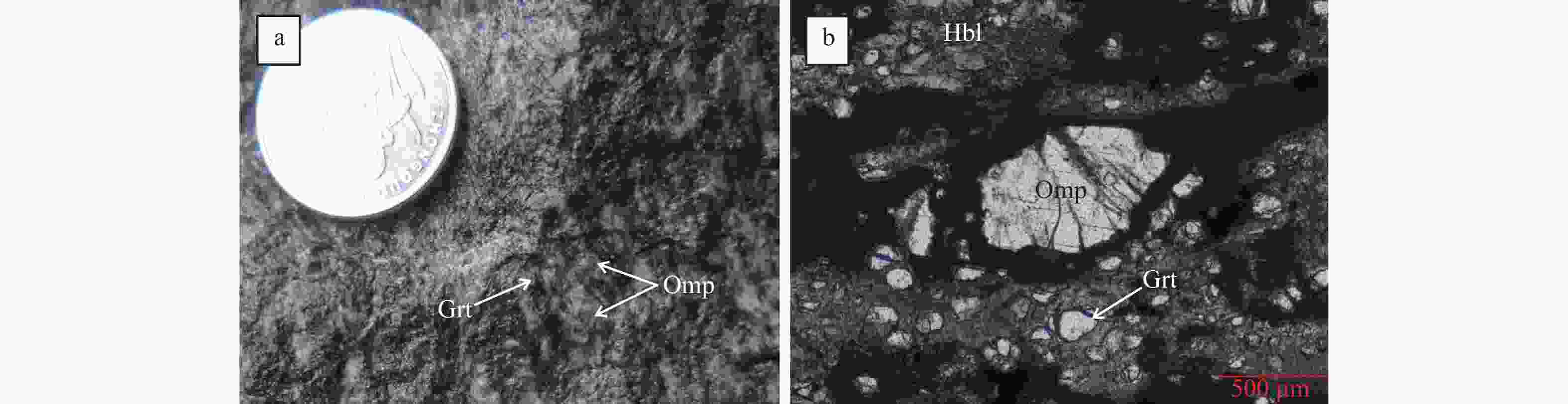
Recognition of eclogites in the Huangzhuling area of eastern Hainan Island
-
-
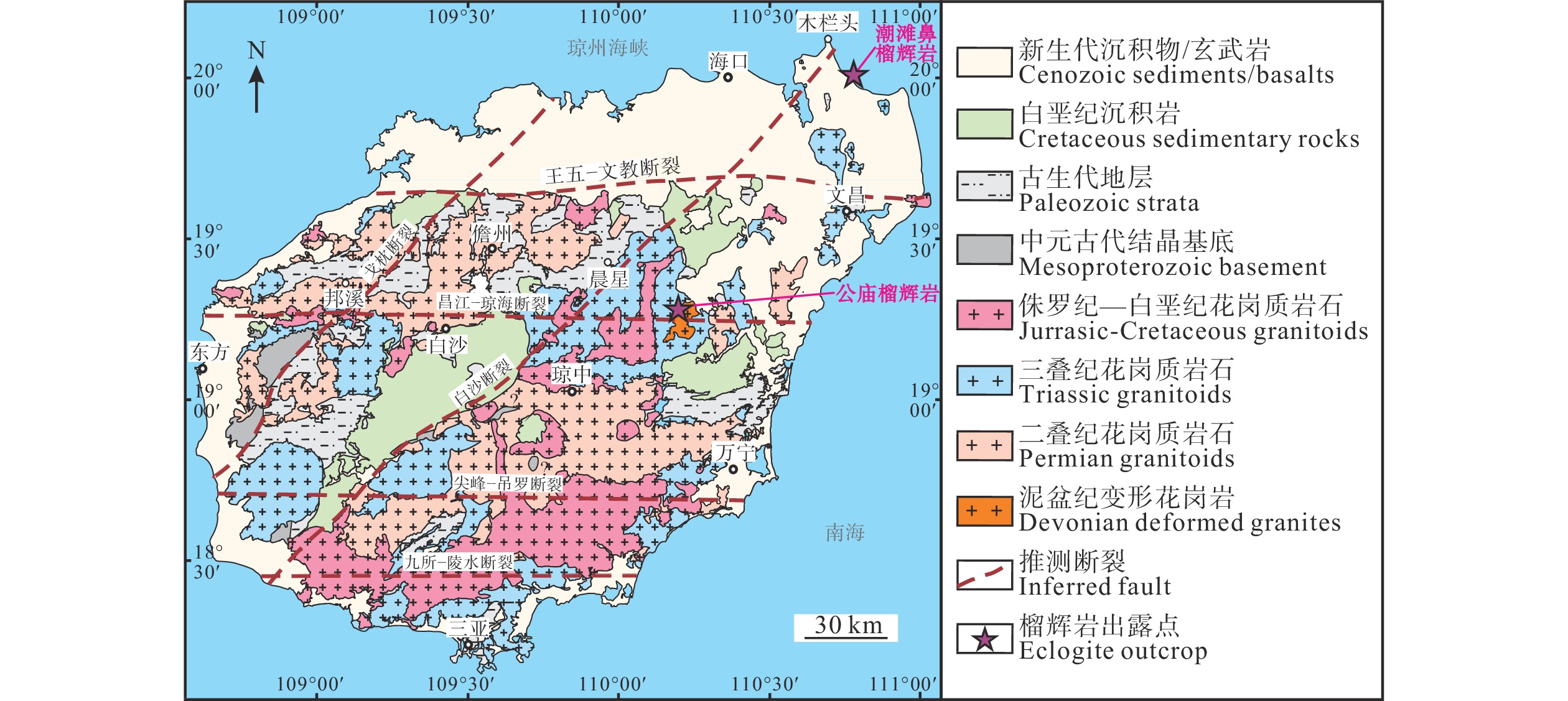
图 1 海南岛地质简图及榴辉岩的出露位置(据海南省地质调查院, 2017; Shen et al., 2018修改)
Figure 1. Simplified geological map of Hainan Island and exposed locations of eclogites (modified after Hainan Institute of Geological Survey, 2017; Shen et al., 2018)
-
[1] Hainan Institute of Geological Survey, 2017. Regional geology of China, Hainan Province[M]. Beijing: Geology Press: 1-908. (in Chinese) [2] LIU X C, CHEN Y, WANG W, et al., 2021. Carboniferous eclogite and garnet-omphacite granulite from northeastern Hainan Island, South China: Implications for the evolution of the eastern Palaeo-Tethys[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 39(1): 101-132. doi: 10.1111/jmg.12563 [3] LIU X C, HU J, CHEN L Y, et al., 2021. Oceanic-type high-temperature eclogites from Hainan Island, South China: general characteristics and unsolved problems[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 37(1): 143-161. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.01.10 [4] SHEN L W, YU J H, O’REILLY S Y, et al., 2018. Subduction-related middle Permian to early Triassic magmatism in central Hainan Island, South China[J]. Lithos, 318-319: 158-175. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2018.08.009 [5] ZHOU D, HU J, WANG L, et al. , 2021. Geological map of the Huangzhuling area in Hainan Province (1: 50 000 scale)[Z]. China Geological Survey. (in Chinese) [6] 海南省地质调查院,2017. 中国区域地质志·海南志[M]. 北京:地质出版社:1-908. [7] 刘晓春,胡娟,陈龙耀,等,2021. 海南洋壳型高温榴辉岩:基本特征及待解问题[J]. 岩石学报,37(1):143-161. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.01.10 [8] 周岱,胡军,王磊,等,2021. 海南黄竹岭地区1:50000地质图[Z]. 中国地质调查局. -




 下载:
下载: