Characterization of the Holocene extensional structures in the Wuwei Basin, northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau, and their formation mechanism
-
摘要: 武威盆地位于青藏高原东北缘北祁连山与龙首山之间的河西走廊东端,全新世期间处于北东向挤压环境中。野外地质调查发现,武威盆地内部发育有两组走向近于垂直的正断层,即北西西走向和北东走向的正断层。光释光测年结果表明,两组正断层在0.70 ka、0.49~0.18 ka发生了两期构造活动。分析结果认为,北西西走向正断层是由武威盆地内部坟门山隆起持续隆升所产生的垂直于地层层面的差异应力作用所形成;北东走向正断层可能是盆地两侧近东西走向左旋走滑断裂控制下形成的张性破裂(T破裂),也不排除是由在青藏高原北东向挤压作用下,与挤压应力相垂直方向上的伸展作用形成。因此,晚全新世期间武威盆地的构造变形受到青藏高原东北缘构造的控制。Abstract: The Wuwei Basin at the eastern end of the Hexi Corridor, between the North Qilian Mountain and the Longshou Mountain in the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau, was in a NE-trending compressional environment during the Holocene. Our field survey results indicate that there are two groups of near-vertical normal faults, namely the NWW-trending and NE-trending faults. The OSL dating results show that the two groups of normal faults experienced two periods of tectonic activity in 0.70 ka and 0.49~0.18 ka. The analysis concludes that the NWW-trending normal faults were formed by the differential stress perpendicular to the stratigraphy, which was produced by the continuous uplift of the Fenmenshan uplift in the Wuwei Basin. The NE-trending normal faults could be the extensional rupture (T rupture) produced by the nearly EW-trending sinistral strike-slip faults on both sides of the Wuwei Basin, or be formed by the extension vertical to the NE-trending compression of the Tibetan Plateau. Therefore, the tectonic deformation in the Wuwei Basin was controlled by the tectonic activities in the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau during the late Holocene.
-
Key words:
- northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau /
- Wuwei Basin /
- Holocene /
- normal fault /
- Hexi Corridor
-
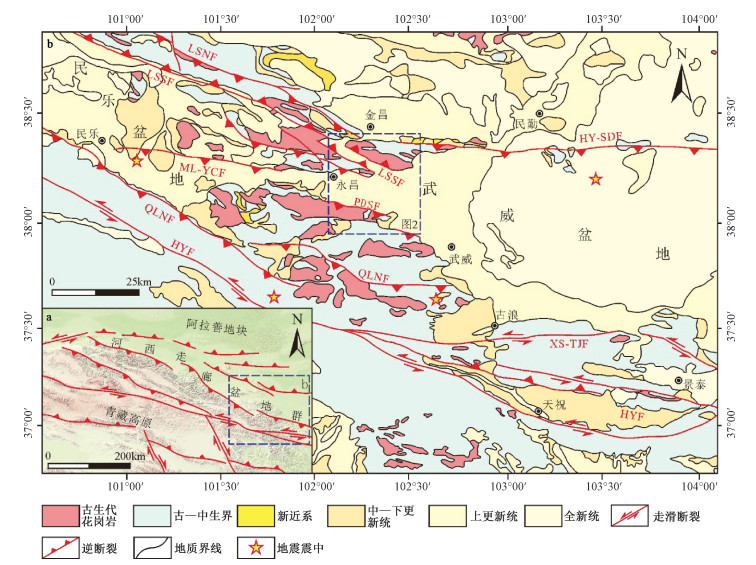
图 1 武威盆地区域构造简图(据Zheng et al., 2010修改)
QLNF—祁连山北缘断裂;HYF—海原断裂;XS-TJF—香山-天景山断裂;ML-YCF—民乐-永昌断裂;HY-SDF—红崖山-四道山断裂;LSSF—龙首山南缘断裂;LSNF—龙首山北缘断裂;PDSF—盆地南缘断裂
Figure 1. Regional structural sketch of the Wuwei Basin (modified from Zheng et al., 2010)
QLNF-Northern Qilianshan Fault; HYF-Haiyuan Fault; XS-TJF-Xiangshan-Tianjingshan Fault; ML-YCF-Minle-Yongchang Fault; HY-SDF-Hongyashan-Sidaoshan Fault; LSSF-Southern Longshoushan Fault; LSNF-Northern Longshoushan Fault; PDSF-Southern Basin Fault
图 2 武威盆地研究区地质简图(据何翔等,2022修改)
LSSF—龙首山南缘断裂;HY-SDF—红崖山-四道山断裂;LS-WW-GHF—狼山-武威-共和断裂;FMNF—坟门山北缘断裂;FMSF—坟门山南缘断裂;PDSF—盆地南缘断裂
Figure 2. Geological sketch of the Wuwei Basin (modified from He et al., 2022)
LSSF-Southern Longshoushan Fault; HY-SDF-Hongyashan-Sidaoshan Fault; LS-WW-GHF-Langshan-Wuwei-Gonghe Fault; FMNF-Northern Fenmenshan Fault; FMSF-Southern Fenmenshan Fault; PDSF-Southern Basin Fault
图 3 武威盆地北西西走向断层剖面图(地层划分据何翔等,2022)
a—点D1处北西西走向正断层照片;b—点D2处北西西走向正断层照片;c—点D1处北西西走向正断层素描图;d—点D2处北西西走向正断层素描图
Figure 3. Profiles of the NWW-trending faults in the Wuwei Basin (Stratigraphic division is from He et al., 2022)
(a) Photo showing the NWW-trending normal fault at D1; (b) Photo showing the NWW-trending normal fault at D2; (c) Geologic sketch showing the NWW-trending normal fault at D1; (d) Geologic sketch showing the NWW-trending normal fault at D2
图 4 武威盆地北东走向断层剖面图(地层划分据何翔等,2022)
a—点D3处北东走向正断层照片;b—点D3处北东走向正断层素描图;c—点D4处北东走向正断层照片;d—点D4处北东走向正断层素描图
Figure 4. Profiles of the NE-trending faults in the Wuwei Basin (Stratigraphic division is from He et al., 2022)
(a) Photo showing the NE-trending normal fault at D3; (b) Geologic sketch showing the NE-trending normal fault at D3; (c) Photo showing the NE-trending normal fault at D4; (d) Geologic sketch showing the NE-trending normal fault at D4
图 5 武威盆地内部断层发育模式图(地层划分据何翔等,2022)
FMNF—坟门山北缘断裂;FMSF—坟门山南缘断裂;HY-SDF—红崖山-四道山断裂;PDSF—盆地南缘断裂;QLNF—祁连山北缘断裂
a—武威盆地内北西西走向正断层分布图;b—武威盆地内北东走向正断层分布图;c—坟门山隆起发育初期的武威盆地示意图;d—坟门山隆起发育后期的武威盆地示意图Figure 5. Fault development model in the Wuwei Basin (Stratigraphic division is from He et al., 2022)
(a) Distribution diagram of the NWW-trending normal faults in the Wuwei Basin; (b) Distribution diagram of the NE-trending normal faults in the Wuwei Basin; (c) Diagram of the Wuwei Basin in the early stage of the Fenmenshan uplift; (d) Diagram of the Wuwei Basin in the late stage of the Fenmenshan uplift
FMNF-Northern Fenmenshan Fault; FMSF-Southern Fenmenshan Fault; HY-SDF-Hongyashan-Sidaoshan Fault; PDSF-Southern Basin Fault; QLNF-Northern Qilianshan Fault表 1 光释光样品测年数据
Table 1. Optically stimulated luminescence data of the five samples
野外编号 U/(μg/g) Th/(μg/g) K/% 环境剂量率/(Gy/ka) 等效剂量/Gy 年龄/ka OSL-1 3.49±0.11 12.3±0.37 1.82±0.05 4.44±0.33 0.77±0.08 0.18±0.02 OSL-2 3.39±0.10 13.8±0.41 1.81±0.05 4.68±0.36 0.90±0.08 0.19±0.02 OSL-3 2.10±0.06 10.3±0.31 1.91±0.06 3.29±0.15 1.41±0.13 0.43±0.04 OSL-4 3.62±0.11 17.9±0.54 2.01±0.06 4.30±0.19 2.12±0.18 0.49±0.05 OSL-5 3.36±0.10 17.5±0.52 1.93±0.06 4.15±0.18 2.88±0.24 0.70±0.07 -
AI S, ZHANG B, FAN C, et al., 2017. Surface tracks and slip rate of the fault along the southern margin of the Wuwei basin in the late Quaternary[J]. Seismology and Geology, 39(2): 408-422. (in Chinese with English abstract) AN Z S, KUTZBACH J E, PRELL W L, et al., 2001. Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan plateau since late Miocene times[J]. Nature, 411(6833): 62-66. doi: 10.1038/35075035 BALLARINI M, WALLINGA J, MURRAY A S, et al., 2003. Optical dating of young coastal dunes on a decadal time scale[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 22(10-13): 1011-1017. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(03)00043-X BOVET P M, RITTS B D, GEHRELS G, et al., 2009. Evidence of Miocene crustal shortening in the North Qilian Shan from Cenozoic stratigraphy of the western Hexi Corridor, Gansu Province, China[J]. American Journal of Science, 309(4): 290-329. doi: 10.2475/00.4009.02 Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Gansu Province, 1997. Stratigraphy(lithostratic) of Gansu province[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press. (in Chinese) CARDELLO G L, TESEI T, 2013. Transtensive faulting in carbonates at different crustal levels: examples from SW Helvetics and central Apennines[J]. Rendiconti Online Societa Geologica Italiana, 29: 20-23. CHAMPAGNAC J D, YUAN D Y, GE W P, et al., 2010. Slip rate at the north-eastern front of the Qilian Shan, China[J]. Terra Nova, 22(3): 180-187. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3121.2010.00932.x CHEN B L, LIU J M, LIU J S, et al., 2006. Study on the activity and chronology of the Gaotai Railway Station fault during Holocene Epoch[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(4): 497-507. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN B L, WANG C Y, CUI L L, et al., 2008. Developing model of thrust fault system in western part of Northern Qilian Mountains margin-Hexi Corridor Basin during late Quaternary[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 15(6): 260-277. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN B L, LIU J S, 2009. Geodetic deformation in Northern Qilianshan margin and Hexi Corridor area, Northwest China and its relation to the earthquake[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(10): 1439-1447. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN W B, 2003. Principal features of tectonic deformation and their generation mechanism in the Hexi Corridor and its adjacent regions since late Quaternary[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administrator. (in Chinese with English abstract) CUI Z H, TANG L J, 2007. A genetic model of normal fault under compressive tectonic setting[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 28(2): 254-256. (in Chinese with English abstract) CUNNINGHAM D, ZHANG J, LI Y F, 2016. Late Cenozoic transpressional mountain building directly north of the Altyn Tagh fault in the Sanweishan and Nanjieshan, north Tibetan foreland, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 687: 111-128. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.09.010 DENG Q D, ZHANG W Q, ZHANG P Z, et al., 1989. Haiyuan strike-slip fault zone and its compressional structures of the end[J]. Seismology and Geology, 11(1): 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) GE X H, LIU J L, 1999. Formation and tectonic background of the Northern Qilian orogenic belt[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 6(4): 223-230. (in Chinese with English abstract) GUO H J, YANG L R, ZHU X H, et al., 2016. River terrace and Quaternary tectonic uplift in the Qilian Mountain[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 35(12): 2033-2044. (in Chinese with English abstract) HE G Y, YANG S F, CHEN H L, et al., 2004. On faults of western Hexi corridor and its vicinity, Northwestern China Ⅰ: Thrust and strike-slip faults of late Cenozoic[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 26(6): 601-608. (in Chinese with English abstract) HE X, DU X X, LIU J, et al., 2022. Sedimentary process and tectonic significance of Wuwei basin during the Quaternary[J]. Seismology and Geology, 44(1): 76-97. (in Chinese with English abstract) HOU K M, ZHENG Q D, LIU B C, 1999. Research on tectonic environment and seismogenic mechanism of 1927 Gulang great earthquake[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 15(4): 339-348. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU X F, 2010. The research on temporal and spatial distributions of erosionrates and tectonic deformation in the Northern Qilianshan[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIANG Z S, MA Z J, ZHANG X, et al., 2001. Analysis of recent horizontal crustal strain field and tectonic deformation in the northeast margin of Qinghai-Tibet block[J]. Seismology and Geology, 23(3): 337-346. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIN S, ZHANG L T, JIN Y J, et al., 2012. Crustal electrical structure along the Hezuo-Dajing profile across the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 55(12): 3979-3990. (in Chinese with English abstract) LAI Z P, OU X J, 2013. Basic procedures of optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating[J]. Progress in Geography, 32(5): 683-693. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI F Q, WANG C S, ZHU L D, et al., 2002. The basin-range coupling under the regional compressional regimes: examples from the Hexi Corridor Basin and North Qilian Mountains[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 22(4): 17-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI J Y, ZHENG W J, WANG W T, et al., 2020. The northward growth of the northeastern Tibetan Plateau in late Cenozoic: Implications from apatite(U-Th)/He ages of Longshoushan[J]. Seismology and Geology, 42(2): 472-491. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI W L, CHENG H H, ZHANG H, et al., 2019. Three-dimensional numerical modeling of the tectonic evolution of the serial basins in the Hexi Corridor in Northwest China[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 36(2): 196-207. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI X, WAN Y G, CUI H W, et al., 2016. Tectonic stress field of 2016, MS6.4 Menyuan, Qinghai earthquake[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 34(2): 36-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Y L, YANG J C, LI B J, et al., 1997. On the tectonic landform of the Yumu Mountain, Hexi Corridor, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 3(4): 20-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU B Y, ZENG W H, YUAN D Y, et al., 2014. Fault parameters and slip properties of the 1954 northern Tengger Desert M7.0 earthquake[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 36(3): 622-627. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU B Y, ZENG W H, YUAN D Y, et al., 2015. The research on fault parameter and sliding behavior of the 1927 Gulang M8.0 earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology, 37(3): 818-828. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU H C, DAI H G, LI L H, et al., 2000. A preliminary study on the 1954 Minqin MS7.0 earthquake in Gansu province[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 22(3): 232-235. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU H F, LIANG H S, CAI L G, et al., 1994. Evolution and structural style of Tianshan and adjacent basins, Northwestern China[J]. Earth Science, 19(6): 727-741. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU X W, YUAN D Y, SU Q, et al., 2020. Late Quaternary tectonic activity and slip rates of active faults in the Western Hexi Corridor, NW China[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 31(5): 968-977. doi: 10.1007/s12583-020-1287-9 MURRAY A S, WINTLE A G, 2000. Luminescence dating of quartz using an improved single-aliquot regenerative-dose protocol[J]. Radiation Measurements, 32(1): 57-73. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(99)00253-X MURRAY A S, WINTLE A G, 2003. The single aliquot regenerative dose protocol: Potential for improvements in reliability[J]. Radiation Measurements, 37(4-5): 377-381. doi: 10.1016/S1350-4487(03)00053-2 PEI H L, 2017. Manifestation of new tectonic activity on the proluvial landform in the northern Yumu Mountain marginal fault[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing). (in Chinese with English abstract) SHI W, LIU Y, LIU Y, et al., 2013. Cenozoic evolution of the Haiyuan fault zone in the northeast margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(4): 1-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) SHI Y J, ZHANG C W, CUN S C, 1995. Discovery of nappe structure in Longshou Mountain and its geological significance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 40(9): 812-813. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/csb1995-40-9-812 SONG C H, 2006. Tectonic uplift and Cenozoic sedimentary evolution in the northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University. (in Chinese with English abstract) TAN L H, YANG J C, DUAN F J, 1998. Stages of Cenozoic tectonic movement in Hexi Corridor, Gansu province[J]. Acta Scicentiarum Naturalum Universitis Pekinesis, 34(4): 523-532. (in Chinese with English abstract) THORNTON J M, MARIETHOZ G, BRUNNER P, 2018. A 3D geological model of a structurally complex Alpine region as a basis for interdisciplinary research[J]. Scientific Data, 5(1): 180238. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2018.238 WALDRON J W F, 2005. Extensional fault arrays in strike-slip and transtension[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 27(1): 23-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2004.06.015 WAN J L, ZHENG W J, ZHENG D W, et al., 2010. Low closure temperature thermochronometry study on the late Cenozoic tectonic active of Northern Qilianshan and its implication for dynamics of Tibetan Plateau growth[J]. Geochimica, 39(5): 439-446. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG C S, DAI J G, LIU Z F, et al., 2009. The uplift history of the Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya and its study approaches and techniques: a review[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 16(3): 1-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG J M, ZHANG J J, LIU K, et al., 2016a. Spatial and temporal evolution of tectonometamorphic discontinuities in the central Himalaya: constraints from P-T paths and geochronology[J]. Tectonophysics, 679: 41-60. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.04.035 WANG W T, KIRBY E, ZHANG P Z, et al., 2013. Tertiary basin evolution along the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau: Evidence for basin formation during Oligocene transtension[J]. GSA Bulletin, 125(3-4): 377-400. doi: 10.1130/B30611.1 WANG W T, ZHANG P Z, ZHENG D W, et al., 2014. Late Cenozoic tectonic deformation of the Haiyuan fault zone in the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(4): 266-274. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG W T, ZHANG P Z, PANG J Z, et al., 2016b. The Cenozoic growth of the Qilian Shan in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau: a sedimentary archive from the Jiuxi Basin[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 121(4): 2235-2257. doi: 10.1002/2015JB012689 WANG W T, ZHENG D W, LI C P, et al., 2020. Cenozoic exhumation of the Qilian Shan in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau: evidence from low-temperature thermochronology[J]. Tectonics, 39(4): e2019TC005705. WANG X L, LI X N, LU Y C, 2004. Red LED and its application to luminescence lighting[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 24(1): 133-137. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIAO K Z, TONG H M, 2020. Progress on strike-slip fault research and its significance[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(2): 151-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIAO Q B, ZHANG J, WANG J J, et al., 2012. Electrical resistivity structures between the Northern Qilian Mountains and Beishan Block, NW China, and tectonic implications[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 200-201: 92-104. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2012.04.008 XIAO Q B, ZHANG J, ZHAO G Z, et al., 2013a. Electrical resistivity structures northeast of the Eastern Kunlun Fault in the Northeastern Tibet: tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 601: 125-138. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2013.05.003 XIAO Q B, SHAO G H, JINGL Z, et al., 2015. Eastern termination of the Altyn Tagh Fault, Western China: constraints from a magnetotelluric survey[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 120(5): 2838-2858. doi: 10.1002/2014JB011363 XIAO W J, WINDLEY B F, ALLEN M B, et al., 2013b. Paleozoic multiple accretionary and collisional tectonics of the Chinese Tianshan orogenic collage[J]. Gondwana Research, 23(4): 1316-1341. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.01.012 YAN C F, YUAN J Y, 2011. Sedimentary environment and hydrocarbon potential of Carboniferous in Wuwei Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 22(2): 267-274. (in Chinese with English abstract) YAN D P, SUN M, GONG L X, et al., 2020. Composite structure and growth of the Longmenshan foreland thrust belt in the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(5): 615-633. (in Chinese with English abstract) YAN M D, FANG X M, VAN DER VOO R, et al., 2013. Neogene rotations in the Jiuquan Basin, Hexi Corridor, China[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 373(1): 173-189. doi: 10.1144/SP373.6 YANG J C, TAN L H, LI Y L, et al., 1998. River terraces and neotectonic evolution at north margin of the Qilianshan mountains[J]. Quaternary Sciences(3): 229-237. (in Chinese with English abstract) YU J X, ZHENG W J, KIRBY E, et al., 2016. Kinematics of late Quaternary slip along the Yabrai fault: implications for Cenozoic tectonics across the Gobi Alashan block, China[J]. Lithosphere, 8(3): 199-218. doi: 10.1130/L509.1 YU J X, ZHENG W J, ZHANG P Z, et al., 2017. Late Quaternary strike-slip along the Taohuala Shan-Ayouqi fault zone and its tectonic implications in the Hexi Corridor and the southern Gobi Alashan, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 721: 28-44. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2017.09.014 YUAN D Y, GE W P, CHEN Z W, et al., 2013. The growth of northeastern Tibet and its relevance to large-scale continental geodynamics: a review of recent studies[J]. Tectonics, 32(5): 1358-1370. doi: 10.1002/tect.20081 YUN L, ZHANG J, WANG J, et al., 2021. Discovery of active faults in the southern Beishan area, NW China: implications for regional tectonics[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(2): 195-207. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG B H, ZHANG J, ZHAO H, et al., 2021a. Kinematics and geochronology of Late Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic ductile deformation in the Alxa Block, NW China: new constraints on the evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic belt[J]. Lithosphere, 2021(1): 3365581. doi: 10.2113/2021/3365581 ZHANG H P, ZHANG P Z, PRUSH V, et al., 2017. Tectonic geomorphology of the Qilian Shan in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau: insights into the plateau formation processes[J]. Tectonophysics, 706-707: 103-115. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2017.04.016 ZHANG J, MA Z J, XIAO W X, et al., 2006. Geological evidences of the deformation in Central-Southern Ningxia in the Miocene and its significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(11): 1650-1659. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG J, LI J Y, LI Y F, et al., 2007. The cenozoic deformation of the Alxa block in central Asia-Question on the northeastern extension of the Altyn Tagh Fault in Cenozoic time[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(11): 1481-1497. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG J, CUNNINGHAM D, CHENG H Y, 2010. Sedimentary characteristics of Cenozoic strata in central-southern Ningxia, NW China: implications for the evolution of the NE Qinghai-Tibetan plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 39(6): 740-759. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.05.008 ZHANG J, CUNNINGHAM D, YUN L, et al., 2021b. Kinematic variability of late Cenozoic fault systems and contrasting mountain building processes in the Alxa block, western China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 205: 104597. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104597 ZHANG K Q, WU Z H, LV T Y, et al., 2015. Review and progress of OSL dating[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(1): 183-203. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG P Z, ZHENG D W, YIN G M, et al., 2006. Discussion on late Cenozoic growth and rise of northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 26(1): 5-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG P Z, ZHANG H P, ZHENG W J, et al., 2014. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of Continental eastern Asia[J]. Seismology and Geology, 36(3): 574-585. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Y Q, LI H L, 2016. Late Cenozoic tectonic events in east Tibetan Plateau and extrusion-related orogenic system[J]. Geology in China, 43(6): 1829-1852. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAO H, ZHANG J, LI Y F, et al., 2019. Characteristics of Cenozoic faults in Langshan area, Inner Mongolia: constraint on the development of normal faults[J]. Geology in China, 46(6): 1433-1453. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAO L Q, ZHAN Y, WANG Q L, et al., 2018. Deep electrical structure beneath the 1954 MS7.0 Minqin, Gansu earthquake and its seismotectonic environment[J]. Seismology and Geology, 40(3): 552-565. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAO Z X, 2021. Late Cenozoic sedimentary, tectonic and geomorphic evolution in the northeastern Qilian Shan[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHENG D W, CLARK M K, ZHANG P Z, et al., 2010. Erosion, fault initiation and topographic growth of the North Qilian Shan (northern Tibetan Plateau)[J]. Geosphere, 6(6): 937-941. doi: 10.1130/GES00523.1 ZHENG W J, YUAN D Y, HE W G, 2004. Characteristics of palaeo-earthquake activity along the active Tianqiaogou-Huangyangchuan fault on the eastern section of the Qilianshan Mountains[J]. Seismology and Geology, 26(4): 645-657. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHENG W J, HE W G, ZHAO G K, et al., 2005. Discussion on the causative structure and mechanism of the 2003 Minle-Shandan, Gansu M6.1, 5.8 earthquakes[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 28(2): 133-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHENG W J, 2009. Geometric pattern and active tectonics of the Hexi Corridor and its adjacent regions[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administrator. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHENG W J, ZHANG P Z, HE W G, et al., 2013. Transformation of displacement between strike-slip and crustal shortening in the northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from decadal GPS measurements and late Quaternary slip rates on faults[J]. Tectonophysics, 584: 267-280. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.01.006 ZHENG W T, YANG J C, DUAN F J, 2000. A study on the relationbetween deformation of river terraces and neotectonic activity for the Wuwei Basin[J]. Seismology and Geology, 22(3): 318-328. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZOU X B, 2018. Study on tectonic deformation and seismogenic mechanism of the Minle-Yongchang active fault in the Hexi Corridor[D]. Lanzhou: China Earthquake Administration Lanzhou Institute of Seismology. (in Chinese with English abstract) 艾晟, 张波, 樊春, 等, 2017. 武威盆地南缘断裂晚第四纪活动地表形迹与活动速率[J]. 地震地质, 39(2): 408-422. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.02.010 陈柏林, 刘建民, 刘建生, 等, 2006. 高台车站断裂全新世活动特征[J]. 地质学报, 80(4): 497-507. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.04.004 陈柏林, 刘建生, 2009. 祁连山北缘-河西走廊地区大地形变与地震的关系[J]. 地质通报, 28(10): 1439-1447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.10.010 陈柏林, 王春宇, 崔玲玲, 等, 2008. 祁连山北缘-河西走廊西段晚新生代逆冲推覆断裂发育模式[J]. 地学前缘, 15(6): 260-277. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.06.033 陈文彬, 2003. 河西走廊及邻近地区最新构造变形基本特征及构造成因分析[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所. 崔泽宏, 汤良杰, 2007. 一种挤压构造背景下正断层的成因模式[J]. 新疆石油地质, 28(2): 254-256. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3873.2007.02.035 邓起东, 张维岐, 张培震, 等, 1989. 海原走滑断裂带及其尾端挤压构造[J]. 地震地质, 11(1): 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ198901000.htm 甘肃省地质矿产局, 1997. 甘肃省岩石地层[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社. 葛肖虹, 刘俊来, 1999. 北祁连造山带的形成与背景[J]. 地学前缘, 6(4): 223-230. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1999.04.004 郭怀军, 杨利荣, 朱小辉, 等, 2016. 祁连山地区河流阶地与第四纪构造隆升[J]. 地质通报, 35(12): 2033-2044. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.12.011 何光玉, 杨树锋, 陈汉林, 等, 2004. 河西走廊西段及邻区主要断裂(一): 晚新生代逆断层与走滑断层的地震剖面解释[J]. 地震学报, 26(6): 601-608. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2004.06.005 何翔, 杜星星, 刘健, 等, 2022. 武威盆地第四纪沉积过程及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 44(1): 76-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ202201006.htm 侯康明, 邓起东, 刘百篪, 1999. 对古浪8级大震孕育和发生的构造环境及发震模型的讨论[J]. 中国地震, 15(4): 339-348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD199904005.htm 胡小飞, 2010. 祁连山北部侵蚀速率的时空分布与构造抬升变形研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. 江在森, 马宗晋, 张希, 等, 2001. 青藏块体东北缘水平应变场与构造变形分析[J]. 地震地质, 23(3): 337-346. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2001.03.001 金胜, 张乐天, 金永吉, 等, 2012. 青藏高原东北缘合作-大井剖面地壳电性结构研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(12): 3979-3990. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.010 赖忠平, 欧先交, 2013. 光释光测年基本流程[J]. 地理科学进展, 32(5): 683-693. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKJ201305003.htm 李奋其, 王成善, 朱利东, 等, 2002. 区域挤压体制下盆-山耦合关系探讨: 以河西走廊和北祁连山为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 22(4): 17-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2002.04.003 李佳昱, 郑文俊, 王伟涛, 等, 2020. 青藏高原东北部龙首山晚新生代剥露历史: 来自磷灰石(U-Th)/He的证据[J]. 地震地质, 42(2): 472-491. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.02.014 李蔚琳, 程惠红, 张怀, 等, 2019. 河西走廊系列盆地构造演化的三维数值模拟[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 36(2): 196-207. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKYB201902004.htm 李祥, 万永革, 崔华伟, 等, 2016. 2016年1月21日青海门源Ms6.4地震构造应力场[J]. 华北地震科学, 34(2): 36-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1375.2016.02.007 李有利, 杨景春, 李保俊, 等, 1997. 河西走廊榆木山边缘断层构造地貌研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 3(4): 20-26. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/article/id/d2220b58-18cb-4d66-bf0b-63651da1663d 刘白云, 曾文浩, 袁道阳, 等, 2014. 1954年腾格里沙漠北7级地震断层面参数和滑动性质研究[J]. 地震工程学报, 36(3): 622-627. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2014.03.0622 刘白云, 曾文浩, 袁道阳, 等, 2015. 1927年古浪8级大地震断层面参数和滑动性质[J]. 地震地质, 37(3): 818-828. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.03.012 刘洪春, 戴华光, 李龙海, 等, 2000. 对1954年民勤7级地震的初步研究[J]. 西北地震学报, 22(3): 232-235. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ200003003.htm 刘和甫, 梁慧社, 蔡立国, 等, 1994. 天山两侧前陆冲断系构造样式与前陆盆地演化[J]. 地球科学, 19(6): 727-741. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.1994.06.005 裴红连, 2017. 榆木山北缘断裂第四纪新构造活动在洪积地貌上的表现[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京). 施炜, 刘源, 刘洋, 等, 2013. 青藏高原东北缘海原断裂带新生代构造演化[J]. 地学前缘, 20(4): 1-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304003.htm 石应骏, 张朝文, 寸树苍, 1995. 龙首山推覆构造的发现及其地质意义[J]. 科学通报, 40(9): 812-813. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1995.09.014 宋春晖, 2006. 青藏高原北缘新生代沉积演化与高原构造隆升过程[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. 谭利华, 杨景春, 段烽军, 1998. 河西走廊新生代构造运动的阶段划分[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 34(4): 523-532. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.1998.04.017 万景林, 郑文俊, 郑德文, 等, 2010. 祁连山北缘晚新生代构造活动的低温热年代学证据[J]. 地球化学, 39(5): 439-446. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201005004.htm 王成善, 戴紧根, 刘志飞, 等, 2009. 西藏高原与喜马拉雅的隆升历史和研究方法: 回顾与进展[J]. 地学前缘, 16(3): 1-30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.03.001 王伟涛, 张培震, 郑德文, 等, 2014. 青藏高原东北缘海原断裂带晚新生代构造变形[J]. 地学前缘, 21(4): 266-274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201404034.htm 王旭龙, 李晓妮, 卢演俦, 2004. 红光固体二极管点阵在释光测年中的光照应用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 24(1): 133-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200401019.htm 肖坤泽, 童亨茂, 2020. 走滑断层研究进展及启示[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(2): 151-166. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.02.015 阎存凤, 袁剑英, 2011. 武威盆地石炭系沉积环境及含油气远景[J]. 天然气地球科学, 22(2): 267-274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201102011.htm 颜丹平, 孙铭, 巩凌霄, 等, 2020. 青藏高原东缘龙门山前陆逆冲带复合结构与生长[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(5): 615-633. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.05.054 杨景春, 谭利华, 李有利, 等, 1998. 祁连山北麓河流阶地与新构造演化[J]. 第四纪研究(3): 229-237. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1998.03.006 云龙, 张进, 王驹, 等, 2021. 甘肃北山南部活动断裂的发现及其区域构造意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(2): 195-207. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.02.019 张进, 马宗晋, 肖文霞, 等, 2006. 宁夏中南部中新世构造活动的地质证据及其意义[J]. 地质学报, 80(11): 1650-1659. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.11.002 张进, 李锦轶, 李彦峰, 等, 2007. 阿拉善地块新生代构造作用: 兼论阿尔金断裂新生代东向延伸问题[J]. 地质学报, 81(11): 1481-1497. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.11.003 张克旗, 吴中海, 吕同艳, 等, 2015. 光释光测年法: 综述及进展[J]. 地质通报, 34(1): 183-203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.01.015 张培震, 郑德文, 尹功明, 等, 2006. 有关青藏高原东北缘晚新生代扩展与隆升的讨论[J]. 第四纪研究, 26(1): 5-13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.01.002 张培震, 张会平, 郑文俊, 等, 2014. 东亚大陆新生代构造演化[J]. 地震地质, 36(3): 574-585. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.03.003 张岳桥, 李海龙, 2016. 青藏高原东部晚新生代重大构造事件与挤出造山构造体系[J]. 中国地质, 43(6): 1829-1852. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201606002.htm 赵衡, 张进, 李岩峰, 等, 2019. 内蒙古狼山地区新生代断层活动特征: 对正断层生长的限定[J]. 中国地质, 46(6): 1433-1453. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201906014.htm 赵凌强, 詹艳, 王庆良, 等, 2018. 1954年甘肃民勤7级地震区深部电性结构特征及地震构造环境研究[J]. 地震地质, 40(3): 552-565. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.03.004 赵子贤, 2021. 祁连山东北缘晚新生代沉积-构造-地貌演化过程[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院. 郑文俊, 袁道阳, 何文贵, 2004. 祁连山东段天桥沟-黄羊川断裂古地震活动习性研究[J]. 地震地质, 26(4): 645-657. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2004.04.011 郑文俊, 何文贵, 赵广坤, 等, 2005. 2003年甘肃民乐-山丹6.1, 5.8级地震发震构造及发震机制探讨[J]. 地震研究, 28(2): 133-140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2005.02.006 郑文俊, 2009. 河西走廊及其邻区活动构造图像及构造变形模式[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所. 郑文涛, 杨景春, 段锋军, 2000. 武威盆地晚更新世河流阶地变形与新构造活动[J]. 地震地质, 22(3): 318-328. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2000.03.012 邹小波, 2018. 河西走廊内部民乐-永昌断裂构造变形特征与发震机制研究[D]. 兰州: 中国地震局兰州地震研究所. -





 下载:
下载: