THE GENERATION, DEVELOPMENT AND ORE-CONTROLLING OF STRUCTURES OF THE FULAICHANG LEAD-ZINC DEPOSIT, NORTHEASTERN GUIZHOU
-
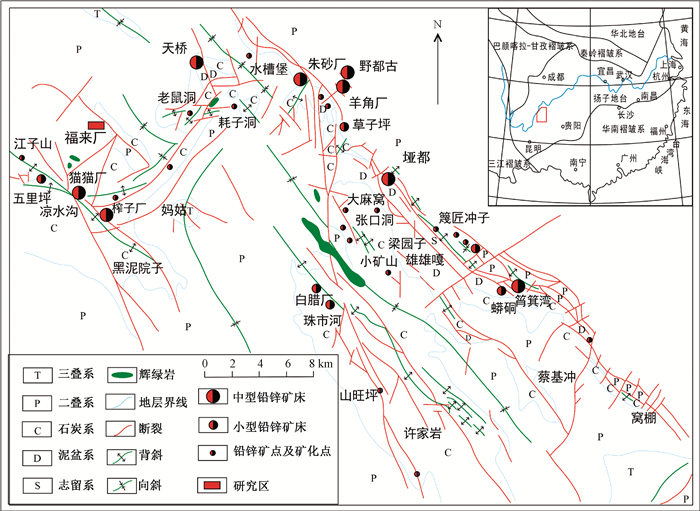
摘要: 福来厂铅锌矿床位于黔西北垭都—蟒硐铅锌成矿带西南部,夹持于天桥与猫猫厂两个铅锌矿床之间,矿床(体)分布严格受构造控制。运用矿田地质力学理论和方法,对福来厂铅锌矿区进行大比例尺构造剖面精测和典型的控矿构造力学性质鉴定以及不同方向断裂、褶皱构造筛分,研究认为自印支晚期—喜马拉雅期以来该区主要经历了三期构造活动,其主压应力方向分别经历了北西向→北东向→近东西向的转变过程,认为矿床的导矿、配矿、容矿构造分别为矿区棋盘格式构造、北东向断裂(倾向北西)与北西西向断裂及其下盘背斜翼部的层间断裂带,此外,矿区存在北西向(倾向北东)破矿构造,明显切割、错移矿体,控制着矿体的空间定位。综合上述,文章在总结了构造控矿规律的基础上,建立了该矿床成矿构造体系,为找矿勘查和矿床成因研究奠定了基础。Abstract: The Fulaichang lead-zinc deposit (FL-ZD) is located in the southwestern part of the Yadu-Mangdong Pb-Zn Metallogenic belt in northwestern Guizhou, China, Which is suited between the Tianqiao lead-zinc deposit and the Maomao lead-zinc deposit, and the distributions of the deposit and its ore bodies are strictly controlled by the structure. Based on the theory and method of geological mechanics of ore-field, the large scale fine survey of structural section and the typical identification of ore-controlling structural mechanical properties, as well as the screening of faults and fold structures in different directions in the lead and zinc mining area of Fulaichang mining area were made. It is believed that since the late Indosinian-Himalayan period, there have been three periods of tectonic activities in this region, and the main compressive stress direction has experienced the transition from NW to NE to near EW respectively. Based on analyzing the ore-controlling characteristics of folds and faults in the mining area, it is concluded that the ore-guiding structure, ore-distribution structure and ore-bearing structure of the deposit are the checkerboard-type structure of the tectonic framework, the NE-trending faults (inclined NW) and NWW fault-trending, and the interlayer fault zones in the lower plate of NWW-trending faults, respectively. In addition, there are NW trending (NNE trending) ore-breaking structures in the mining area, which obviously cut and shift the ore bodies and control the spatial positioning of the ore bodies. On the basis of summarizing the structural ore-controlling regularity, the ore-forming tectonic system of the deposit is established, which lays a foundation for ore prospecting and genetic study of the deposit.
-
图 4 福来厂铅锌矿FL201—205点构造的几何学、运动学分析图解
①—马平组灰岩;②—黄龙组灰色细晶白云岩;③—红褐色、褐色蚀变白云质角砾岩,角砾多呈菱块状、方块状,方解石角砾胶结角砾呈网脉状;④—红褐色、紫红色构造角砾岩,原岩为灰白色白云岩,层间发育片理化,呈紫红色泥状,较松软;⑤—灰色中厚层片理化细晶白云岩,片理化顺层发育,呈紫红色、褐色;⑥—灰色中至厚层细晶白云岩,局部蚀变为粗晶白云岩
a—F1断裂带野外分带照片;b—F1断裂带紫红色片理化带;c—F1断裂构造蚀变岩带;d—F1吴氏网下半球投影图;e—F4吴氏网下半球投影图Figure 4. Geometry and kinematics analysis diagram of FL201~205 in the FL-ZD
表 1 福来厂铅锌矿断裂构造及其矿化蚀变特征简表
Table 1. The chararcteristics of faults, mineralization and alteration in the FL~ZD
类型 产状 形态特征 力学性质 构造岩特征 矿化蚀变特征 走向 倾角 倾向 NW向 NW20°~NW70° 55°~80° NE/SW 舒缓波状、缓波状、平直 左行张(扭)性—压扭性—左行扭压 碎裂岩、碎粉岩、片理化、断层泥、碎斑岩 Py、Lim、Ga、Sp、Cal、Dol NE向 NE20°~NE80° 49°~80° NW/SE 平直、缓波状 扭(压)性—扭(张)性—右行压扭 碎裂岩、片理化 Py、Lim、Cal、Dol 注:Py—黄铁矿化; Lim—褐铁矿化(为黄铁矿氧化产物);Cal—方解石化;Sp—闪锌矿;Ga—方铅矿;Dol—白云石化 表 2 LD8构造岩成矿元素组合特征表
Table 2. Metallogenic element assemblage characteristics of tectonic rocks in LD8
序号 编号 Zn/×10-6 Pb/×10-6 Hg/×10-9 Cd/×10-6 MnO/×10-2 Na2O/×10-2 Sb/×10-6 As/×10-6 Ge/×10-6 In/×10-6 1 LD8C-5 5400 2600 1022 7.9 0.14 0.12 2.4 5.5 0.1 0.072 2 LD8C-6 1341 1132 284 6.6 0.09 0.08 1.8 17 0.2 0.031 3 LD8C-7 24300 6200 1220 7.6 0.15 0.22 3.5 7.7 1.1 0.028 4 LD8C-8 1075 940 127 14.1 0.10 0.11 0.4 1.4 0.1 0.023 5 LD8C-9 19200 3200 722 24.3 0.08 0.17 1.6 7.7 2.4 0.026 6 LD8C-12 1626 460 295 3.0 0.07 0.14 1.0 2.7 0.1 0.028 7 LD8C-25 8100 932 631 7.8 0.05 0.12 2.1 11 0.5 0.033 8 LD8C-26 17400 1047 548 27.1 0.20 0.15 0.9 8.5 2.2 0.034 9 FLC-603 24 30 19 0.3 0.02 0.08 0.4 1.3 0.1 0.014 注:FLC-603为LD8坑道顶部地表样,代表围岩矿化特征。 -
[1] 柳贺昌, 林文达.滇东北铅锌银矿床规律研究[M].昆明.云南大学出版社, 1999, 1~128.LIU Hechang, LIN Wenda. Regularity research of Ag. Zn. Pb ore deposits North-East Yunnan Province[M]. Kunming:Yunnan University Press, 1999, 1~128. (in Chinese) [2] 韩润生, 胡煜昭, 王学琨, 等.滇东北富锗银铅锌多金属矿集区矿床模型[J].地质学报, 2012, 86(2):280~294. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201202007HAN Runsheng, HU Yuzhao, WANG Xuekun, et al. Mineralization model of rich Ge-Ag-bearing Zn-Pb polymetallic deposit concentrated district in northeastern Yunnan, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(2):280~294. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201202007 [3] 韩润生, 王峰, 胡煜昭, 等.会泽型(HZT)富锗银铅锌矿床成矿构造动力学研究及年代学约束[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 38(4):758~771. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2014.04.003HAN Runsheng, WANG Feng, HU Yuzhao, et al. Metallogenic tectonic dynamics and chronology constrains on the huize-type (HZT) germanium-rich silver-zinc-lead deposits[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2014, 38(4):758~771. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2014.04.003 [4] 汤世凯, 马筱, 李学刚, 等.黔西北福来厂铅锌矿床Pb同位素研究及地质意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2012, 36(4):549~558. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2012.04.009TANG Shikai, MA Xiao, LI Xuegang, et al. Pb isotope composition of the Fulaichang lead-zinc ore deposit in northwest Guizhou and its geological implications[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2012, 36(4):549~558. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2012.04.009 [5] 贵州省地质矿产局.中华人民共和国地质矿产部地质专报:(一)区域地质(第7号), 贵州省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1987.Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Guizhou Province. Special report on geology of ministry of geology and mineral resources of the People's Republic of China. Ⅰ, regional geology. No. 7, regional geology of guizhou province[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1987. (in Chinese) [6] 金中国.黔西北地区铅锌矿控矿因素、成矿规律与找矿预测[M].北京:冶金工业出版社, 2008.JIN Zhongguo. The metallogenic regularity and prospecting forecast of lead-zinc ore in northwestern Guizhou[M]. Beijing:Metallurgical Industry Press, 2008. (in Chinese) [7] 张荣强, 周雁, 汪新伟, 等.贵州西南部威-紫-罗断裂带构造特征及演化[J].地质力学学报, 2009, 15(2):178~189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.02.007ZHANG Rongqiang, ZHOU Yan, WANG Xinwei, et al. Structural features and tectonic evolution of the Wei-Zi-Luo fault zone in southwestern Guizhou province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2009, 15(2):178~189. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.02.007 [8] 陈大, 黄智龙, 张伦尉, 等.贵州西北部江子山-蟒硐构造带两类铅锌矿床特征及其形成机制[J].矿物学报, 2012, 32(3):432~442. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KWXB201203013.htmCHEN Da, HUANG Zhilong, ZHANG LUNWEI, et al. Geological characteristics and formation mechanism of two types Pb-Zn deposits in Jiangzi Mountain-Mangdong tectonic belt[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2012, 32(3):432~442. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KWXB201203013.htm [9] 周家喜, 黄智龙, 周国富, 等.黔西北赫章天桥铅锌矿床成矿物质来源:S、Pb同位素和REE制约[J].地质论评, 2010, 56(4):513~524. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201004006ZHOU Jiaxi, HUANG Zhilong, ZHOU Guofu, et al. Sources of the ore metals of the Tianqiao Pb-Zn deposit in northwestern Guizhou Province:constraints form S, Pb isotope and REE geochemistry[J]. Geological Review, 2010, 56(4):513~524. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201004006 [10] 韩润生, 马德云, 刘丛强, 等.陕西铜厂矿田构造成矿动力学[M].昆明:云南科技出版社, 2003.HAN Runsheng, MA Deyun, LIU Congqiang, et al. Dynamics of tectonic ore-forming process of Tongchang Orefield, Shaanxi[M]. Kunming:Yunnan Science and Technology Press, 2003. (in Chinese) [11] 韩润生.初论构造成矿动力学及其隐伏矿定位预测研究内容和方法[J].地质与勘探, 2003, 39(1):5~9. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzykt200301002HAN Runsheng. Preliminary discussion on research contents and methods of tectono-metallogenic dynamics and concealed ore orientation prognosis[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2003, 39(1):5~9. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzykt200301002 [12] 孙家骢, 韩润生.矿田地质力学理论与方法[M].北京:科学出版社, 2016.SUN Jiacong, HAN Runsheng. Theory and method of geological mechanics of mineral field[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 2016. (in Chinese) [13] 罗志立, 金以钟, 朱夔玉, 等.试论上扬子地台的峨眉地裂运动[J].地质论评, 1988, 34(1):11~24. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1988.01.002LUO Zhili, JIN Yizhong, ZHU Kuiyu, et al. On Emei Taphrogenesis of the upper Yangtze platform[J]. Geological Review, 1988, 34(1):11~24. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1988.01.002 [14] 赵江南, 陈守余, 赵鹏大.个旧高松矿田断裂带构造岩稀土元素地球化学特征及意义[J].中国稀土学报, 2011, 29(2):224~232. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgxtxb201102017ZHAO Jiangnan, CHEN Shouyu, ZHAO Pengda. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements for fault tectonite its significance in Gaosong Orefield, Gejiu[J]. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 2011, 29(2):224~232. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgxtxb201102017 [15] 张志斌, 李朝阳, 涂光炽, 等.川、滇、黔接壤地区铅锌矿床产出的大地构造演化背景及成矿作用[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2006, 30(3):343~354. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2006.03.010ZHANG Zhibin, LI Chaoyang, TU Guangchi, et al. Geotectonic evolution background and ore-forming process of Pb-Zn deposits in Chuan-Dian-Qian area of southwest China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2006, 30(3):343~354. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2006.03.010 [16] 刘家铎.扬子地台西南缘成矿规律及找矿方向[M].北京:地质出版社, 2004.LIU Jiaduo. Metallogenic regularity and prospecting direction of southwest margin of Yangtze platform[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2004. (in Chinese) [17] 黄智龙, 陈进, 韩润生, 等.云南会泽超大型铅锌矿床地球化学及成因-兼论峨眉山玄武岩与铅锌成矿的关系[M].北京:地质出版社, 2004.HUANG Zhilong, CHEN Jin, HAN Runsheng, et al. Geochemistry and ore-formation of the Huize giant lead-zinc deposit, Yunnan Province, China[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2004. (in Chinese) [18] 陈宣华, 陈正乐, 杨农.区域成矿与矿田构造研究——构建成矿构造体系[J].地质力学学报, 2009, 15(1):1~19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.01.001CHEN Xuanhua, CHEN Zhengle, YANG Nong. Study on regional mineralizations and ore-field structures:Building of mineralizing tectonic systems[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2009, 15(1):1~19. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.01.001 [19] 顾尚义.黔西北地区铅锌矿硫同位素特征研究[J].贵州工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 36(1):8~11. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzgydx200701003GU Shangyi. Study on the sulfur isotopic compositions of lead-zinc deposits in northwestern Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Guizhou University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 36(1):8~11. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzgydx200701003 [20] 李波, 韩润生, 文书明, 等.滇东北巧家松梁铅锌矿床构造特征及构造地球化学[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 38(4):855~865. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2014.04.011LI Bo, HAN Runsheng, WEN Shuming, et al. Structural characteristics and fault tectono-geochemistry of the Songliang lead-zinc deposit in northeast Yunnan, China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2014, 38(4):855~865. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2014.04.011 [21] 周家喜.黔西北铅锌成矿区分散元素及锌同位素地球化学[D].北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2011.ZHOU Jiaxi. Geochemistry of dispersed elements and zinc isotope in carbonate-hosted lead-zinc ore deposits district, northwest Guizhou Province, China[D]. Beijing: Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2011. (in Chinese) [22] 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李化启, 等.中国大陆印支碰撞造山系及其造山机制[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(6):1697~1709. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201206001XU Zhiqin, YANG Jingsui, LI Huaqi, et al. Indosinian collision-orogenic system of Chinese continent and its orogenic mechanism[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(6):1697~1709. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201206001 [23] 贾承造, 何登发, 陆洁民.中国喜马拉雅运动的期次及其动力学背景[J].石油与天然气地质, 2004, 25(2):121~125, 169. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2004.02.001JIA Chengzao, HE Dengfa, LU Jiemin. Episodes and geodynamic setting of Himalayan movement in China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2004, 25(2):121~125, 169. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2004.02.001 [24] 刘迅.地质力学在矿田构造研究中的应用与进展[J].地质力学学报, 1996, 2(1):25~33. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=19960104&journal_id=dzlxxbLIU Xun. Advance of application of geomechanics to the research of ore-field structures[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 1996, 2(1):25~33. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=19960104&journal_id=dzlxxb -





 下载:
下载: