STABILITY ANALYSIS OF SUB-HORIZONTAL THICK-BEDDED SLOPE IN THREE GORGES RESERVIOR AREA: A CASE STUDY OF JIANCHUANDONG DANGEROUS ROCKMASS IN WUSHAN, CHONGQING
-
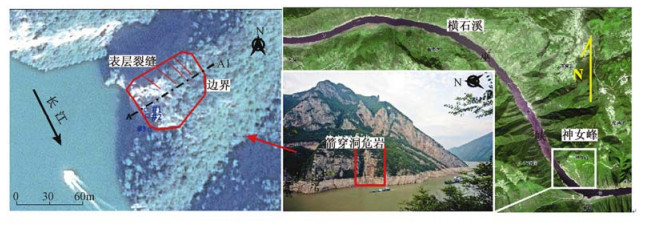
摘要: 以重庆巫山箭穿洞近水平巨厚层危岩体为例,通过地质环境条件、基座位移及应力监测数据等分析,总结归纳了危岩体目前的变形和受力状态,发现危岩体的强度仍在持续降低。同时,运用FLAC2D模拟手段,设置了初始天然、初始饱和、临滑、失稳4种模拟工况,研究了危岩基座岩体及泥质条带灰岩层面对危岩体阻滑规律。研究结果表明,基座泥质条带灰岩层强度的持续降低将会使得危岩体处于临滑乃至失稳状态。该稳定性分析也为进一步的防治设计提供了依据。Abstract: Taking Jianchuandong dangerous rockmass in Wushan for an example, based on analyzsis of geological conditions, displacement of base and stress monitoring data, we summarized the present deformation and stress state of the dangerous rockmass, then found that the strength of it remaining reduce. Meanwhile, using FLAC2D we set up four simulation conditions, including Initial natural, Initial saturation, critical sliding and destabilizing to research the rule of rock base and shale strip limestone when facing up rock slide. The results show that decreasing of base strength of argillaceous limestone will make dangerous rockmass in a state of critical sliding. Stability analysis of the above also provides a basis for further control of the design.
-
图 3 箭穿洞危岩A-A1工程地质剖面图(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 3. A-A1 engineering geological section of the Jianchuandong rockmass
表 1 箭穿洞危岩数值计算参数建议表
Table 1. Mechanical parameters of Jianchuandong rockmass
模型 重度/
(kN·m -3)弹性模量/
MPa泊松比 抗剪强度 抗拉强度/
kPa渗透系数/
(m·d -1)粘聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 基座 26.5 2.06×10 3 0.28 522 32 224 0.10 危岩体 27.1 7.16×10 3 0.22 / / / 0(不透水) 表 2 箭穿洞危岩基座及层面阻滑稳定系数
Table 2. Factors of stability resisted by base rock and bedding plane
工况 抗剪强度 稳定系数 备注 内摩擦角/(°) 粘聚力/kPa 初始天然状态 基座岩体 32 522 1.37 峰值天然强度(145m水位) 基座层面 22 60 初始饱和状态 基座岩体 32 522 1.20 峰值饱和强度(175m水位) 基座层面 18 50 临滑状态 基座岩体 32 522 1.05 层面2/3强度 基座层面 14 40 失稳状态 基座岩体 21 350 0.85 2/3强度 基座层面 14 40 -
[1] Terzaghi K. Stability of steep slopes on hard unweathered rock[J]. Geotechnique, 1962, 12: 251-270. doi: 10.1680/geot.1962.12.4.251 [2] Goodman R E, Bray J W. Toppling of rock slopes[C]//Proc. Specialty Conf. on Rock Engrg. for Foundations and Slopes. ASCE, 1977: 201-234. [3] 陈祖煜.土质边坡稳定分析——原理、方法、程序[M].北京:水利水电出版社, 2003.CHEN Zu-yu. Soil slope stability analysis: Theory, method and program[M]. Beijing: Water & Power Press, 2003. [4] Hungr O, Evens S G. The occurence and classification of massive rock slope failure[J]. Felsbau, 2004, 22(2):16-23. [5] 殷跃平.斜倾厚层山体滑坡视向滑动机制研究——以重庆武隆鸡尾山滑坡为例[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 19(2): 217-226. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201002002.htmYIN Yue-ping. Mechanism of apparent dip slide of inclined bedding rockslide-a case study of Jiweishan rockslide in Wulong, Chongqing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 19(2): 217-226. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201002002.htm [6] 黄波林, 刘广宁, 王世昌等.三峡库区高陡岸坡成灾机理研究[M].北京:科学出版社, 2015.HUANG Bo-lin, LIU Guang-ning, WANG Shi-chang, et al. Failure mechanism of high steep slope in Three Gorges Reservior area[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015. [7] Yin Y P, Huang B L, Liu G N, et al. Potential risk analysis on a Jianchuandong dangerous rockmass-generated impulse wave in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China[J]. Environmental Earth Science, 2015, 74(3): 2595-2607. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4278-x [8] 冯振, 李滨, 贺凯.近水平厚层高陡斜坡崩塌机制研究[J].地质力学学报, 2014, 20(2): 123-131. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20140203&journal_id=dzlxxbFENG Zhen, LI Bin, HE Kai. Rock collapse mechanism on high-steep slope failure in sub-horizontal thick-bedded mountains[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2014, 20(2): 123-131. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20140203&journal_id=dzlxxb [9] 重庆市地质灾害防治工程勘查设计院. 重庆市三峡库区巫山县箭穿洞危岩应急抢险勘(调)查及治理工程初步设计[R]. 重庆: 重庆市地质灾害防治工程勘查设计院, 2013.Chongqing Prospecting and Design Institute of Geological Hazard Control. Preliminary design and improvement of Jianchuandong dangerous rockmass emergency prospect (survey)[R]. Chongqing: Chongqing Prospecting and Design Institute of Geological Hazard Control, 2013. [10] Itasca Consulting Group, Inc.. FLAC (Fast Lagrangian Analysis of Continua) slope user's guide (Version 5.0)[M]. Minneapolis: Itasca Consulting Group, Inc., 2005. -





 下载:
下载: