Basic characteristics and metallogenic potential of banded iron formation(BIF) in the southern Prince Charles Mountains, East Antarctica
-
摘要: 东南极南查尔斯王子山条带状含铁建造(BIF)产于鲁克山古元古代鲁克群的底部,总厚400 m,矿体厚度30~70 m,铁矿平均品位33.5%。该条带状含铁建造形成过程可能与变质火山岩有联系,在成因分类上属于苏必利尔湖型含铁建造和阿尔戈马型含铁建造之间的过渡类型。高精度航磁测量在鲁克山圈定出宽约10 km的北、南两条磁异常条带,延长分别约为50 km和60 km。据此初步建立该地区沉积变质型铁矿预测模型,圈定了含铁建造的资源分布范围,最终估算出铁矿石可开采的资源量大于百亿吨。Abstract: Banded iron formation(BIF) occurs in the lower part of the Paleoproterozoic Ruker Group at Mount Ruker, southern Prince Charles Mountains in East Antarctica. Of all depositional sequence of the Ruker Group, at least 400 m is of iron-bearing formation and 30~70 m is of ore body with an average grade of total Fe about 33.5%. The formation process of the BIF may be related to metamorphic volcanic rocks and the BIF may belong to the transitional type between the Lake Superior type and the Algoma type in genetic classification. High precision aeromagnetic survey identified two major, 10-km-wide, positive aeromagnetic anomalies extending westward from Mount Ruker for 50 km in the north and 60 km in the south, respectively. Based on the aeromagnetic anomaly and high-precision magnetic anomaly data, the prediction model and the distribution range of the BIF are established. The recoverable iron ore resources are finally estimated to be more than ten billion tons.
-
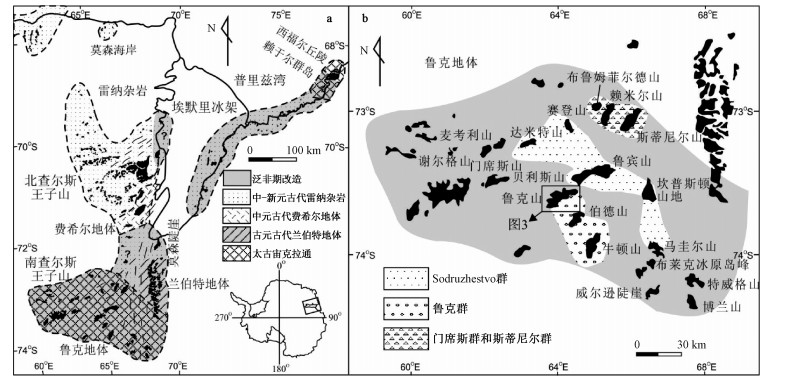
图 1 查尔斯王子山-普里兹湾地区地质简图和鲁克地体地质简图(图中黑色区域为岩石露头)
a-查尔斯王子山-普里兹湾地区地质简图(刘晓春, 2009); b-图a中的鲁克地体地质简图(据Phillips et al., 2005修改)
Figure 1. Geological sketch map of the Prince Charles Moutains-Prydz Bay region showing its location in East Antarctica(a) and Geological sketch map of the Ruker terrane(b)
a is after Liu, 2009; b is modified after Phillips et al., 2005; The black areas represent outcrops.
图 2 南查尔斯王子山年代地层学划分(据Phillips et al., 2006修改)
Figure 2. Regional chronostratigraphic division for the southern Prince Charles Mountains(modified after Phillips et al., 2006)
图 3 鲁克山地质简图(Mikhalsky et al., 2001)
Figure 3. Geological sketch map of Mount Ruker(Mikhalsky et al., 2001)
图 4 埃默里冰架、兰伯特冰川及查尔斯王子山地区航磁异常图和南查尔斯王子山鲁克地体磁异常区划分图
a-埃默里冰架、兰伯特冰川及查尔斯王子山地区航磁异常图(据Golynsky et al., 2002修改);b-南查尔斯王子山鲁克地体磁异常区划分图(据McLean et al., 2008修改)
Figure 4. Colour shaded-relief map of the magnetic anomalies for the Amery Ice Shelf, Lambert Glacier and Prince Charles Mountains(a) and Magnetic signature of the geophysical domains in the southern Prince Charles Mountains(b)
a is modified after Golynsky et al., 2002; b is modified after McLean et al., 2008.
表 1 南查尔斯王子山鲁克地体条带状含铁建造铁矿预测模型
Table 1. The metallogenetic prospect model of iron ore in banded iron formation in the Ruker Terrane, southern Prince Charles Mountains
成矿要素 特征描述 构造位置 南查尔斯王子山鲁克地体古元古代沉积盆地北部边缘 赋矿岩层 磁铁石英岩 矿物组合 石英+磁铁矿+赤铁矿+白云石+方解石+钠闪石+硬绿泥石+磷灰石 结构构造 同沉积构造,条带状构造 控矿构造 被南向逆冲断层和晚期东北向左旋剪切走滑断层控制 矿体规模 矿体产状与地层一致,主矿体为南北两个成矿带,北侧矿体走向近东西向,长约50 km,并以约45°角向南倾斜至地下深度7 km,厚度约30~70 m;南侧矿体走向也是近东西向,长约60 km,也向南陡倾,在地表以下约8 km处尖灭,厚度也估算为30~70 m 矿石品位 矿石品位在24.1%~45.9%之间,平均为33.5% 矿石组构 矿石结构以细粒柱状、粒状变晶结构为主,条带状构造 物探特征 高振幅磁异常区基本圈定铁矿体的形态,主体向南倾斜 注:根据Ravich et al., 1982; McLean et al., 2008资料修改 表 2 南查尔斯王子山鲁克地体条带状含铁建造铁矿预测资源量
Table 2. The potential resource of iron ore in banded iron formation in the Ruker Terrane, southern Prince Charles Mountains
矿体 预测矿体截面积(S)/m2 预测真面积(S′)/m2 倾角 矿体厚度/m 预测矿体体积(V′)/m3 小体重(T)/(t/m3) 预测矿石量(Q′)/亿吨 北侧 50×103×7×103 495×106 45° 30~70 14850×106~34650×106 2.75 408~953 南侧 60×103×8×103 679×106 45° 30~70 20370×106~47530×106 2.75 560~1307 -
BELIATSKY B V, LAIBA A A, MIKHALSKY E V, 1994. U-Pb zircon age of the metavolcanic rocks of Fisher Massif (Prince Charles Mountains, East Antarctica)[J]. Antarctic Science, 6(3): 355-358. doi: 10.1017/S0954102094000544 BIAN R C, HAN Y Z, WANG S C, et al., 2014. Regression analysis on small iron weight value and magnetic iron grade of Zhaicun iron deposit in Jiningcity[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 30(5): 57-58, 64. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI201405016.htm BOGER S D, CARSON C J, FANNING C M, et al., 2002. Pan-African intraplate deformation in the northern Prince Charles Mountains, east Antarctica[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 195(3-4): 195-210. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00587-8 BOGER S D, WILSON C J L, FANNING C M, 2006. An Archaean province in the southern Prince Charles Mountains, East Antarctica: U-Pb zircon evidence for c. 3170 Ma granite plutonism and c. 2780 Ma partial melting and orogenesis[J]. Precambrian Research, 145(3-4): 207-228. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2005.12.003 BOGER S D, MAAS R, FANNING C M, 2008. Isotopic and geochemical constraints on the age and origin of granitoids from the central Mawson Escarpment, southern Prince Charles Mountains, East Antarctica[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 155(3): 379-400. doi: 10.1007/s00410-007-0249-x CARSON C J, BOGER S D, FANNING C M, et al., 2000. SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology from Mount Kirkby, northern Prince Charles Mountains, East Antarctica[J]. Antarctic Science, 12(4): 429-442. doi: 10.1017/S0954102000000523 CHEN T Y, 1996. Main mineral resources of Antarctica[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica: Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 17(1): 65-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQXB601.006.htm CORVINO A F, BOGER S D, HENJES-KUNST F, et al., 2008. Superimposed tectonic events at 2450 Ma, 2100 Ma, 900 Ma and 500 Ma in the North Mawson Escarpment, Antarctic Prince Charles Mountains[J]. Precambrian Research, 167(3-4): 281-302. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2008.09.001 DE VRIES VAN LEEUWEN A T, MORRISSEY L J, KELSEY D E, et al., 2019. Recognition of Pan-African-aged metamorphism in the Fisher Terrane, central Prince Charles Mountains, East Antarctica[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 176(4): 785-798. doi: 10.1144/jgs2018-146 ENGLAND R N, LANGWORTHY A P, 1975. Geological work in Antarctica-1974[R]. Record. 1975/30, 19, Bureau of Mineral Resources, Geology and Geophysics, Canberra. ERNST D M, BAU M, 2021. Banded iron formation from Antarctica: The 2.5 Ga old Mt. Ruker BIF and the antiquity of lanthanide tetrad effect and super-chondritic Y/Ho ratio in seawater[J]. Gondwana Research, 91: 97-111. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2020.11.011 GOLYNSKY A V, ALYAVDIN S V, MASOLOV V N, et al., 2002. The composite magnetic anomaly map of the East Antarctic[J]. Tectonophysics, 347(1-3): 109-120. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(01)00240-2 GOLYNSKY A V, MASOLOV V N, VOLNUKHIN V S, et al., 2006. Crustal provinces of the Prince Charles Mountains region and surrounding areas in the light of aeromagnetic data[M]//FVTTERER D K, DAMASKE D, KLEINSCHMIDT G, et al. Antarctica: Contributions to global earth sciences. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag: 83-94. HALPIN J A, CLARKE G L, WHITE R W, et al., 2007. Contrasting P-T-t paths for Neoproterozoic metamorphism in MacRobertson and Kemp Lands, east Antarctica[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 25(6): 683-701. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.2007.00723.x HALPIN J A, DACZKO N R, MILAN L A, et al., 2012. Decoding near concordant U-Pb zircon ages spanning several hundred million years: Recrystallisation, metamictisation or diffusion?[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 163(1): 67-85. doi: 10.1007/s00410-011-0659-7 LIU Q, ZHANG W, CHENG W, et al., 2013. Developing model and prospect of the deep iron deposits in Anshan-Benxi area, Liaoning province[J]. Geology and Resources, 22(4): 304-307. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD201304009.htm LIU X C, 2009. Polymetamorphism of the Prydz Belt, East Antarctica: Implications for the reconstruction of the Rodinia and Gondwanasupercontinents[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(8): 1808-1818. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/286667958_Polymetamorphism_of_the_Prydz_Belt_East_Antarctica_Implications_for_the_reconstruction_of_the_Rodinia_and_Gondwana_supercontinents MCLEAN M A, RAWLING T J, BETTS P G, et al., 2008. Three-dimensional inversion modelling of a Neoproterozoic basin in the southern Prince Charles Mountains, East Antarctica[J]. Tectonophysics, 456(3-4): 180-193. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2008.04.023 MIKHALSKY E V, SHERATON J W, LAIBA A A, et al., 1996. Geochemistry and origin of Mesoproterozoic metavolcanic rocks from Fisher Massif, Prince Charles Mountains, East Antarctica[J]. Antarctic Science, 8(1): 85-104. doi: 10.1017/S0954102096000120 MIKHALSKY E V, LAIBA A A, BELIATSKY B V, et al., 1999. Geology, age and origin of the Mount Willing area (Prince Charles Mountains, East Antarctica)[J]. Antarctic Science, 11(3): 338-352. doi: 10.1017/S0954102099000437 MIKHALSKY E V, SHERATON J W, LAIBA A A, et al., 2001. Geology of the Prince Charles Mountains, Antarctica[M]. AGSO-Geoscience Australia Bulletin, 247, Canberra, 1-209. MIKHALSKY E V, BELIATSKY B V, SHERATON J W, et al., 2006. Two distinct Precambrian terranes in the southern Prince Charles Mountains, East Antarctica: SHRIMP dating and geochemical constraints[J]. Gondwana Research, 9(3): 291-309. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2005.10.002 MORRISSEY L J, HAND M, KELSEY D E, 2015. Multi-stage metamorphism in the Rayner-Eastern Ghats Terrane: P-T-t constraints from the northern Prince Charles Mountains, east Antarctica[J]. Precambrian Research, 267: 137-163. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2015.06.003 MORRISSEY L J, HAND M, KELSEY D E, et al., 2016. Cambrian high-temperature reworking of the Rayner-Eastern ghats terrane: Constraints from the Northern Prince Charles Mountains region, East Antarctica[J]. Journal of Petrology, 57(1): 53-92. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egv082 PHILLIPS G, WILSON C J L, FITZSIMONS I C W, 2005. Stratigraphy and structure of the southern Prince Charles Mountains, East Antarctica[J]. Terra Antartica, 12(2): 69-86. PHILLIPS G, WILSON C J L, CAMPBELL I H, et al, 2006. U-Th-Pb detrital zircon geochronology from the southern Prince Charles Mountains, East Antarctica-defining the Archaean to Neoproterozoic Ruker Province[J]. Precambrian Research, 148(3-4): 292-306. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2006.05.001 PHILLIPS G, WHITE R W, WILSON C J L, 2007. On the roles of deformation and fluid during rejuvenation of a polymetamorphic terrane: Inferences on the geodynamic evolution of the Ruker Province, East Antarctica[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 25(8): 855-871. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.2007.00732.x PHILLIPS G, KELSEY D E, CORVINO A F, et al., 2009. Continental reworking during overprinting orogenic events, Southern Prince Charles Mountains, East Antarctica[J]. Journal of Petrology, 50(11): 2017-2041. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egp065 RAVICH M G, FEDOROV L V, TARUTIN O A, 1982. Precambrian iron deposits of the Prince Charles Mountains[M]//CRADDOCK C. Antarctic geoscience. Madison, WI: University of Wisconsin Press: 853-858. SOLOVIEV D S, KAMENEV E N, RAVICH G M, 1967. Geological activities in 1965/66[J]. Inf. Byull. Sov. Antarki. Eksped., 62: 10-18. TINGEY R J, 1982. The geologic evolution of the Prince Charles Mountains-An Antarctic Archaean cratonicblock[M]//CRADDOCK C. Antarctic Geoscience. Madison, WI: University of Wisconsin Press: 455-464. TINGEY R J, 1990. Banded iron formations in East Antarctica[M]//SPLETTSTOESSER J F, DRESCHHOFF G A M. Mineral resources potential of Antarctica. Antarctic Research Series. American Geophysical Union, 51: 125-131. TINGEY R J, 1991. The regional geology of Archaean and Proterozoic rocks in Antarctica[M]//TINGEY R J. The Geology of Antarctica. Oxford: Oxford University Press: 1-73. WAN P Y, WANG G H, ZHOU Y, et al., 2020. A study on the prospecting potential of ultra-lean magnetite in Nanjiang area, Sichuan province[J]. China's Manganese Industry, 38(4): 17-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZENG R Y, CHEN D W, HUANG J Y, et al., 2020. Application of high precision magnetic measurement in GPAFAYA iron deposit in North Province, Sierra Leone[J]. Mineral Exploration, 11(8): 1744-1753. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG P, QIAO S Y, JIANG H Y, et al., 2012. Metallogenic regularities and resources potential of the iron deposits in ANSHAN-BENXI area, Liaoning province[J]. Geology and Resources, 21(1): 134-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/313562374_Metallogenic_regularities_and_resources_potential_of_the_iron_deposits_in_Anshan-Benxi_area_Liaoning_Province ZHAO L Q, WANG C N, ZHANG M, et al., 2020. Current exploration status and supply-demand situation of iron ore resources in China mainland[J]. Geology and Exploration, 56(3): 635-643. (in Chinese with English abstract) 边荣春, 韩玉珍, 王仕昌, 等, 2014. 济宁市翟村铁矿小体重值与磁性铁品位的回归分析[J]. 山东国土资源, 30(5): 57-58, 64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2014.05.012 陈廷愚, 1996. 南极洲主要矿产资源[J]. 地球学报: 中国地质科学院院报, 17(1): 65-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB601.006.htm 刘群, 张伟, 成伟, 等, 2013. 辽宁鞍山-本溪地区深部铁矿发育模式与铁矿远景[J]. 地质与资源, 22(4): 304-307. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2013.04.009 刘晓春, 2009. 东南极普里兹带多期变质作用及其对罗迪尼亚和冈瓦纳超大陆重建的启示[J]. 岩石学报, 25(8): 1808-1818. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200908008.htm 万平益, 王光洪, 周勇, 等, 2020. 四川省南江地区超贫磁铁矿找矿潜力探讨[J]. 中国锰业, 38(4): 17-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM202004006.htm 曾瑞垠, 陈德稳, 黄建业, 等, 2020. 高精度磁测技术在塞拉利昂北方省GPAFAYA铁矿勘查中的应用[J]. 矿产勘查, 11(8): 1744-1753. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2020.08.026 张朋, 乔树岩, 姜海洋, 等, 2012. 辽宁鞍本地区铁矿成矿规律与资源潜力分析[J]. 地质与资源, 21(1): 134-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2012.01.020 赵立群, 王春女, 张敏, 等, 2020. 中国铁矿资源勘查开发现状及供需形势分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 56(3): 635-643. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT202003016.htm -





 下载:
下载: