REAEARCH ON THE MECHANISM OF THE INFLUENCE OF DYNAMIC LOAD OF HIGH-SPEED TRAIN ON LAND SUBSIDENCE SUBJECTED TO FAULT EFFECT: A CASE STUDY OF THE HUAILAI SECTION OF THE BEIJING-ZHANGJIAKOU HIGH-SPEED RAILWAY
-
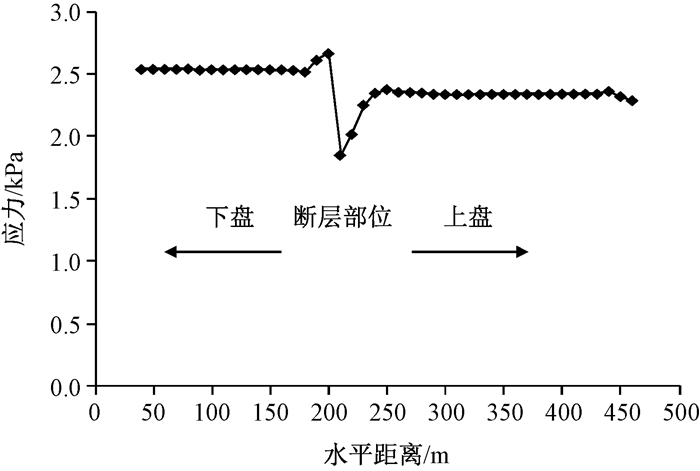
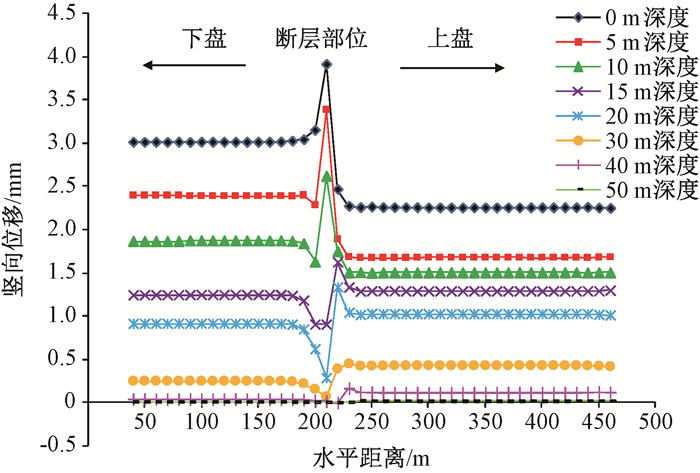
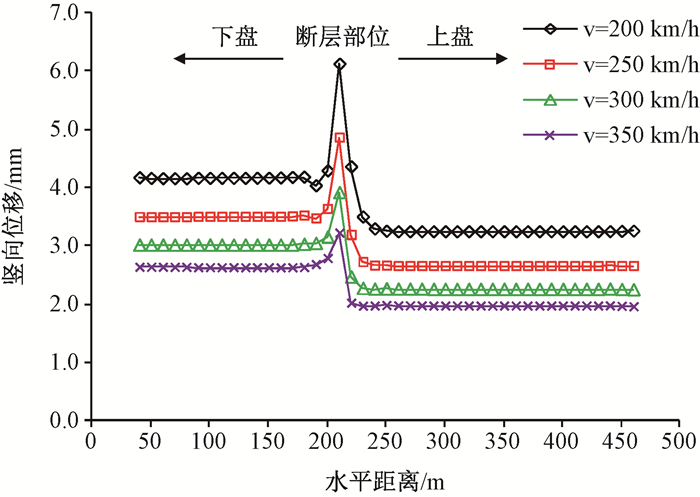
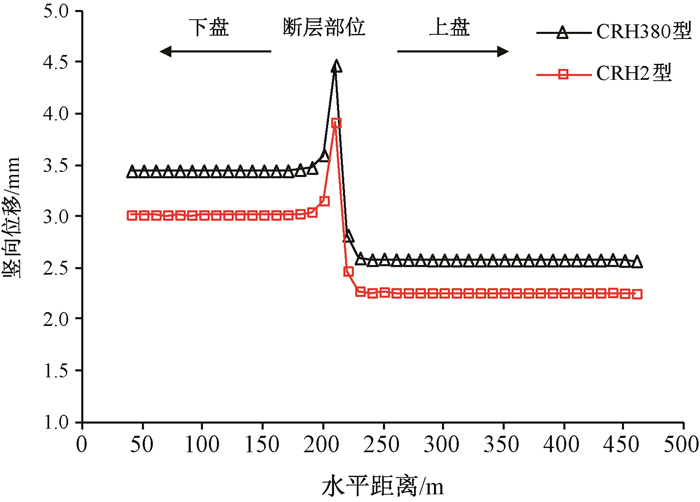
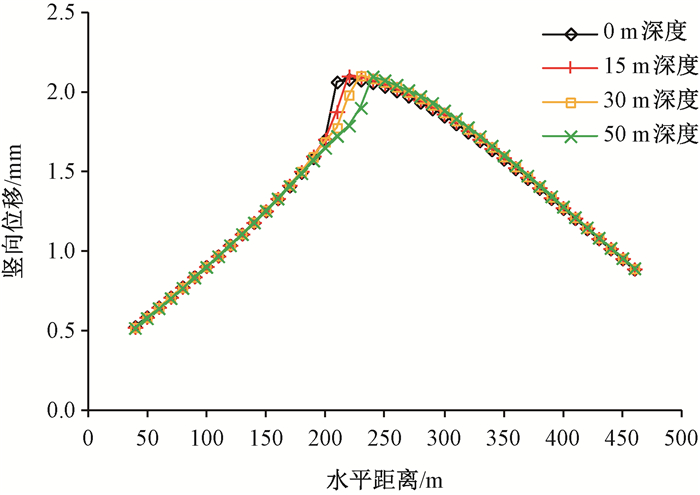
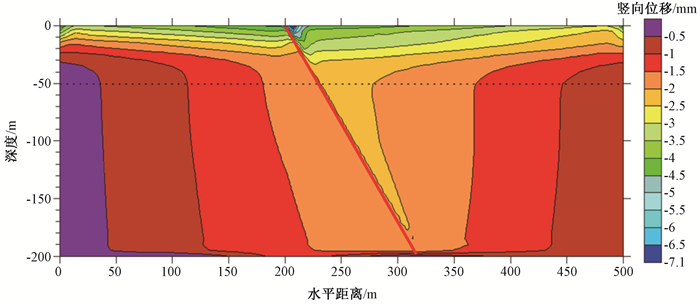
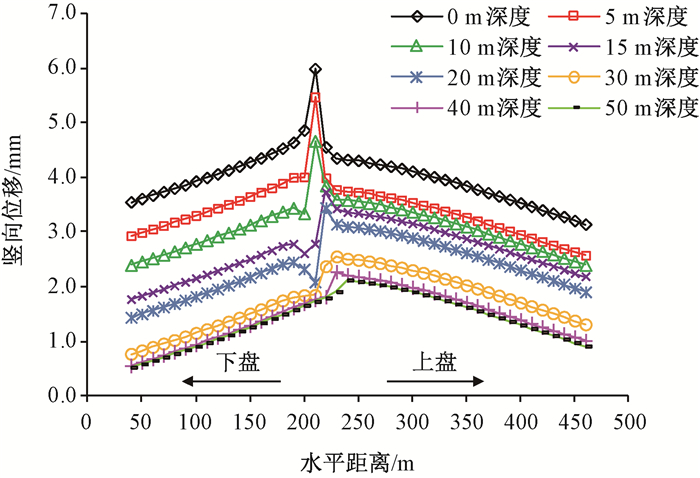
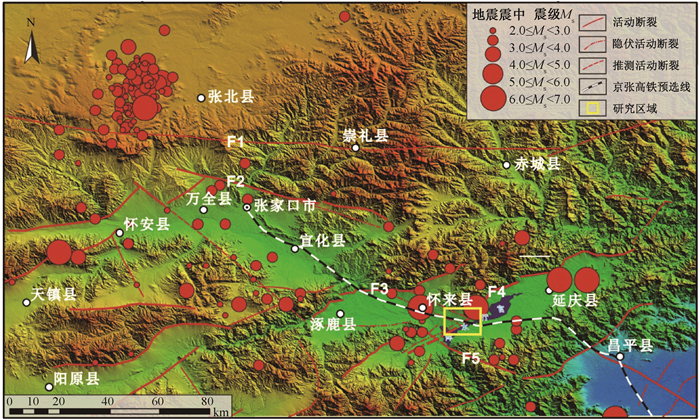
摘要: 京张高铁怀来段位于怀涿、延矾盆地复合部位,盆地内土体工程地质特性的差异及隐伏断裂稳滑活动产生的地面沉降无疑会威胁京张高铁的安全运行。依据工程地质钻孔及地球物理探测资料,构建跨活动断层地基土体二维地层结构模型,通过数值模拟手段开展考虑断层效应的高铁列车动载荷对地面沉降的影响机理研究。研究表明:列车动荷载主要影响50 m深度范围内的土体,随车速增加动荷载造成的土体竖向位移降低,随车重增加竖向位移增加;在列车动荷载和断层滑移双重作用下,随深度增加,土体竖向位移以受列车动荷载影响为主转为以断层滑移影响为主,50 m以下土体竖向位移全部由断层滑移所致,且紧邻断层两侧距离相同位置上盘土体竖向位移大于下盘。Abstract: The Huailai section of Beijing-Zhangjiakou (BZ) high-speed railway is located in the compound position of the Huaizhuo basin and Yanfan basin. The ground subsidence resulted from the difference of engineering geological characteristics of soil and sliding of buried faults in the basin will undoubtedly threaten the safe operation of BZ high-speed railway. Using numerical simulation to study the mechanism of the influence of dynamic load of high-speed train on land subsidence subjected to fault effect, the 2D geological model of soils in the Huailai section of BZ high-speed railway is established based on the field data of engineering geological boreholes and geophysical exploration in this study. The results indicate that the dynamic load of the train mainly affects the soil within the depth of 50m, with increasing displacements accompanying decreasing train velocities and increasing train mass. Under both the dynamic train load and fault slip, the settlement of the soil mainly affected by the dynamic train load tends to be mainly controlled by the fault slip as the depth increases. And the settlement of the soil below 50m is controlled by the fault slip. What's more, the settlement of soil around the fault in the hanging wall is larger than that in the footwall at the same distance from the fault.
-
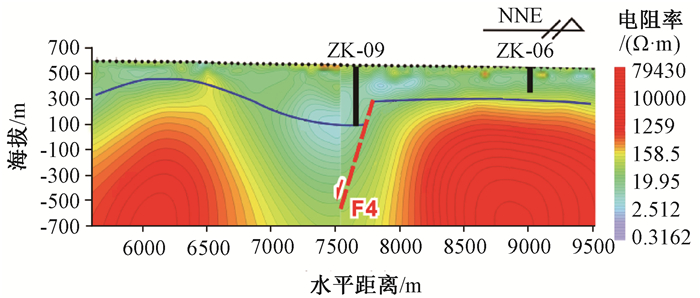
表 1 断层F4标志性地层
Table 1. Characteristics of marked strata of the fault
标志性地层 上盘厚度/m 下盘厚度/m 断距/m 中更新统地层 40 25 68 下更新统地层 169 73 82 新近系地层 155 57 178 表 2 各层土体采用的计算参数
Table 2. Calculation parameters using by each layer of soil
地层序号 土层类型 厚度/m 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 密度/(kg/m3) 粘聚力/kPa 摩擦角/(°) ① 粉土 上盘:5
下盘:1515 0.30 1750 16 28 ② 砾石 上盘a:40;10;30
下盘:540 0.18 2000 10 45 ③ 中粗砂 下盘:10 25 0.22 1800 20 34 ④ 粘土 上盘:40
下盘:3020 0.25 1940 99 27 ⑤ 粉土 上盘:5 15 0.30 1960 30 33 ⑥ 粘土 上盘:10 18 0.27 2000 40 25 ⑦ 有机质粘土 上盘:60
下盘:7020 0.25 2000 106 28 ⑧ 粉质粘土 下盘:70 30 0.2 2100 125 27 断层 / 1.5 0.30 1500 / / 注:a表示②砾石层在上盘有三层,由上而下土层厚度分别为40 m、10 m、30 m -
[1] Pavlides S B, Zouros N C, Fang Z J, et al. Geometry, kinematics and morphotectonics of the Yanqing-Huailai active faults (northern China)[J]. Tectonophysics, 1999, 308(1~2):99~118. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(99)00074-8 [2] 张树轩, 杨为民, 孟华君, 等.京张地区区域地壳稳定性评价[J].地质力学学报, 2018, 24(1):70~77. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2018.24.01.008ZHANG Shuxuan, YANG Weimin, MENG Huajun, et al. Regional crustal stability evaluation in Beijing-Zhangjiakou area[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2018, 24(1):70~77. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2018.24.01.008 [3] 张向营, 张春山, 孟华君, 等.基于GIS和信息量模型的京张高铁滑坡易发性评价[J].地质力学学报, 2018, 24(1):96~105. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2018.24.01.011ZHANG Xiangying, ZHANG Chunshan, MENG Huajun, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment of new Jing-Zhang high-speed railway based on GIS and information value model[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2018, 24(1):96~105. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2018.24.01.011 [4] 梁波, 孙常新.高速铁路路基动力响应中的双峰现象分析[J].土木工程学报, 2006, 39(9):117~122. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCJ201306010.htmLIANG Bo, SUN Changxin. A study on the sudden changes or double peaks in the dynamic response of subgrade of high speed railway[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2006, 39(9):117~122. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCJ201306010.htm [5] 董亮, 赵成刚, 蔡德钩, 等.高速铁路路基的动力响应分析方法[J].工程力学, 2008, 25(11):231~236, 240. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/e39d541514791711cc791796.htmlDONG Liang, ZHAO Chenggang, CAI Degou, et al. Method for dynamic response of subgrade subjected to high-speed moving load[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2008, 25(11):231~236, 240. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/e39d541514791711cc791796.html [6] 周镇勇. 武广客运专线路基动力响应特性试验及数值模拟分析[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10533-2010188758.htmZHOU Zhenyong. Test analysis and numerical simulation of dynamic performance of subgade of Wuhan-Guangzhou passenger dedicated line[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10533-2010188758.htm [7] 刘晓红. 高速铁路无砟轨道红黏土路基动力稳定性研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2011. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y1918485LIU Xiaohong. Research on dynamic stability of red clay subgrade under ballastless track of high-speed railway[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y1918485 [8] 屈畅姿. 高速铁路相邻过渡段路基动响应及长期动力稳定性研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10533-1013358081.htmQU Changzi. Dynamic response and long-term dynamic stability of closely spaced transition sections subgrade for high-speed railway[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10533-1013358081.htm [9] 郭志广, 魏丽敏, 周镇勇, 等.高铁路基动应力数值模拟和现场试验研究[J].水文地质工程地质, 2013, 40(5):51~57. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90596X/201305/1002102003.htmlGUO Zhiguang, WEI Limin, ZHOU Zhenyong, et al. Numerical simulation and field test of the dynamic stress of ballastless track subgrade[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2013, 40(5):51~57. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90596X/201305/1002102003.html [10] 王晅, 张家生, 王启云.无砟轨道路基列车动载激励及动力响应三维数值模拟[J].地震工程学报, 2014, 36(4):857~867. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdzxb201404015WANG Xuan, ZHANG Jiasheng, WANG Qiyun. Three-dimensional numerical simulation for vehicle dynamic load and dynamic response of ballastless track subgrade[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2014, 36(4):857~867. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdzxb201404015 [11] 孔祥辉, 蒋关鲁, 李安洪, 等.基于三维数值模拟的铁路路基动力特性分析[J].西南交通大学学报, 2014, 49(3):406~411. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xnjtdxxb201403006KONG Xianghui, JIANG Guanlu, LI Anhong, et al. Analysis of dynamic characteristics of railway subgrade based on three-dimensional numerical simulation[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(3):406~411. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xnjtdxxb201403006 [12] 黄强兵. 地裂缝对地铁隧道的影响机制及病害控制研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2009. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11941-2009176736.htmHUANG Qiangbing. Study on effect of the active ground fissure on metro tunnel and its hazards control[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11941-2009176736.htm [13] 贺凯, 彭建兵, 黄强兵, 等.近距离平行通过地裂缝的地铁隧道模拟试验研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(S2):4086~4095. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yslxygcxb2014z2086HE Kai, PENG Jianbing, HUANG Qiangbing, et al. Simulation test of metro tunnel parallels ground fissure with short distance[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(S2):4086~4095. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yslxygcxb2014z2086 [14] 孟振江, 彭建兵, 黄强兵, 等.三类勘察场地地裂缝活动对地铁隧道的影响[J].交通运输工程学报, 2017, 17(2):41~51. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-OGTY201411003040.htmMENG Zhenjiang, PENG Jianbing, HUANG Qiangbing, et al. Influence of ground fissure activity on subway tunnel in third-kind surveying site[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2017, 17(2):41~51. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-OGTY201411003040.htm [15] 戚帮申. 张家口地区地壳稳定性研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2017. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82501-1017055359.htmQI Bangshen. Assessment and zonation of regional crustal stability in Zhangjiakou region[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geologecal Sciences, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82501-1017055359.htm [16] 徐锡伟, 于贵华, 冉永康, 等.中国城市活动断层概论[M].北京:地震出版社, 2015.XU Xiwei, YU Guihua, RAN Yongkang, et al. The introduction to urban active faults in China[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 2015. (in Chinese) [17] 刘晶波, 谷音, 杜义欣.一致粘弹性人工边界及粘弹性边界单元[J].岩土工程学报, 2006, 28(9):1070~1075. http://manu31.magtech.com.cn/Jwk_ytgcxb/CN/abstract/abstract12156.shtmlLIU Jingbo, GU Yin, DU Yixin. Consistent viscous-spring artificial boundaries and viscous-spring boundary elements[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2006, 28(9):1070~1075. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://manu31.magtech.com.cn/Jwk_ytgcxb/CN/abstract/abstract12156.shtml [18] Liu J B, Du Y X, Du X L, et al. 3D viscous-spring artificial boundary in time domain[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2006, 5(1):93~102. doi: 10.1007/s11803-006-0585-2 [19] 陈绍绪, 张跃刚, 乔子云, 等.晋冀蒙交界地区主要断裂的现今活动[J].华北地震科学, 2003, 21(2):16~22. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hbdzkx200302003CHEN Shaoxu, ZHANG Yuegang, QIAO Ziyun, et al. The current activity of main faults in the joint area of Shanxi, Hebei and Inner Mongolia[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 2003, 21(2):16~22. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hbdzkx200302003 -





 下载:
下载: