Assessment of regional crustal stability in Shenfu New Area of Liaoning Province, China
-
摘要: 在广泛收集资料和野外调查工作的基础上,经综合分析控制和影响区域地壳稳定性的主要因素和内外动力地质的耦合作用,基于ArcGIS平台采用多因素加权叠加分析方法开展了沈抚新区区域地壳稳定性评价研究。评价因素主要选取活动断裂、地震活动性和深部地球物理以及工程岩组、地形地貌与地表地质灾害等共12个影响因子,并依据评价因素的关联性和重要性进行分类赋值,进而建立了区域地壳稳定性评价模型。对沈抚新区的区域地壳稳定性进行了定量化评价。结果表明,沈抚新区以稳定区和次稳定区为主,面积为728.9 km2,占总面积的81.07%,有利于规划和建设。建议在地下工程穿越不稳定区和次不稳定区时,要采取必要的工程措施,确保基础和边坡的稳定性。规划的地铁9号线主要穿越次不稳定区和次稳定区。施工带在埋深15~25 m之间,该段地层主要为卵砾石堆积层、泥包砾堆积层与变质片麻岩强风化带及其交接部位,施工带处于地下水浸没带或变动带,其支护比较困难,建议尽早确定合理的施工方案,保障施工顺利和安全,此外还需要采取一定降水防腐措施。
-
关键词:
- 沈抚新区 /
- 规划地铁9号线 /
- 多因子加权叠加法 /
- 区域地壳稳定性评价 /
- 工程地质条件与地质灾害
Abstract: In this paper, the main factors controlling and influencing regional crustal stability as well as the coupling action of internal and external dynamic geology in Shenfu New Area were analyzed, using both previous findings and field survey results. Based on the GIS platform, the regional crustal stability assessment was carried out through the multi-factor weighted superposition analysis method. Twelve influencing factors were selected, including fault activity, seismicity, deep geophysical status, engineering rock group, topography and surface geological hazards. The regional crustal stability assessment model was established in terms of relevance and importance of the influencing factors, through which to quantitatively assess the regional crustal stability of Shenfu New Area. And the results show that Shenfu New Area is dominated by the stable and sub-stable areas covering 728.9 km2, accounting for 81.07% of the total area, which is conducive to the planning and construction in this area. Necessary engineering measures are recommended to ensure the stability of foundation and slope when underground engineering, such as the construction of the planned Metro Line 9 at a depth of 15~25 meters, passes through the unstable and sub-unstable areas. The strata in the construction section of Metro Line 9 are generally weathering zones and junction areas of oval-gravel accumulation, mud-clastic accumulation and metamorphic gneiss, situated in groundwater immersed zones or changing zones, which is hard to be provided with protection and support. It is suggested that reasonable construction scheme should be determined as soon as possible to ensure a smooth and safe construction, and precipitation and anticorrosion measures are needed. -
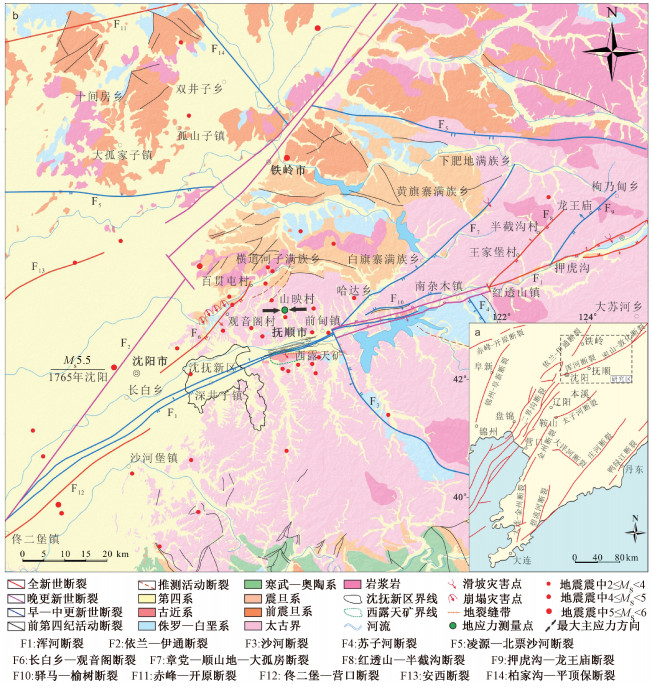
图 1 沈抚新区区域构造略图(据中国地震局官网, https://www.cea.gov.cn/cea/dzpd/zqsd-lsdz/index.html;邓起东等,2002;左建等,2003;吴明大等,2004;侯治华等,2006;王声喜等,2008;万波等, 2010资料,并结合野外调查修编)
Figure 1. Regional tectonic sketch of Shenfu New Area (Map is made based on the following data and modified according to field survey: https://www.cea.gov.cn/cea/dzpd/zqsd-lsdz/index.html, China earthquake administration; Deng et al., 2002; Zuo et al., 2003; Wu et al., 2004; Hou et al., 2006; Wang et al., 2008; Wan et al., 2010.
图 2 沈抚新区及邻区工程地质与地质灾害分布图(据沈阳市地质灾害隐患点排查与复核成果报告(辽宁省环境监测总站,2014);抚顺市地质灾害隐患点排查与复核成果报告(辽宁省第十地质大队,2014);以及2019年野外实际调查资料编制)
Figure 2. Engineering geology and distribution map of geo-hazards in Shenfu New Area and adjacent areas (Map is made based on the following data and actual survey results in 2019:Liaoning Station for Geo-environment Monitoring, 2014; The 10th geological team of Liaoning Province, 2014.)
表 1 稳定性评价因素数据处理的分类赋值规则及权重表
Table 1. Rule of value assignment and weighted table for stability assessment factors in processing data
稳定性分级 1极高 2较高 3中等 4较低 5极低 权值 代码 活动断裂(垂距/m) >3200 1600~3200 800~1600 400~800 < 400 0.15 duanlie 地震动峰值加速度/g < 0.05 0.05 0.10 0.15 >0.20 0.13 dizhen 工程岩组 坚硬块状深变质岩岩组和侵入岩岩组 坚硬厚层状火山碎屑岩岩组和碳酸盐岩岩组 软硬相间层状碎屑岩、碳酸盐岩、浅变质岩组 软弱层状泥岩页岩和碎屑岩岩组 松散冲洪积物堆积层岩组 0.11 yanzu 布格重力/×10-5m/s2 10~-10 -10~-30;10~30 -30~-50;30~50 -50~-70 -70~-90 0.09 zhongli 地震活动强度(震级) <5 5~6 6~7 7~8 >8 0.12 dizhenq 地形变/(mm/a) -2~2 -2~-4;2~4 -4~-7;4~7 -7~-10;7~10 -10~-25;10~12 0.07 xingbian 水系(垂距/m) >3200 1600~3200 800~1600 400~800 < 400 0.06 shuixi 斜坡坡度/(°) 0~5 5~10 10~15 15~25 25~61.43 0.07 podu 斜坡高差/m 0~50 50~100 100~200 200~400 400~417 0.05 gaocha 崩滑流灾点密度/(处/km2) < 0.02 0.02~0.08 0.08~0.17 0.17~0.27 0.27~0.46 0.08 bhl 采空塌陷点密度/(处/km2) < 0.01 0.01~0.05 0.05~0.11 0.11~0.19 0.19~0.29 0.03 caikong 地裂缝点密度/(处/km2) < 0.02 0.02~0.1 0.1~0.18 0.18~0.33 0.33~0.54 0.04 dlf 赋值 1 2 4 7 10 表 2 沈抚新区区域地壳稳定性定量评价分区结果统计表
Table 2. Zoning results of the quantitative assessment of the regional crustal stability in Shenfu New area
稳定程度 面积/km2 占全区面积比/% 稳定区 454.74 50.58 次稳定区 274.16 30.49 次不稳定区 154.82 17.22 不稳定区 15.36 1.71 合计 899.08 100.00 -
CHEN Q X, DAI G X, YANG C Q, et al. 1990. Assessment of the crustal stability of the Shenzhen city, Guangdong province, China[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Geological Science: 134. (in Chinese) http://www.jourlib.org/paper/1559436 CHEN W T, GAN W J, XIAO G R, et al., 2012. The impact of 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake in japan on crustal deformation of northeastern region in China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 34(3): 425-439. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZDZ201203007.htm China Seismological Bureau, 2012. Zoning map of peak acceleration of ground motion in China (1: 4000000)(GB 18306-2015)[M]. Beijing: Standards Press of China. (in Chinese) DENG Q D, ZHANG P Z, RAN Y K, et al., 2002. Basic characteristics of active tectonics of China[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(4): 356-372. DU D J, 1994. Establishment and development of regional stability engineering geology in Chinese[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2(3): 21-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ403.002.htm DU J J, MA Y S, TAN C X, et al., 2008. The evaluation of regional crustal stability in Beijing and Tianjin Area[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 29(4): 502-509. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.oalib.com/paper/1558222 GU D Z, 1979. Fundamentals of geology and mechanics in rock engineering[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) GUO F F, YANG N, MENG H, et al., 2008. Application of the relief amplitude and slope analysis to regional landslide hazard assessments[J]. Geology in China, 35(1): 131-143. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200801016.htm HOU Z H, ZHONG N C, HOU Y K, et al., 2006. Study on neotectonic stress field and present tectonic stress field in the Hunhe fault belt and its adjacent areas[J]. Journal of Institute of Disaster-Prevention Science and Technology, 8(4): 6-9, 63. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-FZJS200604001.htm HU H T, 1983. Preliminary application of a relatively stable (rock) block in site selection of Guangdongnuclear power station[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying (4): 25-29. (in Chinese) HU H T, 2001. The theory and method of evaluation of regional crustal stability based on concept of "Safe Island"[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 7(2): 97-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX200102000.htm LI T, CAI M F, ZUO Y, et al., 2005. Futrues of focal Mechanisms of mining-induced earthquakes: a case study of the Fushun Laohutai coal mine, Liaoning Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 24(2): 136-144. (in Chinese with English abstract) Liaoning Station for Geo-environment Monitoring, 2014. Report on geological hazard survey and reviews in Shenyang city[R]. (in Chinese) LIU C Z, HU H T, 1993. The "Safety Island" theory by multi-scale approaching and optimum seeking in engineering site selection[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 4(1): 28-37, 62. (in Chinese with English abstract) MA X Y, 1989. Lithospheric dynamics atlas of China[M]. Beijing: China Cartographic Publishing House. (in Chinese) PENG J B, 2001. Theory-method system in study of dynamics of the regional stability[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 9(1): 3-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200101000.htm SUN D S, CHEN Q C, ZHANG Y Q, 2020. Analysis on the application prospect of ASR in-situ stress measurement method in underground mine[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(1): 33-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/346847364_Anelastic_strain_recovery_in_situ_stress_measurement_method_and_its_application_prospect_in_underground_mines TAN C X, SUN Y, WU S R, et al., 2009. A consideration on regional crustal stability assessment after MS8.0 WENCHUAN strong earthquake in China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 15(2): 142-150. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98414X/200902/31751835.html TAN C X, FENG C J, ZHANG P, et al., 2014. Major active fracture research and regional crustal stability assessment in Beijing municipality[M]. Beijing: Geological Press. (in Chinese) TANG H M, LI D W, HU X L, 2009. Faulting characteristics of Wenchuan earthquake and evaluation theory of regional crustal stability for engineering[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 17(2): 145-152. (in Chinese with English abstract) Team ten of Liaoning province geological breach, 2014. Report on geological hazard survey and reviews in Fushun city[R]. (in Chinese) WAN B, ZHAO X H, HOU J J, 2010. Determination of seismogenic structure for the Shenyang M5 1/2 earthquake in 1765[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 46(4): 620-628. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201004017.htm WANG S X, ZHANG Q Y, WANG Z, et al., 2008. Relationship between Hunhe fault (Fushun section) short-term activity and geological disaster[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 19(4): 12-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZHB200804003.htm WENG J Q, ZENG L B, LYU W Y, et al., 2020. Width of stress disturbed zone near fault and its influencing factors[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(1): 39-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU M D, ZHONG Y Z, GAO C B, et al., 2004. Activity research on Hunhe fracture (Shenyang-Fushun section)[J]. Seismological Research of Northeast China, 20(1): 25-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DDYJ200401004.htm XIANG J H, 2006. The application of GIS in regional crustal stability assessment in China[J]. Shanxi Architecture, 32(4): 116-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-JZSX200604075.htm YANG J J, XIE Z Q, ZHENG N P, 2004. Application of the fuzzy clustering analysis in the evaluation of regional crustal stability in Xi'an city[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 10(1): 57-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX200401008.htm YANG Q Y, MA X, LI Z Z, et al, 2006. Evaluation of crustal stability in the lower Yellow River region[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51(S): 168-177. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/71135x/201107/23329299.html YAO X, LI L J, ZHANG Y S, et al., 2015. Regional crustal stability assessment of the eastern margin of Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(1): 32-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZQYD201501003.htm YIN Y P, 1985. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of regional crustal stability: Taking the site of Guangdong nuclear power station as an example[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying (5): 31-34. (in Chinese) YIN Y P, HU H T, KANG H D, 1996. An expert system of regional crustal stability evaluation of the siting of key engineering works[J]. Geological Review, 42(2): 174-186. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/295766939_An_expert_system_of_regional_crustal_stability_evaluation_of_the_siting_of_key_engineering_works ZHANG P Z, DENG Q D, ZHANG G M, et al., 2003. Active tectonic blocks and strong earthquakes in the continent of China[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(2): 13-24. ZHANG S X, YANG W M, MENG H J, et al., 2018. Regional crustal stability evaluation in Beijing-Zhangjiakou area[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 24(1): 70-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201801064.htm ZHAO Z, 2001. Restudy of the Shenyang earthquake of M5 1/2 of March 15, 1765[J]. Seismological Research of Northeast China, 17(3): 42-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DDYJ200103007.htm ZHOU F C, 2014. Analysis of influence of site geological condition on seismic damage effect[J]. China Science and Technology Review (7): 336. (in Chinese) ZUO J, KONG Q R, ZUO S, 2007. Evaluation of engineering geology of regional stability in the fault of Hunhe River[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2003, 22(4): 103-107. (in Chinese with English abstract) 陈庆宣, 戴广秀, 杨超群, 等, 1990. 深圳市地壳稳定性评价研究[J]. 中国地质科学院院报: 134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB199001036.htm 陈为涛, 甘卫军, 肖根如, 等, 2012. 3·11日本大地震对中国东北部地区地壳形变态势的影响[J]. 地震地质, 34(3): 425-439. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2012.03.004 邓起东, 张培震, 冉勇康, 等, 2002. 中国活动构造基本特征[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 32(12): 1020-1030. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200212006.htm 杜东菊, 1994. 中国区域稳定工程地质学产生与发展[J]. 工程地质学报, 2(3): 21-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ403.002.htm 杜建军, 马寅生, 谭成轩, 等, 2008. 京津地区区域地壳稳定性评价[J]. 地球学报, 29(4): 502-509. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.04.013 谷德振, 1979. 岩体工程地质学力学基础[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. 郭芳芳, 杨农, 孟晖, 等, 2008. 地形起伏度和坡度分析在区域滑坡灾害评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质, 35(1): 131-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200801016.htm 侯治华, 钟南才, 侯逾昆, 等, 2006. 辽宁浑河断裂带及其邻近地区水系格局构造节理与构造应力场的研究[J]. 防灾科技学院学报, 8(4): 6-9, 63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2006.04.002 胡海涛, 1983. "安全岛"-相对稳定地(岩)块在广东核电站选址中的初步应用[J]. 工程勘察 (4): 25-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC198304007.htm 胡海涛, 2001. 区域地壳稳定性评价的"安全岛"理论及方法[J]. 地质力学学报, 7(2): 97-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2001.02.001 李铁, 蔡美峰, 左艳, 等, 2005. 采矿诱发地震的震源机制特征: 以辽宁省抚顺市老虎台煤矿为例[J]. 地质通报, 24(2): 136-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2005.02.006 辽宁省地质环境监测总站, 2014. 沈阳市地质灾害隐患点排查与复核成果报告[R]. 辽宁省第十地质大队, 2014. 抚顺市地质灾害隐患点排查与复核成果报告[R]. 刘传正, 胡海涛, 1993. 工程选址的"安全岛"多级逼近与优选理论[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 4(1): 28-37, 62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH199301004.htm 马杏垣, 1989. 中国岩石圈动力学地图集[M]. 北京: 中国地图出版社. 彭建兵, 2001. 区域稳定动力学研究(一): 理论与方法体系[J]. 工程地质学报, 9(1): 3-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2001.01.001 孙东生, 陈群策, 张延庆, 2020. ASR法在井下矿山地应力测试中的应用前景分析[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(1): 33-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202001004.htm 谭成轩, 孙叶, 吴树仁, 等, 2009. "5.12"汶川MS8.0大地震后关于我国区域地壳稳定性评价的思考[J]. 地质力学学报, 15(2): 142-150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.02.004 谭成轩, 丰成君, 张鹏, 等, 2014. 北京地区主要活动断裂研究与地壳稳定性评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. 唐辉明, 李德威, 胡新丽, 2009. 龙山门断裂带活动特征与工程区域地壳稳定性评价理论[J]. 工程地质学报, 17(2): 145-152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.02.001 万波, 赵晓辉, 侯建军, 2010. 1765年沈阳5 1/2级地震发震构造判定[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 46(4): 620-628. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201004017.htm 王声喜, 张庆义, 王卓, 等, 2008. 浑河断裂带(抚顺段)近期活动性与地质灾害的关系[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 19(4): 12-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2008.04.003 翁剑桥, 曾联波, 吕文雅, 等, 2020. 断层附近地应力扰动带宽度及其影响因素[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(1): 39-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202001005.htm 吴明大, 钟以章, 高常波, 等, 2004. 浑河断裂(沈阳-抚顺段)活动性研究[J]. 东北地震研究, 20(1): 25-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8565.2004.01.004 相建华, 2006. GIS在中国区域地壳稳定性评价中的应用[J]. 山西建筑, 32(4): 116-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZSX200604075.htm 杨建军, 谢振乾, 郑宁平, 2004. 模糊聚类分析在西安市区域地壳稳定性评价中的应用[J]. 地质力学学报, 10(1): 57-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX200401008.htm 杨勤业, 马欣, 李志忠, 等, 2006. 黄河下游地区地壳稳定性评价[J]. 科学通报, 51(S): 140-147. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB2006S2019.htm 姚鑫, 李凌婧, 张永双, 等, 2015. 青藏高原东缘区域地壳稳定性评价[J]. 地质通报, 34(1): 32-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201501003.htm 殷跃平, 1985. 区域地壳稳定性的模糊综合评判: 以广东核电站选址为例[J]. 工程勘察 (5): 31-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC198505013.htm 殷跃平, 胡海涛, 康宏达, 1996. 区域地壳稳定性评价专家系统研究[J]. 地质论评, 42(2): 174-186. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1996.02.010 张培震, 邓起东, 张国民, 等, 2003. 中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 12-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2003S1001.htm 张树轩, 杨为民, 孟华君, 等, 2018. 京张地区区域地壳稳定性评价[J]. 地质力学学报, 24(1): 70-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201801064.htm 赵振, 2001. 1765年沈阳$M5{}^{1}\!\!\diagup\!\!{}_{2}\;$地震的再研究[J]. 东北地震研究, 17(3): 42-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDYJ199102000.htm 中国地震局, 2015. 中国地震动峰值加速度区划图(1: 4000000) (GB 18306-2015)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. 周福彩, 2014. 场地地质条件对地震震害效应的影响分析[J]. 中国科技博览 (7): 336. 左建, 孔庆瑞, 左莎, 2003. 浑河断裂带区域稳定性评价[J]. 重庆交通学院学报, 22(4): 103-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CQJT200304028.htm -





 下载:
下载: