FACIES ANALYSIS OF RED BEDS AND ITS RELATIONSHIP WITH THE DEVELOPMENT OF DANXIA LANDFORM IN LONGHUSHAN AREA OF JIANGXI PROVINCE: AN EXAMPLE FROM XIANRENCHENG SCENIC SPOT
-
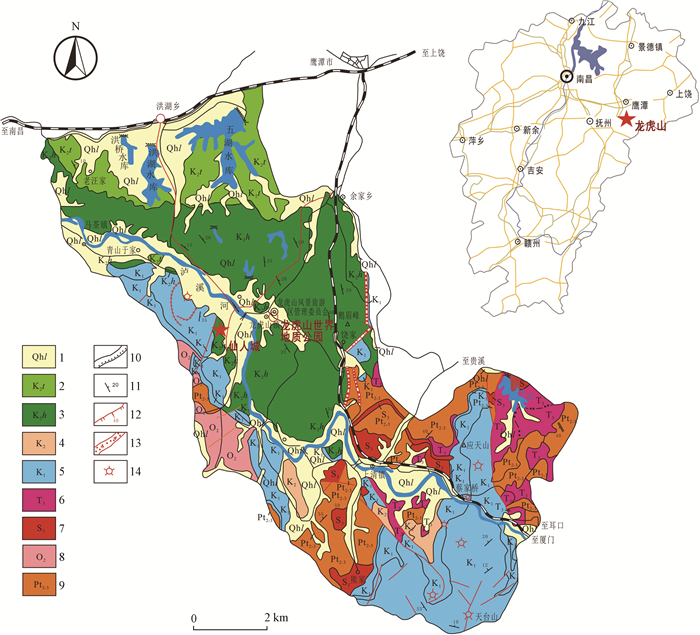
摘要: 江西龙虎山地区以发育老年期丹霞地貌为特色,其成景地层为晚白垩世河口组红层,目前对这套红层的沉积相认识程度还比较低。龙虎山仙人城景区河口组出露厚度达百余米,沉积构造发育,且人工开凿的台阶可以直达山顶,这为沉积相分析提供了便利条件。根据野外露头岩性组成、沉积构造等特点,识别出6种岩相单元:无沉积构造砾岩、正粒序层理砾岩、逆粒序层理砾岩、平行层理砾岩、含砾砂岩、古土壤。砾石统计结果表明,砾石粒径范围主要为3~4 cm,最大可达12.5 cm,成分以紫红色凝灰岩为主,砂岩、花岗岩和石英次之、变质岩(主要是片岩)较少,磨圆度主要为次棱角状,其次为棱角状。在显微镜下,砂岩碎屑颗粒主要呈棱角-次棱角状,分选性较差,粒径为0.05~2.00 mm,主要由石英、长石和岩屑组成,总体具有结构和成分成熟度中等偏低的特点。野外露头宏观和室内显微分析结果表明,仙人城丹霞地貌的成景地层为河流主导的冲积扇沉积体系的产物。在龙虎山地区,丹霞地貌的空间分布与盆地冲积扇沉积相的平面展布具有较好的一致性,盆地边缘冲积扇成因的厚层砾岩为后期丹霞地貌的形成和演化提供了物质基础。Abstract: Longhushan area is characterized by late-staged Danxia landforms with Late Cretaceous red beds of Hekou Formation as the scenery layer. Little is known about depositional facies of these redbeds. The outcrop of the Hekou Formation is more than 100 meters thick with abundant sedimentary structures. The man-made stone steps from the bottom to the top of the hill are favourable for performing detailed observation and measurement for facies analysis in Xianrencheng Scenic Spot in Longhushan area. Six lithofacies units are recognized based on the characteristics of lithology and sedimentary structures:structureless conglomerate, normal bedding conglomerate, inverse bedding conglomerate, parallel bedding conglomerate, pebbly sandstone, and paleosol. Pebble counting results show that gravels dominantly range from 3 cm to 4 cm with the largest one of 12.5 cm in diameter, and they are mainly composed of purple tuffs, followed by sandstones, granites, quartzite and minor amounts of metamorphic rocks (mainly schists). The roundness is mainly subangular, followed by angular. Under a microscope, the detrital grains of the interbedded sandstone samples are mainly angular to subangular, poorly sorted, 0.05~2.00 mm, composed of quartz, feldspar and rock fragments. Overall, the sandstone samples are featured by moderate to low textural and compositional maturities. Both the field macroscopic observation and microscopic analysis indicate that the redbeds were deposited by alluvial fan systems. Moreover, the spatial distribution of Danxia landforms and plane distribution of alluvial fan facies have good consistency. In particular, the coarse-grained sedimentary succession of alluvial fan facies along the basin margin provided the fundamental bedrock for the formation and development of Danxia landforms.
-
Key words:
- depositional facies /
- Alluvial fan /
- Danxia landform /
- Hekou Formation /
- Longhushan Global Geopark
-
表 1 研究区砾石岩性和圆度统计结果
Table 1. Statistics of gravel lithology and roundness in the study area
岩性 磨圆度/% 合计
/%棱角状(A) 次棱角状(B) 次圆状(C) 紫红色凝灰岩 21 20 6 47 砖红色砂岩 2 8 2.5 12.5 灰白色砂岩 6 5 0.5 11.5 灰绿色砂岩 0.5 1.5 2 4 石英 6 5.5 1.5 13 脉石英 0.5 1.5 1 3 片岩 0 1 0.5 1.5 花岗岩 1.5 2.5 3.5 7.5 总计 37.5 45 17.5 100 表 2 河口组红层岩相划分
Table 2. Lithofacies classification of the redbeds of the Hekou Formation
序号 岩相 特征 沉积构造 解释 A 无沉积构造砾岩 砾石支撑、杂基支撑、块状 无粒序层理 沉积物高剪切应力或高粘性作用,沉积速率快,沉积物来不及分选 B 正粒序层理砾岩 杂基支撑 正粒序层理 洪泛水流能量逐渐降低 C 逆粒序层理砾岩 砾石支撑 逆粒序层理 高密度流体在流动过程中,颗粒的分散和上举作用 D 平行层理砾岩 砾石支撑、成层性差 平行层理 高能水流条件下的河道迁移 E 含砾砂岩 细到粗、可含砾石 板状交错层理 直脊沙纹迁移(侧向加积) F 古土壤 钙质结核、遗迹化石 土壤特征 地表氧化环境中的经成壤作用 -
[1] 彭华. 丹霞地貌基本理论问题回顾与探讨. "世界的丹霞"[C]. 第二届丹霞地貌国际学术讨论会论文集, 2011, 125~133.PENG Hua. A review and discussion on the basic theoretical problems of danxia landform[C]. The Second International Symposium on Danxia Landform, 2011, 125~133. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 赵汀, 赵逊, 彭华, 等.关于丹霞地貌概念和分类的探讨[J].地球学报, 2014, 35(3):375~382. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.03.13ZHAO Ting, ZHAO Xun, PENG Hua, et al. A tentative discussion on the definition and classification of Danxia landform[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2014, 35(3):375~382. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.03.13 [3] 黄进, 陈致均, 齐德利.中国丹霞地貌分布(上)[J].山地学报, 2015, 33(4):385~396. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ200500001018.htmHUANG Jin, CHEN Zhijun, QI Deli. Study on distribution of Danxia landform in China (first)[J]. Mountain Research, 2015, 33(4):385~396. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ200500001018.htm [4] 黄进, 陈致均, 齐德利.中国丹霞地貌分布(下)[J].山地学报, 2015, 33(6):649~673. http://www.oalib.com/paper/287863HUANG Jin, CHEN Zhijun, QI Deli. Distribution of Danxia landform in China (Last)[J]. Mountain Research, 2015, 33(6):649~673. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.oalib.com/paper/287863 [5] 彭华, 潘志新, 闫罗彬, 等.国内外红层与丹霞地貌研究述评[J].地理学报, 2013, 68(9):1170~1181. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201309002PENG Hua, PAN Zhixin, YAN Luobin, et al. A Review of the research on red beds and Danxia landform[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2013, 68(9):1170~1181. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11821/dlxb201309002 [6] 黄进.丹霞山地貌[M].北京:科学出版社, 2010.HUANG Jin. Danxia mountain landform[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 2010. [7] 郭福生, 李晓勇, 姜勇彪.龙虎山丹霞地貌与旅游开发[M].北京:地质出版社, 2012.GUO Fusheng, LI Xiaoyong, JIANG Yongbiao. Danxia landform in mount Longhushan and its tourism development[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2012. (in Chinese) [8] 郭福生, 朱志军, 黄宝华, 等.江西信江盆地白垩系沉积体系及其与丹霞地貌的关系[J].沉积学报, 2013, 31(6):954~964. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201405013.htmGUO Fusheng, ZHU Zhijun, HUANG Baohua, et al. Cretaceous sedimentary system and their relationship with Danxia landform in Xinjiang basin, Jiangxi[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(6):954~964. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201405013.htm [9] 巫建华.赣东北白垩纪沉积相及其构造意义[J].华东地质学院学报, 1994, 17(4):313~319. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Shengbiao_Hu/publication/283278467_micangshan/links/56331ec408aefa44c368a3fe/micangshan.pdfWU Jianhua. Sedimentary facies of the Cretaceous in the Northeast of Jiangxi province and its tectonic Signific ance[J]. Journal of East China Geological Institute, 1994, 17(4):313~319. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Shengbiao_Hu/publication/283278467_micangshan/links/56331ec408aefa44c368a3fe/micangshan.pdf [10] 江西省地质矿产局.江西省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1984.Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Jiangxi Province. Regional geology of Jiangxi province[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1984. (in Chinese) [11] 江新胜, 潘忠习, 徐金沙, 等.江西信江盆地晚白垩世风成沙丘的发现及其古风向[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(7):833~838. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zqyd200607011&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQJING Xinsheng, PAN Zhongxi, XU Jinsha, et al. Late Cretaceous eolian dunes and wind directions in Xinjiang basin, Jiangxi Province, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(7):833~838. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zqyd200607011&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [12] 姜勇彪, 郭福生, 胡中华, 等.信江盆地丹霞地貌特征及其景观类型[J].山地学报, 2010, 28(4):505~512. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sdxb201004016JIANG Yongbiao, GUO Fusheng, HU Zhonghua, et al. A study on the features of Danxia landform and its landscape types in Xinjiang Basin[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2010, 28(4):505~512. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sdxb201004016 [13] Shu L S, Zhou X M, Deng P, et al. Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the southeast China block:New insights from basin analysis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 34(3):376~391. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.06.004 [14] Chen L Q, Steel R J, Guo F S, et al. Alluvial fan facies of the Yongchong Basin:Implications for tectonic and paleoclimatic changes during Late Cretaceous in SE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 134:37~54. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.10.010 [15] Kallmeier E, Breitkreuz C, Kiersnowski H, et al. Issues associated with the distinction between climatic and tectonic controls on Permian alluvial fan deposits from the Kotzen and Barnim Basins (North German Basin)[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2010, 223(1~2):15~34. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0037073809002127 [16] Nemec W, Steel R J. Alluvial and coastal conglomerates: Their significant features and some comments on gravelly mass-flow deposits[A]. Koster E H, Steel R J. Sedimentology of Gravels and Conglomerates[C]. Canada: Canadian Society of Petroleum Geology, 1984, 10: 1~31. [17] 陈留勤, 郭福生, 梁伟, 等.江西抚崇盆地上白垩统河口组砾石统计特征及其地质意义[J].现代地质, 2013, 27(3):568~576. http://www.docin.com/p-1267616096.htmlCHEN Liuqin, GUO Fusheng, LIANG Wei, et al. Gravel fabric characteristics of the Upper Cretaceous Hekou formation in Fuzhou-Chongren Basin, Jiangxi and the geological significance[J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(3):568~576. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.docin.com/p-1267616096.html [18] 陈留勤, 郭福生, 杨庆坤, 等.江西永丰-崇仁盆地晚白垩世沉积体及其演化模式[J].山地学报, 2015, 33(4):416~424. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201405013.htmCHEN Liuqin, GUO Fusheng, YANG Qingkun, et al. The Late Cretaceous depositional systems and evolution model of the Yongfeng-Chongren Basin in Jiangxi Province[J]. Mountain Research, 2015, 33(4):416~424. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201405013.htm [19] Chen L Q, Guo F S, Tang C. Evolution of the Late Cretaceous Yongfeng-Chongren basin in Jiangxi province, southeast China:Insights from sedimentary facies analysis and pebble counting[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2016, 13(2):342~351. doi: 10.1007/s11629-014-3387-4 [20] Blair T C. Cause of dominance by sheetflood vs. debris-flow processes on two adjoining alluvial fans, Death Valley, California[J]. Sedimentology, 1999, 46(6):1015~1028. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.1999.00261.x [21] Jullien R, Meakin P, Pavlovitch A. Three-dimensional model for particle-size segregation by shaking[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1992, 69(4):640~643. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.69.640 [22] Collinson JD, Mountney N P, Thompson D B. Sedimentary Structures. 3rd ed. Malta: Dunedin Academic Press Ltd, 2006. [23] 温昌辉, 刘秀铭, 吕镔, 等.江西石城盆地白垩纪地层中成壤特征及古环境分析[J].第四纪研究, 2016, 36(6):1403~1416. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZQYD2018Z1020.htmWEN Changhui, LIU Xiuming, LV Bin, et al. The cretaceous redbeds in Shicheng Basin, Jiangxi Province:Pedogenic and paleoenvironmental characteristics[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2016, 36(6):1403~1416. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZQYD2018Z1020.htm [24] Kraus M J, Woody D T, Smith J J, et al. Alluvial response to the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum climatic event, Polecat Bench, Wyoming (U.S.A.)[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2015, 435:177~192. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.06.021 [25] Chen L Q, Guo F S. Upper Cretaceous alluvial fan deposits in the Jianglangshan Geopark of Southeast China:Implications for bedrock control on Danxia landform evolution[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2017, 14(5):926~935. doi: 10.1007/s11629-016-4024-1 [26] 黄进.丹霞地貌坡面发育的一种基本方式[J].热带地貌, 1982, 3(2):107~134. http://edu.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/Detail/fz200705080HUANG Jin. One of the basic development modes of slopes in "Danxia" terrain[J]. Tropical Geomorphology, 1982, 3(2):107~134. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://edu.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/Detail/fz200705080 -





 下载:
下载: