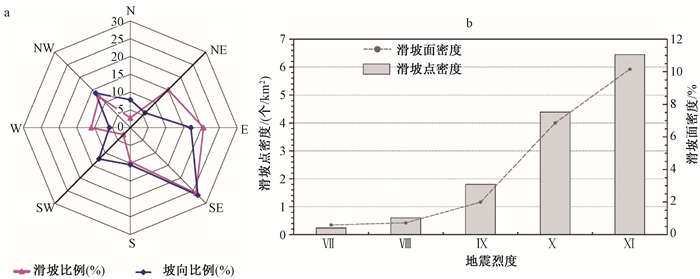
RESEARCH REVIEW ON LONG-TERM ACTIVITY OF POST-EARTHQUAKE GEOHAZARD IN STRONG SEISMIC-DISTURBED REGIONS
-
摘要: 地震通过改变地表岩体的物理力学性质而使得震区滑坡、泥石流等地质灾害显著增强的现象在震后持续相当长的一段时间。在研究分析国内外学者对地震地质灾害研究成果的基础上,系统总结了目前在地震诱发地质灾害的发育分布规律及其演化趋势方面的研究方法及成果,探讨了研究中存在的问题及薄弱环节,并对未来的研究方向及趋势进行了展望。研究认为目前国内外对地震地质灾害长期活动性的研究还没有形成体系,尚缺乏有效的研究方法与技术,并且研究成果存在较大差异性。地震扰动区地质灾害长期活动性研究可为震后地质灾害的长期防灾减灾和风险管控提供科学支持,也能对地震地质灾害相关问题的进一步深入研究提供参考。Abstract: Earthquake can significantly change the physical and mechanical properties of surface rock masses, which leads to an obvious geohazard increase after earthquake for a long period of time. Based on the review and analysis of the current research status of long-term activity of post-earthquake geohazard, the current research methods and achievements of development, distribution rule and evolution trend of earthquake-induced geohazard are systematically summarized, the problems and weaknesses during the research process are discussed, and the prospects and the future research directions and trends are presented. At present, there is no perfect research system and effective research methods and techniques for long-term activity of post-earthquake geohazard, and the research results have a big difference. In-depth scientific research on long-term activity of post-earthquake geohazard in seismic-disturbed regions can provide scientific support for long-term disaster prevention, mitigation and risk control of geohazard after the earthquake and also present a reference for further study of this scientific problem.
-
Key words:
- earthquake /
- geohazard /
- long-term activity /
- active cycle /
- review
-
图 2 台湾集集地震扰动区触发泥石流的小时降雨量和累积降雨量[44]
Figure 2. Plot of the maximum hourly percipitation versus the maximum accumulated precipitation for debris flow events in the Chi-chi earthquake-disturbed areas
表 1 中国典型地震震后有效松弛时间[65]
Table 1. Post-seismic effective relaxation cycles of typical earthquakes in China
地震名称 震级(Ms) 发震时间 测段名称 资料年限 有效松弛时间/年 最大形变量/mm 同震形变/mm 唐山 7.8 1976.7.28 山津26-22 1976—1992 21.6 127.1 206 邢台 7.2 1966.3.22 冯巨7-11 1966—1976 11.1 131.6 273 通海 7.8 1970.1.5 高大1-4 1970—1981 5.5 32.8 未测 炉霍 7.6 1973.2.6 虚墟B-C 1973—1981 4.9 6.5 未测 共和 7.0 1900.4.26 倒花15-18 1990—1995 4.0 25.5 43 -
[1] 党光明, 王赞军.青海昆仑山口西Ms8.1级地震地表破裂带特征与主要震害-对青藏高原区域稳定性评价的制约[J].地质通报, 2002, 21(2):105~108. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz200202013DANG Guangming, WANG Zanjun. Characteristics of the surface rupture zone and main seismic hazards caused by the Ms8. 1 earthquake west of the Kunlun pass, China-Constraints on the regional stability of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2002, 21(2):105~108. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz200202013 [2] 张永双, 雷伟志, 石菊松, 等.四川5.12地震次生地质灾害的基本特征初析[J].地质力学学报, 2008, 14(2):109~116. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080211&flag=1ZHANG Yongshuang, LEI Weizhi, SHI Jusong, et al. General characteristics of 5.12 earthquake-induced geohazards in Sichuan[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2008, 14(2):109~116. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080211&flag=1 [3] 姚鑫, 张永双, 杨农, 等.玉树地震地表变形InSAR观测及初步分析[J].地质力学学报, 2010, 16(2):129~136. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20100202&flag=1YAO Xin, ZHANG Yongshuang, YANG Nong, et al. D-InSAR observation of earth surface deformation in the Ms7.1 Yushu earthquake[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2010, 16(2):129~136. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20100202&flag=1 [4] 张永双, 马寅生, 胡道功, 等.玉树地震地表破裂调查与灾后重建避让选址研究[J].地质学报, 2010, 84(5):593~605. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201005001ZHANG Yongshuang, MA Yinsheng, HU Daogong, et al. Investigation and research on the surface rupture of the Yushu earthquake and reconstruction site selection[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(5):593~605. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201005001 [5] 崔鹏, 陈晓清, 张建强, 等. "4·20"芦山7.0级地震次生山地灾害活动特征与趋势[J].山地学报, 2013, 31(3):257~265. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdxb201303001CUI Peng, CHEN Xiaoqing, ZHANG Jianqiang, et al. Activities and tendency of mountain hazards induced by the Ms7. 0 Lushan Earthquake, April 20, 2013[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2013, 31(3):257~265. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdxb201303001 [6] Qi S W, Xu Q, Lan H X, et al. Spatial distribution analysis of landslides triggered by 2008. 5.12 Wenchuan Earthquake, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2010, 116(1~2):95~108. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0013795210001535 [7] Dai F C, Xu C, Yao X, et al. Spatial distribution of landslides triggered by the 2008Ms8. 0 Wenchuan earthquake, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 40(4):883~895. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.04.010 [8] 许冲, 徐锡伟, 吴熙彦, 等. 2008年汶川地震滑坡详细编目及其空间分布规律分析[J].工程地质学报, 2013, 21(1):25~44. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb201301004XU Chong, XU Xiwei, WU Xiyan, et al. Detailed catalog of landslides triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake and statistical analyses of their spatial distribution[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2013, 21(1):25~44. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb201301004 [9] Wei F Q, Chernomorets S, Aristov K, et al. A seismically triggered landslide in the niujuanvalley near the epicenter of the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2010, 21(6):901~909. doi: 10.1007/s12583-010-0143-8 [10] Lan H X, Li L P, Zhang Y S, et al. Risk assessment of debris flow in Yushu seismic area in China:a perspective for the reconstruction[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2013, 13(11):2957~2968. doi: 10.5194/nhess-13-2957-2013 [11] 兰恒星, 周成虎, 高星, 等.四川雅安芦山地震灾区次生地质灾害评估及对策建议[J].地理科学进展, 2013, 32(4):499~504. doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2013.04.001LAN Hengxing, ZHOU Chenghu, GAO Xing, et al. Secondary geological hazard assessment and hazard mitigation countermeasures in Lushan, Ya'an Earthquake, Sichuan Province[J]. Progress in Geography, 2013, 32(4):499~504. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11820/dlkxjz.2013.04.001 [12] 陈宁生, 黄蓉, 李欢, 等.汶川5·12地震次生泥石流沟应急判识方法与指标[J].山地学报, 2009, 27(1):108~114. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdxb200901016CHEN Ningsheng, HUANG Rong, LI Huan, et al. Emergency judge method and index of debris-flow sites triggered by 5·12 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2009, 27(1):108~114. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdxb200901016 [13] 陈宁生, 刘丽红, 邓明枫, 等. "4·20"芦山地震后的四川地质灾害形势预测与防治对策[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 40(4):371~378. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cdlgxyxb201304003CHEN Ningsheng, LIU Lihong, DONG Mingfeng, et al. Tendency prediction and prevention strategy of geohazards triggered by Lushan Ms7 earthquake, Sichuan, Province, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science and Technology Edition), 2013, 40(4):371~378. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cdlgxyxb201304003 [14] 刘凤民, 张立海, 刘海青, 等.中国地震次生地质灾害危险性评价[J].地质力学学报, 2006, 12(2):127~131. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060220&flag=1LIU Fengmin, ZHANG Lihai, LIU Haiqing, et al. Danger assessment of earthquake-induced geological disasters in China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2006, 12(2):127~131. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060220&flag=1 [15] 黄润秋.汶川地震地质灾害后效应分析[J].工程地质学报, 2011, 19(2):145~151. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb201102001HUANG Runqiu. After effect of geohazards induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2011, 19(2):145~151. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb201102001 [16] Huang R Q, Li W L. Post-earthquake landsliding and long-term impacts in the Wenchuan earthquake area, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2014, 182:111~120. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.07.008 [17] 苏鹏程, 韦方强, 冯汉中, 等. "8. 13"四川清平群发性泥石流灾害成因及其影响[J].山地学报, 2011, 29(3):337~347. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SDYA201103013.htmSU Pengcheng, WEI Fangqiang, FENG Hanzhong, et al. Causes and effects of group-occurring debris flow disasters in Qingping town, Mianyuan river upstream, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2011, 29(3):337~347. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SDYA201103013.htm [18] Wei X L, Chen N S, Cheng Q G, et al. Long-term activity of earthquake-induced landslides:A case study from Qionghai Lake Basin, Southwest of China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2014, 11(3):607~624. doi: 10.1007/s11629-013-2970-4 [19] Ghazanfar A K, Owen L A, Kamp U, et al. Evolution of earthquake-triggered landslides in the Kashmir Himalaya, northern Pakistan[J]. Geomorphology, 2010, 115(1~2):102~108. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.09.035 [20] Nakamura H, Tsuchiya S, Inoue K, et al. Sabo against Earthquakes[C]. Kokon Shoin, Tokyo, Japan, 2000, 190~220. [21] Lin CW, Liu SH, Chang WS, et al. The impact of the Chi-Chi earthquake on the subsequent rain fall induced landslides in the epicentral area of central Taiwan[A]. Proceeding of International Conference in Commemoration of 10th Anniversary of the Chi-Chi Earthquake[C]. 2009, 336~338. [22] 王伟. 地震动的山体地形效应[D]. 哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所, 2011. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gjzt201203009&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQWANG Wei. Effect of hill topography on ground motion[D]. Harbin:Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration, 2011. (in Chinese) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gjzt201203009&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [23] 陈桂华, 徐锡伟, 郑荣章, 等. 2008年汶川Ms8.0地震地表破裂变形定量分析-北川-映秀断裂地表破裂带[J].地震地质, 2008, 30(3):723~738. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gjzt201203009&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQCHEN Guihua, XU Xiwei, Zheng Rongzhang, et al. Quantitative analysis of the co-seismic surface rupture of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan, China along the Beichuan-Yingxiu fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2008, 30(3):723~738. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gjzt201203009&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [24] 陈桂华, 徐锡伟, 于贵华, 等. 2008年汶川Ms8.0地震多断裂破裂的近地表同震滑移及滑移分解[J].地球物理学报, 2009, 52(5):1384~1391. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gjzt201006014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQCHEN Guihua, XU Xiwei, YU Guihua, et al. Co-seismic slip and slip partitioning of multi-faults during the Ms8. 02008 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(5):1384~1391. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gjzt201006014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [25] Jiao Q J, Zhang B, Liu L Y, et al. Assessment of spatio-temporal variations in vegetation recovery after the Wenchuan earthquake using Landsat data[J]. Natural Hazards, 2014, 70(2):1309~1326. doi: 10.1007/s11069-013-0875-8 [26] Zhang Y S, Cheng Y L, Yin Y P, et al. High-position debris flow:a long-term active geohazard after the Wenchuanearthquake[J]. Engineering Geology, 2014, 180:45~54. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.05.014 [27] 倪化勇, 郑万模, 唐业旗, 等.汶川震区文家沟泥石流成灾机理与特征[J].工程地质学报, 2011, 19(2):262~270. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb201102019NI Huayong, ZHENG Wanmo, TANG Yeqi, et al. Mechanism and characteristics of Wenjia-gully debris flow in epicenter area of Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2011, 19(2):262~270. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb201102019 [28] Jóonsson S, Segall P, Pedersen R, et al. Post-earthquake ground movements correlated to pore-pressure transients[J]. Nature, 2003, 424(6945):179~183. doi: 10.1038/nature01776 [29] Wasowski J, Keefer D K, Lee C T. Toward the next generation of research on earthquake-induced landslides:Currentissues and future challenges[J]. Engineering Geology, 2011, 122(1~2):1~8. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.06.001 [30] Keefer D K, Larsen M C. Assessing landslide hazards[J]. Science, 2007, 316(5828):1136~1138. doi: 10.1126/science.1143308 [31] 殷跃平.汶川八级地震滑坡特征分析[J].工程地质学报, 2009, 17(1):29~38. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb200901004YIN Yueping. Features of landslides triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(1):29~38. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb200901004 [32] 许强, 李为乐.汶川地震诱发滑坡方向效应研究[J].四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2010, 42(S1):7~14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SCLH2010S1003.htmXU Qiang, LI Weile. Study on the direction effects of landslides triggered by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 2010, 42(S1):7~14. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SCLH2010S1003.htm [33] 唐川.汶川地震区暴雨滑坡泥石流活动趋势预测[J].山地学报, 2010, 28(3):341~349. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdxb201003012TANG Chuan. Activity tendency prediction of rainfall induced landslides and debris flows in the Wenchuan earthquake areas[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2010, 28(3):341~349. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdxb201003012 [34] 许冲, 戴福初, 徐锡伟.汶川地震滑坡灾害研究综述[J].地质评论, 2011, 56(6):860~874. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201006013XU Chong, DAI Fuchu, XU Xiwei. Wenchuan earthquake-induced landslides:an overview[J]. Geological Review, 2011, 56(6):860~874. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201006013 [35] 李忠生.国内外地震滑坡灾害研究综述[J].灾害学, 2003, 18(4):64~70. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhx200304013Li Zhongsheng. The state of the art of the research on seismic landslide hazard at home and abroad[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2003, 18(4):64~70. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhx200304013 [36] 许冲, 戴福初, 陈剑, 等.汶川Ms8.0地震重灾区次生地质灾害遥感精细解译[J].遥感学报, 2009, 13(4):754~762. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20090416XU Chong, DAI Fuchu, CHEN Jian, et al. Identification and analysis of secondary geological hazards triggered by a magnitude 8.0 Wenchuan Earthquake[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2009, 13(4):754~762. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11834/jrs.20090416 [37] 吴树仁, 王涛, 石玲, 等. 2008汶川大地震极端滑坡事件初步研究[J].工程地质学报, 2008, 18(2):145~159. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb201002001WU Shuren, WANG Tao, SHI Ling, et al. Study on catastrophic landslides triggered by 2008 great Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2008, 18(2):145~159. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb201002001 [38] Chen X L, Zhou Q, Ran H, et al. Earthquake-triggered landslides in southwest China[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2012, 12(2):351~363. doi: 10.5194/nhess-12-351-2012 [39] 张永双, 成余粮, 姚鑫, 等.四川汶川地震-滑坡-泥石流灾害链形成演化过程[J].地质通报, 2013, 32(12):1900~1910. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz201312003ZHANG Yongshuang, CHENG Yuliang, YAO Xin, et al. The evolution process of Wenchuan earthquake-landslide-debris flow geohazard chain[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2013, 32(12):1900~1910. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz201312003 [40] 殷跃平.汶川八级地震地质灾害研究[J].工程地质学报, 2008, 16(4):433~444. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb200804001YIN Yueping. Researches on the geo-hazards triggered by Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2008, 16(4):433~444. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb200804001 [41] 殷跃平, 张永双, 吴树仁, 等.汶川地震工程地质与地质灾害[M].北京:科学出版社, 2013.YIN Yueping, ZHANG Yongshuang, WU Shuren, et al. Engineering Geology and Geological Hazards in Wenchuan Earthquake[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 2013. (in Chinese) [42] Xu C, Xu X W, Yao X, et al. Three (nearly) complete inventories of landslides triggered by the May 12, 2008 Wenchuan Mw7.9 earthquake of China and their spatial distribution statistical analysis[J]. Landslides, 2014, 11(3):441~461. doi: 10.1007/s10346-013-0404-6 [43] 黄润秋, 李为乐. "5·12"汶川大地震触发地质灾害的发育分布规律研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(12):2585~2592. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.12.028HUANG Runqiu, LI Weile. Research on development and distribution rules of Geohazards induced by Wenchuan Earthquake on 12th May, 2008[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(12):2585~2592. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.12.028 [44] Lin C W, Shieh C L, Yuan B D, et al. Impact of Chi-Chi earthquake on the occurrence of landslides and debris flows:example from the Chenyulan River watershed, Nantou, Taiwan[J]. Engineering Geology, 2004, 71(1/2):49~61. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S001379520300125X [45] Lin C W, Liu S H, Lee S Y, et al. Impacts of the Chi-Chi earthquake on subsequent rainfall-induced landslides in central Taiwan[J]. Engineering Geology, 2006, 86(2/3):87~101. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0013795206001037 [46] 张瑛, 成余粮, 李长顺, 等.汶川地震灾区地震前后地质灾害发育对比研究[J].工程地质学报, 2011, 19(S):179~185. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7624765ZHANG Ying, CHENG Yuling, LI Changshun, et al. Comparatives study on geological disasters before and after Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2011, 19(S):179~185. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7624765 [47] Zhou W, Tang C. Rainfall thresholds for debris flow initiationin the Wenchuan earthquake-stricken area, southwestern China[J]. Landslides, 2014, 11(5):877~887. doi: 10.1007/s10346-013-0421-5 [48] Yu B, Wu Y F, Chu S M. Preliminary study of the effect of earthquakes on the rainfall threshold of debris flows[J]. Engineering Geology, 2014, 182:130~135. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.04.007 [49] Tang C, Zhu J, Li W L, et al. Rainfall-triggered debris flows following the Wenchuan Earthquake[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2009, 68(2):187~194. doi: 10.1007/s10064-009-0201-6 [50] 陈源井, 余斌, 朱渊, 等.地震后泥石流临界雨量变化特征-以汶川地震区小岗剑沟为例[J].山地学报, 2013, 31(3):356~361. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=sdya201303015&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQCHEN Yuanjing, YU Bin, ZHU Yuan, et al. Characteristics of critical rainfall of debris flow after earthquake-a case study of the Xiaogangjian gully[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2013, 31(3):356~361. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=sdya201303015&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [51] Koi T, Hotta N, Ishigaki I, et al. Prolonged impact of earthquake-induced landslides on sediment yield in a mountain watershed:The Tanzawa region, Japan[J]. Geomorphology, 2008, 101(4):692~702. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.03.007 [52] Khan S F, Kamp U, Owen L A. Documenting five years of landsliding after the 2005 Kashmir earthquake, using repeat photography[J]. Geomorphology, 2013, 197:45~55. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.04.033 [53] Saba S B, Van Der Meijde M, Van Der Werff H. Spatiotemporal landslide detection for the 2005 Kashmir earthquake region[J]. Geomorphology, 2010, 124(1/2):17~25. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2010Geomo.124...17S [54] 崔鹏, 韦方强, 何思明, 等. 5.12汶川地震诱发的山地灾害及减灾措施[J].山地学报, 2008, 26(3):280~282. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdxb200803006CUI Peng, WEI Fangqiang, HE Siming, et al. Mountain disasters induced by the earthquake of May 12 in Wenchuan and the disasters mitigation[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2008, 26(3):280~282. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdxb200803006 [55] 崔鹏, 韦方强, 陈晓清, 等.汶川地震次生山地灾害及其减灾对策[J].中国科学院院刊, 2008, 23(4):317~323. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkxyyk200804008CUI Peng, WEI Fangqiang, CHEN Xiaoqing, et al. Geo-hazards in Wenchuan eathquake area and countermeasures for disaster reduction[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2008, 23(4):317~323. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkxyyk200804008 [56] 崔鹏, 庄建琦, 陈兴长, 等.汶川地震区震后泥石流活动特征与防治对策[J].四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2010, 42(5):10~19. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7681080CUI Peng, ZHUANG Jianqi, CHEN Xingchang, et al. Characteristics and countermeasures of debris flow in Wenchuan area after the earthquake[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 2010, 42(5):10~19. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7681080 [57] 陈晓清, 崔鹏, 赵万玉.汶川地震区泥石流灾害工程防治时机的研究[J].四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2009, 41(3):125~130. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=sclh200903021&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQCHEN Xiaoqing, CUI Peng, ZHAO Wanyu. Optimal timing for the control of debris flow in Wenchuan earthquake area[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 2009, 41(3):125~130. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=sclh200903021&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [58] 谢洪, 钟敦伦, 矫震, 等. 2008年汶川地震重灾区的泥石流[J].山地学报, 2009, 27(4):501~509. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdxb200904017XIE Hong, ZHONG Dunlun, JIAO Zhen, et al. Debris flow in Wenchuan Quake-hit area in 2008[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2009, 27(4):501~509. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdxb200904017 [59] 陈晓清, 崔鹏, 李泳, 等.汶川地震后北川干溪沟山地灾害及长期发展趋势初步分析[J].四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2010, 42(S1):22~32. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/9032141CHEN Xiaoqing, CUI Peng, LI Yong, et al. Mountain hazard induced by Wenchuan earthquake and its long-term development trends of Ganxi gully, Beichuan[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 2010, 42(S1):22~23. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/9032141 [60] 游勇, 柳金峰.汶川8级地震对岷江上游泥石流灾害防治的影响[J].四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2009, 41(S1):16~22. doi: 10.1002-lary.20808/YOU Yong, LIU Jinfeng. The influence on debris flow prevention in the upriver of Minjiang after Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 2009, 41(S1):16~22. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1002-lary.20808/ [61] Chang K T, Chiang S H, Hsu M L. Modeling typhoon-and earthquake-induced landslides in a mountainous watershed using logistic regression[J]. Geomorphology, 2007, 89(3/4):335~347. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169555X07000049 [62] Shou K J, Hong C Y, Wu C C, et al. Spatial and temporal analysis of landslides in Central Taiwan after 1999 Chi-Chi earthquake[J]. Engineering Geology, 2011, 123(1/2):122~128. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0013795211000779 [63] Liu S H, Lin C W, Tseng C M. A statistical model for the impact of the 1999 Chi-Chi earthquake on the subsequent rainfall-induced landslides[J]. Engineering Geology, 2013, 156:11~19. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.01.005 [64] Liu C N, Huang H F, Dong J J. Impacts of September 21, 1999 Chi-Chi earthquake on the characteristics of gully-type debris flows in central Taiwan[J]. Natural Hazards, 2008, 47(3):349~368. doi: 10.1007/s11069-008-9223-9 [65] 王庆良, 张希, 王文萍, 等. 中国典型强震震后形变有效松弛时间研究[A]. 中国地震学会第七次学术大会论文摘要集[C]. 中国地震学会, 1998, 13.Wang Qingliang, Zhang Xi, Wang Wenping, et al. The research on effective relaxation cycle of postseismic deformation of typical earthquakes in China[A]. Abstract Proceedings of Seventh Academic Conference of the Seismological Society of China[C]. Seismological Society of China, 1998, 13. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: