞湖,导致“三川”竭流。此后区内又先后受到周边地区强烈地震的影响(如1556年华县8.25级地震,1654年天水南8.0级地震及1920年海原Ms 8.5级地震等),形成群发地质灾害。在近年来的调查中,受2008年汶川地震的影响,尽管研究区相距地震震中400~500 km,在多个区县仍然至少诱发了30余处崩滑、地裂缝及砂土液化灾害,尤其以陈仓区的灾害响应最为显著。
宝鸡市群发崩塌、滑坡、泥石流地质灾害的周期性主要表现在与强降雨复发周期的一致性,具体反映在两方面:① 从降雨量分布特征分析,各区县每年强降雨集中分布的7—9月份通常是地质灾害频发的高峰期;② 从气象水文统计规律分析,尽管宝鸡市各区县的丰水年与干旱年出现周期不尽相同,但整体以8~10 a的复发周期为主,同时也大致奠定了降雨型群发地质灾害的复发周期。以太白县为例,丰水年与干旱年经常呈现间隔性的周期出现,地质灾害也表现出与强降雨年份近似同步的“十年一大灾、五年一小灾、年年都有灾”的特征,在1981年、1990年及1998年等降雨峰值分布的年份表现明显。
宝鸡市区大型滑坡数量众多,造成人员伤亡和财产损失的主要灾害类型是降雨诱发的浅层黄土崩塌和滑坡,崩滑体岩性以Q2—Q3黄土为主,土体结构疏松,离间粘结强度较低,水敏性较强,且浅表层坡体或陡崖坡肩处通常发育大量孔洞裂隙。随着强降雨入渗作用,黄土体胶结溶陷、强度丧失及变形破坏过程较快,许多在干燥状态下不致于失稳的陡崖或坡体在降雨期间发生了崩滑。由于坡体节理裂隙较为发育,因此坡体变形失稳机制主要取决于局部的锁固段部位,往往从坡体开始变形到整体破坏历时较短,且变形过程的表观征兆不易被发现,具有明显的突发性质。典型的灾害例如:2003年8月24日,凤翔县长青镇高咀头崩塌突然暴发,造成房屋倒崩,2人被埋在废墟中,因抢救及时,未造成伤害;1982年正月初五日,麟游县丈八乡西坡突然发生滑坡,滑距约130 m,历时仅几分钟;1988年8月13日,陇县庙岭梁突然发生滑坡,滑距约40 m,历时也在数分钟内,这种突发性显著增加了地质灾害的预测预报难度。
宝鸡市许多崩塌、滑坡、泥石流灾害的形成机制和演化过程,在时空分布上并非孤立存在,而是存在相互联系和作用机制,具有典型的链生性和继承性。具体表现为3种方式:
① 崩塌-滑坡-泥石流灾害链。先成的崩滑堆积物分布在沟谷沿线的岸坡地带,积累成为潜在泥石流的物源,在暴雨期间只要具备了汇流和启动条件,就会演化成为泥石流灾害。例如:陈仓区天王镇至关儿下公路边,由于修路过度开挖坡脚,暴雨诱发小型滑塌,保通施工期间将滑塌堆积体丢弃于路边,2008年强降雨再度诱发形成坡面流,冲毁一处水渠,形成了典型的人类工程地质灾害链;贾村镇塬边泥石流沟的形成区和流通区分布一系列崩塌和滑坡,尤其在流通区的下游崩塌体经常堵塞沟谷,形成串珠状微型堰塞湖,湖体溃决后形成泥石流,在2003年和2009年就爆发了2次泥石流。
② 古老滑坡的局部复活。宝鸡市区发育许多大型古老滑坡,尽管目前整体已经趋稳,但是由于河流侵蚀、人类工程活动切坡改造,经常导致局部滑体发生活动,形成大型古老滑坡嵌套小型新生滑坡形态,此类现象在渭河北岸长约百公里的塬边斜坡带较为常见;另外其他区县也时有分布,例如凤翔县五曲湾滑坡,在老滑坡的基础上已发育新的裂缝,造成民房开裂,在滑壁北侧和滑体前缘发育多处小型崩塌和滑坡,主要对房屋等承灾体构成威胁。
③ 黄土丘陵区沟谷中的对冲式滑坡。在渭河及千河等主要河流的一级和二级冲沟中,侵蚀切割作用对岸坡的改造强烈,易发生崩滑灾害;由于这些冲沟的发育特征处于旺年期,沟谷形态相对紧闭,一侧滑坡形成后往往堆覆至对岸坡脚,同时推挤沟道向对岸改道,加剧对岸的坡脚下切侧蚀作用,进一步导致对岸坡体发生崩滑;在沟谷沿线,新老滑坡相互交错,前后叠置,形成链状分布的对冲式滑坡群。此类现象在有黄土丘陵(梁峁、沟壑)分布的麟游县、千阳县及陇县等区县均有分布。
滑坡是宝鸡市分布最广、数量最多的地质灾害类型,其发育特征各具特色。
黄土滑坡是指纯黄土斜坡或者黄土及古土壤互层斜坡发生的滑坡,滑带较浅的滑坡主要形成于马兰黄土或与下伏古土壤交界处,滑带稍深者可以切穿数层古土壤,发育在离石或午城黄土中。黄土滑坡主要分布于黄土塬边及梁峁区的斜坡地带,一般发育在厚层黄土与古土壤组成的陡坡部位。平面形态呈半圆弧躺椅型,在黄土塬内冲沟两岸黄土滑坡具有对滑型群发特征[17](见图 2);剖面上滑带呈近圆弧形,后缘受垂直节理控制,较陡直、光滑,形成初期坡度可达60°—70°,下部滑带近水平产出,有利于滑体势能向动能的快速转换,剪出口相对坡脚位置高低不定,当剪出口较高,且坡体前缘地形开阔临空时,滑动距离一般较远。
黄土滑坡是宝鸡地区最具代表性的滑坡,规模以中小型为主。黄土滑坡时代以新滑坡—老滑坡为主,且老滑坡通常为自然诱发因素所致,而新滑坡多由降雨和人类工程诱发复活所致。由于黄土斜坡对降雨有显著的敏感性,因此,每年汛期在强降雨作用下,都可能诱发小型黄土滑坡和崩塌,特别是居民房前屋后频繁发生的小型黄土滑坡,是目前群测群防监测预警的重点,也是宝鸡市减灾防灾关注的重点。
黄土-硬土软岩滑坡是指由上覆黄土与下伏红色硬土软岩组成的斜坡沿层位接触部位发生剪切滑移的滑坡,其中上覆黄土包括Q2—3黄土,下伏地层包括新近系(N1—2)红色硬土软岩和下更新统(Q1)三门组红色、灰绿色等杂色含砂质硬黏土两类地层。新近系红色硬土软岩主要包括中新统甘肃群(N1g)和上新统(N2)三趾马红土两套地层,是干旱氧化环境条件下形成的河湖相为主的红色碎屑沉积,以含三趾马动物群的化石为特征;另外,在秦岭山前还沉积一套中更新世(Q2)晚期仙游寺黏土,成因以坡洪积为主。下更新统三门组是潮湿还原环境条件下形成的湖相为主的含灰绿色沉积物的沉积。两类下伏地层存在过渡相变或交替出现的情况。黄土-硬土软岩接触型滑坡主要分布于区内黄土梁峁斜坡区及河谷岸坡地段,且为数众多,是宝鸡地区最主要的地质灾害类型之一。
随着分布地段不同,黄土-硬土软岩滑坡的结构形态也不相同。在古分水岭发育的黄土丘陵区如麟游县,薄层黄土批覆于渭河与泾河的近东西向分水岭——页岭之上,下伏红层古地形向南北两侧倾伏,倾角10°以上,上覆黄土坡体沿着红层风化壳倾向冲沟底部发生滑移破坏;由于黄土厚度一般较小,滑体规模也较小。在古渭河盆地边缘的金台区塬边和丘陵区,上覆黄土及下伏硬土软岩沉积厚度均比较大,且不整合面产状近水平,因此滑带发育形态基本继承了近水平特征,同时滑带后部呈高角度产出,滑带整体形态呈坐滑式的L型,滑体规模一般较大。典型滑坡包括渭北台塬福临堡、簸箕山及卧龙寺滑坡,金陵河焦家沟滑坡群和岳家坡滑坡,长寿沟刘家泉滑坡群(见图 3)等。其中沿渭河干流及金陵河等一级支流,从上游向下游发展,滑带呈现出由下部的三趾马红土、三门组层位不断向上部阶地相黏土层转移的特点。
黄土-基岩滑坡是指原始斜坡由上覆黄土与下伏基岩构成的岩性组合关系,在中间不整合接触带部位通常发育风化壳,成为关键的控滑层位。区内下伏基岩类型以白垩系砂砾岩—粉砂岩为主。此类斜坡主要分布于黄土(丘陵)梁峁及基岩山区黄土盆地区原始坡度在10°—20°的斜坡上,坡体前缘在沟谷切割作用下形成临空面,坡体上部的黄土古土壤渗透系数相对较大,地表水沿节理裂隙向下渗透,至相对隔水的基岩顶面或者黏粒含量较高的风化壳层位,逐渐积聚,从物理和化学方面导致该层位土体抗剪强度逐渐降低,加之不整合接触层位也是应力集中的部位,从而最终发生剪切滑移,坡体失稳形成滑坡。
需要注意的是,若黄土与下伏基岩间存在的风化壳为泥质成分,则降雨入渗风化壳后沿该层面上部向下流动,滑坡往往沿着不整合接触带发生滑动;如果风化壳为渗透性较好的砂砾石层,则降雨入渗到风化壳后继续向下入渗至较新鲜基岩中相对隔水层位,继而诱发滑坡。黄土-基岩接触型滑坡的典型案例包括陈仓区县功镇北侧的刘家山滑坡(见图 4),麟游县酒房乡闹林村西沟湾滑坡,凤翔县五曲湾滑坡、亢家湾滑坡和朱家沟滑坡,凤县凤州镇苍坪胡家山滑坡。
残坡积层滑坡是宝鸡市南部秦岭、西部陇山及东北部局部基岩山区分布最为普遍的滑坡类型,其形成机制源于山区基岩表层广泛堆积了岩体风化、剥蚀、搬运和堆积形成的残坡积松散层,被茂密的植被所覆盖,在干燥条件下相对稳定。然而,残坡积层物质组成主要含角砾、碎石等粗颗粒的粉质—黏质土体,通常厚薄不一,土体强度很低,山区进行公路切坡、建房削坡及采矿扰动等各种工程活动会造成植被破坏,使残坡积层剥露,失去支撑,在降雨、河流侵蚀及地表排水等作用下,易发生浅表层滑坡。如太白县黄柏塬乡湑水河水库东岸滑坡,坡体表层为中生代混合花岗岩的残坡积物,由于2010年8月19日强降雨诱发滑坡,滑体将坡底公路掩埋阻断,坡体上部仍残留孤石,有崩落的危险,对行人和车辆构成威胁。
残坡积层滑坡具有分布广泛、规模较小、牵引式浅表层滑动的特征。残坡积物厚度一般1~5 m,滑体厚度一般小于10 m。滑体规模主要取决于下伏基岩面形态和上覆松散堆积层厚度,若下伏基岩面为凹形,且上覆坡残积物厚度大,则相应的滑体规模也较大。
宝鸡市河流水系十分发达,河谷阶地岸坡分布较为广泛,因此阶地滑坡发育数量众多。阶地滑坡发育特征与水系的级别密切相关,主要可以分为2类:
① 在渭河及千河等大型河谷两侧的塬边斜坡地段多发育大型阶地滑坡,斜坡主要由中—晚更新世黄土及河流阶地组成。例如在渭河北岸滑坡主滑面深入至河流阶地中的黏土中或其表面,滑体后缘处滑面最大深度一般超过70 m,前缘坡脚滑面位置一般在地面5~15 m以下;滑坡后缘滑壁较陡,倾角一般45°—70°,后缘深部滑面近圆弧形,中部主滑段平缓近水平,前缘滑面呈圆弧状反坡翘起,倾角在5°—10°左右。此类典型滑坡包括眉县塬边的祁家村滑坡、魏家堡滑坡、杨家村滑坡及张家台滑坡等。
② 在基岩山区和梁峁区中小型河谷沿岸多以中小型阶地滑坡为主。以太白县为例,秦岭山地的持续隆升和河流强烈下切导致谷岸坡较为陡峭,同时下伏基岩基座较为稳定,保持了较高的坡体高度,上覆阶地层岩土物质粒度混杂,粗粒物质以卵砾石-漂石为主,粒间充填粉黏质的细粒物质,整体胶结强度低,尤其降雨入渗,粒间胶结弱化,导致阶地物质顺粉黏质层位或者基座顶面发生剪切滑移,形成小型滑坡,且多成群成带发育,危及道路及过往车辆安全。此类典型滑坡包括太白县黄柏塬乡太洋公路92 km+300 m及89 km+500 m处滑坡等。
岩质滑坡在宝鸡地区分布较广,但为数不多,主要集中在秦岭和陇山山地的工程扰动地段,在东北部北山及页岭分水岭两侧也有局部发育。岩质滑坡主控因素取决于岩体结构面组合关系,通常包括原生顺坡向的层理、片理、节理裂隙面或软弱带等,易形成滑坡的岩性较多,包括块状坚硬侵入岩类、火山岩类及深变质的片麻岩类及白垩系砂泥岩互层等。
以秦岭山区为代表的岩体经历了复杂的构造变形及变质作用,岩体原生节理丰富。由于区内地质构造密集复杂,不同规模的构造面十分发育,在公路、采矿等工程活动切割卸荷作用下,易发生滑动破坏。滑坡的形成并不需要斜坡十分陡峭,坡角35°—45°或更小时也可发生,如太白县鹦鸽镇梁家山大理岩老矿滑坡。同时,在山区公路沿线常发育中小型岩质滑坡,滑体物质一般为顺层岩体或风化较严重的碎裂岩体。
在麟游县页岭两侧冲沟中还发育白垩系砂泥岩地层滑坡,岩层呈软硬相间产出,其滑动面主要沿相对软弱的泥岩层位滑动,剪出口一般位于冲沟的下部或底部,前缘常形成剪裂带,个别可见滑动面擦痕或者因滑动而形成的小揉皱。滑体厚度一般变化较大,从数米至数十米不等。
宝鸡市崩塌灾害在各区县均有分布,绝大部分是由于人类工程切坡扰动形成的陡坡或陡崖,在强降雨或地震作用下演化成崩塌,一般体积较小,但更具突发性特征。按照原始斜坡组成岩性可以分为黄土崩塌和基岩崩塌2种。
黄土崩塌主要分布于黄土区的工程切坡地段,数量多于基岩崩塌,且危害更为广泛,以倾倒式的中小型崩塌为主。崩塌前的坡型多为陡崖或陡坎,通常因村民挖窑、建房以及修建公路等切坡形成,各地坡体高度不一,一般在5~30 m,坡度为50°—80°,甚至近直立,陡崖浅部通常发育宽窄不一的卸荷裂隙,在强降雨期间,易发生底部锁骨段变形破坏,形成崩塌,如陈仓区赤沙镇姚花沟一组崩塌、千河镇田胥崖崩塌,凤翔县孙家南头崩塌、罗钵寺崩塌和铁炉村崩塌,扶风县后河村崩塌、绛帐镇古水村一组崩塌等。
此外,5.12汶川地震波及宝鸡地区,在部分区县诱发形成崩塌灾害,典型实例包括陈仓区天王镇光明村一组崩塌,麟游县天堂镇西坡村崩塌,凤翔县水沟村三组崩塌等。
基岩崩塌主要分布于秦岭、陇山及北山等基岩山区的工程切坡地段,尤其以秦岭山区的公路沿线边坡最为典型。人工修路切坡形成的高约数十米的陡崖,岩体在构造节理、原生沉积结构面切割作用下形成块体,边坡开挖后,斜坡表层发生拉张卸荷作用,在斜坡肩部后缘形成一系列拉裂缝。雨水浸润、风化剥蚀等外营力导致岩体的强度降低,使岩体沿着裂隙向下顺结构面滑塌。按照崩塌体的块度组成,可以将基岩崩塌分为2类,分别为碎裂化板岩或千枚岩等表层崩塌,以及厚层或块状岩体被结构面切割形成的岩块式崩塌。
以秦岭腹地的太白县为例,浅表层崩塌的岩性条件多以层状次坚硬—次软质浅变质岩类及薄层状软质浅变质千枚岩类为主,具体包括中薄层砂板岩为主夹砂岩、千枚岩、砂质灰岩,以及泥盆系星红铺组千枚岩,夹砂岩、灰岩薄层及石炭系泥、页岩等岩性。此类岩体层厚较小,强度软硬相间,岩体结构基本为碎裂化状态,表层风化严重,十分破碎,呈散体化状态。在干燥状态时,坡体表层岩体碎屑在公路车辆振动及风荷载作用下,易形成干碎屑流,通常仅限于表层碎块石,灾害体积规模较小,危害程度也较小。在强降雨条件下,浅表层松散的岩质碎屑则易演化成为坡面泥石流,体积规模及破坏能力取决于松散碎屑的储量,一般会导致路面湿滑加剧、掩埋或阻断公路,对人员及过往车辆威胁较大。
岩块式崩塌的岩性条件通常以节理化的厚层状、块状坚硬—次坚硬侵入岩、火山岩、深变质片麻岩类、碳酸盐岩类为主,具体包括各期二长、斜长花岗岩,闪长岩类,古生界中基性、中酸性火山熔岩,各类片麻岩、片岩,少量变粒岩、大理岩、石墨大理岩及古道岭组灰岩等。此类岩石力学强度高,岩体结构质量相对较好,多属于块裂、节理化、镶嵌结构、层状及厚层状等,在公路沿线主要由于工程切坡卸荷作用,发生浅部切割块体状崩塌灾害,一般单体崩积岩块的块度较大,灾害整体规模较大。在高陡的工程边坡中,还时常发育孤石滚落方式的崩塌,尽管整体规模不一定很大,但是单块滚石的破坏能力也很强。可见,此类切割块体式崩塌总体危害程度较高,需谨慎防范。
宝鸡市泥石流灾害主要以汛期暴雨诱发的中小型为主,根据泥石流发育形态和物质来源可将区内泥石流灾害或隐患分成3类,分别为沟谷型泥石流、坡面型泥石流以及采矿弃渣潜在泥石流。
暴雨诱发的沟谷型泥石流是区内致灾效应严重的一类泥石流灾害,一般规模相对较大,主要分布于黄土丘陵区及基岩山区。根据物质组成分析,主要包括泥石流和水石流2类。
沟谷型水石流以太白县较为典型,通常具有较明显的形成区、流通区和堆积区。堆积物以砂、砾、卵、漂石为主,偶含巨石(长轴块度大于1 m),粗粒物质占固体物质总量的85%~90%,而细粒物质如粉砂、黏土等仅占10%~15%。这些水石流沟在1981年、1990年、1998年等多雨季节都曾不同程度爆发过灾害,桃川河、石头河作为排泄和堆积区,河床中卵石-漂石等冲积块石遍布。水石流爆发经常导致河流倒岸,河道及沟谷两侧毁地严重,典型实例如太白县桃川镇沙沟峡水石流灾害点。
沟谷型泥石流主要表现为混杂堆积,物质分选性较差,砾石一般呈次棱状,磨圆度相对较差,但个别物质来源中混杂了河床相物质,则显现出较好的磨圆度。砾石成分主要由物源区及流通区下垫面岩性决定。区内泥石流堆积物中最大砾径可达1 m有余。堆积物大都成扇形,自沟口向扇前堆积厚度逐渐变薄;但由于泥石流堆积区主要位于河谷及沟谷附近,除个别冲刷能力弱的河谷外,其堆积扇大都被河水或季节性洪水冲蚀破坏,堆积扇不很完整。陈仓区贾村镇泥石流即属于此种类型。
与沟谷型泥石流相比,坡面型泥石流具有更易发、规模小、分布广,且形成、流通及堆积分区不明显等时空发育特征,根据物质组成可以分为浅层新近堆积黄土泥流和残坡积层坡面流2种灾害形式。
新近堆积黄土(Q42-3)是指全新统近代(距今几千年或数百年甚至数十年)以来堆积的黄土,多为黄土状土。其工程地质特性主要表现为固结较差、土质疏松及高压缩性等,尤其是对水的响应十分灵敏,在自然降雨或人工排水条件下,新近堆积黄土极易形成浅层饱和流滑,或者表层坡面泥流。由于流滑体结构和强度几乎完全丧失,难以支挡治理,对多处居民房屋和院落造成威胁,给生产和生活带来诸多不便。例如太白县高龙乡四林庄泥流、嘴头镇强里川村小石沟泥流,麟游县招贤镇永丰村岭南组泥流等。
残坡积物组成的坡面泥石流通常先以滑坡形式启动,而后迅速转变为浅表层泥石流,兼有滑坡和泥石流发育特征,通常发育在基岩山区经工程切坡扰动的斜坡上。物质组成包括残坡积成因的黏性土,含少量块石或碎石,级配较好,且土层厚度较小。在连阴雨或短时暴雨作用下,土体局部发生启动流滑,进而在持续动水压力作用下倾泻造浆形成坡面泥石流。陈仓区坪头镇北坡面泥石流属于此种类型。
不稳定斜坡通常指可能演化成为滑坡或崩塌灾害的斜坡地段,或称潜在滑坡或崩塌,按照斜坡岩性可以分为土质不稳定斜坡和岩质不稳定斜坡,主要集中分布在黄土区及基岩山区的人类工程扰动地段。
岩质不稳定斜坡绝大部分位于主干公路沿线及建房切坡周边的崩滑灾害多发地段。主干公路所穿越地貌和地层区段主要集中在基岩峡谷区,公路工程穿越切割的基岩峡谷区多形成结构松动的高陡边坡。由于不稳定斜坡是指可能发生崩塌或滑坡的斜坡地段,因此坡体的变形迹象较为明显,但尚未演化为显著破坏或失稳现象。此类斜坡通常动辄数十米,坡面陡峭,且时有悬臂式的鹰嘴岩发育,岩体结构松弛,结构类型呈块裂—碎裂状态不一,在自然风化条件下的持续变形即可能发生失稳破坏,当遭遇降雨入渗、工程振动等外荷载作用时,则更易演化为崩滑灾害,对公路和居民点等相关承灾体构成威胁。如太白县太洋公路苏家沟段岩质高陡斜坡,斜坡高约25 m,坡长35 m,坡宽约100 m,坡体表层卸荷节理裂隙发育,潜在崩塌体积约3000 m3。
黄土地区的不稳定斜坡,主要由于村民开挖窑洞和公路切坡而形成,因此集中在人口密集的高陡斜坡地带。斜坡土体由中—上更新统黄土组成,直立性强,坡面陡峭,演化趋势以黄土崩塌为主,通常沿窑洞外的“崖面子”一线威胁到一户或几户村民。由于坡体下部窑洞或者取土开挖卸荷,坡体上部树木根劈作用,部分地段黄土斜坡的坡肩至中上部发育纵向卸荷拉张节理-裂隙,成为黄土斜坡失稳的关键结构控制因素。被裂隙切割的柱状黄土危岩体通常以外向倾倒或坐落式破坏方式,形成崩塌或滑塌灾害,尤其在强降雨期间,发生危岩体失稳危险性更高。典型案例包括陈仓区天王镇曹家沟四组不稳定斜坡、赤沙镇产东村一组不稳定斜坡。
在对宝鸡市地质灾害编录空间数据库搜集整理和综合分析的基础上,总结阐述了宝鸡地区主要地质灾害类型的空间分布和发育特征。
宝鸡市地质灾害类型主要包括滑坡、崩塌、泥石流及不稳定斜坡4类,总体发育特征具有群发性、突发性、周期性和链生性。其中,滑坡和崩塌数量多、危害大,特别是汛期降雨诱发的群发浅层小型滑坡和崩塌灾害最具代表性;泥石流相对发育较少,不稳定斜坡多与崩塌相伴生,大多发展为崩塌灾害。
宝鸡市黄土地区发育大量的黄土滑坡和崩塌,大规模厚层黄土滑坡多发育在黄土塬边河谷深切地带,多属于古—老滑坡,新发生的黄土斜坡变形多为小型黄土滑坡和崩塌。由于黄土斜坡对降雨入渗的变形响应十分敏感,因此,每年汛期在强降雨作用下,都可能诱发小型黄土滑坡和崩塌,特别是城镇居民房前屋后的小型黄土滑坡和崩塌频繁发生,是目前群测群防监测预警的重点,也是宝鸡市减灾防灾关注的重中之重。
宝鸡市基岩山区发育大量的表层松散堆积物小型滑坡和崩塌,特别是在山区公路切坡、建房削坡及采矿扰动等作用下,使残坡积层剥露出来,并失去支撑,在降雨、河流侵蚀及地表排水等作用下,极易发生小型浅表层滑坡和崩塌,对人员、房屋、公路和车辆等威胁严重,是山区减灾防灾关注的重点。
致谢: 本文是在宝鸡项目组持续7年的地质灾害详细调查、编录和数据库资料、及相关专题研究和综合研究成果分析的基础上完成,在此向全体宝鸡项目组成员表示衷心感谢。| [1] |
王驹, 陈伟明, 苏锐, 等.高放废物地质处置及其若干关键科学问题[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 4(25):801~812. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb200604015
WANG Ju, CHEN Weiming, SU Rui, et al. Geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste and its key scientific issues[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechancis and Engineering, 2006, 4(25):801~812. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb200604015
|
| [2] |
孙德安, 张龙.盐溶液饱和高庙子膨润土膨胀特性及预测[J].岩土力学, 2013, 34(10):2790~2795. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201310007
SUN Dean, ZHANG Long. Swelling characteristics of Gaomiaozi bentonite saturated by salt solution and their prediction[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(10):2790~2795. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201310007
|
| [3] |
Sun Z M, Yu J, Zheng S L, et al. Effect of salt in aqueous solution on the swelling and water-retention capacity of bentonite[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 194~196:2039~2045. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.194-196
|
| [4] |
Alawaji H A. Swell and compressibility characteristics of sand-bentonite mixtures inundated with liquids[J]. Applied Clay Science, 1999, 15(3/4):411~430. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=11109b69d94d9eb124098a127c33ed9b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
|
| [5] |
Zhang L, Sun D A, Jia D. Shear strength of GMZ07 bentonite and its mixture with sand saturated with saline solution[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2016, 132~133:24~32. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2016.08.004
|
| [6] |
Tabiatnejad B, Siddiqua S, Siemens G. Impact of pore fluid salinity on the mechanical behavior of unsaturated bentonite-sand mixture[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(22):1434. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-6246-5
|
| [7] |
Maio D C. Shear strength of clays and clayey soils: the influence of pore fluid composition[A]. Loret B, Huyghe J M. Chemo-Mechanical Couplings in Porous Media Geomechanics and Biomechanics[M]. Vienna: Springer, 2004, 45~55.
|
| [8] |
Rao S M, Thyagaraj T. Swell-compression behaviour of compacted clays under chemical gradients[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2007, 44(5):520~532. doi: 10.1139/t07-002
|
| [9] |
Barbour S L, Fredlund D G. Mechanisms of osmotic flow and volume change in clay soils[J]. Canadian Geotechnial Journal, 1989, 26(4):551~562. doi: 10.1139/t89-068
|
| [10] |
Xu Y F, Xiang G S, Jiang H, et al. Role of osmotic suction in volume change of clays in salt solution[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2014, 101:354~361. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2014.09.006
|
| [11] |
Miller D J, Nelson J D. Osmotic suction in unsaturated soil mechanics[A]. Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Unsaturated Soils[C]. Arizona:American Society of Civil Engineers, 2006, 1382~1393.
|
| [12] |
Apelblat A, Dov M, Wisniak J, et al. The vapour pressure of water over saturated aqueous solutions of malic, tartaric, and citric acids, at temperatures from 288 K to 323 K[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 1995, 27(1):35~41. doi: 10.1006/jcht.1995.0004
|
| [13] |
Wijmans J G, Baker R W. The solution-diffusion model:a review[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 1995, 107(1~2):1~21. doi: 10.1016/0376-7388(95)00102-I
|
| [14] |
Fernández D P, Goodwin A R H, Lemmon E W, et al. A formulation for the static permittivity of water and steam at temperatures from 238 K to 873 K at pressures up to 1200 MPa, including derivatives and Debye-Hückel coefficients[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1997, 26(4):1125~1166. doi: 10.1063/1.555997
|
| [15] |
Scatchard G. Excess free energy and related properties of solutions containing electrolytes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1968, 90(12):3124~3127. doi: 10.1021/ja01014a027
|
| [16] |
Pitzer K S, Mayorga G. Thermodynamics of electrolytes. Ⅱ. activity and osmotic coefficients for strong electrolytes with One or both ions univalent[J]. Pitzer, 1973, 77(19):2300~2308. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ026170697/
|
| [17] |
Pitzer K S, Mayorga G. Thermodynamics of electrolytes. Ⅲ. activity and osmotic coefficients for 2~2 electrolytes[J]. Journal of Solution Chemistry, 1974, 3(7):539~546. doi: 10.1007/BF00648138
|
| [18] |
Hamer W J, Wu Y C. Osmotic coefficients and mean activity coefficients of uni-univalent electrolytes in water at 25℃[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1972, 1(4):1047~1099. doi: 10.1063/1.3253108
|
| [19] |
Clarke E C W, Glew D N. Evaluation of the thermodynamic functions for aqueous sodium chloride from equilibrium and calorimetric measurements below 154℃[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1985, 14(2):489~610. doi: 10.1063/1.555730
|
| [20] |
Guendouzi M E L, Mounir A, Dinane A. Water activity, osmotic and activity coefficients of aqueous solutions of Li2SO4, Na2SO4, K2SO4, (NH4)2SO4, MgSO4, MnSO4, NiSO4, CuSO4, and ZnSO4 at T=298.15 K[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2003, 35(2):209~220. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9614(02)00315-4
|
| [21] |
Castellanos E, Villar M V, Romero E, et al. Chemical impact on the hydro-mechanical behaviour of high-density FEBEX bentonite[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 2008, 33(S1):S516-S526. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223791226_Chemical_impact_on_the_hydro-mechanical_behavior_of_high-density_FEBEX_bentonite
|
| [22] |
Pitzer K S, Kim J J. Thermodynamics of electrolytes. Ⅳ. Activity and osmotic coefficients for mixed electrolytes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1974, 96(18):5701~5707. doi: 10.1021/ja00825a004
|
| [23] |
Dinane A, El Guendouzi M, Mounir A. Hygrometric determination of water activities, osmotic and activity coefficients of (NaCl+KCl)(aq) at T=298.15 K[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2002, 34(4):423~441. doi: 10.1006/jcht.2001.0845
|
| 1. | 郑新江,徐永福. 盐溶液饱和高庙子膨润土的强度特性. 岩土工程学报. 2021(04): 783-788 .  |