Sedimentary characteristics of the Lower Cambrian Shuijingtuo Formation in the E’Xi trough and its petroleum geological significance
-
摘要: 中国南方下寒武统富有机质页岩具有整体厚度大、热演化程度高的特点,近期的页岩气勘探已经在中扬子地区获得下寒武统页岩气工业气流。为了进一步调查中国南方下寒武统页岩气资源潜力,以中扬子地区下寒武统水井沱组为重点,结合地表露头观察和钻井资料,研究分析了其沉积特征和沉积过程,划分了下寒武统页岩三级地层层序格架,构建了中扬子地区鄂西海槽早寒武世的沉积模式,并指明了中扬子地区下寒武统页岩气勘探方向。研究表明:中扬子地区下寒武统水井沱组主要发育浅水陆棚相和深水陆棚相沉积,其底部和顶部发育浅水碳酸盐岩沉积;下寒武统富有机质页岩可划分为5个三级层序,并可与上扬子地区进行对比;水井沱组发育于震旦纪—早寒武世鄂西海槽的充填阶段,主要为泥质碎屑岩沉积。富有机质页岩分布于深水相区,在鄂西海槽识别出恩施、宜昌长阳2个次级凹陷,是页岩气勘探的重点地区;下寒武统水井沱组与下伏震旦系灯影组和陡山沱组形成“三明治”式常规油气组合,是下一步鄂西常规油气勘查的重点领域。Abstract:
Objective The organic-rich shales of the Lower Cambrian in South China are characterized by significant thickness and high thermal maturity. Recent explorations have yielded industrial gas flows from the Lower Cambrian shales in the Middle Yangtze region. To further investigate the shale gas resource potential of the Lower Cambrian in South China, this study focuses on the Lower Cambrian Shuijingtuo Formation in the Middle Yangtze region. Methods Through an integrated analysis of outcrop observations and drilling data, we analyzed its sedimentary characteristics and processes. A third-order stratigraphic sequence framework for the Lower Cambrian shale was established, and a sedimentary model of the Early Cambrian E’Xi Trough in the Middle Yangtze region was constructed, clarifying exploration targets. Results The Lower Cambrian Shuijingtuo Formation in the Middle Yangtze region primarily consists of shallow-water and deep-water shelf facies, with shallow carbonate deposits at both the bottom and top. The Lower Cambrian organic-rich shales can be divided into five third-order sequences, which are correlatable with those in the Upper Yangtze region. The Shuijingtuo Formation formed during the filling stage of the E’xi Trough, primarily consisting of argillaceous clastic sedimentary rocks. Conclusion Organic-rich shales are distributed in deep-water facies, with two identified subsags within the E’xi Trough (the Enshi and Yichang–Changyang depressions) serving as key exploration targets. The Lower Cambrian Shuijingtuo Formation, together with the underlying Sinian Dengying and Doushantuo Formations, forms a "sandwich-like" conventional hydrocarbon assemblage, which is a priority area for future conventional oil and gas exploration in Western Hubei. -
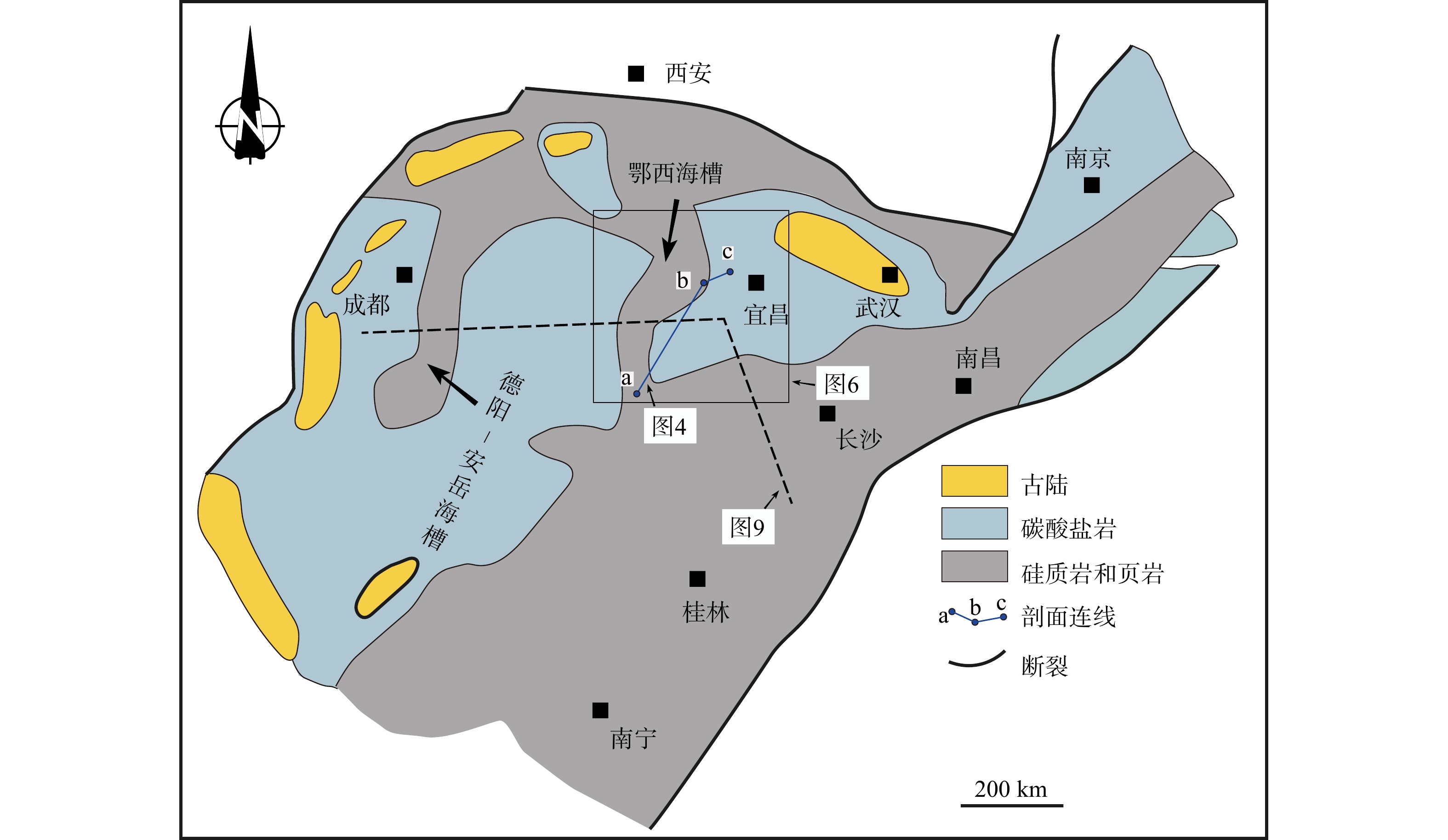
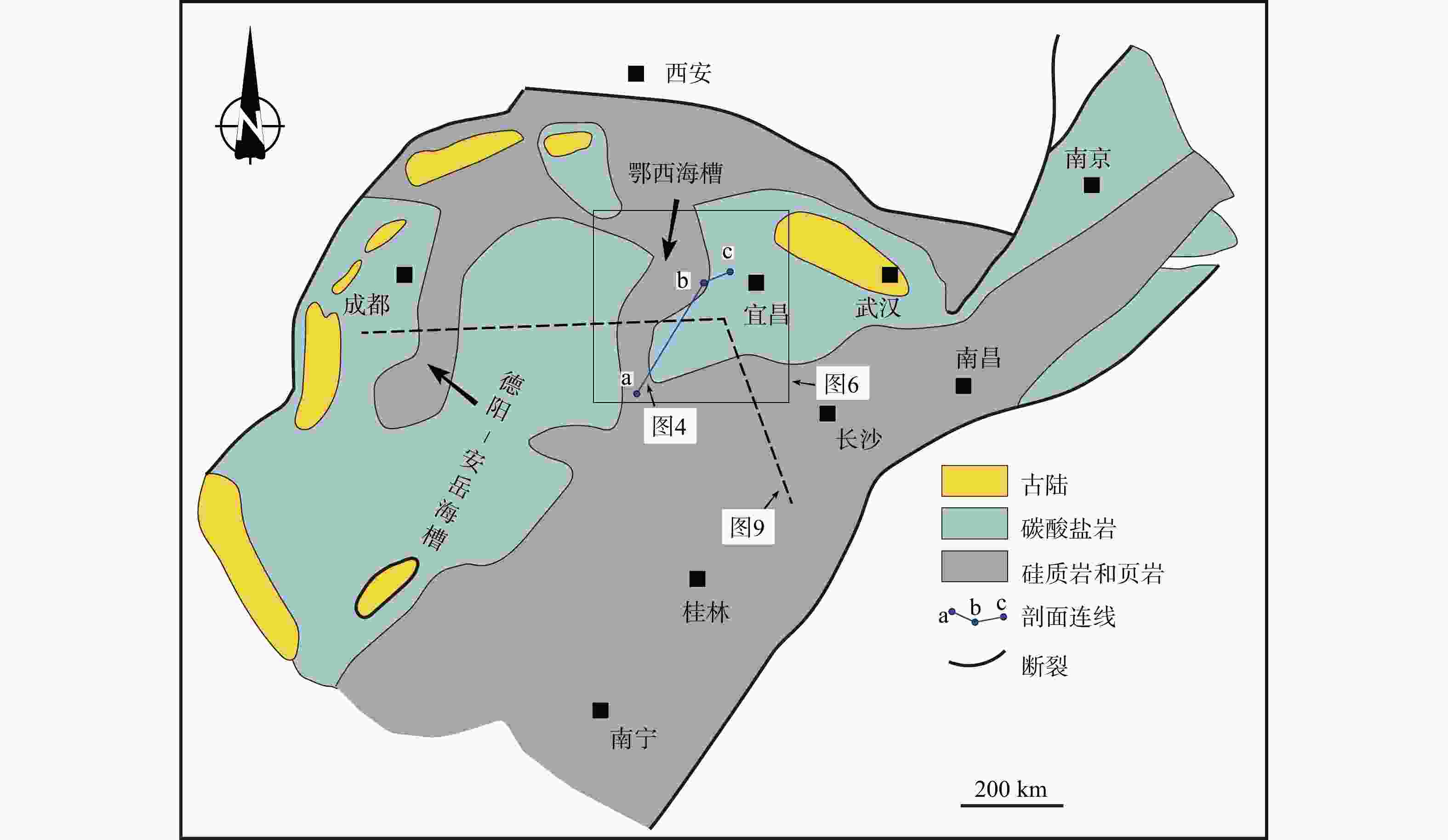
图 1 扬子地区早寒武世古地理图(据Wang et al.,2012;刘忠宝等,2018;赵建华等,2019修改)
Figure 1. Paleogeographic map of the Yangtze region during the Early Cambrian(modified after Wang et al.,2012;Liu et al.,2018;Zhao et al.,2019)
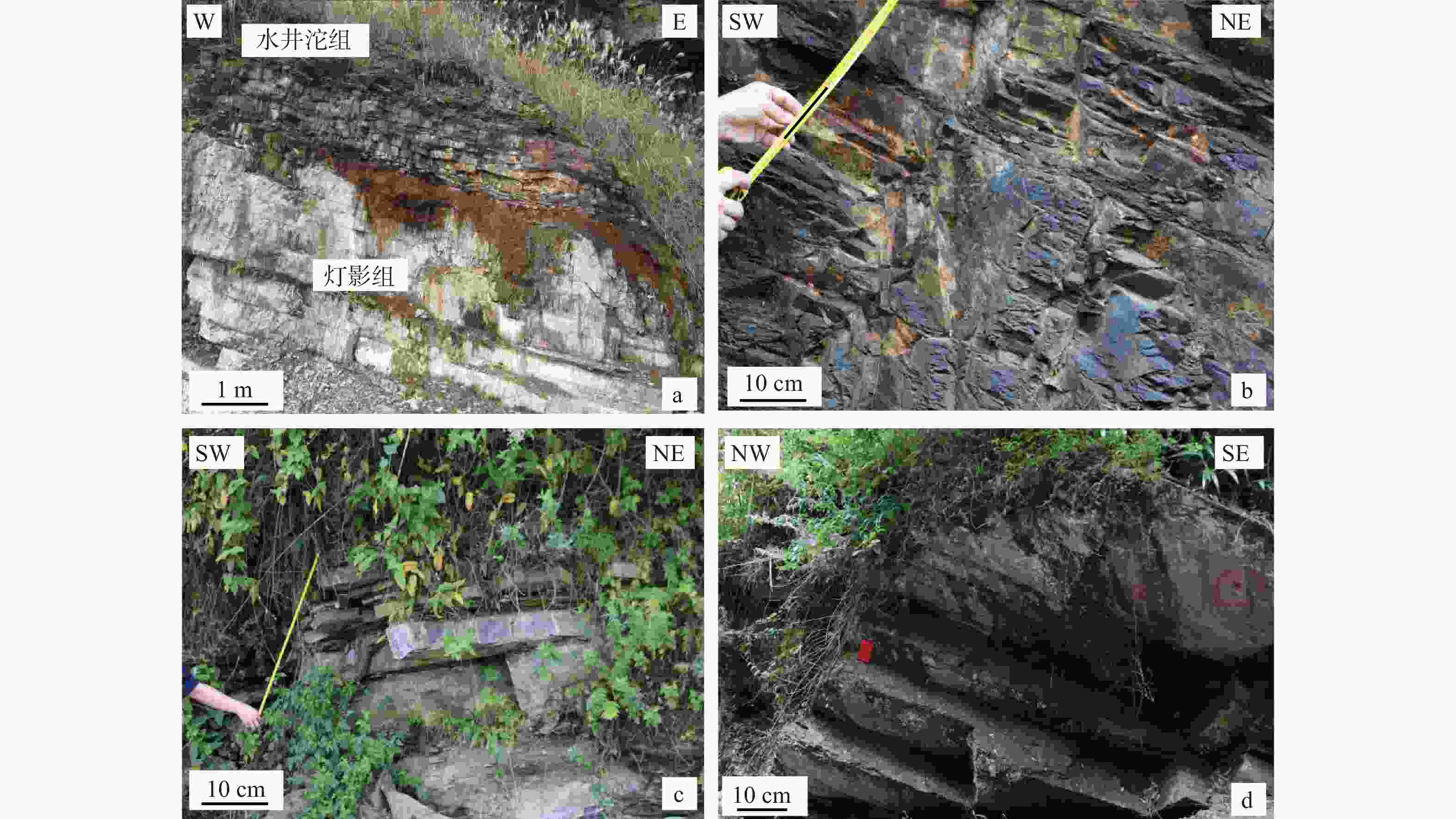
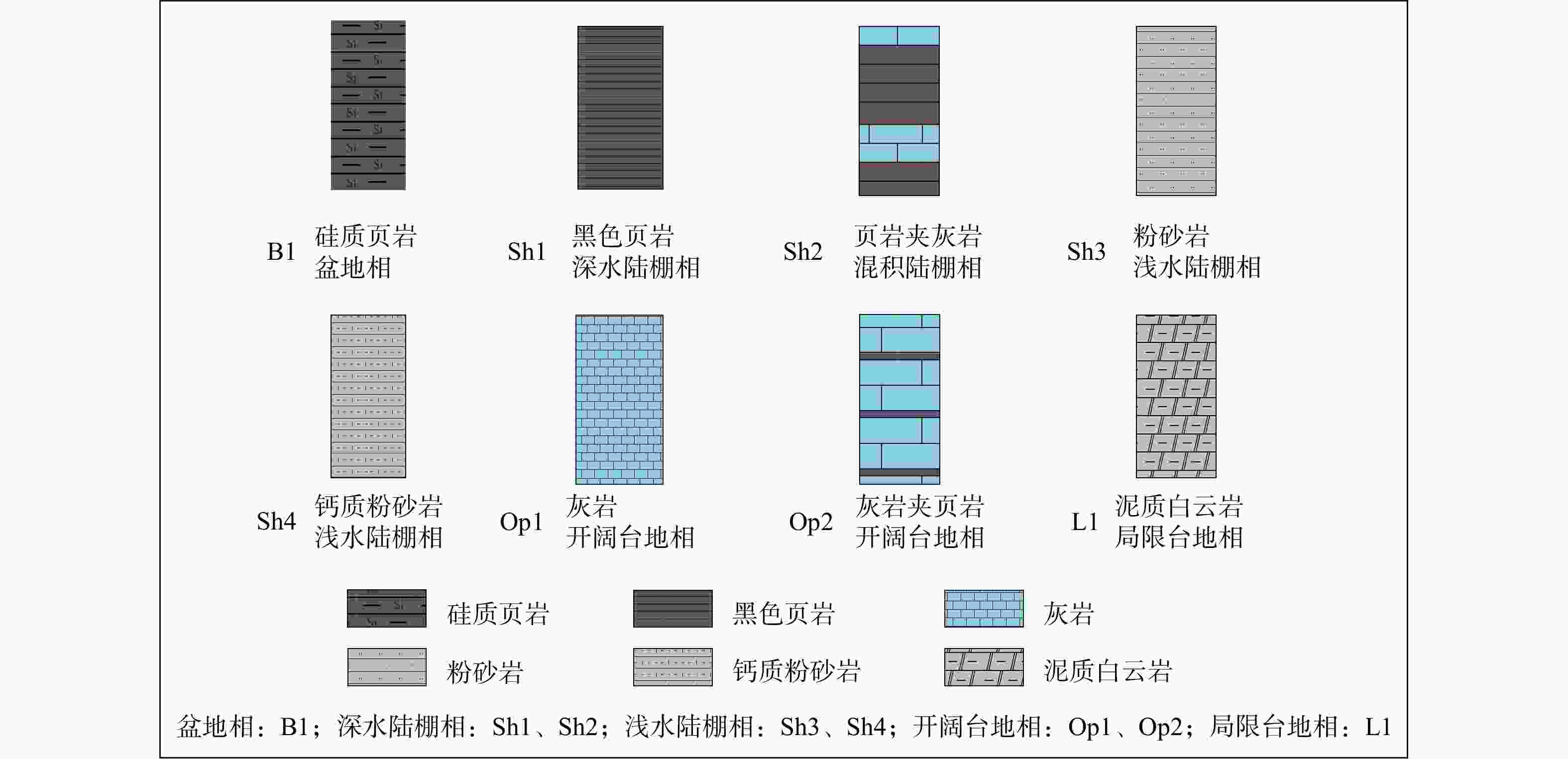
图 2 典型野外剖面露头岩石特征
a—宜昌鹤峰水井沱组与灯影组间平行不整合;b—宜昌滚石坳剖面水井沱组富有机质泥岩;c—宜昌滚石坳剖面水井沱组上部中—厚层灰岩夹薄层泥页岩;d—宜昌秭归泗溪剖面石牌组厚层灰黄色泥岩夹粉砂岩
Figure 2. Rock characteristics of typical outcrop sections
(a) Disconformity between the Shuijingtuo Formation and the Dengying Formation at the Hefeng section in Yichang; (b) Organic-rich mudstone of the Shuijingtuo Formation at the Gunshi'ao section in Yichang; (c) Upper part of the Shuijingtuo Formation at the Gunshi'ao section in Yichang, characterized by medium-to-thick-bedded limestone interbedded with thin layers of mudstone and shale; (d) Thick-bedded grayish–yellow mudstone intercalated with siltstone of the Shipai Formation at the Sixi section in Zigui, Yichang
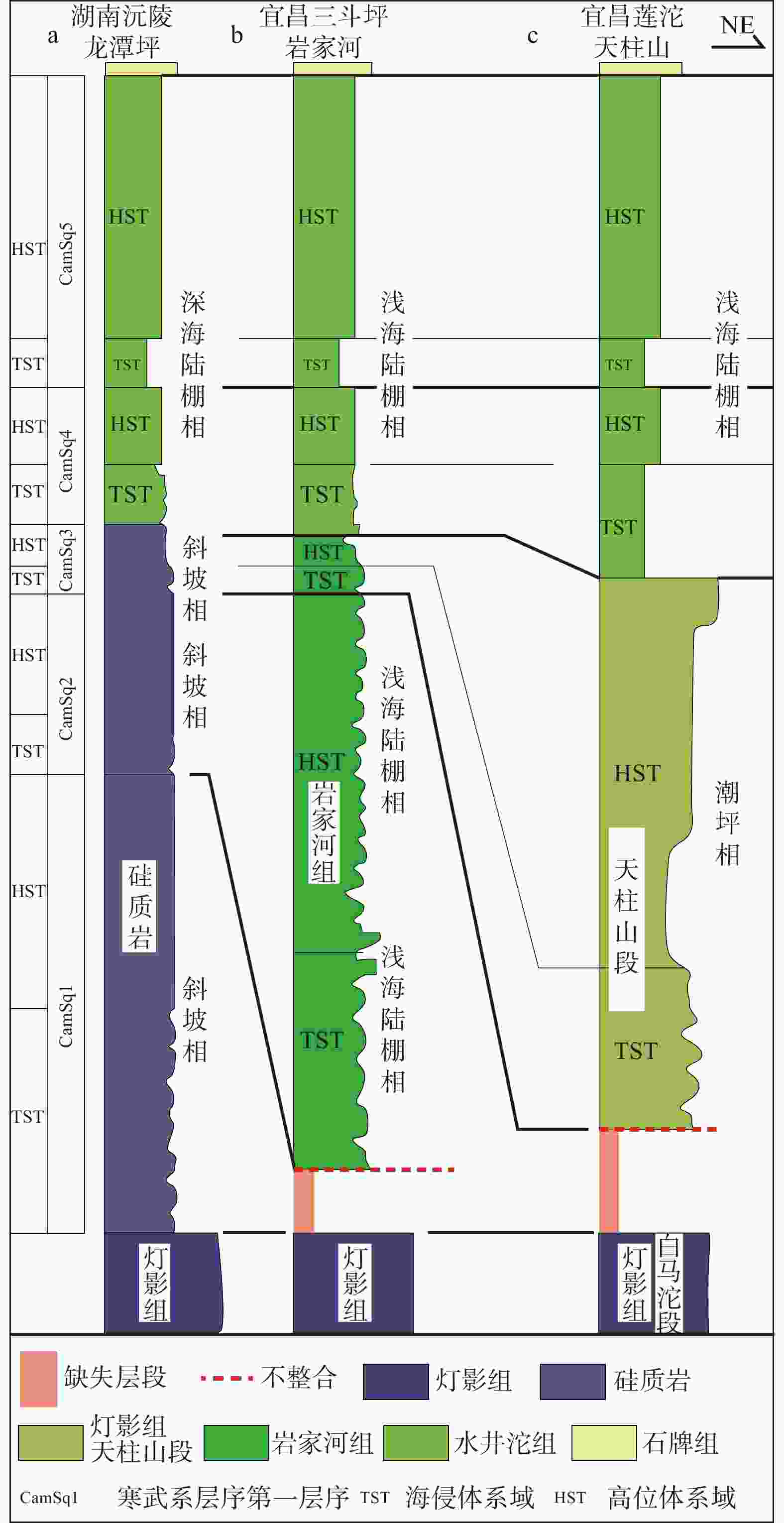
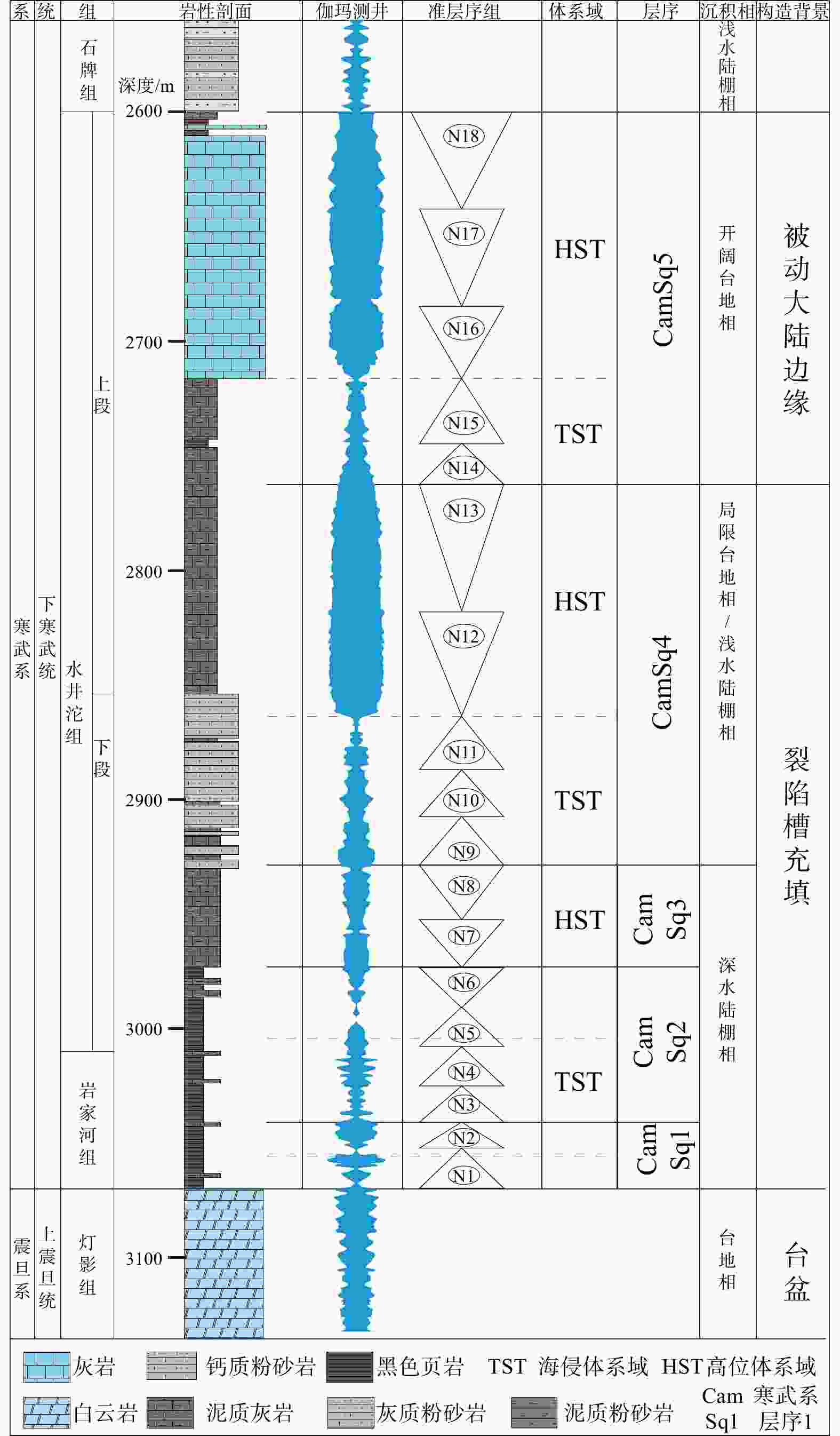
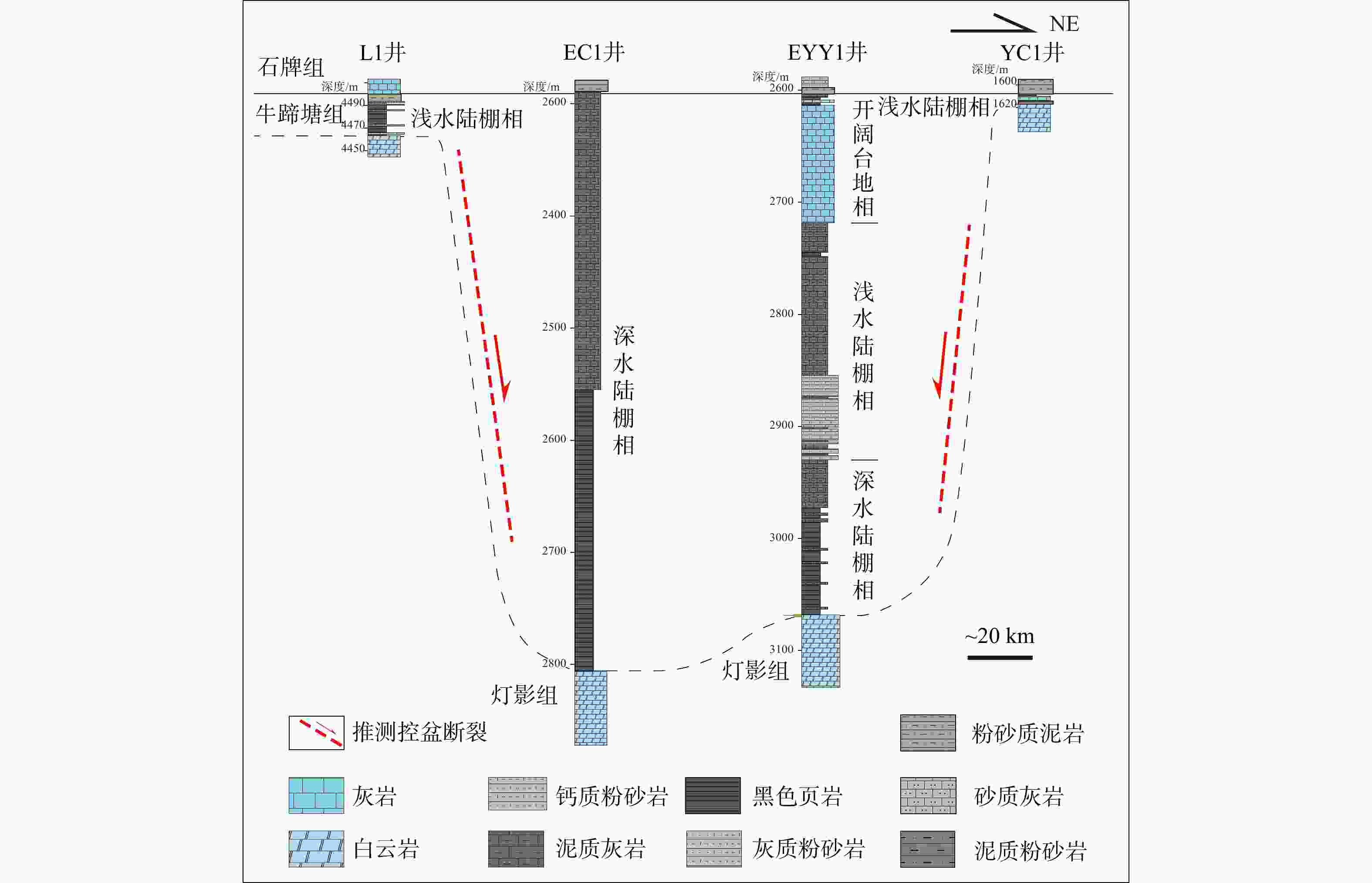
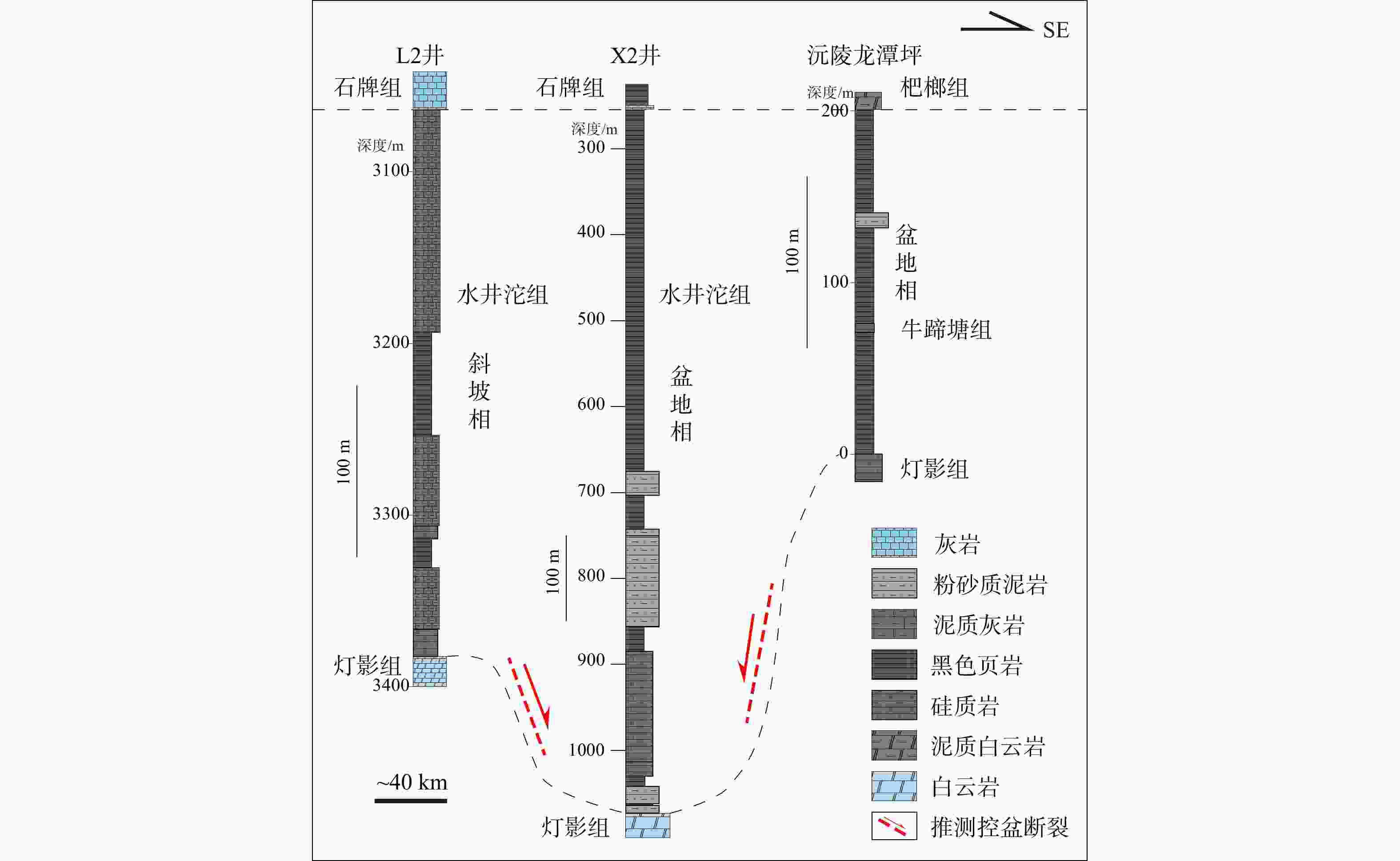
图 4 中扬子地区下寒武统层序地层划分柱状图(剖面位置见图1;据王传尚等,2012修改)
Figure 4. Sequence stratigraphic column of the Lower Cambrian in the Middle Yangtze Region (The location is shown in Fig.1; modified after Wang et al.,2012)
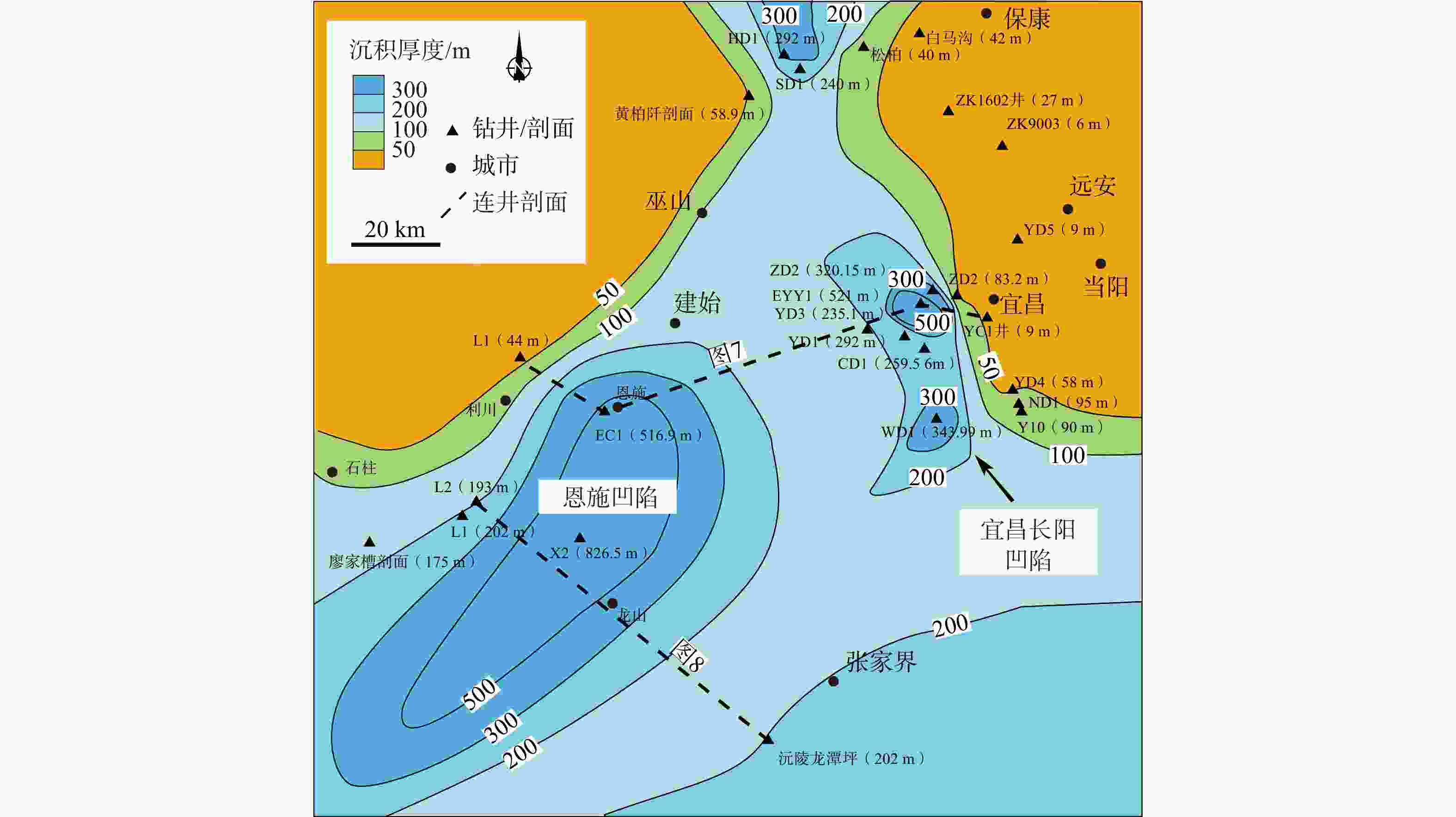
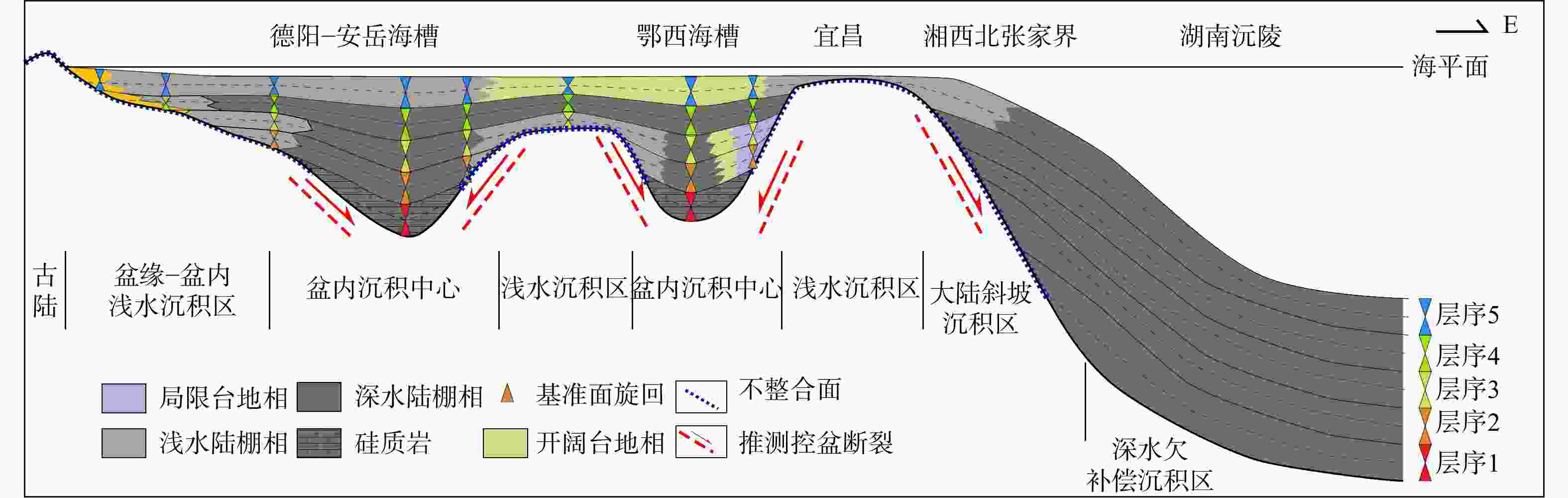
图 9 中上扬子地区下寒武统富有机质页岩沉积模式图(上扬子地区数据据刘忠宝等,2018修改)
Figure 9. Depositional model of Lower Cambrian organic-rich shales in the Middle–Upper Yangtze region (The data for the Upper Yangtze region are modified from Liu et al.,2018)
表 1 中上扬子地区下寒武统地层对比表
Table 1. Stratigraphic correlation of the Lower Cambrian in the Middle–Upper Yangtze region
系 四川盆地 黔北 中扬子 寒武系 沧浪铺组 沧浪铺组 石牌组 筇竹寺组 上段 牛蹄塘组 三段 水井沱组 上段 下段 二段 下段 麦地坪组 一段 岩家河组/天柱山段 震旦系 灯影组 灯影组 灯影组 -
[1] BAO S J, GE M N, ZHAO P R, et al., 2025. Status-quo, potential, and recommendations on shale gas exploration and exploitation in China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 46(2): 348-364. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] CHEN K, ZHAI G Y, BAO S J, et al., 2020. Tectonic evolution of the Huangling uplift and its control effect on shale gas preservation in South China[J]. Geology in China, 47(1): 161-172. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] CHEN K, LU Y X, LI F, et al., 2024. Sedimentary characteristics of Doushantuo Formation in middle-upper Yangtze Region and its significance for oil and gas geology[J]. Geological Survey of China, 11(5): 92-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] CHEN X, BU K, RUAN Y P, et al., 1997. Correlation between geologically marked climatic changes and extinctions[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 4(3-4): 123-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] CHEN X H, WEI K, ZHANG B M, et al., 2018. Main geological factors controlling shale gas reservoir in the Cambrian Shuijingtuo Formation in Yichang of Hubei Province as well as its and enrichment patterns[J]. Geology in China, 45(2): 207-226. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] DENG L, YAN Q R, YANG J, et al., 2025. Environmental drivers of biotic turnover: insight from tectono-sedimentary environment transition during the terminal Ediacaran to Early Cambrian[J]. Precambrian Research, 417: 107666. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2024.107666 [7] FENG Z Z, PENG Y M, JIN Z K, et al., 2001. Lithofacies palaeogeography of the Cambrian in South China[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 3(1): 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] FU Y, ZHOU W X, WANG H J, et al., 2021. The relationship between environment and geochemical characteristics of black rock series of Lower Cambrian in northern Guizhou[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(2): 536-548. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] GAO J, LI Y Q, HE S, et al., 2021. Exploration discovery of shale gas and its indicative significance to mineralization of MVT lead-zinc deposit in Yichang area, West Hubei[J]. Earth Science, 46(6): 2230-2245. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] GU H D, HU J, AN Z H, et al., 2021. Sedimentary characteristics of Doushantuo Formation in Shennongjia area: implications for "West Hubei Trough"[J]. Earth Science, 46(8): 2958-2972. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] GUO T L, DENG H C, ZHAO S, et al., 2025. Formation mechanisms and exploration breakthroughs of new type of shale gas in Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 52(1): 57-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] HAN W, JIANG X C, WANG J Q, et al., 2024. Tectonic evolution and geological conditions for the formation of Cambrian shale gas in Hanzhong area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 98(6): 1829-1839. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] HE Q, GAO J, DONG T, et al., 2021. Elemental geochemistry and paleo-environmental conditions of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang shale in western Hubei Province[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 39(3): 686-703. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] HE X, CHEN G S, WU J F, et al., 2022. Deep shale gas exploration and development in the southern Sichuan Basin: new progress and challenges[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 42(8): 24-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] LI L Y, TOPPER T P, BETTS M J, et al., 2023. Calcitic shells in the aragonite sea of the earliest Cambrian[J]. Geology, 51(1): 8-12. doi: 10.1130/G50533.1 [16] LIU Y Z, ZHAI G Y, XU X F, et al., 2022. Logging Identification of high quality shale of Niutitang Formation and Doushantuo Formation in western Hubei[J]. Earth Science, 47(5): 1791-1804. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] LIU Z B, GAO B, ZHANG Y Y, et al., 2017. Types and distribution of the shale sedimentary facies of the Lower Cambrian in Upper Yangtze area, South China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 44(1): 21-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] LIU Z B, DU W, GAO B, et al., 2018. Sedimentary model and distribution of organic-rich shale in the sequence stratigraphic framework: a case study of Lower Cambrian in Upper Yangtze Region[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 48(1): 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] MA Y S, CHEN H D, WANG G L, et al. , 2009. Sequence stratigraphy and paleogeography in Southern China[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) [20] MEI M X, ZHANG C, ZHANG H, et al., 2006a. Sequence-Stratigraphic frameworks and their forming backgrounds of paleogeography for the Lower Cambrian of the Upper-Yangtze Region[J]. Geoscience, 20(2): 195-208. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] MEI M X, ZHANG H, MENG X Q, et al., 2006b. Sequence stratigraphic division and framework of the Lower Cambrian in the Upper Yangtze Region[J]. Geology in China, 33(6): 1292-1304. (in Chinese with English abstract) [22] MEN Y P, YAN J F, QI M H, et al., 2020. Effects of bottom and top layers of Niutitang Formation on preservation of shale gas in southern Guizhou[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 40(1): 53-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] PAN X Q, HUA H, DAI Q K, et al., 2023. Fossil assemblages and their stratigraphic distribution in the Shuijingtuo Formation (Cambrian Series 2, Stage 3) in Yichang area, Hubei Province, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 30(3): 28-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] PANG W H, DING X Z, GAO L Z, et al., 2011. Characteristics of Sequence Stratigraphy and Plaeoenvironmental Evolution of Lower Cambrian strata in Hunan Province[J]. Geology in China, 38(3): 560-576. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] The Three Gorges Stratigraphic Research Group of Hubei Provincial Bureau of Geology, 1978. Paleontology of Sinian to Permian strata in the eastern Xiadong Region[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. (in Chinese) [26] WANG C S, LI X B, LI Z H, et al., 2012. Cambrian sequence-stratigraphy in the middle and Upper Yangtze platform[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 36(4): 773-783. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] WANG J G, CHEN D Z, WANG D, et al., 2012. Petrology and geochemistry of chert on the marginal zone of Yangtze platform, western Hunan, South China, during the Ediacaran-Cambrian transition[J]. Sedimentology, 59(3): 809-829. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.2011.01280.x [28] WANG X F, YAO H Z, 2019. Yangtze Basin, China: a unique fossil-lagerstatten for the Cambrian explosion and diverse radiation evolution in the world[J]. Journal of Central China Normal University (Natural Sciences), 53(6): 821-833. (in Chinese with English abstract) [29] WANG X L, 2004. Criteria for defining and recognizing the various orders of sequences in outcrop sequence stratigraphy[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 47(7): 618-629. doi: 10.1360/03yd0195 [30] WANG X F, NI S Z, ZENG Q L, et al. , 1987. Biostratigraphy of the Yangtze Gorges Area (2) Early Paleozoic Stratigraphy[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 43-142. (in Chinese) [31] WANG Z C, JIANG H, CHEN Z Y, et al., 2020. Tectonic Paleogeography of Late Sinian and its significances for petroleum exploration in the middle-upper Yangtze Region, South China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 47(5): 884-897. (in Chinese with English abstract) [32] WANG Z X, ZENG X W, MIAO F B, et al., 2023. Geochemical characteristics of elements and their geological significance in the boundary between Yanjiahe Formation and Shuijingtuo Formation of the Early Cambrian in Yichang area[J]. South China Geology, 39(2): 320-332. (in Chinese with English abstract) [33] XIA W J, DU S G, XU X H, et al. , 1994. Sinian lithofacies paleogeography and mineralization in South China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 50-61. (in Chinese) [34] XU S Q, YANG J L, LI F Q, et al., 1997. Sedimentary sequence and paleoenvironments of “Bianmachong Formation” in Early Cambrian in the boundary area of Sichuan, Guizhou and Hunan[J]. Earth Science——Journal of China University of Geosciences, 22(5): 520-525. (in Chinese with English abstract) [35] ZHAI G Y, WANG Y F, LIU G H, et al., 2020. Accumulation model of the Sinian-Cambrian shale gas in western Hubei Province, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(5): 696-713. (in Chinese with English abstract) [36] ZHANG G T, CHEN X H, WANG B Z, et al., 2022. Geochemical characteristics of black rock series in the transition zone between Sinian and Cambrian systems in the Xuefengshan area: implications for their provenances, paleoclimate and tectonic setting[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 41(2): 414-428. (in Chinese with English abstract) [37] ZHANG W T, LI J J, QIAN Y Y, et al., 1957. Cambrian and Ordovician Strata in Eastern Yangtze Gorge, Hubei[J]. Science Bulletin, (5): 145-146. (in Chinese) [38] ZHAO J H, JIN Z J, LIN C S, et al., 2019. Sedimentary environment of the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation shale in the Upper Yangtze Region[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 40(4): 701-715. (in Chinese with English abstract) [39] ZOU C N, ZHAO Z F, PAN S Q, et al., 2024. Unveiling the oldest industrial shale gas reservoir: insights for the enrichment pattern and exploration direction of Lower Cambrian shale gas in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Engineering, 42: 278-294. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2024.03.007 [40] 包书景, 葛明娜, 赵培荣, 等, 2025. 中国页岩气勘探开发现状、潜力与发展建议[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 46(2): 348-364. [41] 陈科, 翟刚毅, 包书景, 等, 2020. 华南黄陵隆起构造演化及其对页岩气保存的控制作用[J]. 中国地质, 47(1): 161-172. [42] 陈科, 卢妍欣, 李飞, 等, 2024. 中上扬子地区陡山沱组沉积特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 中国地质调查, 11(5): 92-103. [43] 陈孝红, 危凯, 张保民, 等, 2018. 湖北宜昌寒武系水井沱组页岩气藏主控地质因素和富集模式[J]. 中国地质, 45(2): 207-226. [44] 陈旭, 布科, 阮亦萍, 等, 1997. 显生宙全球气候变化与生物绝灭事件的联系[J]. 地学前缘, 4(3-4): 123-128. [45] 冯增昭, 彭勇民, 金振奎, 等, 2001. 中国南方寒武纪岩相古地理[J]. 古地理学报, 3(1): 1-14. [46] 付勇, 周文喜, 王华建, 等, 2021. 黔北下寒武统黑色岩系的沉积环境与地球化学响应[J]. 地质学报, 95(2): 536-548. [47] 高键, 李英强, 何生, 等, 2021. 鄂西宜昌地区页岩气勘探发现对MVT铅锌矿成矿的指示意义[J]. 地球科学, 46(6): 2230-2245. [48] 谷昊东, 胡军, 安志辉, 等, 2021. 神农架陡山沱组沉积特征及其对“鄂西海槽”的启示[J]. 地球科学, 46(8): 2958-2972. [49] 郭彤楼, 邓虎成, 赵爽, 等, 2025. 四川盆地寒武系筇竹寺组新类型页岩气形成机理与勘探突破[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 52(1): 57-69. [50] 韩伟, 蒋兴超, 王建强, 等, 2024. 汉中地区构造演化及寒武系页岩气形成地质条件研究[J]. 地质学报, 98(6): 1829-1839. [51] 何庆, 高键, 董田, 等, 2021. 鄂西地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩元素地球化学特征及沉积古环境恢复[J]. 沉积学报, 39(3): 686-703. [52] 何骁, 陈更生, 吴建发, 等, 2022. 四川盆地南部地区深层页岩气勘探开发新进展与挑战[J]. 天然气工业, 42(8): 24-34. [53] 湖北省地质局三峡地层研究组, 1978. 峡东地区震旦纪至二迭纪地层古生物[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. [54] 刘俞佐, 翟刚毅, 徐笑丰, 等, 2022. 鄂西地区牛蹄塘组和陡山沱组优质页岩测井识别[J]. 地球科学, 47(5): 1791-1804. [55] 刘忠宝, 高波, 张钰莹, 等, 2017. 上扬子地区下寒武统页岩沉积相类型及分布特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 44(1): 21-31. [56] 刘忠宝, 杜伟, 高波, 等, 2018. 层序格架中富有机质页岩发育模式及差异分布: 以上扬子下寒武统为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 48(1): 1-14. [57] 马永生, 陈洪德, 王国力, 等, 2009. 中国南方层序地层与古地理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. [58] 梅冥相, 张丛, 张海, 等, 2006a. 上扬子区下寒武统的层序地层格架及其形成的古地理背景[J]. 现代地质, 20(2): 195-208. [59] 梅冥相, 张海, 孟晓庆, 等, 2006b. 上扬子区下寒武统的层序地层划分和层序地层格架的建立[J]. 中国地质, 33(6): 1292-1304. [60] 门玉澎, 闫剑飞, 戚明辉, 等, 2020. 黔南地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩气顶底板特征研究[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 40(1): 53-59. [61] 潘晓强, 华洪, 代乔坤, 等, 2023. 宜昌地区寒武系水井沱组(第二统第三阶)生物组合面貌及其地层分布[J]. 地学前缘, 30(3): 28-43. [62] 庞维华, 丁孝忠, 高林志, 等, 2011. 湖南下寒武统层序地层特征与古环境演化变迁[J]. 中国地质, 38(3): 560-576. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.03.006 [63] 王传尚, 李旭兵, 李志宏, 等, 2012. 中上扬子区寒武纪层序地层划分与对比[J]. 地层学杂志, 36(4): 773-783. [64] 汪啸风, 倪世钊, 曾庆銮, 等, 1987. 长江三峡地区生物地层学(二)早古生代分册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 43-142. [65] 汪啸风, 姚华舟, 2019. 中国扬子海盆: 世界上罕见寒武纪生命大爆发和辐射进化的化石库[J]. 华中师范大学学报(自然科学版), 53(6): 821-833. [66] 汪泽成, 姜华, 陈志勇, 等, 2020. 中上扬子地区晚震旦世构造古地理及油气地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 47(5): 884-897. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.05.04 [67] 汪宗欣, 曾雄伟, 苗凤彬, 等, 2023. 湖北宜昌早寒武世岩家河组-水井沱组界线元素地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 华南地质, 39(2): 320-332. [68] 夏文杰, 杜森官, 徐新煌, 等, 1994. 中国南方震旦纪岩相古地理与成矿作用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 50-61. [69] 徐世球, 杨家騄, 李富强, 等, 1997. 川黔湘交境早寒武世“变马冲组”沉积层序与古环境[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 22(5): 520-525. [70] 翟刚毅, 王玉芳, 刘国恒, 等, 2020. 鄂西地区震旦系—寒武系页岩气成藏模式[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(5): 696-713. [71] 张国涛, 陈孝红, 王保忠, 等, 2022. 雪峰山地区震旦系-寒武系之交黑色岩系地球化学特征: 物源、气候与构造背景[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 41(2): 414-428. [72] 张文堂, 李积金, 钱义元, 等, 1957. 湖北峡东寒武纪及奥陶纪地层[J]. 科学通报, (5): 145-146. [73] 赵建华, 金之钧, 林畅松, 等, 2019. 上扬子地区下寒武统筇竹寺组页岩沉积环境[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 40(4): 701-715. -




 下载:
下载: