The application of sedimentary microfacies on the fracability of tight sandstone reservoir in Chang 7 member of Longdong area in the Ordos Basin
-
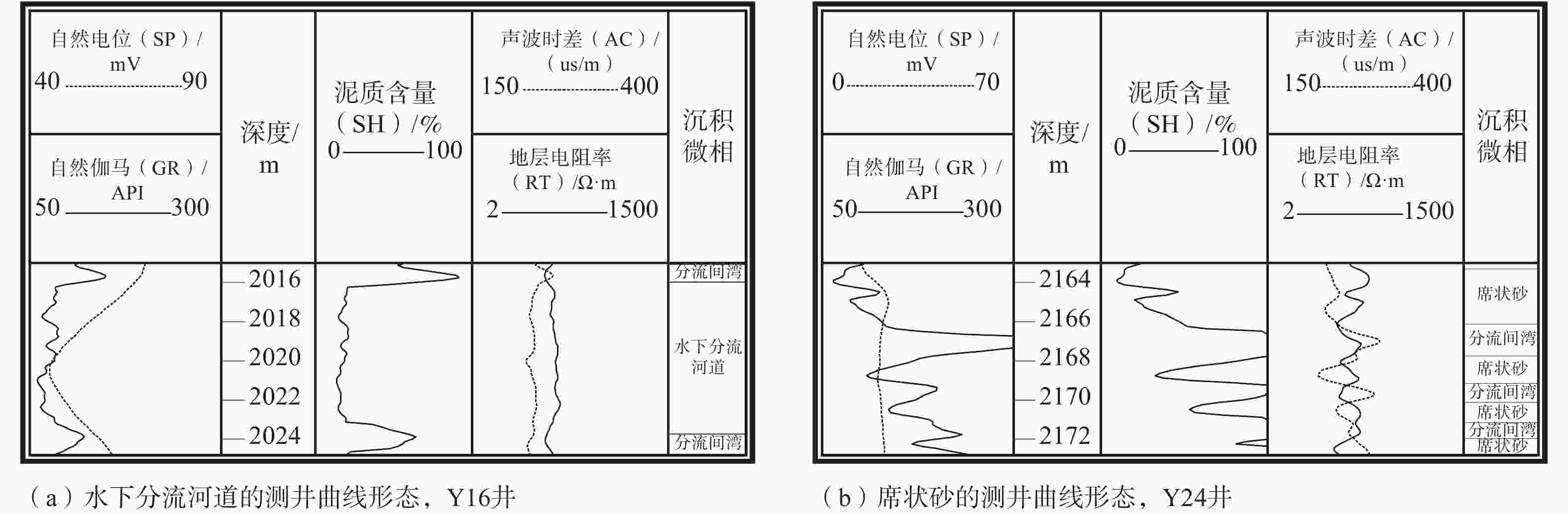
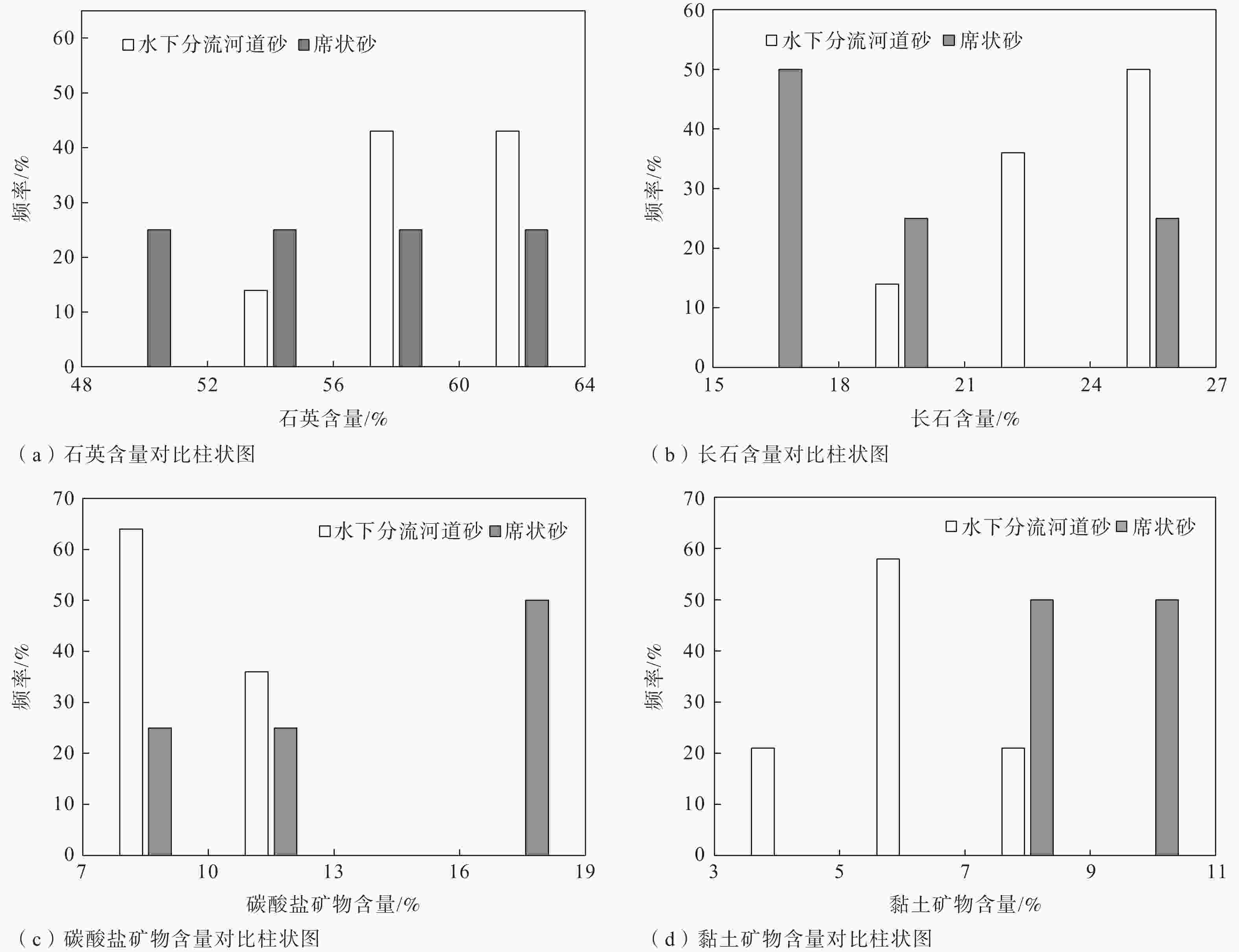
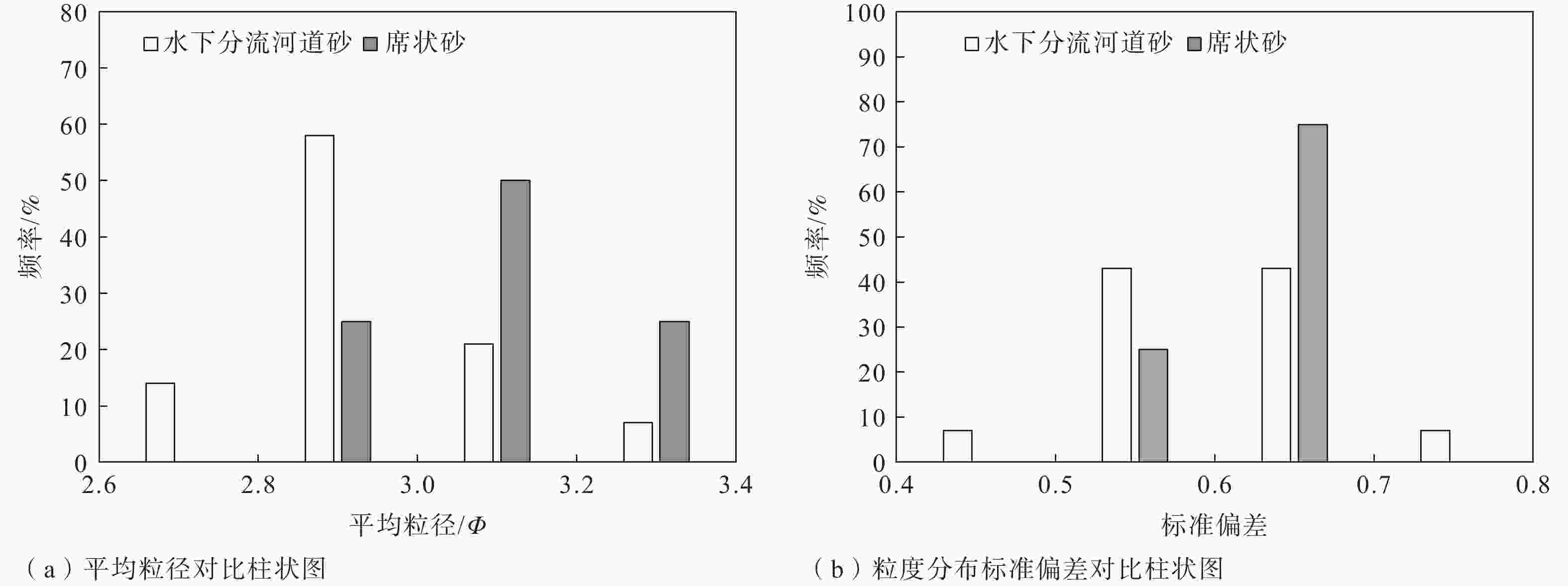
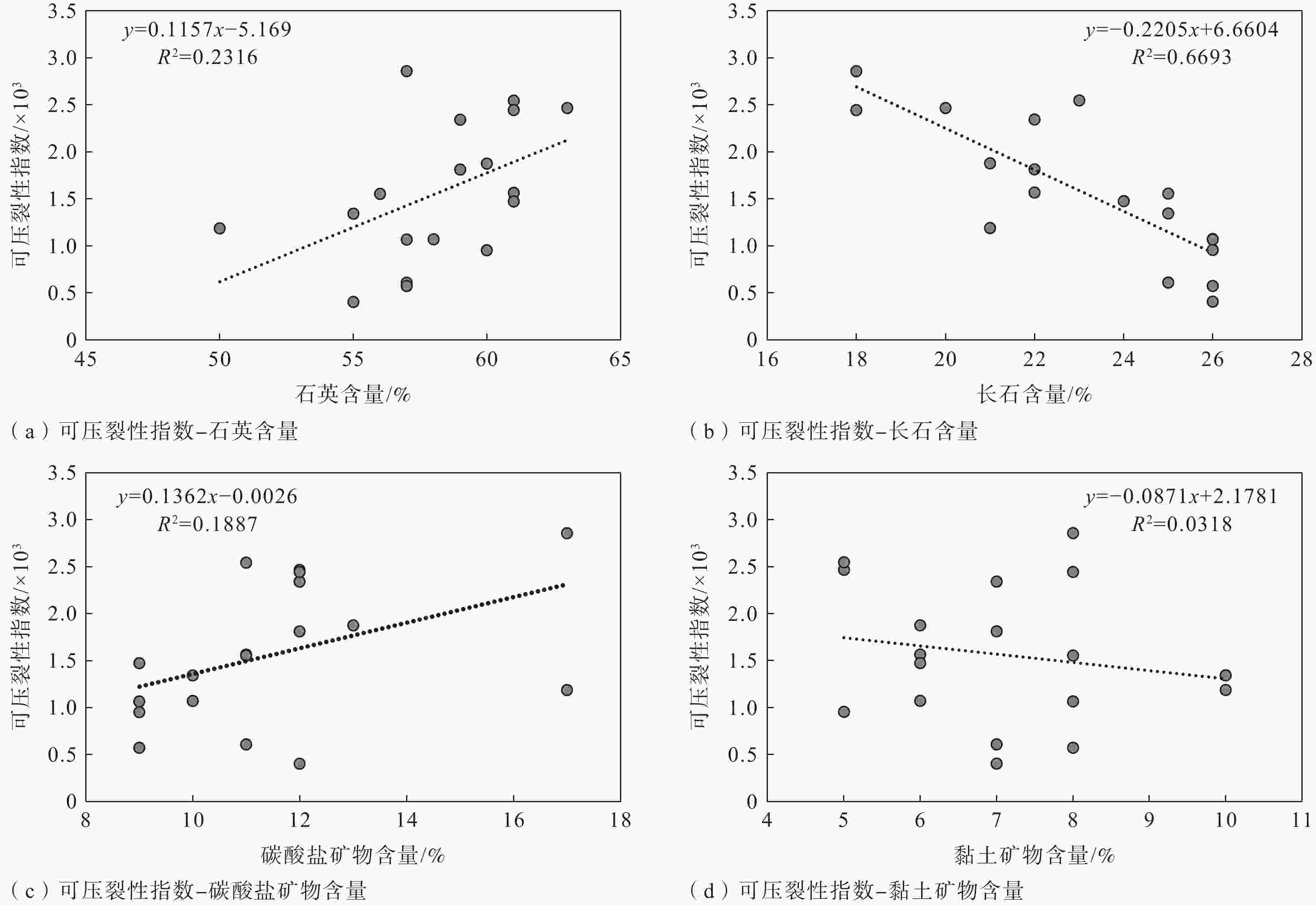
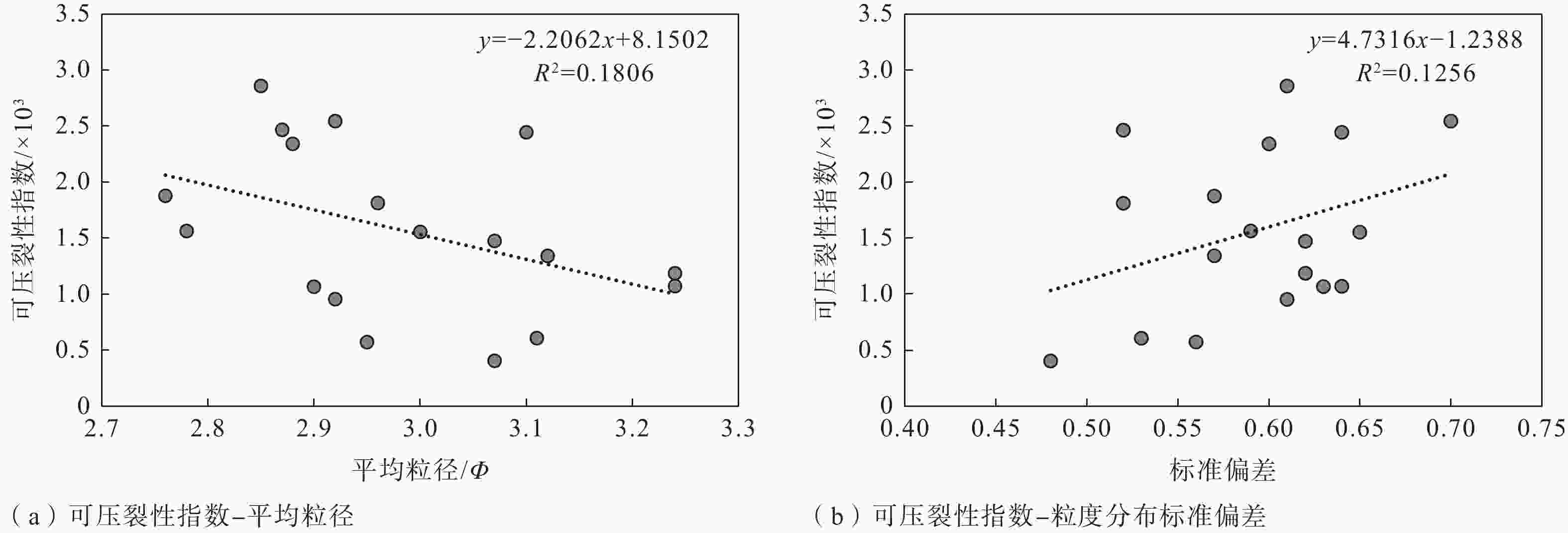
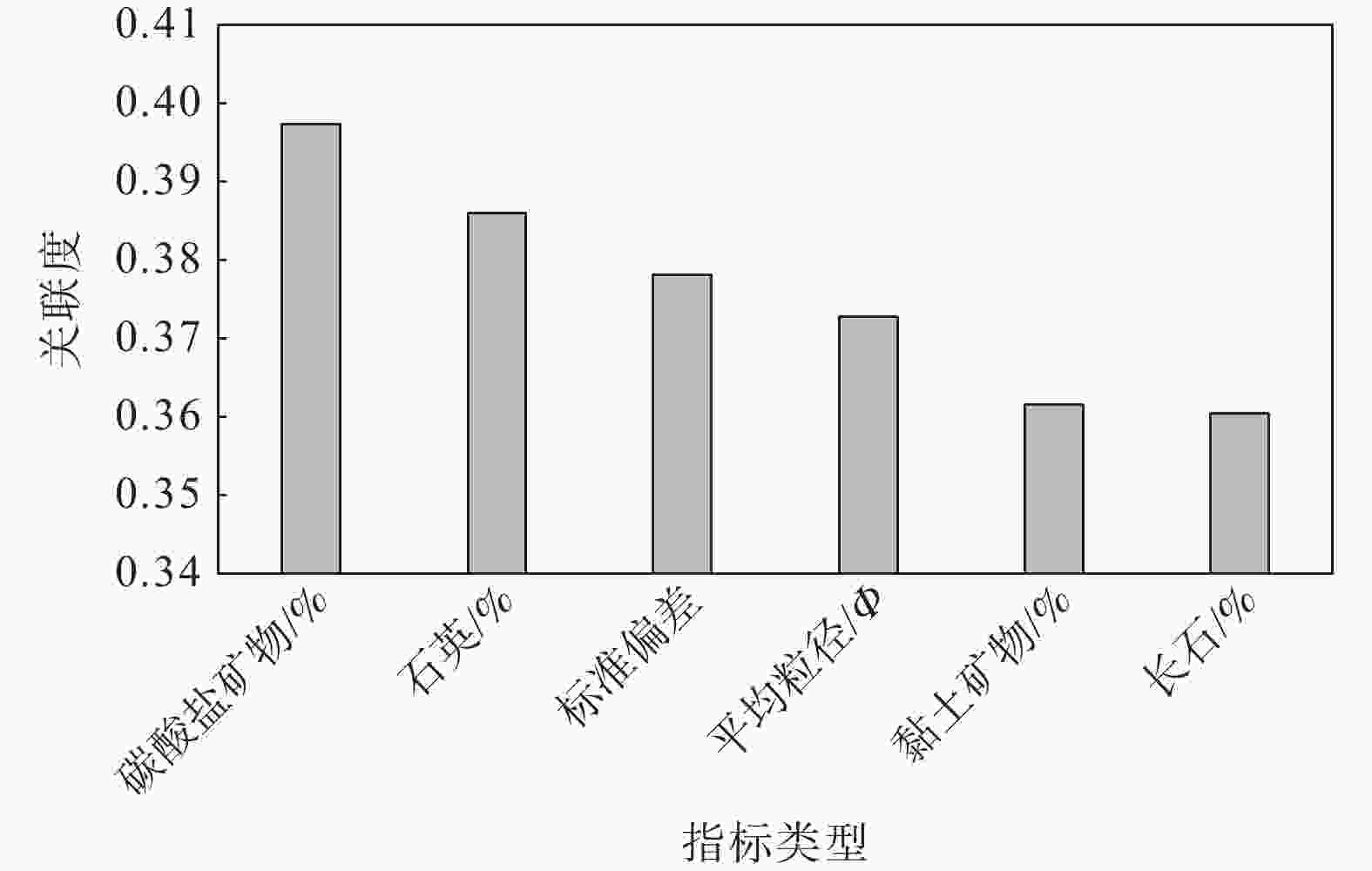
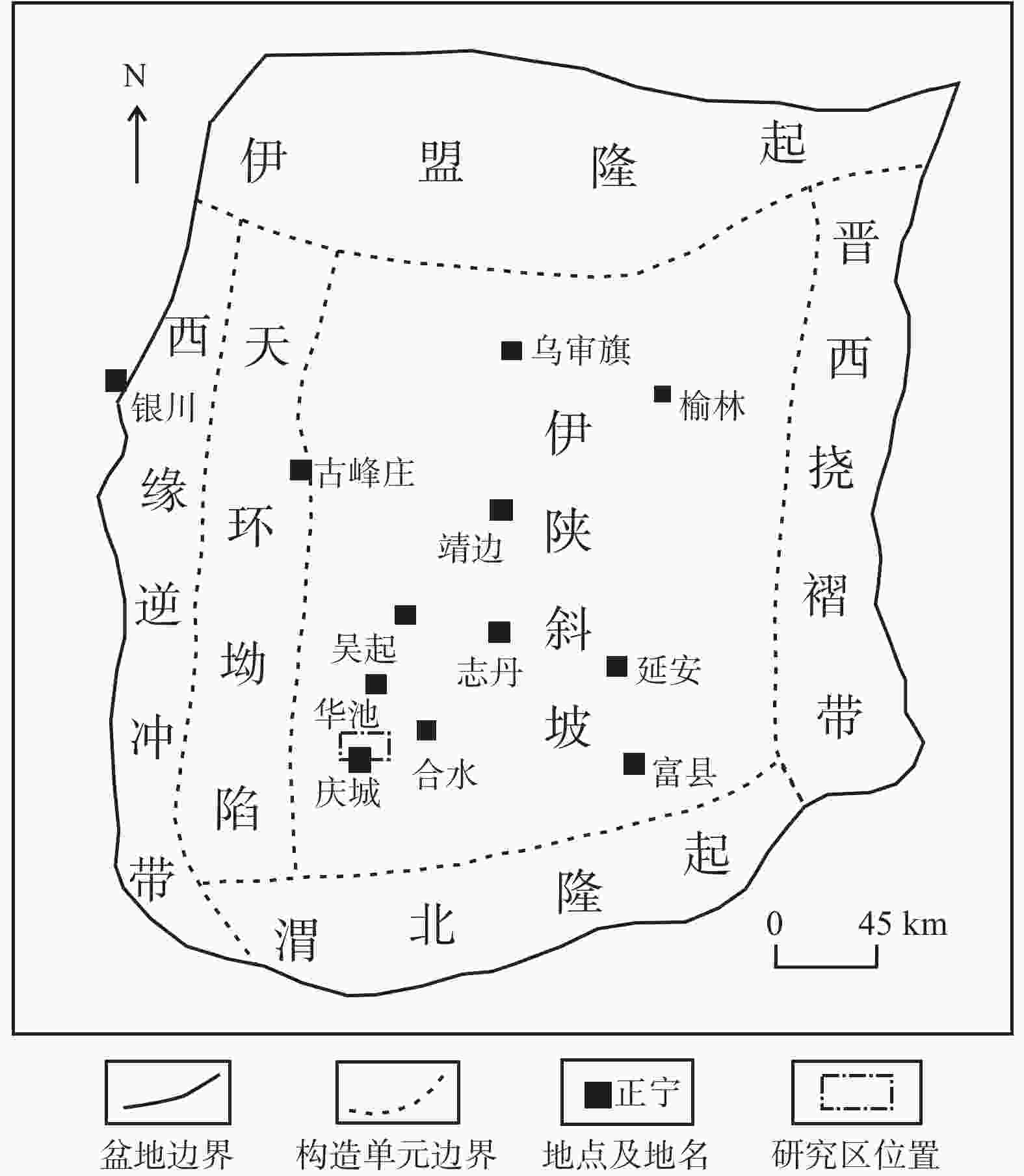
摘要: 沉积特征差异是控制储层非均质性的关键因素之一,利用沉积微相来分析储层的非均质性通常是油气田开发和储层甜点预测的重要手段,也可以尝试用其评价致密砂岩储层的可压裂性。以鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区延长组7段(长7段)的致密砂岩为研究对象,在通过岩芯、测井等资料识别不同沉积微相类型基础上,利用全岩X射线衍射(XRD)分析、铸体薄片观察得到致密砂岩样品的矿物成分和结构参数,并结合岩石力学实验,采用脆性指数和三轴抗压强度的比值来表征岩石的可压裂性。将致密砂岩的沉积微相、成分结构和可压裂性进行对比分析后得到以下认识:长7段致密砂岩主要发育水下分流河道和席状砂2种沉积微相,不同沉积微相之间的矿物成分、结构存在明显差异;与席状砂相比,水下分流河道砂体的平均粒径更大,分选更好,碳酸盐矿物和黏土矿物含量更低,杂基含量更少;可压裂性指数与砂岩的石英含量、碳酸盐矿物含量、粒度分布标准偏差具有正相关性,与长石含量、平均粒径具有负相关性。灰色关联分析表明碳酸盐矿物含量、粒度分布标准偏差、粒径是影响长7段致密砂岩可压裂性的最主要因素,整体上席状砂的可压裂性指数要高于水下分流河道砂,更易于压裂。由于砂岩颗粒的粒度分布标准偏差、粒径受沉积微相控制,碳酸盐矿物含量受砂岩厚度直接控制、受沉积微相间接控制,故在致密砂岩油气储层压裂的实际工程中可以依据沉积微相差异来判断致密砂岩的可压裂性变化,简化可压裂性的评价流程。Abstract:
Objective Sedimentary differences are the key factor in controlling reservoir heterogeneity. Analyzing reservoir heterogeneity through sedimentary microfacies is crucial for oil and gas field development and sweet spot prediction, and it also informs the evaluation of fracturing in tight sandstone reservoirs. There are many types and complex lithologies of unconventional oil and gas reservoirs in the Ordos Basin as well as many factors controlling reservoir fracability. At present, mechanical experiments are used to comprehensively characterize the fracturing property; however the research cost is high and the experimental process is complicated, making it unnsuitable for large-scale oilfield development and use. Therefore, this study attempted to analyze and compare the fracability of tight sandstones with different sedimentary microfacies from the perspective of sedimentary microfacies controlling the lithology and reservoir development to provide a reference for oilfield development plans. Methods Taking the compact sandstone of Chang 7 member of Yanchang Formation in the Longdong area of Ordos Basin as the research object, the different types of microfacies are identified through the data of core and cast slice, the mineral composition and structural parameters of rock samples were obtained by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, and rock mechanics experiments were conducted to quantitatively described the fracturing property. Results The results are as follows: (1) Two sedimentary microfacies, namely underwater distributary channel and sheet sand, mainly developed in Chang 7 Member of Yanchang Formation in the study area. Among them, the single sand body thickness of the underwater distributary channel is greater than 2 m, the sheet sand is mostly a medium thin and thick sand mudstone interlayer, and the single sand body thickness is generally less than 2 m. (2) The composition and structure of the two sedimentary sandstone microfacies are obviously different: the content of carbonate minerals, clay minerals, and heterobases in the sheet sand microfacies are relatively high, the particle size is finer, and the sorting is worse, which are the main internal factors that cause the difference in tight sandstone fracability and are the basis for judging the fracability of tight sandstone by sedimentary microfacies. (3) The fracability index was related to the composition and structure of sandstone. In terms of composition, the fracability index was positively correlated with quartz mineral content as well as carbonate mineral content and negatively correlated with feldspar mineral content. In terms of structure, there is a negative correlation between the fracability index and the average particle diameter φ. The larger the particle size, the higher the fracability index. The fracability index was positively correlated with the standard deviation of the particle size, indicating that the worse the particle separation, the higher the fracability index. (4) Through grey correlation analysis, it was found that the degree of influence of sandstone parameters on fracability was in the order of carbonate mineral content, quartz content, standard deviation of particle size, and average particle size from high to low, while clay minerals and feldspar content were in a relatively weak position. Conclusion The results indicate that the higher the contents of carbonate and quartz and the higher the standard deviation of particle size (the worse the sorting), the better the fracability. The finer the particle size, the higher the feldspar content and the worse the fracability. Grey correlation analysis showed that the carbonate mineral content, separation and particle size play a major role in the fracability of tight sandstone. Compared with distributary channel microfacies, sheet sand has a higher carbonate minerals content, worse sorting, and little difference in quartz content. Although the microphase particle size of the sheet sand is slightly finer, the average particle size has a relatively minor effect on the fracability; thus, sheet sand as a whole shows better fracability. Significance Since the standard deviation (sorting) and particle size of sandstone particles are controlled by sedimentary microfacies, and the content of carbonate minerals is directly controlled by sandstone thickness and indirectly affected by sedimentary microfacies, the change in the tight sandstone fracability index can be judged according to the difference in sedimentary microfacies in practical engineering, and the working process can be simplified. -
Key words:
- Yanchang Formation /
- tight sandstone /
- fracability /
- sedimentary microfacies /
- distributary channel /
- sheet sand
-
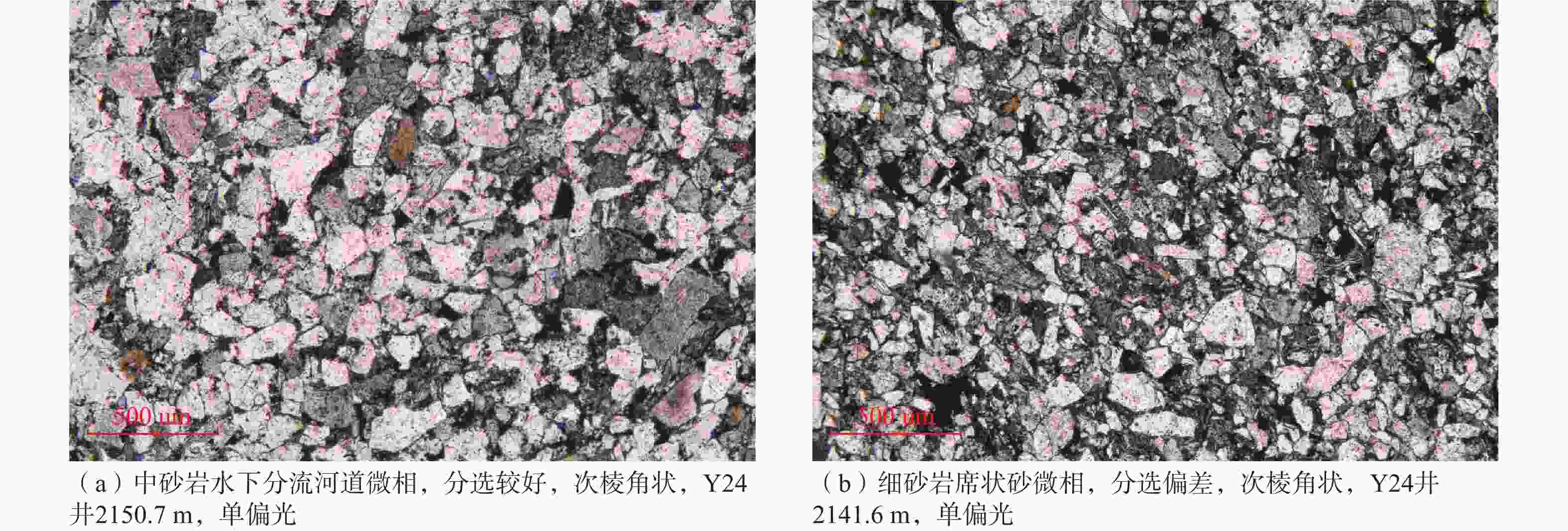
图 2 不同沉积微相砂岩样品的显微镜下特征
Figure 2. The characteristics of different sandstone microfacies under the microscope
(a) Underwater distributary channel microfacies of sandstone, with good sorting, sub-angular, well Y24 at 2150.7 m, under monochromatic polarized light; (b) Sheet sand microfacies of fine sandstone, poor sorting, sub-angular, well Y24 at 2141.6 m, under monochromatic polarized light
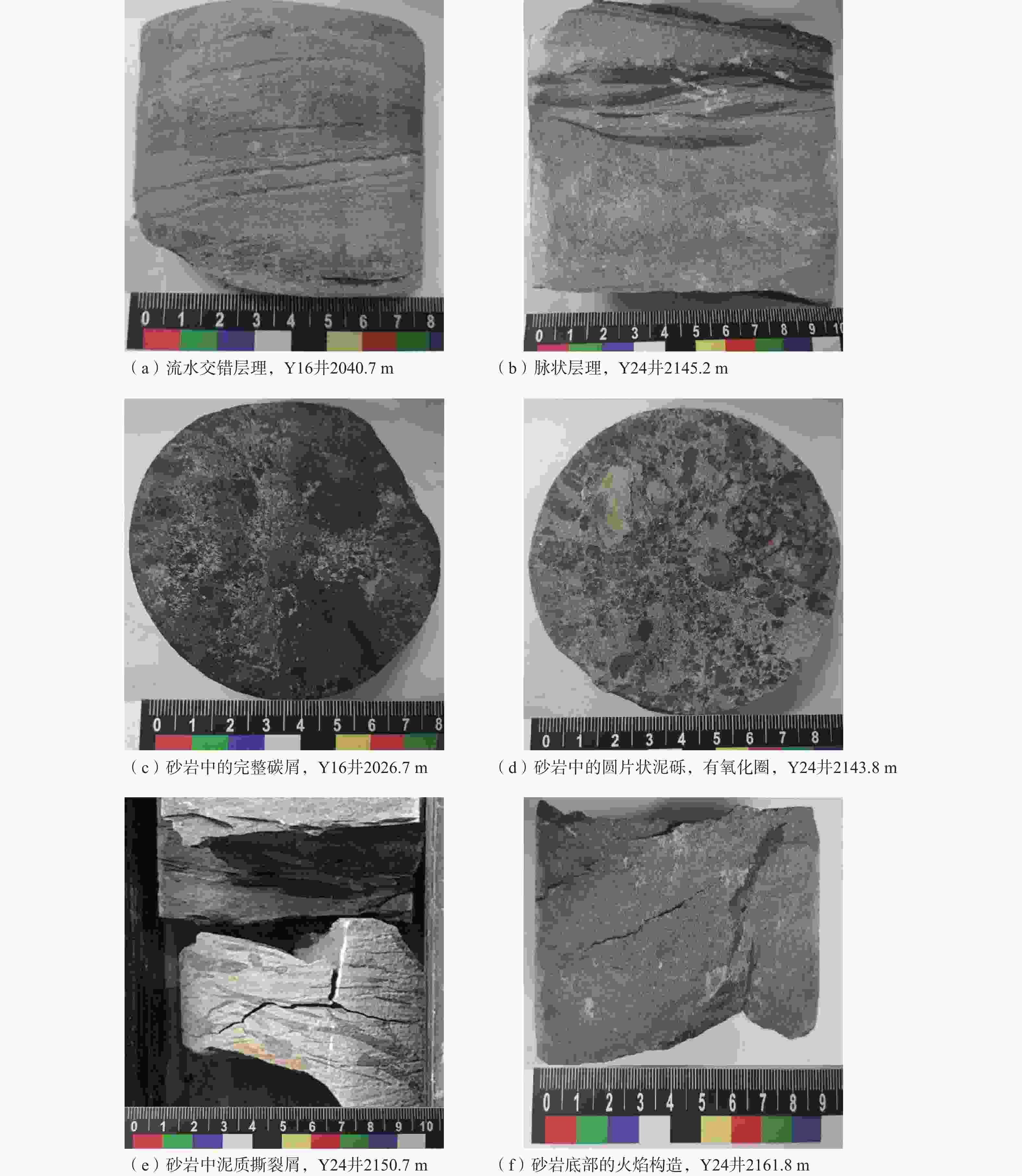
图 3 岩芯中典型的沉积相标志
Figure 3. Typical sedimentary phenomena in rock cores
(a) Fluvial cross-bedding, well Y16 at 2040.7 m; (b) Flaser bedding, well Y24 at 2145.2 m; (c) Intact carbon debris in sandstone, well Y16 at 2026.7 m; (d) Disc-shaped mud chips in sandstone with oxidation halo, well Y24 at 2143.8 m; (e) Muddy rip-up clasts in sandstone, well Y24 at 2150.7 m; (f) Flame structure at the base of sandstone, well Y24 at 2161.8 m
表 1 陇东地区延长组地层划分及岩性特征
Table 1. Stratigraphic division and lithological characteristics of the Yanchang Formation in the Longdong region
地层时代 地层岩性 统 组 段 上三叠统 延长组 1 深灰色泥、页岩夹煤层,局部为厚层块砂 2 灰绿色中—细砂岩夹灰色—深灰色泥岩、黑褐色炭质泥岩 3 4+5 深灰色—灰黑色泥、页岩与灰色—灰绿色粉砂岩互层,下部发育一套油页岩、泥岩夹薄层凝灰岩 6 7 8 深灰色—灰黑色泥岩与浅灰绿色—褐灰色中—细砂岩互层 9 10 灰绿色厚层块中—粗长石砂岩夹深灰色及暗紫色泥岩 -
[1] BAI M, 2016. Why are brittleness and fracability not equivalent in designing hydraulic fracturing in tight shale gas reservoirs[J]. Petroleum, 2(1): 1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.petlm.2016.01.001 [2] CAO Y, LIU Y Z, DUAN X T, et al., 2018. Sedimentary geological significance of reservoir in the lower Member of Yanchang Formation in Dingbian Area[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 38(1): 137-144. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] ESTUPIÑAN J, MARFIL R, DELGADO A, et al., 2007. The impact of carbonate cements on the reservoir quality in the Napo Fm sandstones (Cretaceous Oriente Basin, Ecuador)[J]. Geologica Acta, 5(1): 89-108. [4] FAN H, ZHANG S, GOU X P, et al., 2011. A new numerical calibration of the critical stress intensity factor for the CCNBD specimens used in rock fracture toughness test[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 28(4): 416-422. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] FOWELL R J, 1995. Suggested method for determining mode I fracture toughness using cracked chevron notched Brazilian disc (CCNBD) specimens[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 32(1): 57-64. [6] Frankie M A, Mohd K A K, Mohd E T, et al. , 2016 Sediment Classification using Envirometric Technique: A Study Case in Pahang River, Malaysia[J]. The Malaysian Journal of Analytical Sciences, 20 (5): 1171-1180. [7] FU J H, LUO S S, NIU X B, et al., 2015. Sedimentary characteristics of channel Type Gravity Flow of the member 7 of Yanchang Formation in the Longdong area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 34(1): 29-37. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] FU J H, WANG X Z, ZHANG L X, 2015. Geological controls on artificial fracture networks in continental shale and its fracability evaluation: a case study in the Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 26: 1285-1293. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2015.08.034 [9] HE R, YANG Z Z, LI X G, et al., 2019. A comprehensive approach for fracability evaluation in naturally fractured sandstone reservoirs based on analytical hierarchy process method[J]. Energy Science & Engineering, 7(2): 529-545. [10] HOLT R M, FJÆR E, STENEBRÅTEN J F, et al., 2015. Brittleness of shales: relevance to borehole collapse and hydraulic fracturing[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 131: 200-209. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2015.04.006 [11] JIA X M, WANG Q Z, 2003. Wide range calibration of the stress intensity factor for the fracture toughness specimen CCNBD[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 24(6): 907-912. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] JIN X C, SHAH S N, ROEGIERS J C, et al., 2015. An integrated petrophysics and geomechanics approach for fracability evaluation in shale reservoirs[J]. SPE Journal, 20(3): 518-526. doi: 10.2118/168589-PA [13] KIVI I R, AMERI M, MOLLADAVOODI H, 2018. Shale brittleness evaluation based on energy balance analysis of stress-strain curves[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 167: 1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.03.061 [14] LI J B, LU S F, CHEN G H, et al., 2015. Friability evaluation for the mud shale reservoirs based on the mineralogy and rock mechanics[J]. Petroleum Geology and Oilfield Development in Daqing, 34(6): 159-164. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] LI N Y, DAI J X, LIU C, et al., 2016. Feasibility research on volume acid fracturing to tight carbonate gas reservoir and its construction effect: a case study of lower Paleozoic carbonate gas reservoir in Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 23(3): 120-126. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] LI X B, LIU H Q, CHEN Q L, et al., 2010. Characteristics of slope break Belt in large Depression lacustrine basin and its controlling effect on Sandbody and petroleum: taking the Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin as an example[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 28(4): 717-729. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] LI Z Y, FAN M M, MA Y, et al.,2012. Depositional facies of Chang 7 oil formation of the Triassic Yanchang formation in southeast Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Shaanxi University of Science & Technology,30(1):106-110+121. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] LIAO J J, ZHU X M, DENG X Q, et al., 2013. Sedimentary characteristics and model of gravity flow in Triassic Yanchang Formation of Longdong area in Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(2): 29-39. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] LIU F, ZHU X M, LI Y, et al., 2015. Sedimentary characteristics and facies model of gravity flow deposits of Late Triassic Yanchang Formation in southwestern Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 42(5): 577-588. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] LIU J, HUI C, FAN J M, et al., 2021. Distribution characteristics of the present-day in-situ stress in the Chang 6 tight sandstone reservoirs of the Yanchang Formation in the Heshui Area, Ordos Basin, China and suggestions for development[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(1): 31-39. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] LIU L Q, LI Y, KANG L M, et al., 2010. Mudstone distribution features of maximum flooding time in late Triassic in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 40(5): 866-871. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] LONG Z L, WEN Z T, LI H, et al., 2020. An evaluation method of shale reservoir crushability based on grey correlation analysis[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 10(1): 37-42. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] MU L J, ZHAO Z F, LI X W, et al., 2019. Fracturing technology of stimulated reservoir volume with subdivision cutting for shale oil horizontal wells in Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 40(3): 626-635. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] REN Y, CAO H, YAO F C, et al., 2018. Brittleness and fracability prediction for tight oil reservoir in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 53(3): 511-519. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] RICKMAN R, MULLEN M, PETRE E, et al. , 2008. A practical use of shale petrophysics for stimulation design optimization: all shale plays are not clones of the Barnett Shale[C]//SPE annual technical conference and exhibition. Denver: SPE: 21-24. [26] SUN Y,JIANG Y Q,XIONG X Y,et al.,2022. Lithofacies and sedimentary environment evolution of the Shan2 3 Sub-member transitional shale of the Shanxi Formation in the Daning-Jixian area, eastern Ordos Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,50(9):104-114.(in Chinese with English abstract [27] SUI L L, JU Y, YANG Y M, et al., 2016. A quantification method for shale fracability based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Energy, 115: 637-645. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2016.09.035 [28] WANG D B, GE H K, WANG X Q, et al., 2015. A novel experimental approach for fracability evaluation in tight-gas reservoirs[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 23: 239-249. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2015.01.039 [29] WANG Q Z, 1998. Stress intensity factors of the ISRM suggested CCNBD specimen used for mode-I fracture toughness determination[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 35(7): 977-982. doi: 10.1016/S0148-9062(98)00010-2 [30] WU J J, ZHANG S H, CAO H, et al., 2018. Fracability evaluation of shale gas reservoir-A case study in the Lower Cambrian Niutitang formation, northwestern Hunan, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 164: 675-684. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.11.055 [31] YANG F,MEI W B,LI L,et al.,2023. Propagation of hydraulic fractures in thin interbedded tight sandstones[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,51(7):61-71. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] YANG H, DOU W T, LIU X Y, et al., 2010. Analysis on sedimentary facies of Member 7 in Yanchang formation of Triassic in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 28(2): 254-263. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] YAO J L, DENG X Q, ZHAO Y D, et al., 2013. Characteristics of Tight oil in triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 40(2): 150-158. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(13)60018-X [34] YUAN J L, DENG J G, ZHANG D Y, et al., 2013. Fracability evaluation of shale-gas reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 34(3): 523-527. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] ZHANG H L, DENG N T, ZHANG Z H, et al. , 2014. Geochemical characteristics and oil-source correlation of the Mesozoic Crude Oils in the Southern Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 20(2): 309-316. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] ZHANG X H, FENG S Y, LIANG X W, et al., 2020. Sedimentary microfacies identification and inferred evolution of the Chang 7 member of Yanchang Formation in the Longdong area, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(3): 957-967. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] ZHANG Z H, WEI X S, GONG H J, et al., 2020. Diagenesis characteristics and evolution of porosity of Chang7 tight sandstone reservoir in Dingbian oilfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 27(2): 43-52. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] ZHAO J Y, JI D S, WU J, et al., 2022. Research on rock mechanics parameters of the Jurassic-Cretaceous reservoir in the Sikeshu sag, Junggar Basin, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(4): 573-582. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] ZHONG D K, ZHU X M, LI S J, et al., 2007. Influence of early carbonate cementation on the evolution of sandstones: a case study from Silurian sandstones of Manjiaer depression, Tarim basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 25(6): 885-890. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] TANG S H, LUO Y S, ZHOU Z B, 2008. Plastic variational principle based on the least work consumption principle[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 15(S1): 39-42. doi: 10.1007/s11771-008-0310-6 [41] ZOU C N, ZHAO Z Z, YANG H, et al., 2009. Genetic mechanism and Distribution of sandy Debris flows in Terrestrial lacustrine basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 27(6): 1065-1075. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] ZOU C N, YANG Z, ZHANG G S, et al., 2014. Conventional and unconventional petroleum "Orderly accumulation": concept and practical significance[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 41(1): 14-27. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(14)60002-1 [43] 曹跃,刘延哲,段昕婷,等,2018. 定边地区延长组下部储层的沉积地质意义[J]. 西安科技大学学报,38(1):137-144. [44] 樊鸿,张盛,苟小平,等,2011. 岩石断裂韧度试样CCNBD临界应力强度因子的全新数值标定[J]. 应用力学学报,28(4):416-422. [45] 付金华,罗顺社,牛小兵,等,2015. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长7段沟道型重力流沉积特征研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,34(1):29-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.01.003 [46] 贾学明,王启智,2003. 断裂韧度试样CCNBD宽范围应力强度因子标定[J]. 岩土力学,24(6):907-912. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2003.06.007 [47] 李进步,卢双舫,陈国辉,等,2015. 基于矿物学和岩石力学的泥页岩储层可压裂性评价[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,34(6):159-164. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1000-3754.2015.06.029 [48] 李年银,代金鑫,刘超,等,2016. 致密碳酸盐岩气藏体积酸压可行性研究及施工效果:以鄂尔多斯盆地下古生界碳酸盐岩气藏为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率,23(3):120-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2016.03.022 [49] 李相博,刘化清,陈启林,等,2010. 大型坳陷湖盆沉积坡折带特征及其对砂体与油气的控制作用:以鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组为例[J]. 沉积学报,28(4):717-729. [50] 李兆扬,范萌萌,马瑶,等,2012,鄂尔多斯盆地东南部长7油层组沉积相研究[J]. 陕西科技大学学报(自然科学版),30(01):106-110+121. [51] 廖纪佳,朱筱敏,邓秀芹,等,2013. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区延长组重力流沉积特征及其模式[J]. 地学前缘,20(2):29-39. [52] 刘芬,朱筱敏,李洋,等,2015. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南部延长组重力流沉积特征及相模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发,42(5):577-588. [53] 刘建,惠晨,樊建明,等,2021. 鄂尔多斯盆地合水地区长6致密砂岩储层现今地应力分布特征及其开发建议[J]. 地质力学学报,27(1):31-39. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.01.004 [54] 刘联群,李勇,康立明,等,2010. 鄂尔多斯盆地晚三叠世最大湖泛泥岩分布特征[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版),40(5):866-871. [55] 龙章亮,温真桃,李辉,等,2020. 一种基于灰色关联分析的页岩储层可压性评价方法[J]. 油气藏评价与开发,10(1):37-42. [56] 慕立俊,赵振峰,李宪文,等,2019. 鄂尔多斯盆地页岩油水平井细切割体积压裂技术[J]. 石油与天然气地质,40(3):626-635. doi: 10.11743/ogg20190317 [57] 孙越,蒋裕强,熊先钺,等,2022. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘大宁–吉县地区山西组山2 3亚段海陆过渡相页岩岩相与沉积环境变化[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,50(9):104-114. [58] 杨帆,梅文博,李亮,等, 2023. 薄互层致密砂岩水力压裂裂缝扩展特征研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,51(7):61-71. [59] 杨华,窦伟坦,刘显阳,等,2010. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7沉积相分析[J]. 沉积学报,28(2):254-263. [60] 姚泾利,邓秀芹,赵彦德,等,2013. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组致密油特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发,40(2):150-158. doi: 10.11698/PED.2013.02.03 [61] 袁俊亮,邓金根,张定宇,等,2013. 页岩气储层可压裂性评价技术[J]. 石油学报,34(3):523-527. doi: 10.7623/syxb201303015 [62] 张海林,邓南涛,张枝焕,等,2014. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部中生界原油地球化学特征及油源分析[J]. 高校地质学报,20(2):309-316. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2014.02.016 [63] 张晓辉,冯顺彦,梁晓伟,等,2020. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区延长组长7段沉积微相及沉积演化特征[J]. 地质学报,94(3):957-967. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.03.020 [64] 张哲豪,魏新善,弓虎军,等,2020. 鄂尔多斯盆地定边油田长7致密砂岩储层成岩作用及孔隙演化规律[J]. 油气地质与采收率,27(2):43-52. [65] 赵进雍,冀冬生,吴见,等,2022. 准噶尔盆地四棵树凹陷侏罗系—白垩系储层岩石力学参数研究[J]. 地质力学学报,28(4):573-582. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021158 [66] 钟大康,朱筱敏,李树静,等,2007. 早期碳酸盐胶结作用对砂岩孔隙演化的影响:以塔里木盆地满加尔凹陷志留系砂岩为例[J]. 沉积学报,25(6):885-890. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2007.06.010 [67] 邹才能,赵政璋,杨华,等,2009. 陆相湖盆深水砂质碎屑流成因机制与分布特征:以鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J]. 沉积学报,27(6):1065-1075. [68] 邹才能,杨智,张国生,等,2014. 常规-非常规油气“有序聚集”理论认识及实践意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发,41(1):14-27. doi: 10.11698/PED.2014.01.02 -




 下载:
下载: