EVOLUTION OF SEDIMENTARY ENVIRONMENT IN THE NORTH HETAO BASIN SINCE 344 Ka
-
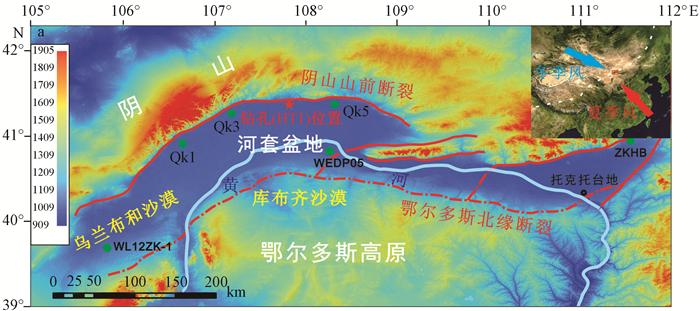
摘要: 通过对河套盆地北部获取的377 m钻孔岩芯进行沉积相及粒度特征分析,并结合多种测年手段,揭示了河套盆地北部中更新世晚期以来的沉积环境演变过程。根据粒度参数特征变化把钻孔划分为6个沉积环境阶段:344~326 ka为滨湖相沉积环境;326~165 ka为半深湖相沉积环境;165~130 ka为滨湖三角洲相沉积环境;130~100 ka为浅湖相沉积环境;100~10 ka为滨湖—河流相沉积环境;10 ka~今为河漫滩相沉积环境。河套盆地中更新世晚期到晚更新世期间存在统一的古大湖,晚更新世以后古大湖分解并消失。Abstract: Through analysis of sedimentary facies and grain size characteristics from 377 m drilling cores in the north Hetao Basin, combined with different dating methods, the evolution of sedimentary environment in the north Hetao Basin since late Middle Pleistocene is revealed. According to the characteristics of grain size parameters, sedimentary environment can be divided into 6 stages:lakeshore (344~326 ka)-semi-deep lake (326~165 ka)-lakeshore delta (165~130 ka) -shallow lake (130~100 ka)-lakeshore-fluvial (100~10 ka)-washland (10 ka~now). Comprehensive research shows that a unified paleo-megalake has been existed in the Hetao Basin from middle Pleistocene to late Pleistocene. After late Pleistocene, the paleo-megalake disintegrated and disappeared.
-
Key words:
- grain size /
- sedimentary environment /
- paleolake evolution /
- the Hetao Basin
-
表 1 钻孔光释光年代数据
Table 1. OSL dating data of the drilling core
原始编号 埋藏深度/m 含水率/% U/×10-6 Th/×10-6 K/% 剂量率(Gy/ka) 等效剂量(Gy) 年龄/ka C2-29 45.54 11±5 1.82±0.03 8.87±0.03 1.57±0.01 2.45±0.09 70.67±3.46 28.83±1.77 C2-44 79.98 13±5 2.77±0.04 13.16±0.32 1.93±0.04 3.89±0.23 307.63±11.40 79.16±5.60 C2-53 96.18 32±5 1.31±0.02 6.36±0.06 1.93±0.05 2.04±0.08 168.55±2.15 82.70±3.34 C2-64 118.78 20±5 2.57±0.06 14.02±0.11 2.09±0.03 3.76±0.22 382.15±20.35 101.61±8.02 C2-75 145.12 26±5 2.22±0.02 11.63±0.14 1.98±0.02 2.65±0.09 354.37±11.65 133.62±6.35 C2-92 187.61 24±5 1.13±0.01 5.95±0.04 2.10±0.01 2.26±0.09 356.93±2.61 158.00±6.68 表 2 钻孔14C年代数据
Table 2. 14C dating results of the drilling core
原始样号 测年材料 深度/m AMS14C年代/a BP 13C/‰ 校正年代/a BP 日历年代/Cal a BP HL-223 有机质全样 5.57 4470±30 -24.2 4480±30 4995±20 HL-1028 有机质全样 25.9 13790±50 -24.1 13800±50 14747±172 表 3 钻孔230Th年代数据
Table 3. 230Th dating results of the drilling core
样号 238U/×10-9 232Th/×10-12 230Th/232Th δ234U* 230Th Age/yr(校正) δ234UInitial**(校正) 230Th Age/yr BP zk1 2886±4 2251524±45118 24.8±0.5×10-6 170.2±1.8 319945±13649 420±17 319880±13649 -
[1] 国家地震局鄂尔多斯周缘活动断裂系课题组.鄂尔多斯周缘活动断裂系[M].北京:地震出版社, 1988, 1~328.The Research Group on "Active Fault System around Ordos massif", State Seismological Bureau. Active fault system around Ordos massif[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 1988, 1~328. (in Chinese) [2] Rao W B, Chen J, Tan H B, et al. Sr-Nd isotopic and REE geochemical constraints on the provenance of fine-grained sands in the Ordos deserts, north-central China[J]. Geomorphology, 2011, 132(3/4):123~138. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169555X11002182 [3] Li G Q, Jin M, Chen X M, et al. Environmental changes in the Ulan Buh Desert, southern Inner Mongolia, China since the middle Pleistocene based on sedimentology, chronology and proxy indexes[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2015, 128:69~80. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.09.010 [4] Nie J S, Stevens T, Rittner M, et al. Loess Plateau storage of northeastern Tibetan Plateau-derived Yellow River sediment[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6:8511. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9511 [5] 陈发虎, 范育新, 春喜, 等.晚第四纪"吉兰泰-河套"古大湖的初步研究[J].科学通报, 2008, 53(10):1207~1219. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=kxtb200810013&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQCHEN Fahu, FAN Yuxin, CHUN Xi, et al. Preliminary research on Megalake Jilantai-Hetao in the arid areas of China during the Late Quaternary[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(11):1725~1739. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=kxtb200810013&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [6] 范育新, 陈发虎, 范天来, 等.乌兰布和北部地区沙漠景观形成的沉积学和光释光年代学证据[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2010, 40(7):903~910. http://earth.scichina.com:8080/sciD/CN/abstract/abstract418328.shtmlFAN Yuxin, CHEN Fahu, FAN Tianlai, et al. Sedimentary documents and Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL) dating for formation of the present landform of the northern Ulan Buh Desert, northern China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2010, 53(11):1675~1682. http://earth.scichina.com:8080/sciD/CN/abstract/abstract418328.shtml [7] 蒋复初, 王书兵, 李朝柱, 等.内蒙古托克托台地湖相地层及其初步意义[J].第四纪研究, 2012, 32(5):931~937. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dsjyj201205010JIANG Fuchu, WANG Shubing, LI Chaozhu, et al. On study of lacustrine formation and its meaning in the Togtoh Platform, inner Mongolia[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2012, 32(5):931~937. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dsjyj201205010 [8] Jia L Y, Zhang X J, Ye P S, et al. Development of the alluvial and lacustrine terraces on the northern margin of the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia, China:Implications for the evolution of the Yellow River in the Hetao area since the late Pleistocene[J]. Geomorphology, 2016, 263:87~98. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.03.034 [9] 公王斌, 胡健民, 李振宏, 等.河套盆地西缘山前低台地沉积特征对"吉兰泰-河套"古湖消退过程及其控制因素的指示意义[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(4):190~198. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/yj/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_dxqy201304015GONG Wangbin, HU Jianmin, LI Zhenhong, et al. The sediment features of lower piedmont platforms along western Hetao Basin and implication for subsiding process and controlling factors of "Jilantai-Hetao" megalake[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(4):190~198. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/yj/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_dxqy201304015 [10] Li B F, Sun D H, Xu W H, et al. Paleomagnetic chronology and paleoenvironmental records from drill cores from the Hetao Basin and their implications for the formation of the Hobq Desert and the Yellow River[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2017, 156:69~89. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.11.023 [11] 曹刚.内蒙古地震研究[M].北京:地震出版社, 2001, 1~40.CAO Gang. Study on the paleoseism in inner Mongolia autonomous region[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2001, 1~40. (in Chinese) [12] Reimer P J, Bard E, Bayliss A, et al. IntCal13 and Marine13 radiocarbon age calibration curves 0~50, 000 years cal BP[J]. Radiocarbon, 2013, 55(4):1869~1887. doi: 10.2458/azu_js_rc.55.16947 [13] Aitken M J. An introduction to optical dating[M]. Oxford:Oxford University Press, 1998, 1~60. [14] Aitken M J. Thermoluminescence dating[M]. London:Academic Press Inc Ltd, 1985, 67. [15] Prescott J R, Hutton J T. Cosmic ray contributions to dose rates for luminescence and ESR dating:large depths and long-term time variations[J]. Radiation Measurements, 1994, 23(2/3):497~500. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/1350448794900868 [16] 刘哲, 赵华, 王成敏, 等.临河凹陷晚更新世以来沉积地层的光释光年龄[J].干旱区地理, 2014, 37(3):439~446. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqdl201403004LIU Zhe, ZHAO Hua, WANG Chengmin, et al. OSL ages of sedimentary layers in Linhe Depression since Late Pleistocene[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2014, 37(3):439~446. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqdl201403004 [17] Folk R L, Ward W C. Brazos River bar[Texas]:a study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1957, 27(1):3~26. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D [18] 成都地质学院陕北队.沉积岩(物)粒度分析及其应用[M].北京:地质出版社, 1976, 1~147.Shanxi Team of Chengdu College of Geology. Grain size Analysis and application of sediment rock[M]. Beijing:Geological Press, 1976, 1~147. (in Chinese) [19] 李建彪, 冉勇康, 郭文生.呼包盆地第四纪地层与环境演化[J].第四纪研究, 2007, 27(4):632~644. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dsjyj200704020LI Jianbiao, RAN Yongkang, GUO Wensheng. Division of quaternary beds and environment evolution in Hubao Basin in China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 27(4):632~644. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dsjyj200704020 [20] Chun X, Chen F H, Fan Y X, et al. Formation of Ulan Buh desert and its environmental changes during the Holocene[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science in China, 2008, 2(3):327~332. doi: 10.1007/s11707-008-0039-4 [21] 李建彪, 冉勇康, 郭文生.河套盆地托克托台地湖相层研究[J].第四纪研究, 2005, 25(5):630~639. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4883584LI Jianbiao, RAN Yongkang, GUO Wensheng. Research on the lacustrine strata of the Tuoketuo mesa, Hetao Basin, China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2005, 25(5):630~639. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.oalib.com/paper/4883584 -





 下载:
下载: