Study on regional stress background and prevention of the rock burst accident on October 20th, 2018 in the Longyun Coal Industry area, Shandong, China
-
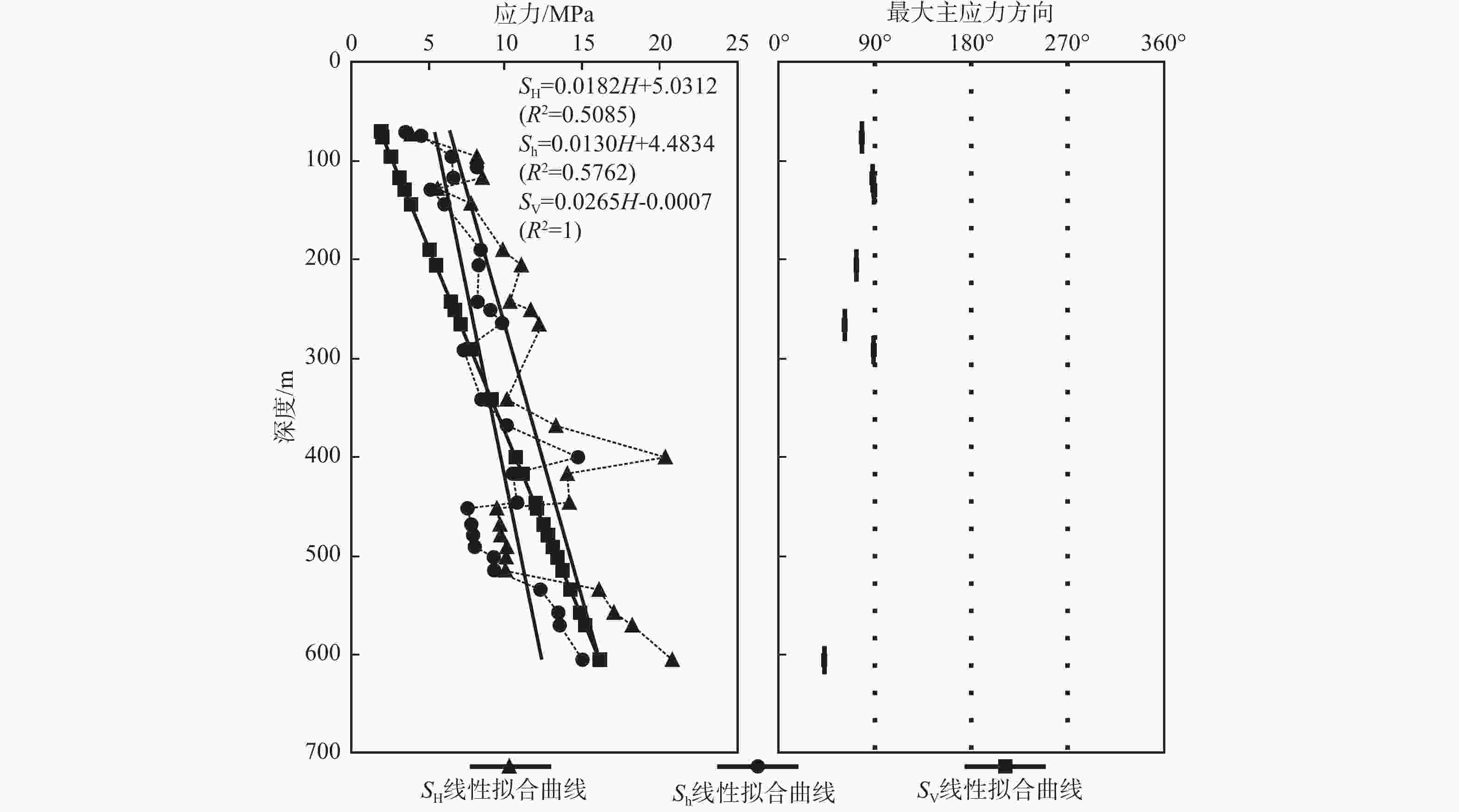
摘要: 矿山巷道、交通隧道等地下硐室围岩稳定与岩体所处区域地应力环境息息相关。分析区域深部地应力与地下硐室走向、形状等因素的关系,有助于提前规避硐室开挖风险。文章以山东龙郓煤业10•20冲击地压事故为背景,通过地应力测量与监测工作,初步揭示了山东西部地壳浅表层现今地应力环境,结合龙郓煤业矿区附近现今地应力场特征,探讨此次冲击地压事故产生的区域应力背景,并从地应力角度提出相应的防控建议。研究结果表明:测量深度范围内主应力大小总体上与深度成正比线性关系,最大水平主应力值为3.48~20.76 MPa,随深度增加梯度为0.0182 MPa/m;最小水平主应力值为3.44~14.95 MPa,随深度增加梯度为0.0130 MPa/m;区内最大水平主应力方位为北东43°~89°,平均方位为北东75°;地壳浅表层构造作用以水平构造作用为主,但随着深度的增加,逐渐向垂直构造作用转变;龙郓煤业10•20冲击地压事故的诱发机制主要是垂向应力大于水平主应力,现今处于拉张应力环境,尤其是巷道走向平行于最大水平主应力方向;建议龙郓煤业巷道轴线与最大水平主应力方向的夹角为60°~90°,同时巷道顶板可以采用拱形顶板,确保巷道岩体稳定。Abstract:
Objective The stability of underground chambers such as mine tunnels and transportation tunnels is closely related to the stress environment of the surrounding rock mass and the geological conditions of the area. Analyzing the relationship between deep-seated stress and factors such as the orientation and shape of underground chambers can help to proactively mitigate the risks associated with chamber excavation. Methods This study, set against the background of the rock burst accident on October 20th in the Longyun Coal Industry area in Shandong, reveals the current stress environment of the shallow crustal layers in western Shandong through in-situ stress measurement and monitoring work. Results According to the characteristics of the current ground stress field near the Longyun coal mining area, the study investigates the regional stress background that led to the rock burst accident and proposes corresponding prevention and control suggestions from the perspective of ground stress. The results indicate that the magnitude of the principal stress generally increases linearly with depth within the measurement range, with the maximum horizontal principal stress ranging from 3.48 to 20.76 MPa and a gradient of 0.0182 MPa/m with increasing depth, while the minimum horizontal principal stress ranges from 3.44 to 14.95 MPa with a gradient of 0.0130 MPa/m. The maximum horizontal principal stress azimuth in the area ranges from NE 43°to 89°, with an average azimuth of NE 75°. The tectonic action in the shallow crust is mainly horizontal, but with increasing depth, they gradually transition to vertical. Conclusion The triggering mechanism of the rock burst accident in the Longyun Coal Industry area on 20th October is primarily attributed to the vertical stress exceeding the horizontal principal stress, indicating a current extensional stress environment, especially when the tunnel orientation is parallel to the direction of maximum horizontal principal stress. It is suggested that the angle between the tunnel axis and the direction of maximum horizontal principal stress in the Longyun Coal Industry area should be between 60° and 90°, and that the tunnel roof can be designed as an arch-shaped roof to ensure the stability of the tunnel rock mass. -
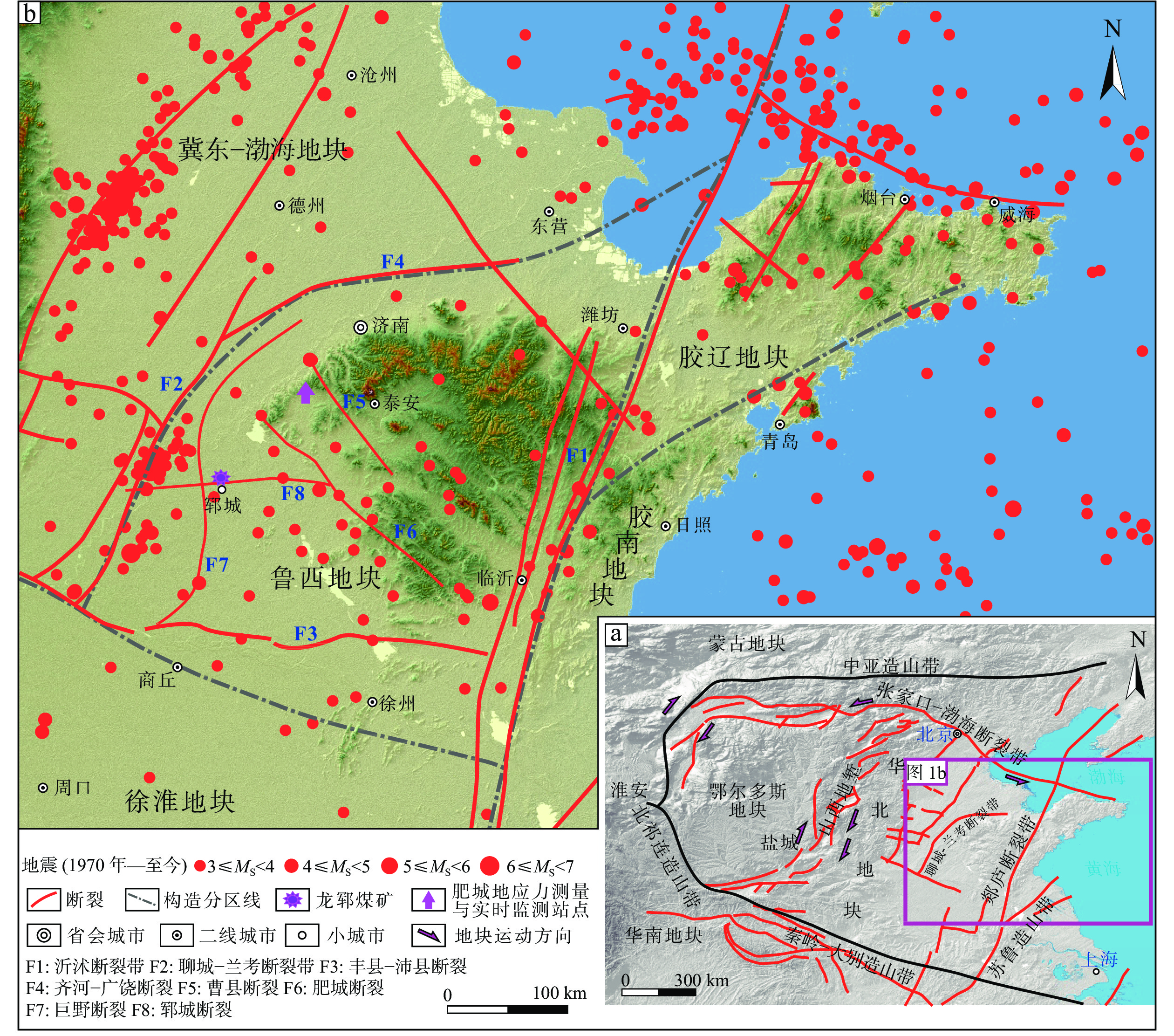
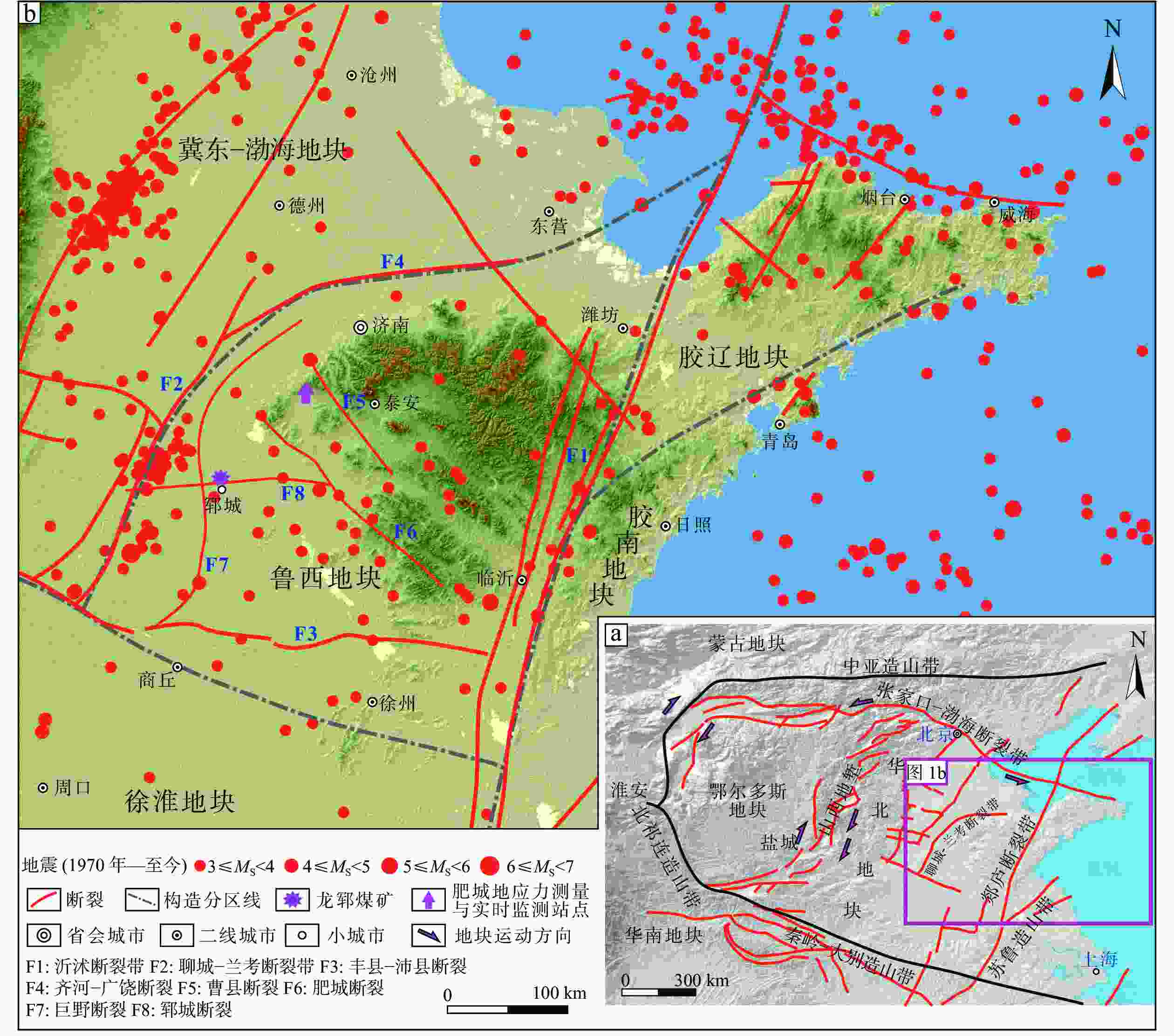
图 1 龙郓煤业矿区及周边区域构造地质背景图
a—华北地块及邻区构造纲要图; b—山东半岛主要活动断裂及事故点位图
Figure 1. Regional tectonic and geologial background map of Longyun Coal Industry and surrounding area
(a) Geotectonic outline of North China block and adjacent areas; (b) Map showing the main active faults and accident locations of Shandong Peninsula
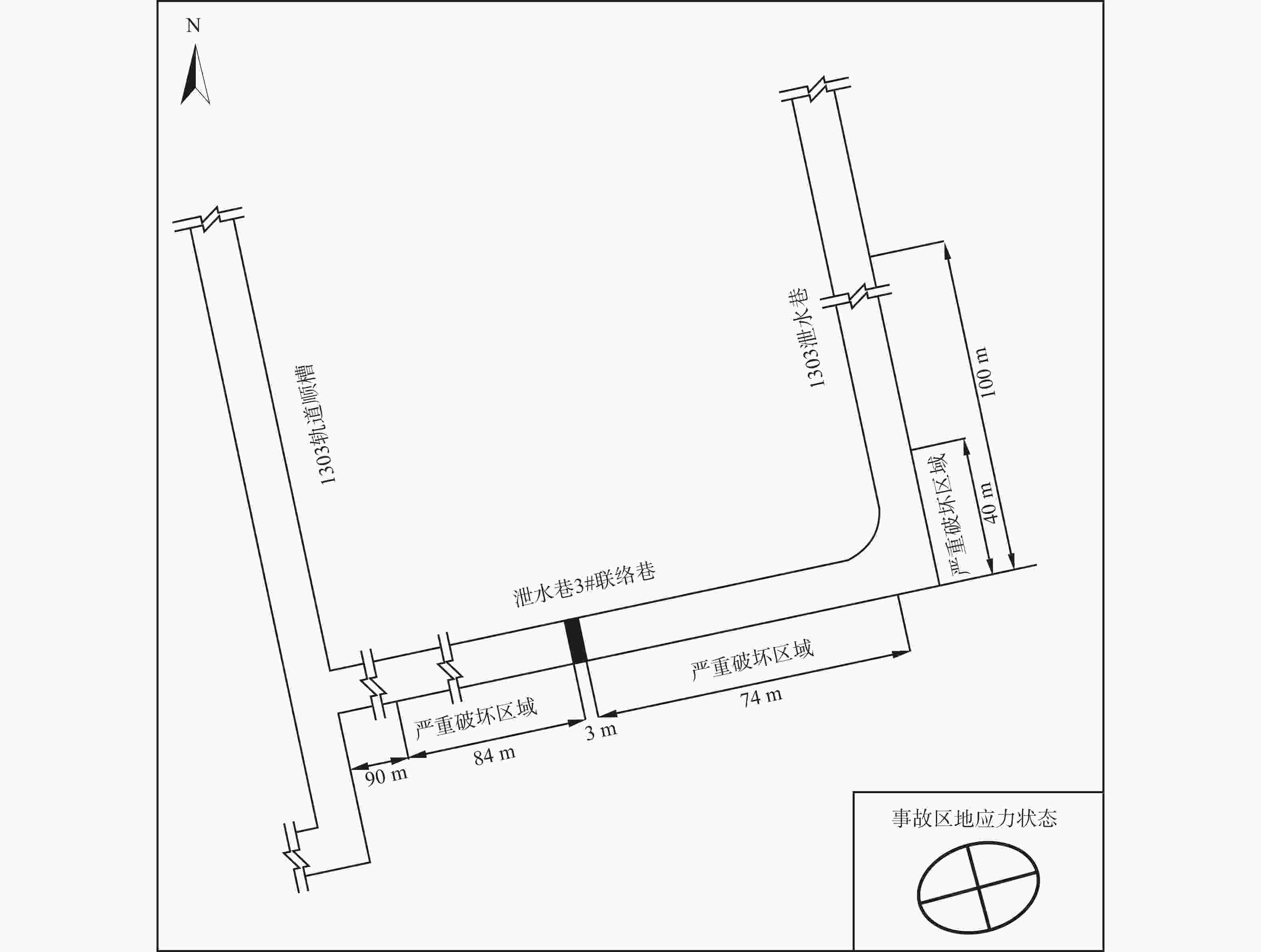
图 2 1303泄水巷及其3#联络巷示意图与巷道顶板破坏情况
a—1303泄水巷及其3#联络巷示意图;b—顶部锚杆被勒入顶板;c—顶部底鼓;d—两帮收敛,顶板下沉;e—顶板下沉,锚索梁开裂
Figure 2. Schematic diagram and photos showing 1303 drainage tunnel and its 3# connecting tunnel, illustrating the damage condition of the tunnel roof
(a) Schematic diagram of 1303 drainage tunnel and its 3# connecting tunnel; (b) Photo showing the anchoring rod being squeezed into the roof; (c) Photo showing the roof bottom drumming; (d) Photo showing convergence of both sides and roof subsidence; (e) Photo showing roof subsidence and cracking of the anchor beam
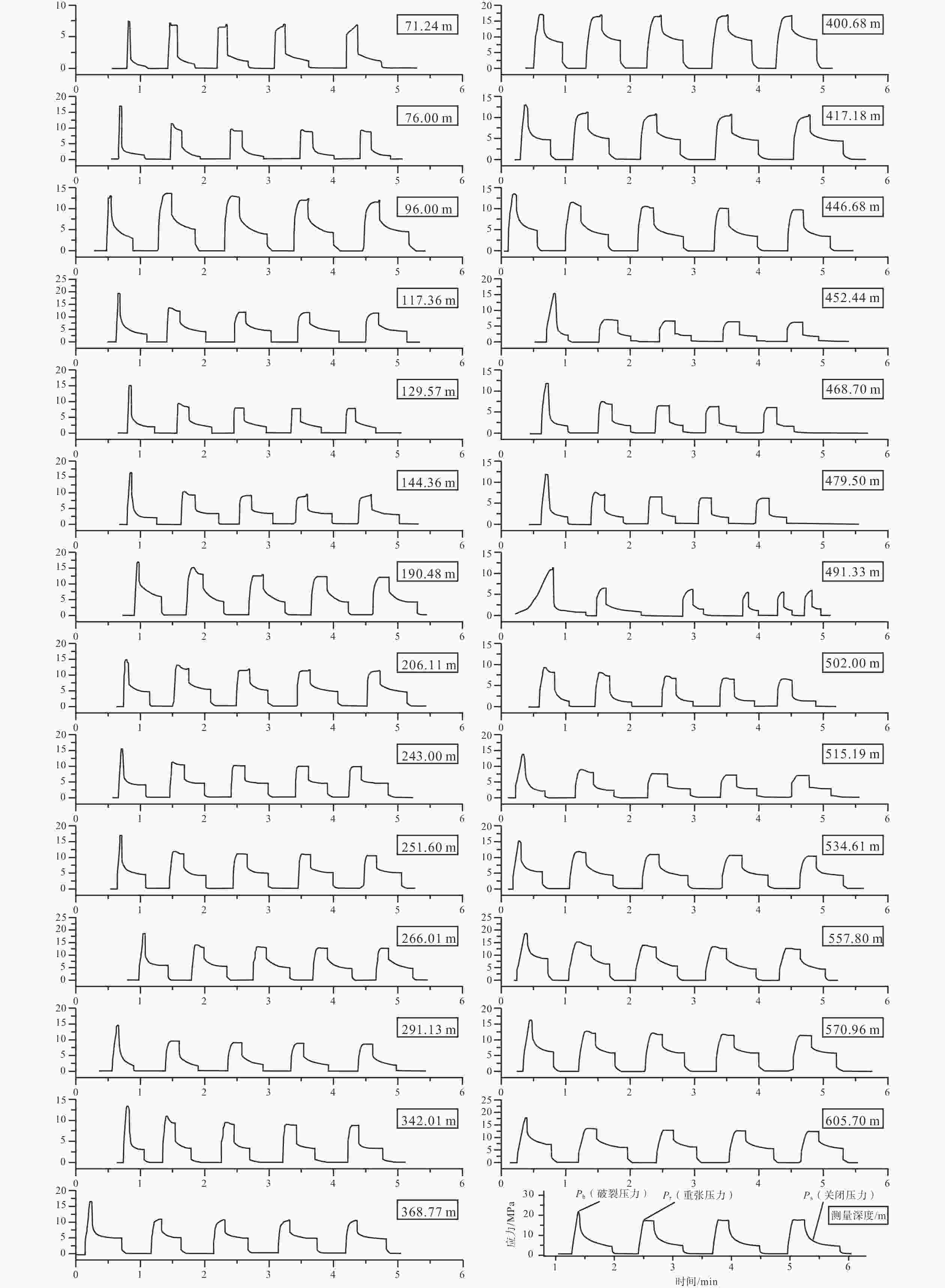
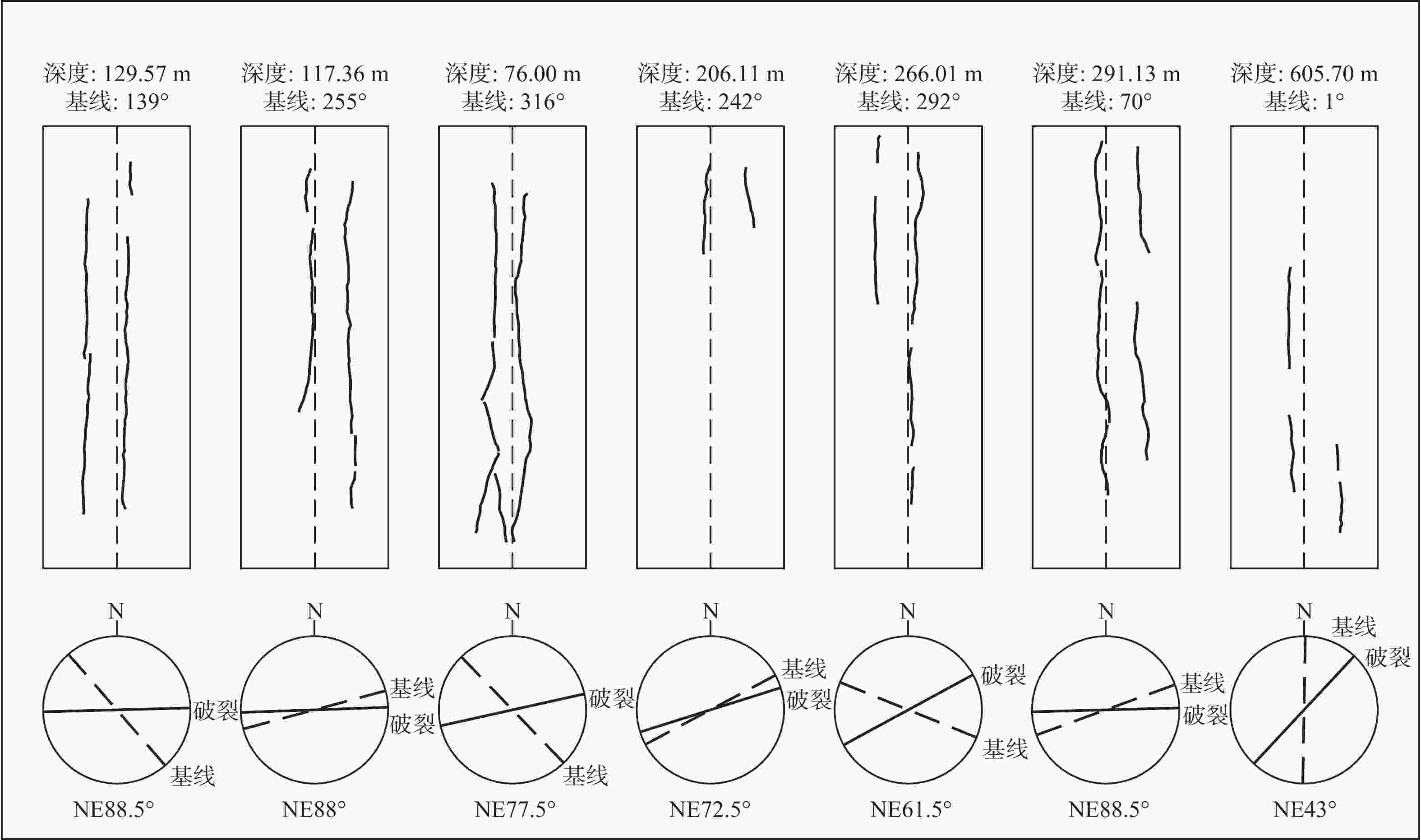
表 1 山东省肥城深孔水压致裂地应力测量结果
Table 1. Results of in-situ stress in the deep drilling core measured by hydraulic fracturing in Feicheng, Shandong Province
序号 深度/m 压裂参数/MPa 主应力值/MPa 水平侧压系数 SH方位 PH P0 Pb Pr Ps SH Sh Sv KH Kh 1 71.24 0.71 0.71 8.38 6.13 3.44 3.48 3.44 1.89 1.84 1.82 2 76.00 0.76 0.76 18.24 8.55 4.46 4.07 4.46 2.01 2.02 2.21 北东78° 3 96.00 0.96 0.96 14.20 10.37 6.48 8.11 6.48 2.54 3.19 2.55 4 117.36 1.17 1.17 20.71 10.11 6.58 8.46 6.58 3.11 2.72 2.12 北东88° 5 129.57 1.30 1.30 17.51 8.85 5.12 5.21 5.12 3.43 1.52 1.49 北东89° 6 144.36 1.44 1.44 17.61 8.75 6.00 7.81 6.00 3.83 2.04 1.57 7 190.48 1.90 1.90 18.95 13.36 8.35 9.79 8.35 5.05 1.94 1.66 8 206.11 2.06 2.06 16.68 11.62 8.22 10.98 8.22 5.46 2.01 1.51 北东73° 9 243.00 2.43 2.43 17.97 11.73 8.14 10.26 8.14 6.44 1.59 1.26 10 251.60 2.52 2.52 19.71 12.83 8.98 11.59 8.98 6.67 1.74 1.35 11 266.01 2.66 2.66 22.28 14.58 9.79 12.13 9.79 7.05 1.72 1.39 北东62° 12 291.13 2.91 2.91 18.31 10.09 7.61 9.83 7.61 7.71 1.27 0.99 北东89° 13 342.01 3.42 3.42 17.20 11.73 8.40 10.05 8.40 9.06 1.11 0.93 14 368.77 3.69 3.69 20.40 12.82 9.91 13.22 9.91 9.77 1.35 1.01 15 400.68 4.01 4.01 4.01 19.63 14.65 20.31 14.65 10.62 1.91 1.38 16 417.18 4.17 4.17 17.37 13.17 10.43 13.95 10.43 11.06 1.26 0.94 17 446.68 4.47 4.47 17.99 13.59 10.72 14.10 10.72 11.84 1.19 0.91 18 452.44 4.52 4.52 19.96 8.58 7.50 9.40 7.50 11.99 0.78 0.63 19 468.70 4.69 4.69 16.64 8.95 7.75 9.61 7.75 12.42 0.77 0.62 20 479.50 4.80 4.80 16.76 9.13 7.86 9.65 7.86 12.71 0.76 0.62 21 491.33 4.91 4.91 16.28 8.96 7.97 10.04 7.97 13.02 0.77 0.61 22 502.00 5.02 5.02 5.02 12.55 9.19 10.00 9.19 13.30 0.75 0.69 23 515.19 5.15 5.15 19.05 12.58 9.23 9.96 9.23 13.65 0.73 0.68 24 534.61 5.35 5.35 20.58 15.29 12.22 16.02 12.22 14.17 1.13 0.86 25 557.80 5.58 5.58 24.36 17.58 13.38 16.98 13.38 14.78 1.15 0.91 26 570.96 5.71 5.71 22.23 16.53 13.47 18.17 13.47 15.13 1.20 0.89 27 605.70 6.06 6.06 24.11 18.03 14.95 20.76 14.95 16.05 1.29 0.93 北东43° 注:Pb—破裂压力;Pr—重张压力;Ps—关闭压力;PH—静水柱压力;P0—孔隙压力;SH—最大水平主应力;Sh—最小水平主应力;Sv—垂向主应力(岩石容重取2650 kg/m3);最大水平侧压力系数KH=SH/Sv;最小水平侧压力系数Kh=Sh/Sv 表 2 研究区不同深度主应力回归计算结果
Table 2. Regression calculated results of principal stresses at different depths in the study area
深度/m SH/MPa Sh/MPa SV/MPa 500 14.1312 10.9834 13.2500 600 15.9512 12.2834 15.9000 610 16.1332 12.4134 16.1650 700 17.7712 13.5834 18.5500 800 19.5912 14.8834 21.2000 900 21.4112 16.1834 23.8500 1000 23.2312 17.4834 26.5000 1027 23.7226 17.8344 27.2155 1067 24.4506 18.3544 28.2755 1100 25.0512 18.7834 29.1500 1200 26.8712 20.0834 31.8000 -
[1] CHEN X F, YAO C C, ZHAO J, 2015. Simulating Analyses for Excavation Methods of Deep Buried Large-section Highway Tunnels[J]. Highway Engineering, 40(3): 152-156. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] CHEN Z Y, ZHOU J X, WANG H J, 1994. Soil Mechanics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press. (in Chinese) [3] DING G Y, 1991. Introduction to lithospheric dynamics in China[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press. (in Chinese) [4] DOU L M, ZHAO C G, YANG S G, et al. , 2006. Prevention and control of rock burst in coal mine[M]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology Press. (in Chinese) [5] FAN Y L, TAN C X, ZHANG P, et al., 2020. A Study of Current In-situ Stress State and Its Influence on Tectonic Stability in the Xiongan New Area[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 41(4): 481-491. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] FENG C J, CHEN Q C, TAN C X, et al., 2013. Analysis on current in-situ stress state in northern segment of Longmenshan fault belt[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 28(3): 1109-1121. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] FENG C J, LI B, LI H, et al., 2022. Estimation of in-situ stress field surrounding the Namcha Barwa region and discussion on the tectonic stability[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(6): 919-937. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] HOEK E, BROWN E T, 1980. Empirical Strength Criterion for Rock Masses[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering Division, 106(9): 1013-1035. doi: 10.1061/AJGEB6.0001029 [9] HOEK E, WOOD D, SHAH S, 1992. A modified Hoek-Brown criterion for jointed rock masses[C]// Proceedings of the Rock Characterization, Symposium of ISRM. London: British Geotechnical Society. 209-214. [10] HU B Q, GAO H D, WANG Y, et al., 2021. A preliminary study on the Mesozoic massive gold metallogenic mechanism of the deep-large fault coupling with critical water in the Jiaodong area, China.[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(4): 585-595. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] HU W D, CAO W G, YUAN Q S, 2017. Upper bound solution for ultimate bearing capacity of ground adjacent to slope based on nonlinear failure criterion[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 38(6): 1639-1646. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] JIN Z K, LIU Z R, SHI Z Z, 1999. Distribution patterns and formation mechanism of faults in the West Shandong Province[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China, 23(5): 1-5. (in Chinese) [13] KONG Q Y, ZHANG T Z, YU X F, et al. , 2006. Deposits in Shandong province[M]. Ji’nan: Shandong Science and Technology Press. (in Chinese) [14] LI P, GUO Q F, LIU H T, et al., 2017. Characteristics of current in-situ stress field and stress accumulation in Shandong region[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 36(9): 2220-2231. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] LI P , YUAN W , ZHANG G M, et al, 2023. Three-dimensional Geostress Inversion Method and Application for Long and Deeply Buried Tunnels: Taking the Yinhe Mountain Tunnel as an example[J]. Railway Investigation and Surveying, 49(6): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] LI S L, LI Z L, HUANG G F, 2014. Application of Hoek-Brown failure criterion to stability analysis of tunnel rock mass[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 31(5): 43-46. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] LI S Z, WANG J D, LIU J Z, et al., 2005. Mesozoic structure and its tectonic setting in the western Shandong block[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(4): 487-497. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] LIAO C T, SHI Z X, 1983. In-situ stress measurements and their application to engineering design in the Jinchuan mine[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2(1): 103-112. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] LIU S J, 2009. Causes and impact of pressure[J]. Coal Technology, 28(1): 179-181. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] QI L, MA Q C, 2000. On the selection of longitudinal direction and stability of underground opening based on the analysis of in-situ stress field[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 19(S): 1120-1123. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] REN G Y, 2019. The risk of high stress rock burst in large mining depth is high, the understanding is shallow, and heavy casualties are prevented from concentration of sparse personnel: analysis of the "10.20" major accident of Shandong Longyun Coal Industry Co. , LTD. , Shandong Energy Longmine Group[J]. Jilin Labour Protection(4): 41-43. (in Chinese) [22] SHAN C L, LI Y H, LI X, et al. , 2007. Characteristics of the focal mechanism for parts of moderate and small earthquakes in Shandong and its neighboring region[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 25(4): 27-30, 41. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] SHAN C L, LI X, FAN P L, et al., 2013. The properties of earthquake fault slip and features of crustal stress field in Shandong and nearby regions[J]. Seismological and Geomagnetic Observation and Research, 34(5-6): 32-39. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] SONG M C, 2008. The composing, setting and evolution of tectonic units in Shandong province[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 31(3): 165-175. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] SUN Y, 1998. Quantitative assessment and research of regional crustal stability[M]. Beijing: Geology Press. (in Chinese) [26] SUN Y C, XIN M G, WANG Y, et al. , 2022. Measurement and regression analysis of the tunnel Geostress of a heavy haul railway[J]. Railway Investigation and Surveying, 48(1): 16-20, 44. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] TAN C X, SUN Y, WANG L J, 2003. Some problems of in-situ crustal stress measurements[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 9(3): 275-280, 260. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] TAN C X, ZHANG P, FENG C J, et al., 2014. An approach to deep borehole crustal stress measuring and real - time monitoring and its application in seismogeology research in capital Beijing region[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(8): 1436-1452. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] WANG C H, 2014. Brief review and outlook of main estimate and measurement methods for in-situ stresses in rock mass[J]. Geological Review, 60(5): 971-996. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] WANG W, WANG L J, WANG H C, et al., 2002. Stability analysis of Kunlun Mountain tunnel for Qinghai-Tibet railway[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 23(4): 359-362. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] WEN X Q, 2019. Press conference | Interpretation of 《Measures for the prevention and control of rock burst in coal mines in Shandong province》[EB/OL]. (2019-08-27). http://www.shandong.gov.cn/art/2019/8/27/art_81283_35398.html. (in Chinese) [32] WU Z H, ZHOU C J, TAN C X, et al., 2016. The active tectonics and regional crustal stability features in the area of Yangtze River Economic Belt[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 22(3): 379-411. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] XIANG H F, WANG X C, HAO S J, et al., 2000. Activity of Liaocheng-Lankao buried fault in quaternary[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 16(4): 307-315. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] XIE F R, CUI X F, ZHAO J T, et al., 2004. Regional division of the recent tectonic stress field in China and adjacent areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 47(4): 654-662. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] XIE K K, SHEN Z, HUANG L H, et al., 2019. Analysis and simulation of the impact of stress distribution law on rock burst[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 15(S2): 920-925. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] YANG S X, YAO R, CUI X F, et al., 2012. Analysis of the characteristics of measured stress in Chinese mainland and its active blocks and North-South seismic belt[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 55(12): 4207-4217. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] YANG X L, WANG Z W, 2010. Limit analysis of earth pressure on shallow tunnel using nonlinear failure criterion[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 41(1): 299-302. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] YIN G Z, XIAN X F, JIN L P, et al., 1997. The effect of crustal stresses on rock burst and evaluation of zone prone to rock burst[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 22(2): 132-137. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] YU L, YOU Z M, CHEN J P, et al., 2015. Rock classification for tunnels in high Geostress areas[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 52(3): 23-30. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] YU L, LV C, DUAN R Y, et al., 2020. Upper bound limit analysis of three-dimensional collapse mechanism of shallow buried soil tunnel under Pore pressure based on nonlinear Mohr-Coulomb criterion[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 41(1): 194-204. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] YU X F, LI D P, SHAN W, et al., 2022. Yanshanian gold metallogenic system and metallogenic model of the Guilaizhuang gold ore field, western Shandong[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(5): 821-841. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] ZHANG L, ZHOU C Y, WANG F J, et al., 2004. Characteristics of stress field in each subregion of Shandong area[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 22(4): 12-15. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] ZHANG P, QIN X H, FENG C J, et al., 2013. In-situ stress measurement of deep borehole in Shandong segment of Tan-Lu fracture belt and analysis of its activity[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 34(8): 2329-2335. (in Chinese with English abstract [44] ZHAO W S, HAN L J, ZHAO Z N, et al., 2015. Influence of principal stress on surrounding rock stability of roadway intersection[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 36(6): 1752-1760. (in Chinese with English abstract [45] ZHU H H, ZHANG Q, ZHANG L Y, 2013. Review of research progresses and applications of Hoek-Brown strength criterion[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 32(10): 1945-1963. (in Chinese with English abstract [46] ZHU R X, CHEN L, WU F Y, et al., 2011. Timing, scale and mechanism of the destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 54(6): 789-797. doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4203-4 [47] 陈雪峰,姚晨晨,赵杰, 2015. 深埋大断面公路隧道开挖方法数值模拟分析[J]. 公路工程,40(3):152-156. [48] 陈仲颐,周景星,王洪瑾,1994. 土力学[M]. 北京:清华大学出版社. [49] 丁国瑜,1991. 中国岩石圈动力学概论[M]. 北京:地震出版社. [50] 窦林名,赵从国,杨思光,等,2006. 煤矿开采冲击矿压灾害防治[M]. 徐州:中国矿业大学出版社. [51] 范玉璐,谭成轩,张鹏,等, 2020. 雄安新区现今地应力环境及其对构造稳定性影响研究[J]. 地球学报,41(4):481-491. [52] 丰成君,陈群策,谭成轩,等, 2013. 龙门山断裂带东北段现今地应力环境研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,28(3):1109-1121. [53] 丰成君,李滨,李惠,等, 2022. 南迦巴瓦地区地应力场估算与构造稳定性探讨[J]. 地质力学学报,28(6):919-937. [54] 胡宝群,高海东,王运,等, 2021. 胶东中生代巨量金矿堆积的深大断裂-临界水耦合成矿机制新探[J]. 地质力学学报,27(4):585-595. [55] 胡卫东,曹文贵,袁青松, 2017. 基于非线性破坏准则的临坡地基承载力上限分析[J]. 岩土力学,38(6):1639-1646. [56] 金振奎,刘泽容,石占中, 1999. 鲁西地区断裂构造类型及其形成机制[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版),23(5):1-5. [57] 孔庆友,张天祯,于学峰,等,2006. 山东矿床[M]. 济南:山东科学技术出版社. [58] 李鹏,郭奇峰,刘洪涛,等, 2017. 山东地区现今地应力场特征与应力积累水平分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,36(9):2220-2231. [59] 李鹏,袁维,张光明,等. 长大深埋高铁隧道三维地应力场反演方法及应用:以银河山隧道为例[J]. 铁道勘察,2023,49(6):1-7. [60] 李三忠,王金铎,刘建忠,等, 2005. 鲁西地块中生代构造格局及其形成背景[J]. 地质学报,79(4):487-497. [61] 李守龙,李宗利,黄高峰, 2014. Hoek-Brown强度准则在隧道岩体稳定分析中的应用研究[J]. 长江科学院院报,31(5):43-46. [62] 廖椿庭,施兆贤, 1983. 金川矿区原岩应力实测及在矿山设计中的应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2(1):103-112. [63] 刘士君, 2009. 冲击地压的成因浅析[J]. 煤炭技术,28(1):179-181. [64] 戚蓝,马启超, 2000. 在地应力场分析的基础上探讨地下洞室长轴向选取和围岩稳定性[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,19(S):1120-1123. [65] 任广艳,2019. 大采深高应力 冲击地压风险高悬 认识浅防范疏 人员集中伤亡惨重:山东能源龙矿集团山东龙郓煤业有限公司“10.20”重大事故分析[J]. 吉林劳动保护(4):41-43. [66] 山长仑,李永红,李霞,等, 2007. 山东及附近区域部分中小地震震源机制特征分析[J]. 华北地震科学,25(4):27-30,41. [67] 山长仑,李霞,范培乐,等, 2013. 山东及附近区域地震断层错动性质与地壳应力场特征[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究,34(5-6):32-39. [68] 宋明春, 2008. 山东省大地构造单元组成、背景和演化[J]. 地质调查与研究,31(3):165-175. [69] 孙叶,1998. 区域地壳稳定性定量化评价[M]. 北京:地质出版社. [70] 孙元春,辛明高,汪洋,等, 2022. 某重载铁路隧道地应力测试与反演分析[J]. 铁道勘察,48(1):16-20,44. [71] 谭成轩,孙叶,王连捷, 2003. 地应力测量值得注意的若干问题[J]. 地质力学学报,9(3):275-280,260. [72] 谭成轩,张鹏,丰成君,等, 2014. 探索首都圈地区深孔地应力测量与实时监测及其在地震地质研究中应用[J]. 地质学报,88(8):1436-1452. [73] 王成虎, 2014. 地应力主要测试和估算方法回顾与展望[J]. 地质论评,60(5):971-996. [74] 王薇,王连捷,王红才,等, 2002. 青藏铁路昆仑山隧道稳定性分析[J]. 地球学报,23(4):359-362. [75] 温向前,2019. 新闻发布会| 解读《山东省煤矿冲击地压防治办法》[EB/OL]. (2019-08-27). http://www.shandong.gov.cn/art/2019/8/27/art_81283_35398.html. [76] 吴中海,周春景,谭成轩,等, 2016. 长江经济带地区活动构造与区域地壳稳定性基本特征[J]. 地质力学学报,22(3):379-411. [77] 向宏发,王学潮,郝书俭,等, 2000. 聊城-兰考隐伏断裂的第四纪活动性:中国东部平原区一条重要的隐伏活动断裂[J]. 中国地震,16(4):307-315. [78] 谢富仁,崔效锋,赵建涛,等, 2004. 中国大陆及邻区现代构造应力场分区[J]. 地球物理学报,47(4):654-662. [79] 谢克坷,沈泽,黄练红,等, 2019. 地应力分布对冲击地压影响分析与模拟研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,15(S2):920-925. [80] 杨树新,姚瑞,崔效锋,等, 2012. 中国大陆与各活动地块、南北地震带实测应力特征分析[J]. 地球物理学报,55(12):4207-4217. [81] 杨小礼,王作伟, 2010. 非线性破坏准则下浅埋隧道围岩压力的极限分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),41(1):299-302. [82] 尹光志,鲜学福,金立平,等, 1997. 地应力对冲击地压的影响及冲击危险区域评价的研究[J]. 煤炭学报,22(2):132-137. [83] 余莉,尤哲敏,陈建平,等, 2015. 高地应力地区隧道围岩分级研究[J]. 现代隧道技术,52(3):23-30. [84] 于丽,吕城,段儒禹,等, 2020. 考虑孔隙水压力及非线性Mohr-Coulomb破坏准则下浅埋土质隧道三维塌落机制的上限分析[J]. 岩土力学,41(1):194-204. [85] 于学峰,李大鹏,单伟,等, 2022. 鲁西归来庄金矿田燕山期金成矿系统及成矿模式[J]. 地质力学学报,28(5):821-841. [86] 张玲,周翠英,王锋吉,等, 2004. 山东地区各分区地震应力场特征分析[J]. 华北地震科学,22(4):12-15. [87] 张鹏,秦向辉,丰成君,等, 2013. 郯庐断裂带山东段深孔地应力测量及其现今活动性分析[J]. 岩土力学,34(8):2329-2335. [88] 赵维生,韩立军,赵周能,等, 2015. 主应力对巷道交岔点围岩稳定性影响研究[J]. 岩土力学,36(6):1752-1760. [89] 朱合华,张琦,章连洋, 2013. Hoek-Brown强度准则研究进展与应用综述[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,32(10):1945-1963. [90] 朱日祥,陈凌,吴福元,等, 2011. 华北克拉通破坏的时间、范围与机制[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,41(5):583-592. -




 下载:
下载: