Diagenesis of microbial dolomite reservoirs in the second Member of Dengying Formation of Ediacaran in the Penglai area, Sichuan Basin: Insights into the formation and evolution of high-quality reservoirs
-
摘要: 四川盆地蓬莱地区埃迪卡拉系灯影组二段(灯二段)微生物岩广泛分布,被视为深层碳酸盐岩的潜在油气勘探目标。与常规的孔隙型和岩溶缝洞型优质储层不同,灯二段碳酸盐岩主要由微生物白云岩组成,其优质储层成因及成岩演化过程尚不清晰。研究基于野外露头和钻井取芯资料,结合岩石薄片、扫描电镜、阴极发光、CT扫描等测试手段,对灯影组微生物岩白云岩储层进行详细分析,旨在深入理解成岩作用对孔隙形成及优质储层发育的影响。研究结果显示,研究区微生物岩储层以低孔、特低渗,裂缝−孔隙(洞)型微生物石白云岩为主,储集空间以粒间溶孔、残余格架溶孔、粒内溶孔及中小型溶洞为主,并发育少量晶间孔及晶间溶孔;灯二段经历了多种成岩作用的叠加改造,其准同生溶蚀及早表生溶蚀作用是提高孔隙度的关键因素。研究成果加深了对四川盆地埃迪卡拉系微生物岩优质储层成因的认识,为四川盆地深层油气勘探开发提供了有益信息。Abstract:
Objective The microbial dolomite of the second Member of the Dengying Formation(Deng 2 Member) in the Penglai area of the Sichuan Basin is widely distributed and considered a potential target for deep carbonate oil and gas exploration. Unlike conventional high-quality reservoirs characterized by porosity and karst fractures, the carbonate rocks of the Deng 2 Member mainly consist of microbial dolomite. The genesis and diagenetic evolution of these high-quality reservoirs remain unclear. Methods This study employed petrographic thin sections, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), cathodoluminescence, and computed tomography (CT)scanning to conduct a detailed analysis of the microbial dolomite reservoirs in the Dengying Formation, using field outcrop and core samples. The aim was to gain a deeper understanding of the effects of diagenesis on pore formation and the development of high-quality reservoirs. Results and Conclusion The microbial carbonate reservoirs in the study area were characterized by low porosity and very low permeability, predominantly consisting of fracture-porosity (cavity) type microbial dolomite. The reservoir space was primarily composed of intergranular dissolution pores, residual framework dissolution pores, intragranular dissolution pores, and small to medium-sized dissolution cavities, with minor occurrences of intercrystalline pores and intercrystalline dissolution pores. The Deng 2 Member has undergone multiple diagenetic processes; penecontemporaneous dissolution and early epigenetic dissolution were key factors in enhancing porosity. Significance These findings enhance the understanding of the genesis of high-quality microbial carbonate reservoirs in the Ediacaran System of the Sichuan Basin and provide valuable information for deep oil and gas exploration and development in the region. -
Key words:
- reservoir genesis /
- microbial dolomite /
- Dengying Formation /
- Penglai area /
- Sichuan Basin
-
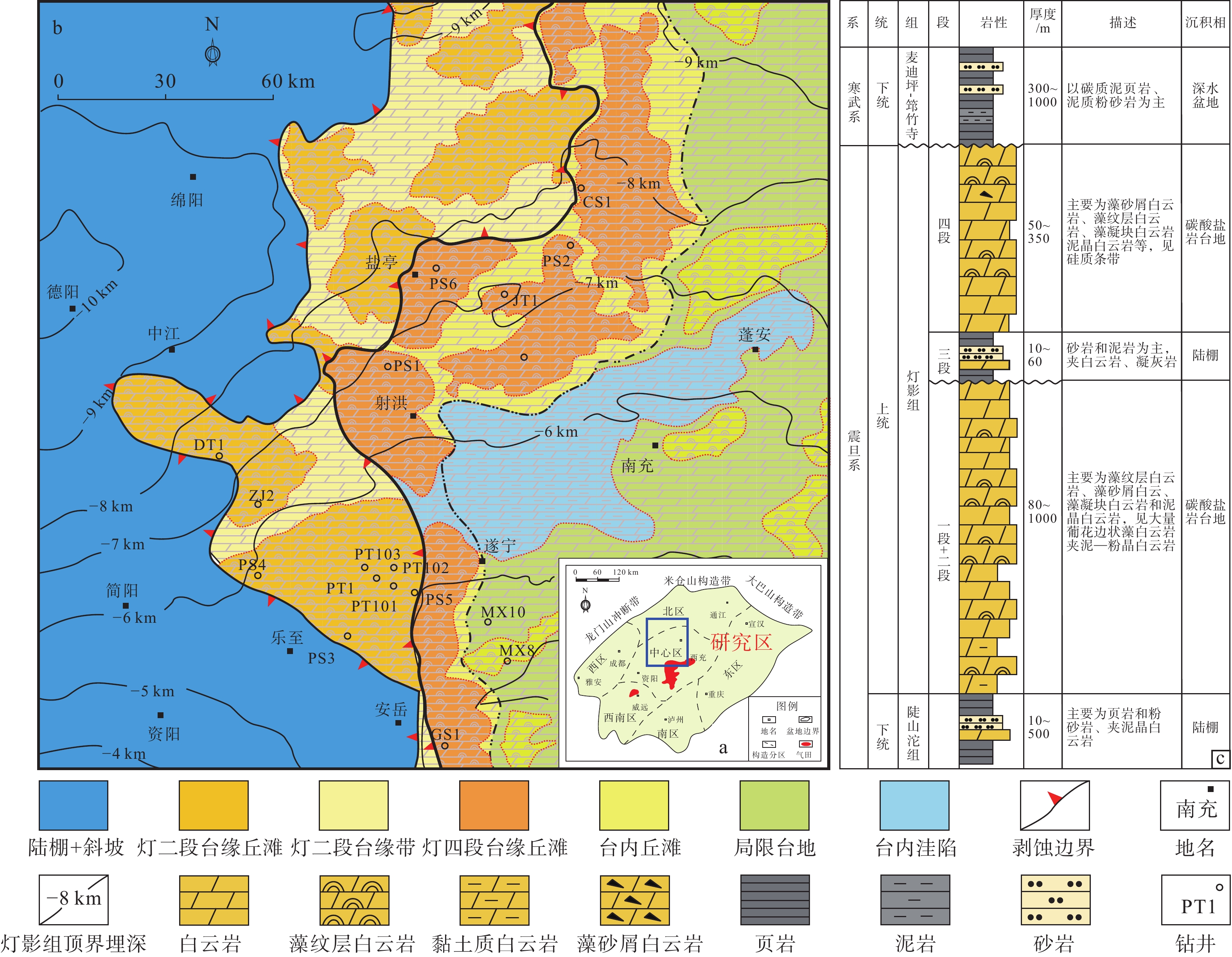
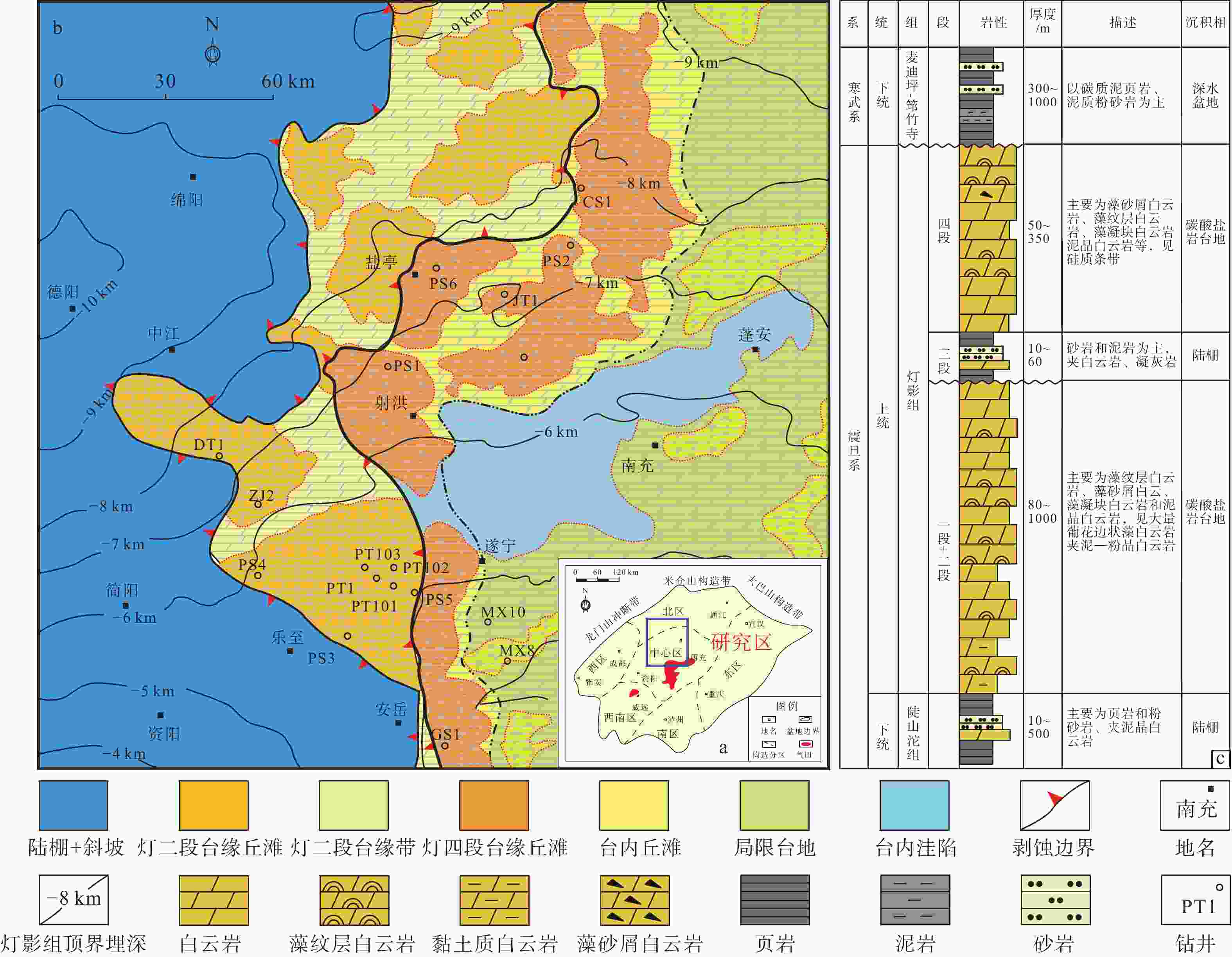
图 1 研究区位置及构造和地层发育特征
a—四川盆地轮廓及蓬莱气区位置图(Wang et al.,2019);b—蓬莱气区埃迪卡拉系灯影组优势相带平面分布图;c—蓬莱气区埃迪卡拉系灯影组综合柱状图(据文龙等,2023修改)
Figure 1. The location of the study area and the characteristics of tectonic and stratigraphic development
(a) Contour map of Sichuan Basin and location of the Penglai gas field (Wang et al., 2019); (b) Plane distribution map of the dominant facies of Dengying Formation in the Penglai gas area; (c) Comprehensive histogram of the Ediacaran Dengying Formation in the Penglai gas area (modified according to Wen et al., 2023)
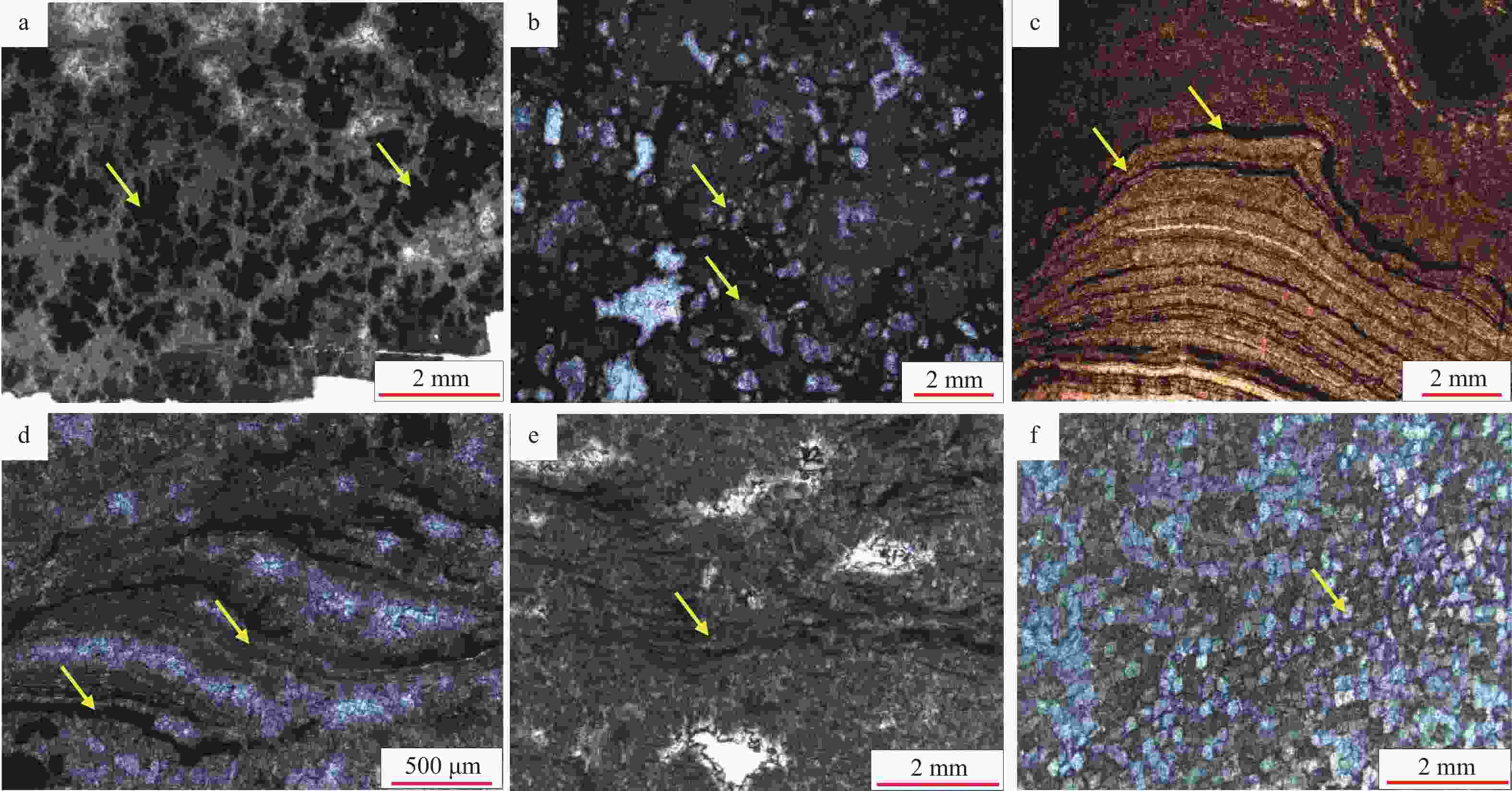
图 2 蓬莱地区灯影组二段岩石薄片特征
a—凝块石云岩,黄色箭头为藻凝块,蓬探101井5750.93 m,单偏光;b—泡沫绵层白云岩,黄色箭头为泡沫棉层,中深102井6056.47 m,单偏光;c—叠层石云岩,黄色箭头为叠层构造,蓬深4井6185.70~6185.91 m,单偏光;d—微生物纹层云岩,早期孔隙被充填,黄色箭头为微生物纹层,蓬探101井5765.36 m,单偏光;e—粉晶云岩,局部见藻纹层,孔洞发育,黄色箭头为微生物纹层,蓬探101井5751.82 m,单偏光;f—细晶白云岩,黄色箭头为细晶白云石,蓬探101井5744.40 m,正交偏光
Figure 2. Microscopic rock thin section characteristics of the second Member of Dengying Formation in the Penglai area
(a) Clotted dolomite, algae clots (yellow arrows), Well Pengtan 101 5750.93 m, under plane-polarized light; (b) Foam spongy dolomite, foam structure (yellow arrows), Well Zhongshen 102 6056.47 m, under plane-polarized light; (c) Stromatolite dolomite, laminated structure (yellow arrows), Well Pengshen 4 6185.70~6185.91 m, under plane-polarized light; (d) Microbial laminated dolomite, early pores were filled, microbial laminae (yellow arrows), Well Pengtan 101 5765.36 m, under plane-polarized light; (e) Powder crystal dolomite, with localized algal laminations and developed pores, microbial laminae (yellow arrows), Well Pengtan 101 5751.82 m, under plane-polarized light; (f) Fine crystalline dolomite, fine crystalline dolomite (yellow arrows), Well Pengtan 101 5744.40 m, under cross-polarized light
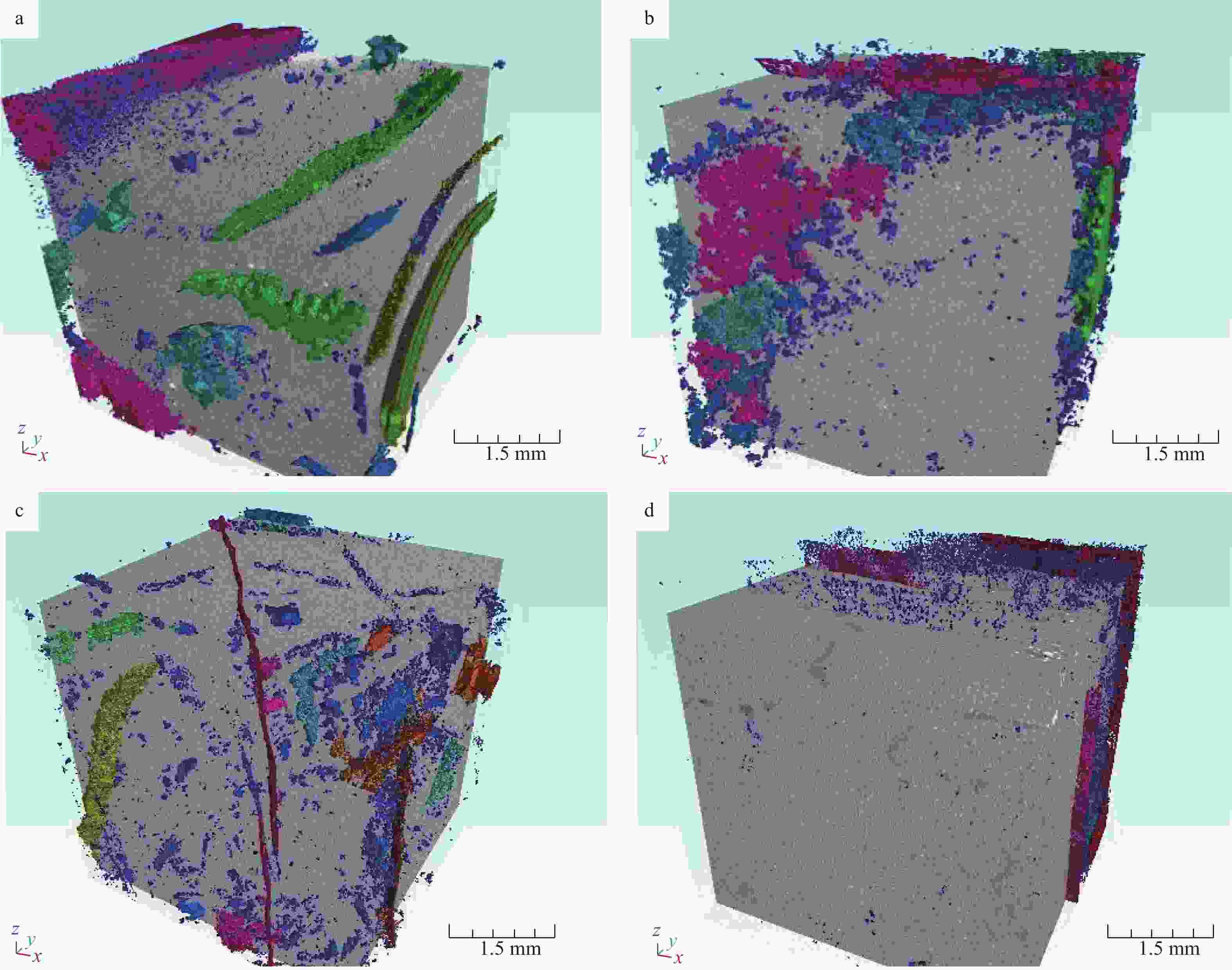
图 3 蓬莱地区灯影组二段岩石CT扫描结果
a—储集空间包括溶洞(红色)、溶孔(蓝色)、裂缝(绿色),孔隙度为11.72%,蓬探101井5757.86 m;b—储集空间包括溶洞(红色)、溶孔(蓝色),孔隙度9.94%,蓬探101井5762.05 m;c—储集空间主要为溶孔(蓝色),少量微裂缝(红色),孔隙度4.13%,蓬探102井5863.38 m;d—储集空间以溶孔(蓝色)为主,孔隙度2.25%,蓬探101井5881.37 m
Figure 3. Computed tomography (CT) scan results of rocks in the second Member of Dengying Formation in the Penglai area
(a) The reservoir space includes caves (red), pores (blue), and fractures (green), with a porosity of 11.72 %, Well Pengtan 101 5757.86 m.; (b) The reservoir space includes caves (red) and pores (blue), with a porosity of 9.94 %, Well Pengtan 101 5762.05 m ; (c) The reservoir reservoir space is mainly pores (blue), a small amount of fractures (red), with a porosity of 4.13 %, Well Pengtan 102l 5863.38 m; (d) The reservoir space is dominated by pores (blue), with a porosity of 2.25 %, Well Pengtan 101 5881.37 m
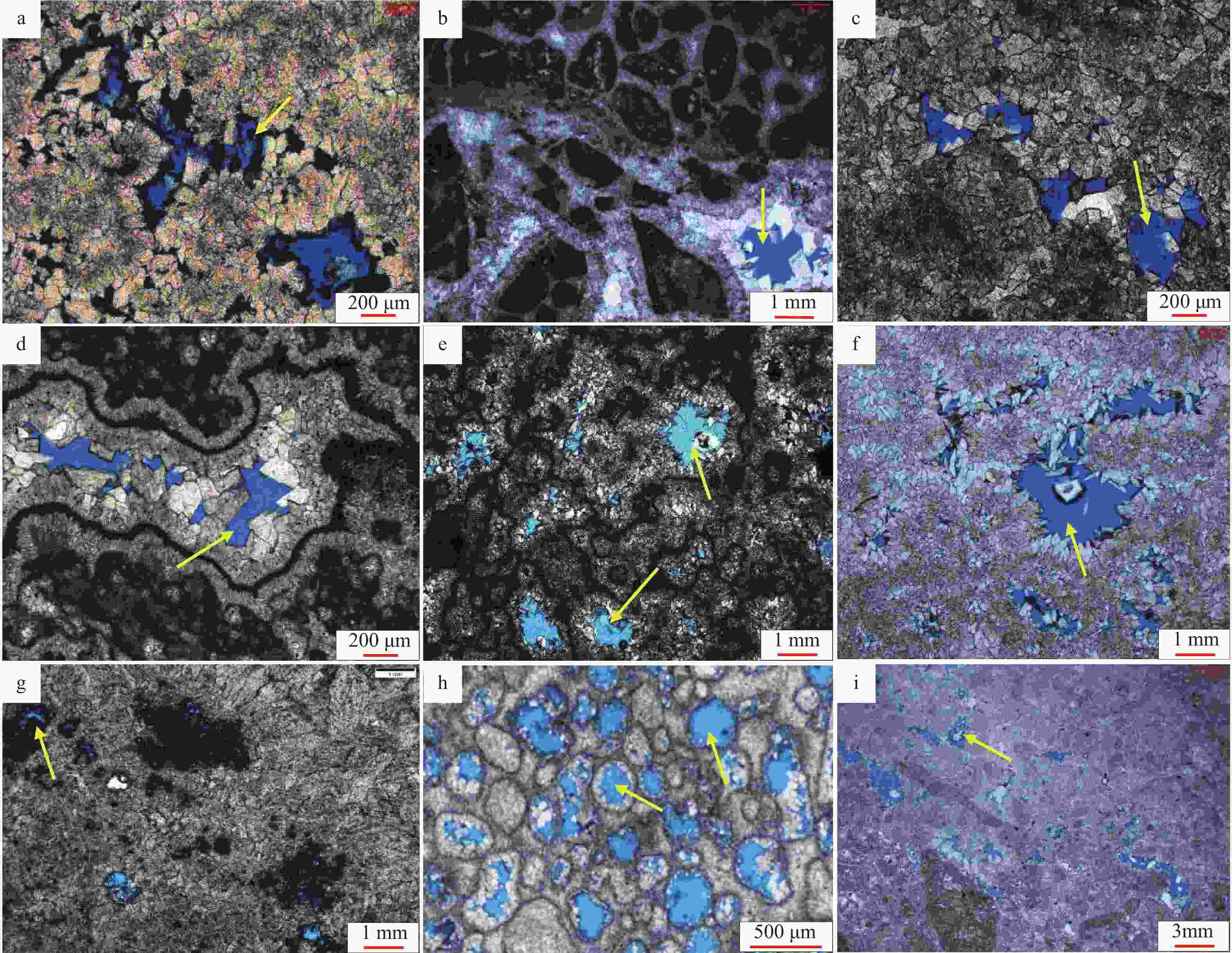
图 4 蓬莱地区灯影组二段岩石铸体薄片特征
a—凝块石白云岩,粒间溶孔,蓬探103井5943.69 m,黄色箭头为粒间溶孔;b—凝块石白云岩,见残余粒间溶孔,蓬深5井5669.00 m,黄色箭头为残余粒间溶孔;c—藻屑白云岩,粒间溶孔发育,蓬探1井5734.51 m,黄色箭头为粒间溶孔;d—凝块石白云岩,残余格架孔,蓬探1井5774.45 m,黄色箭头为残余格架孔;e—凝块石白云岩,残余格架孔发育,蓬深5井5711.84 m,黄色箭头为残余格架孔;f—粉晶—细晶白云岩,晶间孔较发育,中深102井6037.00 m,黄色箭头为晶间孔;g—凝块石白云岩,粒内溶孔,面孔率5%,蓬探101井5729.29 m,黄色箭头为粒内溶孔;h—藻泡沫绵层白云岩,铸模孔发育,面孔率15%,蓬探1井5731.25 m,黄色箭头为铸模孔;i—砂屑白云岩,粒内溶孔较发育,面孔率3%~5%,中深103井5883.66 m,黄色箭头为粒内孔
Figure 4. Characteristics of rock cast thin sections of the second Member of of Dengying Formation in the Penglai area
(a) Tuff dolomite, intergranular dissolved pores, Well Pengtan 103 5943.69 m, intergranular pores (yellow arrows); (b) Thrombolite dolomite, with residual intergranular dissolved pores, Well Pengshen 5 5669.00 m, residual intergranular pores (yellow arrows) ; (c) Algae dolomite, intergranular dissolved pore development, Well Pengtan 1 5734.51 m, intergranular pores (yellow arrows); (d) Tuff dolomite, residual framework hole, Well Pengtan 1 5774.45 m, residual grid holes (yellow arrows); (e) Tuff dolomite, residual framework hole development, Well Pengshen 5 5711.84 m, residual grid holes (yellow arrows); (f) Powder-fine grained dolomite, intergranular pores are more developed, Well Zhongshen 102 6037.00 m, intercrystalline pores (yellow arrows); (g) Tuff dolomite, intragranular dissolved pores, face rate of 5 %, Well Pengtan 101 5729.29 m, intragranular pores (yellow arrows); (h) Algae foam spongy dolomite, mold hole development, the surface porosity is 15 %, Well Pengtan 1 5731.25 m, mold hole (yellow arrows); (i) Sandy dolomite, intragranular dissolved pores are more developed, the surface porosity is 3%−5%, Well Zhongshen 103 5883.66 m, intragranular pores (yellow arrows)
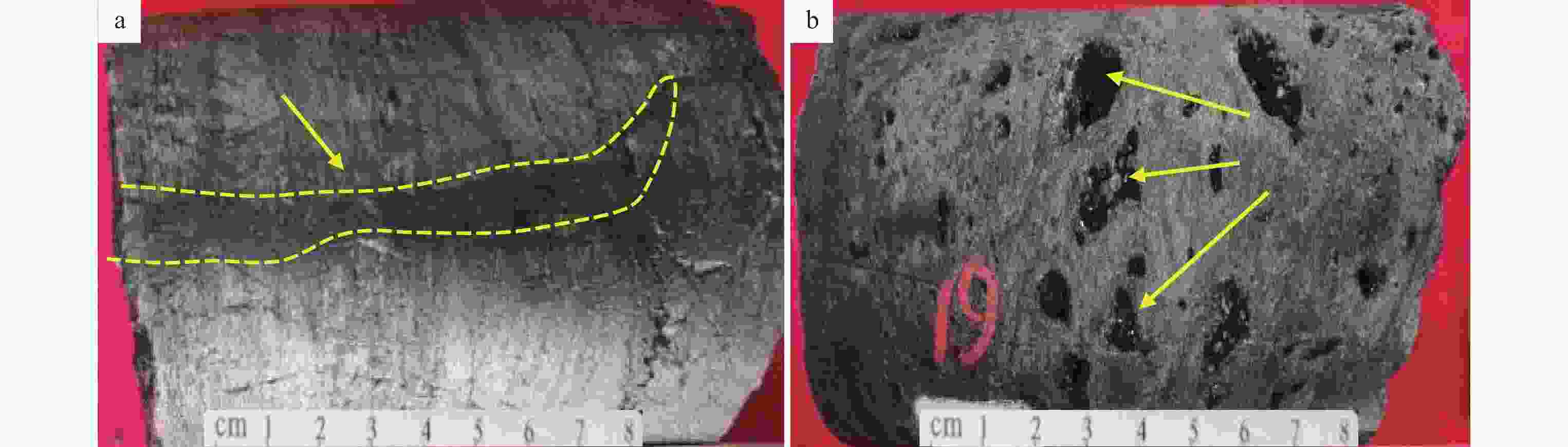
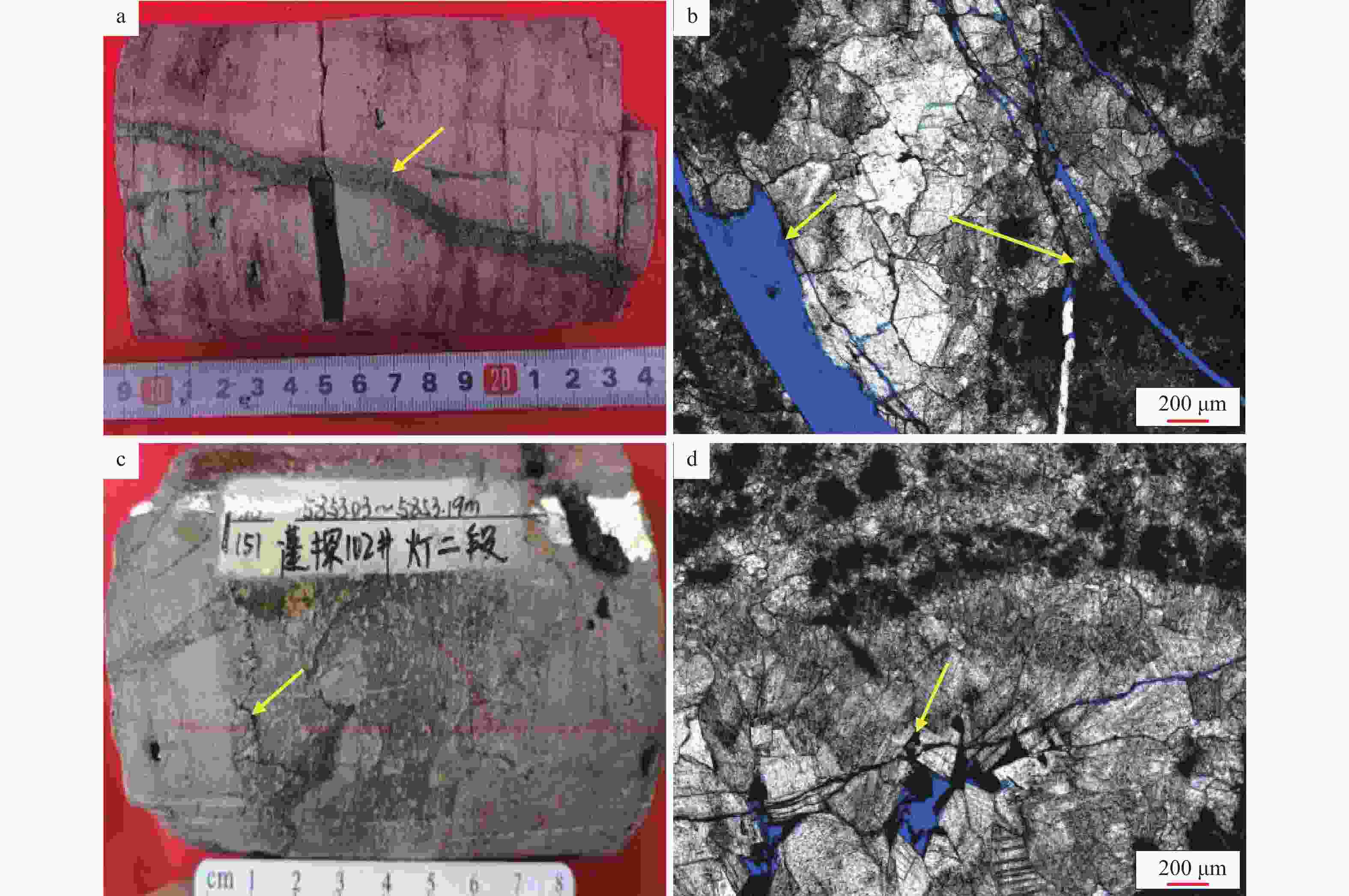
图 5 蓬莱地区灯影组二段储层溶蚀孔发育特征
a—凝块石白云岩,溶沟被泥质半充填—近全充填,蓬探101井5712.65~5712.79 m,黄色箭头指向溶沟充填;b—凝块石白云岩,蜂窝状溶洞,蓬探101井5773.13~5773.33 m,黄色箭头指向蜂窝状溶洞
Figure 5. Characteristics of dissolution pore development of the second Member of Dengying Formation in the Penglai area
(a) Condensate dolomite, karst ditch is semi-filled by mud-nearly full-filled, Well Pengtan 101 5712.65−5712.79 m, filled karst gully (yellow arrows); (b) Tuff-dolomite, honeycomb-shaped cave, Well Pengtan 101 5773.13−5773.33 m, honeycomb-shaped cave (yellow arrow)
图 6 蓬莱地区灯影组二段裂缝发育特征
a—砂屑白云岩,高角度裂缝发育,蓬探1井5729.80~5729.85 m,黄色箭头指向高角度裂缝;b—凝块石白云岩,多期构造缝发育,蓬探1井5785.59 m,黄色箭头指向构造裂缝;c—凝块石白云岩,压溶缝及溶沟,蓬探103井5734.07~5734.27 m,黄色箭头指向压溶缝;d—凝块石白云岩,裂缝切穿孔隙,蓬探1井5780.84 m,黄色箭头指向孔隙被裂缝切穿
Figure 6. Fracture development characteristics of the second Member of Dengying Formation in the Penglai area
(a) Sandy dolomite, high angle fracture development, Well Pengtan 1 5729.80m to 5729.85 m, high-angle fracture (yellow arrows); (b) Tuff dolomite, multi-stage structural fracture development, Well Pengtan 1 5785.59 m, structural fractures (yellow arrows); (c) Tuff dolomite, pressure solution fracture and solution ditch, Well Pengtan 103 5734.07 m to 5734.27 m, pressure dissolved pores (yellow arrow); (d) Tuff dolomite, fractures cut through pores, Well Pengtan 1 5780.84 m, pores cut through by cracks (yellow arrows)
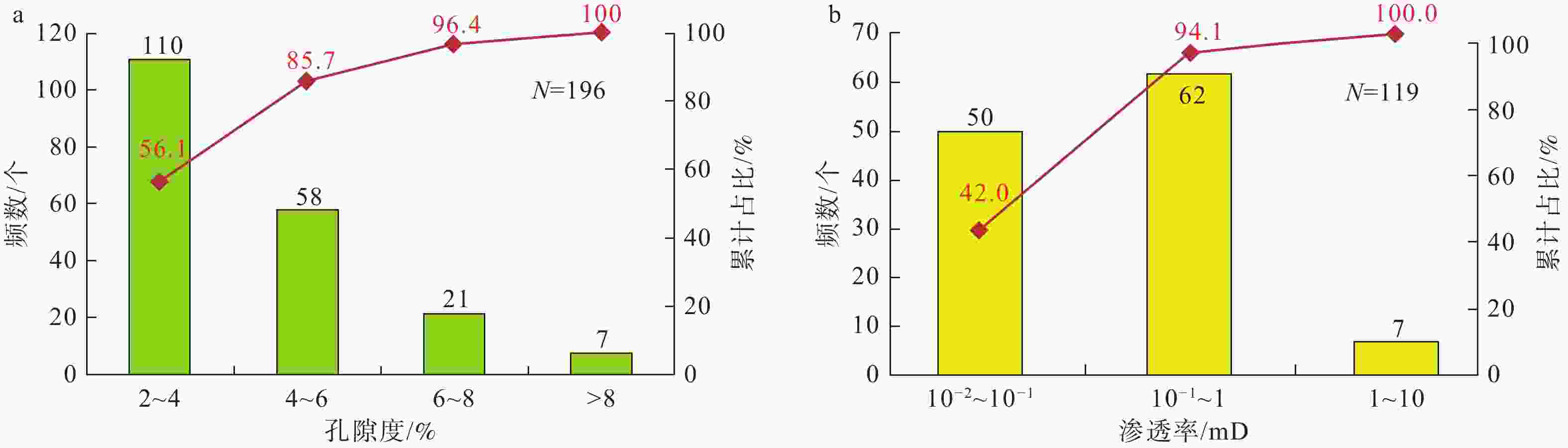
图 7 蓬莱地区灯影组二段储层孔隙度和渗透率分布直方图
a—全直径岩芯孔隙度频率分布直方图;b—全直径岩芯样渗透率频率直方图
Figure 7. Porosity and permeability distribution histogram of reservoir in the second Member of Dengying Formation in the Penglai area
(a) Full-diameter core porosity frequency distribution histogram; (b) Full-diameter core sample permeability frequency histogram
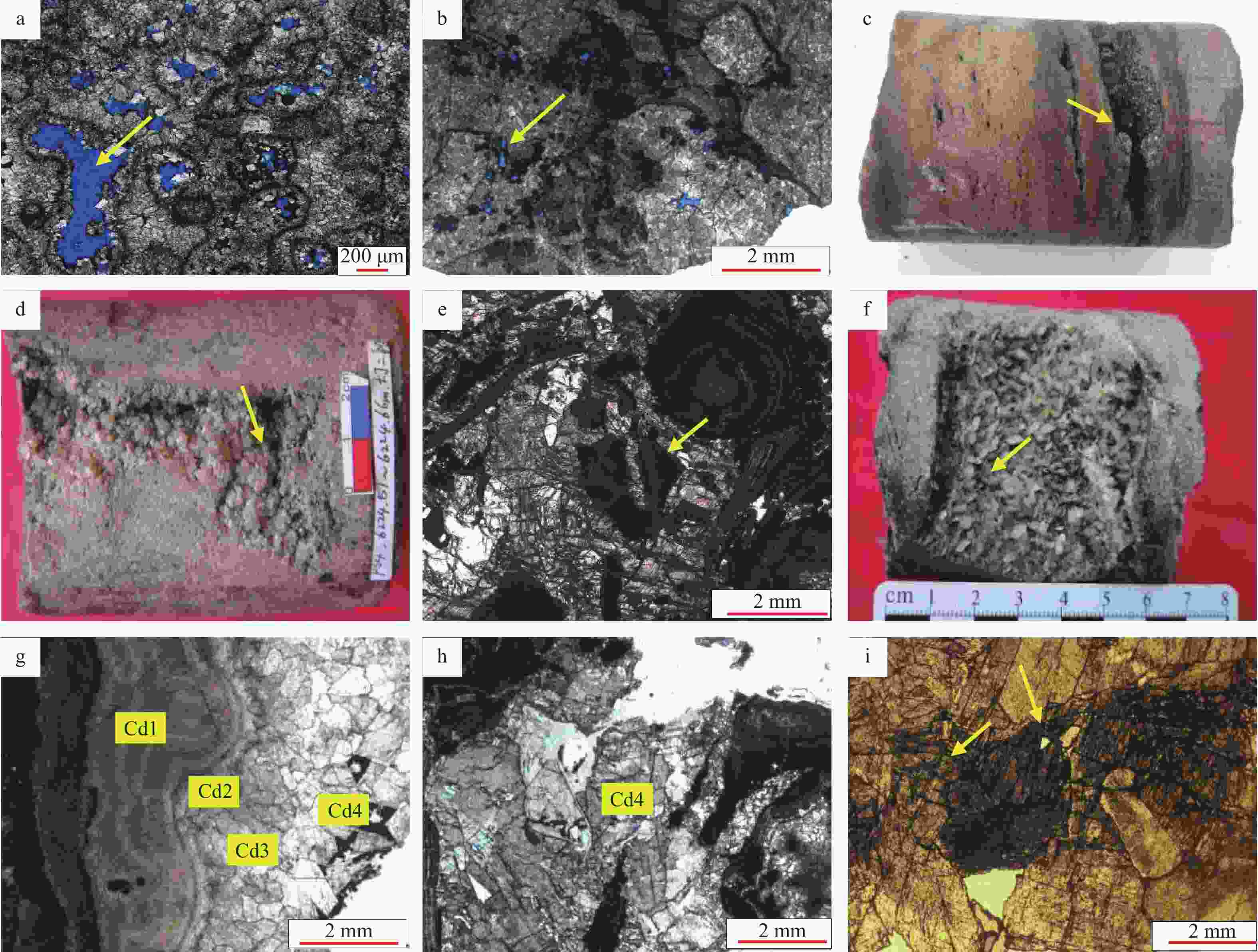
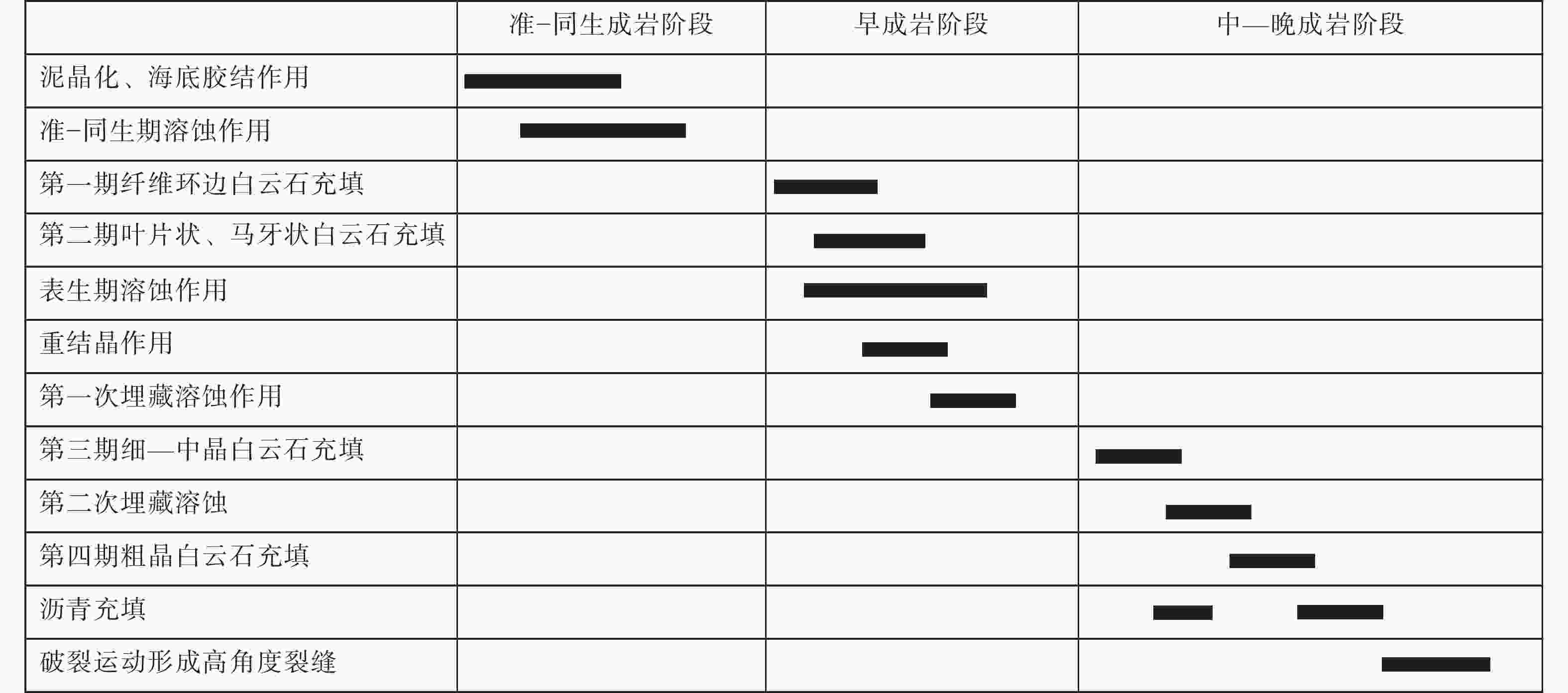
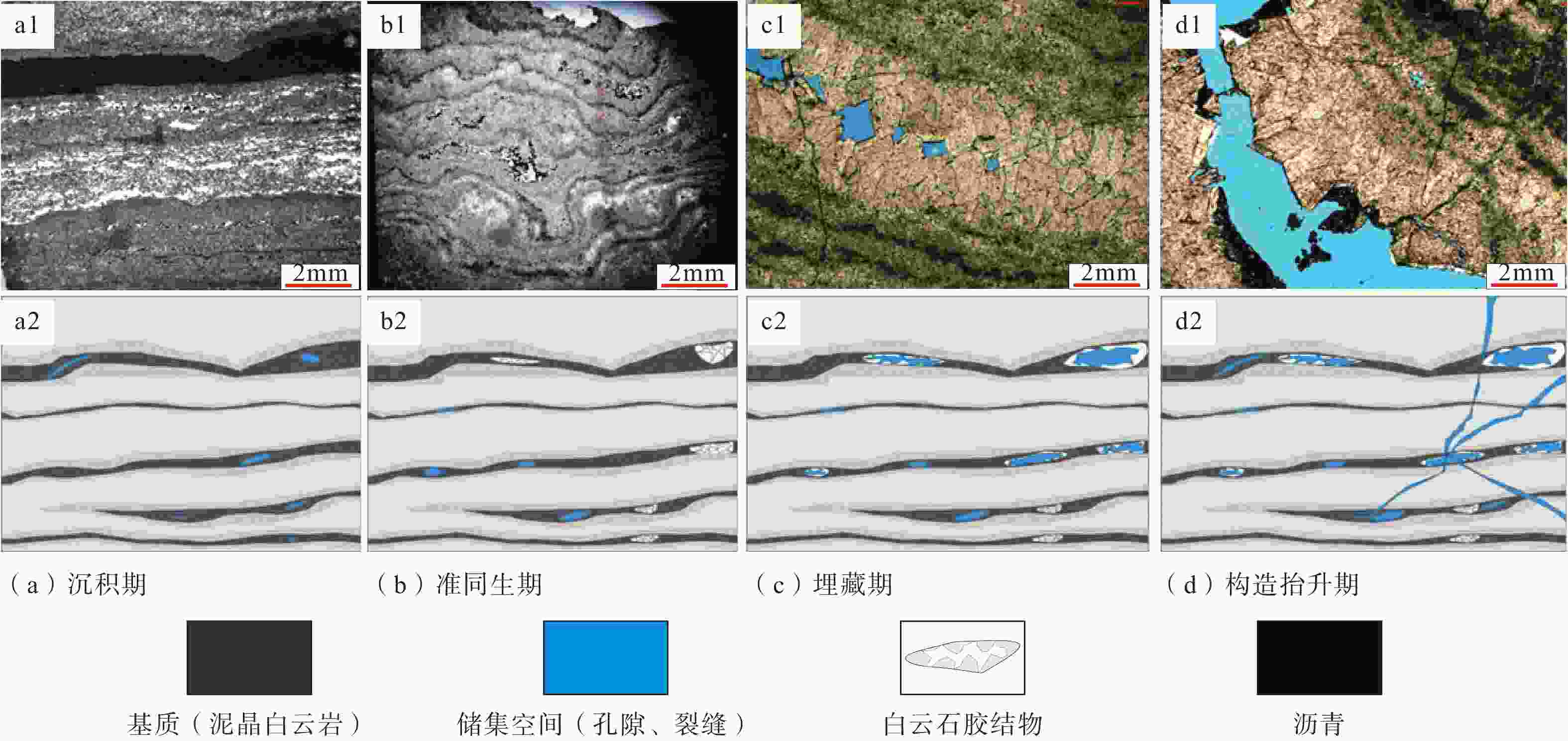
图 8 蓬莱地区灯二段主要成岩作用
a—藻凝块白云岩,粒内溶孔发育(准同生),蓬探1井5731.29 m,黄色箭头指向格架孔;b—藻凝块白云岩,选择性溶蚀(准同生),蓬探101井5757 m,黄色箭头指向格架孔;c—顺层孔洞(准同生),蓬探1井5740.83~5740.95 m,黄色箭头指向早表生溶洞;d—凝块石白云岩溶沟及溶洞,半充填(表生),蓬深4井6224.51~6224.66 m,黄色箭头指向早表生溶洞;e—花边云岩,见岩溶角砾,溶蚀孔洞多期白云石−沥青半充填(表生),蓬深4井6197.67 m,黄色箭头指向岩溶角砾;f—埋藏溶洞及伴生鞍状(埋藏),蓬探103井5929.02~5929.11 m,黄色箭头指向鞍状白云石;g—藻砂屑云岩,发育葡萄花边构造,残余孔中充填沥青(表生),蓬探101井5712.74 m,Cd1、Cd2、Cd3、Cd4分别为纤维状白云石胶结物、叶片状白云石胶结物、细—中晶白云石胶结物和粗晶鞍状白云石胶结物;h—角砾状白云岩,砾间被粗晶鞍状白云石胶结(埋藏),蓬探101井5762.70 m,Cd4为粗晶鞍状白云石胶结物;i—岩溶角砾,溶蚀孔洞部分被中—粗晶鞍状白云石胶结物充填,蓬深5井5672.77 m,黄色箭头为细—中晶白云岩
Figure 8. Main diagenesis of the second Member of Dengying Formation in the Penglai area
(a) Algae clotted dolomite, with well-developed intragranular pores (quasi-syngenetic), framework pores (yellow arrows), Well Pengtan 1 5731.29 m; (b) Algae clotted dolomite, selective dissolution (quasi-syngenetic), framework pores (yellow arrows), Well Pengtan 101 5757 m; (c) Bedding pores and caves (quasi-syngenetic), early epigenetic caves (yellow arrows), Well Pengtan 1 5740.83−5740.95 m,; (d) Thrombolite dolomite karst gullies and caves, semi-filled (supergenetic), early epigenetic caves (yellow arrows), Well Pengshen 4 6224.51−6224.66 m; (e) Lace dolomite, with karst breccia, and the dissolved pores and caves are semi-filled with multi-stage dolomite-asphalt (supergene), karst breccia (yellow arrows), Well Pengshen 4 6197.67 m,; (f) Buried karst caves and associated saddles (buried), saddle dolomite (yellow arrows), Well Pengtan 103 5929.02-5929.11 m, ; (g) Algae sand-clast dolomite, with grape lace structure developed, and residual pores filled with asphalt (supergene),Well Pengtan 101 5712.74 m, Cd1, Cd2, Cd3, Cd4 are fibrous dolomite cement, foliated dolomite cement, fine-medium crystalline dolomite cement and coarse-crystalline saddle dolomite cement, respectively; (h) Brecciated dolomite, with coarse-crystalline saddle dolomite cemented between gravels (buried), Well Pengtan 101 5762.70 m, Cd4 is coarse-crystalline saddle dolomite cement; (i) Karst breccia, with dissolved pores partially filled with medium-coarse crystalline saddle dolomite cement, fine-medium-crystalline dolomite (yellow arrows), Well Pengshen 5 5672.77 m
表 1 蓬莱地区灯影组灯二段储层孔隙度
Table 1. Reservoir porosity of the second Member of Dengying Formation in the Penglai area
井号 孔隙度/% 样品
个数最低 最高 平均 中值 蓬深5 2.01 7.81 3.46 3.00 34 蓬探1 2.71 6.68 4.85 4.60 8 蓬探101 2.00 12.78 4.61 4.22 97 蓬探102 2.00 5.31 3.18 3.22 21 蓬探103 2.23 8.92 4.52 3.56 23 中深103 2.08 7.06 3.26 2.90 13 表 2 蓬莱地区灯影组灯二段储层渗透率
Table 2. Reservoir permeability of the second Member of Dengying Formation in the Penglai area
井号 渗透率/mD 样品
个数最低 最高 平均 中值 蓬深5 0.017 4.860 0.394 0.140 32 蓬探1 0.014 0.129 0.058 0.035 7 蓬探101 0.040 0.857 0.206 0.099 29 蓬探102 0.038 0.569 0.175 0.100 18 蓬探103 0.013 0.647 0.237 0.200 20 中深103 0.011 3.100 0.908 0.617 13 -
[1] AHR W M, MANCINI E A, PARCELL W C, 2011. Pore characteristics in microbial carbonate reservoirs[JC]//AAPG annual convention and exhibition. Houston: Datapages, IncAAPG Search & Discovery Article, 30167: 10-13. [2] AL HADDAD S, MANCINI E A, 2013. Reservoir characterization, modeling, and evaluation of Upper Jurassic Smackover microbial carbonate and associated facies in Little Cedar Creek field, southwest Alabama, eastern Gulf coastal plain of the United States[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 97(11): 2059-2083. doi: 10.1306/07081312187 [3] AMINU M D, NABAVI S A, ROCHELLE C A, et al., 2017. A review of developments in carbon dioxide storage[J]. Applied Energy, 208: 1389-1419. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.09.015 [4] BERGMANN K D, GROTZINGER J, OSBURN M, 2012. Telling time in microbial carbonates: a case study from the Latest Precambrian, Sultanate of Oman[C]//2012 AAPG annual convention and exhibition. Long Beach: Datapages, Inc. [5] CHEN H W, WANG S L, HE Y, et al. , 2024. Sedimentary facies and reservoir characteristics of the fourth member of Dengying Formation in Well DB1l area, north-central Sichuan Basin[J/OLJ]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 1-11[2024-07-06]. https://doi.org/10.13673/j.pgre.202308035.31(3): 31-411-11[2024-05-25]. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] CHEN J T, LEE J H, 2014. Current progress on the geological record of microbialites and microbial carbonates[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 88(1): 260-275. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12196 [7] CHEN X Q, TIAN X B, SHI J B, et al. , 2024. Sequence stratigraphic division and its control on favorable reserviors of Hechuan-Tongnan area in Sichuan Basin based on wavelet transform analysis: taking Member 4 of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation as an example[J/OL]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 1-9[2024-05-25]. https://doi.org/10.19597/J.ISSN.1000-3754.202309051. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] CHIDSEY JR T C, VANDEN BERG M D, EBY D E, 2015. Petrography and characterization of microbial carbonates and associated facies from modern Great Salt Lake and Uinta Basin's Eocene Green River Formation in Utah, USA[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 418(1): 261-286. doi: 10.1144/SP418.6 [9] COLLINS J, KENTER J, PLAYTON T, et al. , 2012. Characterization and controls on slope geometry, framework and internal heterogeneity in the unit 1 Tengiz Field (Kazakhstan), and comparison with outcrop analogs. Abstract[C]//American Association of Petroleum Geologists AAPG annual convention and exhibition. Long BeachMeeting, CA, 84: Datapages, Inc. : 79-88. [10] CROSS M M, MANNING D A C, BOTTRELL S H, et al., 2004. Thermochemical sulphate reduction (TSR): experimental determination of reaction kinetics and implications of the observed reaction rates for petroleum reservoirs[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 35(4): 393-404. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2004.01.005 [11] DAVIES G R, SMITH JR L B, 2006. Structurally controlled hydrothermal dolomite reservoir facies: an overview[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 90(11): 1641-1690. doi: 10.1306/05220605164 [12] DU J H, HE H Q, ZHAO X Z, et al., 2017. Significant exploration breakthrough in Yangshuiwu ultra-deep and ultra-high temperature Ordovician buried-hill in Langgu sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 22(32): 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] DUAN J B, DAI L C, LI B S, et al., 2019. Reservoir characeteristices and their controlling factors of the fourth Member of Upper Sinian Dengying Fm in the northern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 39(7): 9-20. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] DUPRAZ C, REID R P, BRAISSANT O, et al., 2009. Processes of carbonate precipitation in modern microbial mats[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 96(3): 141-162. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2008.10.005 [15] FENG M Y, QIANG Z T, SHEN P, et al., 2016. Evidences for hydrothermal dolomite of Sinian Dengying Formation in Gaoshiti-Moxi area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 37(5): 587-598. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] FU X D, ZHANG B J, WANG Z C, et al., 2023. Functions on Hydrocarbon Accumulation Strike-slip faults in central and western Sichuan Basin and their control functions on hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Earth Science, 48(6): 2221-2237. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] GUO X S, HU D F, DUAN J B, et al., 2018. Rock features and sedimentary environment of the fourth member of Dengying Formation in Huijiaba section of Ningqiang, northern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 40(6): 749-756. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] HE ZY L, JIN Z J, LI S J, et al., 2023. Prototypes, modifications, and hydrocarbon enrichment variations in basins influenced by Tethyan evolution: a comparative analysis of the Persian Gulf Basin and the Sichuan Basin[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 66(12): 2871-2897. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1007/s11430-023-1207-x [19] HE ZY L, MA Y S, ZHU D Y, et al., 2021. Theoretical and technological progress and research direction of deep and ultra-deep carbonate reservoirs[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 42(3): 533-546. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] HUANG S P, JIANG H, WANG T S, et al., 2023. Accumulation conditions and favorable exploration zones for natural gas in 8000 meters marine ultra-deep strata in the Sichuan basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 97(5): 1544-1560. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] JIANG L, HU A P, OU Y L, et al., 2023. Diagenetic evolution and effects on reservoir development of the Dengying and Longwangmiao formations, Central Sichuan Basin, Southwestern China[J]. Petroleum Science, 20(6): 3379-3393. doi: 10.1016/j.petsci.2023.09.025 [22] JIANG L, HU S Y, ZHAO W Z, et al., 2018a. Diagenesis and its impact on a microbially derived carbonate reservoir from the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 102(12): 2599-2628. doi: 10.1306/05111817021 [23] JIANG L, WORDEN R H, CAI C F, et al., 2018c. Contrasting diagenetic evolution patterns of platform margin limestones and dolostones in the Lower Triassic Feixianguan Formation, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 92: 332-351. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.10.029 [24] JIANG L, WORDEN R H, YANG C B, 2018b. Thermochemical sulphate reduction can improve carbonate petroleum reservoir quality[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 223: 127-140. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2017.11.032 [25] JIAO F Z, 2018. Significance and prospect of ultra-deep carbonate fault-karst reservoirs in Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 39(2): 207-216. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] LI P W, LUO P, SONG J M, et al., 2015. Characteristics of Upper Sinian dolostonedolomite reservoirs in northwestern margin of Tarim Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 20(4): 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] LI Y, WANG X Z, FENG M Y, et al., 2019. Reservoir characteristics and genetice differences between the second and fourth members of Sinian Dengying Formation in northern Sichuan Basin and its surrounding areas[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 46(1): 52-64. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] LI Z W, RAN B, XIAO B, et al., 2019. Sinian to Early Cambrian uplift-depression framework along the northern margin of the Sichuan Basin, central China and its implications for hyvdrocarbhon expnloration[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 26(1): 59-85. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] LIU Q Y, ZHU D Y, MENG Q Q, et al., 2024. Organic-inorganic interactions in the Earth's multi-spheres and resources effects[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 35(5): 741-762. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] LUO B, YANG Y M, LUO W J, et al., 2015. Controlling factors and distribution of reservoir development in Dengying Formation of paleo-uplift in central Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 36(4): 416-426. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] LUO B, YANG Y, ZHOU G, et al., 2018. Basic characteristics and accumulation mechanism of Sinian−Cambrian giant highly mature and oil-cracking gas reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 36(4): 568-590. [32] MA X H, YANG Y, WEN L, et al., 2019. Distribution and exploration direction of medium- and large-sized marine carbonate gas fields in Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 46(1): 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(19)30001-1 [33] MA Y S, CAI X Y, ZHAO P R, et al., 2010. Formation mechanism of deep-buried carbonate reservoir and its model of three-element controlling reservoir: a case study from the Puguang Oilfield in SichuanThe development mechanism of deep ultra-deep carbonate high-quality reservoirs and the' ternary reservoir control' model[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(8): 1087-1094235. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] MANCINI E A, PARCELL W C, AHR W M, et al., 2008. Upper Jurassic updip stratigraphic trap and associated Smackover microbial and nearshore carbonate facies, eastern Gulf coastal plain[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 92(4): 417-442. doi: 10.1306/11140707076 [35] MUNIZ M C, BOSENCE D, 2012. Carbonate platforms in non-marine rift system in the Early Cretaceous (Pre-salt) of the Campos Basin, Brazil[C]//AAPG annual convention and exhibition. Long Beach: Datapages, Inc22-25. [36] REN Y, ZHONG D K, GAO C L, et al., 2015. Characteristics and controlling factors of the Lower Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation reservoirs in eastern Sichuan Basin and its adjacent areas[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 17(6): 829-840. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] SHI Y P, LIU Z G, WANG S C, et al. , 2024. Genetic mechanism and main controlling factors of high-quality clastic rock reservoirs in deep and ultra-deep layers: a case study of Oligocene Linhe Formation in Linhe Depression, Hetao Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 51(3): 478-4891-12[2024-05-25]. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] SI C S, HAO Y, ZHOU J G, et al., 2014. Reservoir Characteristics and main controlling factors of reservoir in Sinian Dengying Formation, in Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 41(3): 266-273. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] SONG J M, LIU S G, SUN W, et al., 2013. Control of Xingkai taphrogenesis on Dengying Formation high quality reservoirs in Upper Sinian of Sichuan Basin, ChinaThe control effect of Xingkai ground fissure movement on the high quality reservoir of Dengying Formation in Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 40(6): 658-670. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] TULL S J, 1997. The diversity of hydrocarbon habitat in Russia[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 3(4): 315-325. doi: 10.1144/petgeo.3.4.315 [41] WANG B S, YUAN H F, WANG T, et al. , 2024. Reservoir diagenesis, pore evolution and oil and gashydrocarbon charging inof the fourth member of the Sinian Dengying Formation in the Penglai area, central Sichuan Basin[J/OL]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1-24[2024-05-25]. https://doi.org/10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2024.012. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] WANG G Z, LIU S G, LI N, et al., 2014. Formation and preservation mechanism of high quality reservoir in deep burial dolomite in the Dengying Formation on the northern margin of the Sichuan basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(3): 667-678. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] WANG J Q, DENG J X, LIU Z H, et al., 2023. Petrophysical properties and their influencing factors of carbonates in the fourth member of Sinian Dengying Formation, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 50(6): 1185-1198. (in Chinese with English abstract [44] WANG W Y, PANG X Q, CHEN Z X, et al., 2019. Quantitative prediction of oil and gas prospects of the Sinian-Lower Paleozoic in the Sichuan Basin in central China[J]. Energy, 174: 861-872. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2019.03.018 [45] WANG Z C, JIANG H, CHEN Z Y, et al., 2020. Tectonice paleogeography of Late Sinian and its significances for petroleum exploration in the middle-upper Yangtze region, South China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 47(5): 884-897. (in Chinese with English abstract [46] WANG Z W, ZHANG K, WU Q H, et al.,2023. A method for predicting fractures in carbonate reservoirs based on fracture identification-sensitive log-seismic parameter model[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,51(6):163-174. (in Chinese with English abstract [47] WEI G Q, DU J H, XU C C, et al., 2016. Characteristics and accumulation mode of large-scale Sinian-Cambrian gas reservoirs in the Gaoshiti-Moxi region, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Research, 1(2): 164-177. doi: 10.1016/S2096-2495(17)30040-6 [48] WEN L, ZHANG J Y, PAN L YG, et al., 2023. Characteristics, controlling factors and exploration prospects of microbial dolomite reservoirs in the second member of Dengying Formation, Penglai-Zhongijiang area of central Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 45(5): 982-993. (in Chinese with English abstract [49] XIE J R, ZHANG Z L, ZHONG Y, et al., 2022. New understanding and potential analysis of natural gas exploration ofin the Dengying Member 2second member of Dengying Formation in central-northern area of Sichuan Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 27(3): 225-235. (in Chinese with English abstract [50] XIE W R, YANG W, WANG Z C, et al., 2021. Characteristics and main controlling factors on the development of a platform margin belt and its effect on hydrocarbon accumulation: a case study of Dengying Formation in Sichuan BasinCharacteristics of platform margin zone, main controlling factors of formation and their control on hydrocarbon accumulation: A case study of Dengying Formation in Sichuan Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology(Scientia Geologica Sinica), 56(3): 867-883. (in Chinese with English abstract [51] XING F C, HU H R, HOU M C, et al., 2018. Carbonate reservoirs cycles and assemblages under the tectonic and palaeogeography control: a case study from Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth Science, 43(10): 3540-3552. (in Chinese with English abstract [52] XU C C, SHEN P, YANG Y M, et al., 2020. New understandings and potential of Sinian-Lower Paleozoic natural gas exploration in the central Sichuan paleo-uplift of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 40(7): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract [53] XU S L, MA K, YANG Q, et al., 2024. Reservoir characteristics of the second member of Sinian Dengying Formation in Penglai gas area of Sichuan Basin and their controlling factors[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 31(2): 47-56. (in Chinese with English abstract [54] YANG W, WEI G Q, WU S JWEI Y, GUOQI W E I, SAIJUN W U, et al., 2023. Regional unconformities and their controls on hydrocarbon accumulation in Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 50(3): 573-587. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(23)60411-2 [55] YANG Y, HUANG X P, ZHANG J, et al., 2014. Features and geologic significances of the top Sinian karst landform before the Cambrian deposition in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 34(3): 38-43. (in Chinese with English abstract [56] YANG Y, WEN L, ZHOU G, et al., 2023. New fields, new types and resource potentials of hydrocarbonoil and gas exploration in Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 44(12): 2045-2069. (in Chinese with English abstract [57] ZHANG B J, MA H L, LI W Z, et al., 2023a. Reservoir characteristics and main controlling factors in the second member of the Dengying Formation in the Penglai Gas Field, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 34(11): 1899-1915. (in Chinese with English abstract [58] ZHANG B J, ZHONG Y, ZHOU G, et al., 2023b. Sedimentary microfacies evolution and gas reservoir comprehensive evaluation of gas reservoirthe second member of the Dengying Member 2Formation in Penglai area, central Sichuan Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 28(1): 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract [59] ZHANG X H, LI Y, ZHANG B J, et al., 2023. Characteristics and formation mechanism of high quality reservoir of the second member of the Dengying Formation in Zhongjiang-Penglai area, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 50(3): 301-312. (in Chinese with English abstract [60] ZHANG Y Y, LI Y, MUNNECKE A, 2014. Late Ordovician microbial reefs in the Lianglitag Formation (Bachu, Tarim, NW China)[J]. Facies, 60(2): 663-684. doi: 10.1007/s10347-014-0396-2 [61] ZHANG Z L, QIAO Y P, DOU S, et al., 2024. Karst paleogeomorphology and reservoir control model of the 2nd member of Dengying Formation in Penglai gas area, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 45(1): 200-214. (in Chinese with English abstract [62] ZHAO H, SUN Y, WU Y, et al., 2023. Seismic identification and favorable area prediction of hilly-shoal reservoir in the second member of Dengying Formation in Zhongjiang-Penglai area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 34(6): 980-991. (in Chinese with English abstract [63] ZHAO W Z, SHEN A J, HU S Y, et al., 2012. Geological conditions and distributional features of large-scale carbonate reservoirs onshore China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 39(1): 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(12)60010-X [64] ZHENG J, WEN L, GE Y H, et al., 2023. U–Pb dating of fibrous dolomite in the hydrothermal dolostone of the Dengying Formation, central Sichuan Basin, and its response to supercontinent breakup[J]. Minerals, 13(10): 1353. doi: 10.3390/min13101353 [65] ZHOU J G, YAO G S, YANG G, et al., 2015. Genesis mechanism of the Sinian-Cambrian reservoirs in the Anyue gas field, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 35(1): 36-44. (in Chinese with English abstract [66] ZHU D Y, JIN Z J, ZHANG R Q, et al., 2014. Characteristics and developing mechanism of Sinian Dengying Formation dolomite reservoir with multi-stage karstSuperimposed development characteristics and mechanism of multi-stage karst reservoirs in dolomite of Sinian Dengying Formation[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(6): 335-345. (in Chinese with English abstract [67] ZOU C N, DU J H, XU C C, et al., 2014. Formation, distribution, resource potential and discovery of the Sinian-Cambrian giant gas field, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 41(3): 278-293. (in Chinese with English abstract [68] 陈泓位,王时林,和源,等,2024. 四川盆地中北部DB1井区灯影组四段沉积相及储层特征[J/OL]. 油气地质与采收率:1-11[2024-07-06]. https://doi.org/10.13673/j.pgre.202308035. [69] 陈孝全,田小彬,师江波,等,2024. 四川盆地合川-潼南地区基于小波变换的层序地层划分及其对有利储层的控制作用:以上震旦统灯影组四段为例[J/OL]. 大庆石油地质与开发,1-9[2024-05-25]. https://doi.org/10.19597/J.ISSN.1000-3754.202309051. [70] 杜金虎,何海清,赵贤正,等,2017. 渤海湾盆地廊固凹陷杨税务超深超高温奥陶系潜山油气勘探重大突破实践与启示[J]. 中国石油勘探,22(32):1-12. [71] 段金宝,代林呈,李毕松,等,2019. 四川盆地北部上震旦统灯影组四段储层特征及其控制因素[J]. 天然气工业,39(7):9-20. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.07.002 [72] 冯明友,强子同,沈平,等,2016. 四川盆地高石梯−磨溪地区震旦系灯影组热液白云岩证据[J]. 石油学报,37(5):587-598. doi: 10.7623/syxb201605003 [73] 付小东,张本健,汪泽成,等,2023. 四川盆地中西部走滑断裂及其对油气成藏控制作用[J]. 地球科学,48(6):2221-2237. [74] 郭旭升,胡东风,段金宝,等,2018. 四川盆地北部宁强胡家坝灯影组四段岩石特征及沉积环境分析[J]. 石油实验地质,40(6):749-756. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201806749 [75] 何治亮,金之钧,李双建,等,2023. 特提斯演化控制下盆地原型、改造与油气差异富集:基于波斯湾盆地与四川盆地的比较分析[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,53(12):2914-2936. [76] 何治亮,马永生,朱东亚,等,2021. 深层—超深层碳酸盐岩储层理论技术进展与攻关方向[J]. 石油与天然气地质,42(3):533-546. doi: 10.11743/ogg20210301 [77] 黄士鹏,姜华,王铜山,等,2023. 四川盆地8000m海相超深层天然气成藏条件及有利勘探区带[J]. 地质学报,97(5):1544-1560. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2023.05.013 [78] 焦方正,2018. 塔里木盆地顺北特深碳酸盐岩断溶体油气藏发现意义与前景[J]. 石油与天然气地质,39(2):207-216. doi: 10.11743/ogg20180201 [79] 李朋威,罗平,宋金民,等,2015. 塔里木盆地西北缘上震旦统白云岩储层特征[J]. 海相油气地质,20(4):1-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2015.04.001 [80] 李勇,王兴志,冯明友,等,2019. 四川盆地北部及周缘地区震旦系灯影组二段、四段储集层特征及成因差异[J]. 石油勘探与开发,46(1):52-64. doi: 10.11698/PED.2019.01.05 [81] 李智武,冉波,肖斌,等,2019. 四川盆地北缘震旦纪—早寒武世隆−坳格局及其油气勘探意义[J]. 地学前缘,26(1):59-85. [82] 刘全有,朱东亚,孟庆强,等,2024. 地球多层圈有机—无机相互作用的资源效应[J]. 天然气地球科学,35(5):741-762. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2024.04.001 [83] 罗冰,杨跃明,罗文军,等,2015. 川中古隆起灯影组储层发育控制因素及展布[J]. 石油学报,36(4):416-426. doi: 10.7623/syxb201504003 [84] 马新华,杨雨,文龙,等,2019. 四川盆地海相碳酸盐岩大中型气田分布规律及勘探方向[J]. 石油勘探与开发,46(1):1-13. doi: 10.11698/PED.2019.01.01 [85] 马永生,蔡勋育,赵培荣,等,2010. 深层超深层碳酸盐岩优质储层发育机理和“三元控储”模式:以四川普光气田为例[J]. 地质学报,84(8):1087-1094235. [86] 任影,钟大康,高崇龙,等,2015. 川东及其周缘地区下寒武统龙王庙组储集层特征与控制因素[J]. 古地理学报,17(6):829-840. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2015.06.068 [87] 史原鹏,刘占国,王少春,等,2024. 深层—超深层优质碎屑岩储层成因及主控因素:以河套盆地临河坳陷古近系渐新统临河组为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,51(3):478-4891-12[2024-05-25]. [88] 斯春松,郝毅,周进高,等,2014. 四川盆地灯影组储层特征及主控因素[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),41(3):266-273. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2014.03.02 [89] 宋金民,刘树根,孙玮,等,2013. 兴凯地裂运动对四川盆地灯影组优质储层的控制作用[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),40(6):658-670. [90] 汪泽成,姜华,陈志勇,等,2020. 中上扬子地区晚震旦世构造古地理及油气地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发,47(5):884-897. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.05.04 [91] 王炳森,袁海锋,王涛,等,2024. 川中蓬莱地区震旦系灯影组四段储层成岩作用、孔隙演化及油气充注[J/OL]. 沉积学报,1-24[2024-05-25]. https://doi.org/10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2024.012. [92] 王国芝,刘树根,李娜,等,2014. 四川盆地北缘灯影组深埋白云岩优质储层形成与保存机制[J]. 岩石学报,30(3):667-678. [93] 王佳庆,邓继新,刘忠华,等,2023. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组四段碳酸盐岩岩石物理特征及影响因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发,50(6):1185-1198. doi: 10.11698/PED.20230303 [94] 王志伟, 张凯, 武群虎, 等,2023. 基于井震裂缝识别敏感性参数模型的碳酸盐岩储层裂缝预测方法[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,51(6):163-174 [95] 文龙,张建勇,潘立银,等,2023. 川中蓬莱—中江地区灯二段微生物白云岩储层特征、发育主控因素与勘探领域[J]. 石油实验地质,45(5):982-993. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202305982 [96] 谢继容,张自力,钟原,等,2022. 四川盆地中部—北部地区灯影组二段天然气勘探新认识及潜力分析[J]. 海相油气地质,27(3):225-235. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2022.03.001 [97] 谢武仁,杨威,汪泽成,等,2021. 台缘带特征、形成主控因素及其对油气成藏的控制:以四川盆地灯影组为例[J]. 地质科学,56(3):867-883. doi: 10.12017/dzkx.2021.045 [98] 邢凤存,胡华蕊,侯明才,等,2018. 构造和古地理控制下的碳酸盐岩储集体旋回和集群性探讨:以四川盆地为例[J]. 地球科学,43(10):3540-3552. [99] 徐春春,沈平,杨跃明,等,2020. 四川盆地川中古隆起震旦系—下古生界天然气勘探新认识及勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业,40(7):1-9. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.07.001 [100] 徐少立,马奎,杨强,等,2024. 四川盆地蓬莱气区震旦系灯影组二段储层特征及其控制因素[J]. 特种油气藏,31(2):47-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2024.02.006 [101] 杨雨,黄先平,张健,等,2014. 四川盆地寒武系沉积前震旦系顶界岩溶地貌特征及其地质意义[J]. 天然气工业,34(3):38-43. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.03.0016 [102] 杨雨,文龙,周刚,等,2023. 四川盆地油气勘探新领域、新类型及资源潜力[J]. 石油学报,44(12):2045-2069. doi: 10.7623/syxb202312004 [103] 张本健,马华灵,李文正,等,2023a. 四川盆地蓬莱气区灯二段储集层特征及主控因素[J]. 天然气地球科学,34(11):1899-1915. [104] 张本健,钟原,周刚,等,2023b. 四川盆地中部蓬莱地区灯二段沉积微相演化及气藏综合评价[J]. 海相油气地质,28(1):1-10. [105] 张玺华,李勇,张本健,等,2023. 四川盆地中江−蓬莱地区灯二段储层特征及优质储层成因机制[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),50(3):301-312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2023.03.05 [106] 张自力,乔艳萍,豆霜,等,2024. 四川盆地蓬莱气区震旦系灯影组二段岩溶古地貌与控储模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质,45(1):200-214. doi: 10.11743/ogg20240114 [107] 赵虎,孙勇,吴勇,等,2023. 四川盆地中江—蓬莱地区灯二段丘滩体储层地震识别及有利区预测[J]. 天然气地球科学,34(6):980-991. [108] 赵文智,沈安江,胡素云,等,2012. 中国碳酸盐岩储集层大型化发育的地质条件与分布特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发,39(1):1-12. [109] 周进高,姚根顺,杨光,等,2015. 四川盆地安岳大气田震旦系—寒武系储层的发育机制[J]. 天然气工业,35(1):36-44. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.01.004 [110] 朱东亚,金之钧,张荣强,等,2014. 震旦系灯影组白云岩多级次岩溶储层叠合发育特征及机制[J]. 地学前缘,21(6):335-345. [111] 邹才能,杜金虎,徐春春,等,2014. 四川盆地震旦系—寒武系特大型气田形成分布、资源潜力及勘探发现[J]. 石油勘探与开发,41(3):278-293. doi: 10.11698/PED.2014.03.03 -




 下载:
下载: