TECTONIC DYNAMICS OF FLUIDS AND METALLOGENESIS
-
摘要: 流体是地球的重要物质组成,其构造作用与动力学是地质力学与构造学重要的研究方向。流体构造动力学是介于流体地质学、地质力学和构造地质学之间的一个交叉学科。文章介绍了流体构造动力学的概念、主要研究内容、流体的构造作用方式及构造类型与特征,总结了近年来在流体构造动力学与成矿研究过程中取得的一系列重要进展。主要有提出液压致裂的新动力学机制、发现斑晶堆积构造并指出斑岩是岩浆房中部分结晶残余岩浆再侵位的产物及发现并厘定构造混积岩等多个方面,总结了存在的问题并指出了进一步研究的方向;指出流体作为构造作用的主要参与者和重要组织者,不仅对成矿流体的运移通道及其沉淀与就位的空间进行开拓,更重要的是作为载体运移、富集成矿元素并为最终成矿奠定基础。Abstract: Fluid is an important constitute of the earth, and tectonics and dynamics of fluids are major research branches of geomechanics and tectonics. Tectonic dynamics of fluids is a new interdisplinary subject among fluid geology, geomechanics and structural geology. This contribution introduces the concept and the framework of the subject of tectonic dynamics of fluids. In addition, it summarizes a series of important advances in the study of tectonic dynamics of fluids and metallogenesis in recent years, including coming up with the new mechanics for fracture caused by hydraulic pressure, discovering the porphyry accumulation structure, indicating porphyry as the product of reemplacement of some crystallized residual magma in magma chamber, discovering and determining tectonic peperite, and so on. Moreover, some new research advances are also presented here. Finally, some key scientific questions are pointed out. It is concluded that fluids not only create fractures and spaces for ore-forming fluids to be transported and to precipitate but also transport and enrich ore-forming elements, thus laying a foundation for the final formation of ore deposits.
-
Key words:
- fluid /
- tectonic dynamics /
- metallogenesis
-
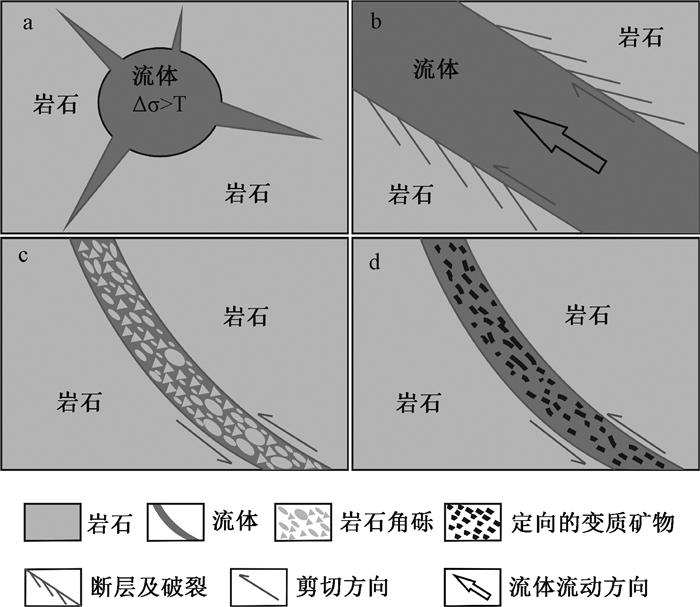
图 2 流体的构造类型与特征照片
a—甘肃白银厂折腰山铜矿床隐爆角砾岩体顶部石英角斑质片岩中的硅质流体与破裂;b—甘肃白银厂折腰山铜矿床隐爆角砾岩体上部棱角状角砾岩;c—滇西北衙金矿区斑岩岩浆侵位于湖相沉积物中形成的混积构造;d—川西攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿床中辉长岩浆与碳酸盐熔体混合形成的包卷构造;e—滇西占河一长石斑岩中更长石的堆积构造[20];f—阿尔金吐格曼花岗岩体中的层状构造,晚期(上部)层状花岗岩对早期(下部)层状花岗岩有明显的截切特征
Figure 2. Photographs showing structural types and characteristics of the fluids
-
[1] 徐兴旺, 蔡新平, 张宝林, 等.流体的构造作用与成矿[J].矿床地质, 1998, 17(增刊):1067~1070. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/199265XU Xingwang, CAI Xinping, ZHANG Baolin, et al. Tectonic function and mineralization of fluids[J]. Mineral Deposits, 1998, 17(Suppl.):1067~1070. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/199265 [2] 徐兴旺, 蔡新平, 王杰, 等.流体构造动力学及其研究现状与进展[J].地球科学进展, 2001, 16(3):324~331. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2001.03.005XU Xingwang, CAI Xinping, WANG Jie, et al. Tectonic dynamics of fluids and its advance[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2001, 16(3):324~331. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2001.03.005 [3] 徐兴旺, 王杰, 张宝林, 等.岩浆运移动力学及其研究进展[J].地球科学进展, 2006, 21(4):361~371. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.04.005XU Xingwang, WANG Jie, ZHANG Baolin, et al. Transport dynamics of magma and its advances[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2006, 21(4):361~371. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.04.005 [4] Rubey W W, Hubbert M K. Role of fluid pressure in mechanics of overthrust faulting:Ⅱ. Overthrust belt in geosynclinal area of western Wyoming in light of fluid-pressure hypothesis[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1959, 70(2):167~206. [5] Bryant D G. Intrusive breccias associated with ore, Warren (Bisbee) Mining District, Arizona[J]. Economic Geology, 1968, 63(1):1~12. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.63.1.1 [6] Zheng Y, Wang Y, Liu R, et al. Sliding-thrusting tectonics caused by thermal uplift in the Yunmeng Mountains, Beijing, China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1988, 10(2):135~144. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(88)90111-3 [7] 钱维宏.地球内部流体运动与全球构造[J].地学前缘, 1996, 3(3/4):152~160. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY603.019.htmQIAN Weihong. The motion of the Earth interior liquid and global tectonics[J]. Earth Science Frontier, 1996, 3(3/4):152~160. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY603.019.htm [8] Meissner R, Wever T. The possible role of fluids for the structuring of the continental crust[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1992, 32(1/2):19~32. doi: 10.1016-0012-8252(92)90010-Q/ [9] Hobbs B E. The influence of metamorphic environment upon the deformation of minerals[J]. Tectonophysics, 1981, 78(1/4):335~383. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3ffcff7258a8f2a370c89f0d21ecdde6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [10] Beach A. Retrogressive metamorphic processes in shear zones with special reference to the Lewisian complex[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1980, 2(1/2):257~263. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=c76ba9060454b6b8d36d36a0dd3d978d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [11] Hammer S. Segregation bands in plagioclase:non-dilational quartz veins formed by strain enhanced diffusion[J]. Tectonophysics, 1981, 79(3/4):T53~T61. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=e280cf3996cc820eb3a060c230a20847&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [12] Rubie D C. Reaction-enhanced ductility:the role of solid-solid univariant reactions in deformation of the crust and mantle[J]. Tectonophysics, 1983, 96(3/4):331~352. doi: 10.1016-0040-1951(83)90225-1/ [13] 徐兴旺, 李东旭.北京怀柔地区韧性剪切带中矿物的变质粒化作用、脆性粒化作用及糜棱岩分类[A].大陆构造学术讨论会论文摘要[C]. 1994, 140~141.XU Xingwang, LI Dongxu. Metamorphic and cataclastic granularization of mineral in ductile shear zone and classification of mylonites in the Huairou area, Beijing[A]. Tectonics Symposium Abstracts[C]. 1994, 140~141. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] Xu X W, Cai X P, Zhang B L, et al. Explosive Microfractures induced by K-metasomatism[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23(3):307~319. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00135-4 [15] Tullis J, Yund R A. Hydrolytic weakening of experimentally deformed Westerly granite and Hale albite rock[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1980, 2(4):439~451. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(80)90005-X [16] Urai J L. Water-enhanced dynamic recrystallization and solution transfer in experimentally deformed carnallite[J]. Tectonophysics, 1985, 120(3/4):285~317. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=844df2fa41eb32b3a45abdd70d50bbf9&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [17] Urai J L, Spiers C J, Zwart H J, et al. Weakening of rock salt by water during long-term creep[J]. Nature, 1986, 324(6097):554~557. doi: 10.1038/324554a0 [18] Griggs D. Hydrolytic weakening of quartz and other silicates[J]. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 1967, 14(1/4):19~31. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a41032bea0d4ef378bfa0efc7861cac3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [19] Bell T H. The deformation and recrystallization of biotite in the Woodroffe thrust mylonite zone[J]. Tectonophysics, 1979, 58(1/2):139~158. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ee975615cae74162704630d32324ffb2&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [20] Xu X W, Jiang N, Yang K, et al. Accumulated phenocrysts and origin of feldspar porphyry in the Chanho area, western Yunnan, China[J]. Lithos, 2009, 113(3/4):595~611. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6832b98e6aee527ed610d69576d01a2b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [21] Xu X W, Cai X P, Zhong J Y, et al. Formation of tectonic peperites from alkaline magmas intruded into wet sediments in the Beiya area, western Yunnan, China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2007, 29(8):1400~1413. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2007.04.007 [22] 徐兴旺, 蔡新平, 梁光河等.山东七宝山次火山杂岩区隐伏含矿角砾岩筒位-形-域精细预测[J].黄金科学技术, 1999, (2):10~19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HJKJ902.001.htmXU Xingwang, CAI Xingpin, LIANG Guanghe, et al. Detailed prediction on position, shape and size of concealed ore-bearing breccia pipes in the subvolcanic complex in Qibaoshan area in Shandong Province[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 1999, (2):10~19. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HJKJ902.001.htm [23] Hofstra A H, Leventhal J S, Northrop H R, et al. Genesis of sediment-hosted disseminated-gold deposits by fluid mixing and sulfidization:chemical-reaction-path modeling of ore-depositional processes documented in the Jerritt Canyon district, Nevada[J]. Geology, 1991, 19(1):36~40. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1991)019<0036:GOSHDG>2.3.CO;2 [24] Cline J S, Bodnar R J, Rimstidt J D. Numerical simulation of fluid flow and silica transport and deposition in boiling hydrothermal solutions:Application to epithermal gold deposits[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1992, 97(B6):9085~9103. doi: 10.1029/91JB03129 [25] Lichtner P C. Time-space continuum description of fluid/rock interaction in permeable media[J]. Water Resources Research, 1992, 28(12):3135~3155. doi: 10.1029/92WR01765 [26] Roberts S, Sanderson D J, Gumiel P. Fractal analysis of Sn-W mineralization from Central Iberia:insights into the role of fracture connectivity in the formation of an ore deposit[J]. Economic Geology, 1995, 93(3):360~365. doi: 10.2113-gsecongeo.93.3.360/ [27] 谢焱石, 谭凯旋, 郝涛.构造-流体-成矿作用的分形与混沌动力学[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2010, 34(3):378~385. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2010.03.009XIE Yanshi, TAN Kaixuan, HAO Tao. Fractal and chaotic dynamics mechanism for tectonic-fluid-mineralization[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2010, 34(3):378~385. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2010.03.009 [28] Xu X W, Peters S G, Liang G H, et al. Elastic stress transmission and transformation (ESTT) by confined liquid:a new mechanics for fracture in elastic lithosphere of the earth[J]. Tectonophysics, 2016, 672~673:129~138. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.02.004 [29] Hubbert M K, Willis D G. Mechanics of hydraulic fracturing[J]. Transactions of Society of Petroleum Engineers of AIME, 1957, 210:153~166. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/mtxb201408041 [30] Xu X W, Zhang B L, Qin K Z, et al. Origin of lamprophyres by the mixing of basic and alkaline melts in magma chamber in Beiya area, western Yunnan, China[J]. Lithos, 2007, 99(3/4):339~362. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=85ac8098a8e4384f05f0b4b0a29f2e60&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [31] Xu X W, Zhang B L, Liang G H, et al. Zoning of mineralization in hypogene porphyry copper deposits:Insight from comb microfractures within quartz-chalcopyrite veins in the Hongshan porphyry Cu deposit, western Yunnan, SW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 56:218~228. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.05.017 [32] Xu X W, Cai X P, Xiao Q B, et al. Porphyry Cu-Au and associated polymetallic Fe-Cu-Au deposits in the Beiya Area, Western Yunnan Province, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2007, 31(1/4):224~246. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a92ad39e7d4c1dd176825aea0ebfa987&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [33] Xu X W, Cai X P, Qin D J, et al. Fluids double-fracturing genetic mechanism and mineralization of gold-copper of the breccia pipe at Qibaoshan in Shandong Province[J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2000, 43(2):113~121. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXG200002000.htm [34] Xu X W, Sun L Q, Ma T, et al. Structural characteristics, Petrogenesis and Mineralization of the Massive polymetal deposits in Baiyin, Gansu province, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 1996, 2(English Supplement):85~94. -





 下载:
下载: