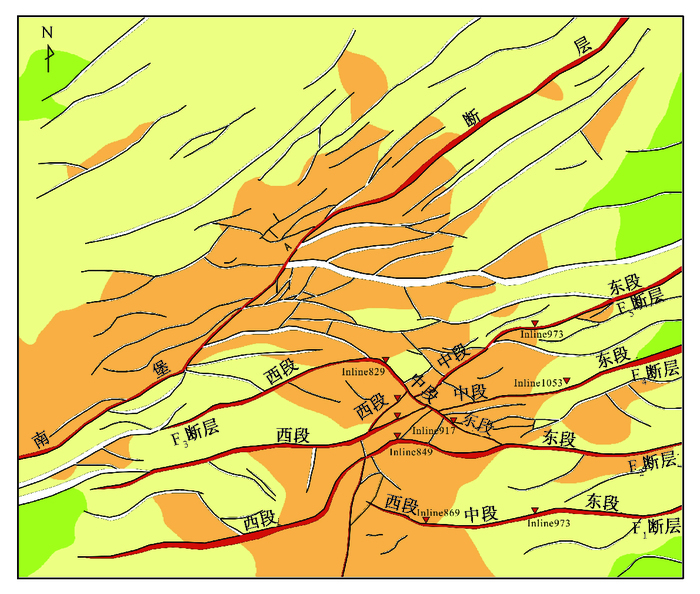
FORECAST OF LOWER ORDER FAULTS IN COMPLEX FAULT BLOCK RESERVOIRS BY NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF TECTONIC STRESS FIELD: TAKING M AREA IN NANPU SAG AS AN EXAMPLE
-
摘要: 针对低级序断层地震资料的多解性,通过构造解析,在确定低级序断层发育时期和构造背景的基础上,对南堡凹陷M区馆陶期构造应力场进行了数值模拟;并以岩石破裂准则为依据,用最小主应力解释了低级序断层的优势发育地区,用平面剪应力解释了低级序断层的优势走向,用剖面剪应力解释了低级序断层的优势视倾向,预测了低级序断层的发育规律。研究结果表明,南堡凹陷M区三级断层活动具有明显的分段性和分期性特点;在区域性南北向拉张和火山喷发造成的局部拱升的共同作用下,研究区中部为东一段低级序断层发育的优势区,发育近北西走向和近北东走向两组低级序断层,东部主要发育一组近北东走向的低级序断层,西部主要发育一组近北西走向低级序断层,断层视倾向以北倾为主。Abstract: The tectonic stress field of Guantao formation is simulated based on the confirmation of development period and tectonic setting about lower order faults. According to the failure criterion of rock, the favorable development regions of the lower order faults are analyzed through the minor principal stress, the favorable directions are discussed by the plane shear stress, and the tendencies are analyzed by the vertical shear stress. The activity of the third faults in M Area of Nanpu Sag presents obvious segment and generation: The middle part of the above studied region is the main region of the lower order faults owing to the coefficient of the regional NS extension and the regional camber stress by paroxysmal eruption, the east part develops a set of nearly NE-trending lower fault, the west part develops a set of nearly NW-trending fault, and the apparent dip mainly presents north tendency.
-
Key words:
- tectonic stress field /
- complex fault block /
- lower order fault /
- Nanpu sag
-
表 1 南堡M区应力场数值模拟力学参数
Table 1. Rock mechanical parameters of M area in Nanpu sag
模拟区块 泊松比 弹性模量/GPa 密度/(kg·m-3) 地层 0.28 18.0 2300 断层 0.35 9.0 2200 -
[1] 李阳.陆相水驱油藏剩余油富集区表征[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2011:94~118.LI Yang. The characterization of the remaining oil enrichment zone in continental water drive reservoir [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2011: 94~118. [2] 戴俊生, 李理.油区构造分析[M].东营:石油大学出版社, 2002:115~118.DAI Jun-sheng, LI Li. Oilfield structural analysis [M]. Dongying: Petroleum University Press, 2002: 115~118. [3] 中国石油冀东油田公司. 南堡油田南堡M区东一段油藏滚动开发研究[R]. 唐山: 中国石油冀东油田公司, 2009. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92021A/201501/664086438.htmlPetroChina Jidong Oilfied Company. Research on the rolling development of oil reservoir of Ed1 in M Area of Nanpu Oilfied[R]. Tangshan: PetroChina Jidong Oilfied Company, 2009. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92021A/201501/664086438.html [4] 中国石油冀东油田公司. 南堡凹陷第三系断裂系统划分及输导和封闭性评价[R]. 唐山: 中国石油冀东油田公司, 2011. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQKX201511006.htmPetroChina Jidong Oilfied Company. Fault system division, transporting and sealing evaluation of E in Nanpu Sag[R]. Tangshan: PetroChina Jidong Oilfied Company, 2011. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQKX201511006.htm [5] 童亨茂, 赵宝银, 曹哲, 等.渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷断裂系统成因的构造解析[J].地质学报, 2013, 87(11):1647~1661. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201311002.htmTONG Heng-mao, ZHAO Bao-yin, CAO Zhe, et al. Structural Analysis of Faulting System Origin in the Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. ACTA Geologica sinica. 2013, 87(11):1647~1661. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201311002.htm [6] 戴俊生.构造地质学及大地构造[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2006:22~36.DAI Jun-sheng. Structural geology and tectonics [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2006: 22~36. [7] 王红才, 王薇, 王连捷, 等.油田三维构造应力场数值模拟与油气运移[J].地球学报, 2002, 23(2):175~178. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200202015.htmWANG Hong-cai, WANG Wei, WANG Lian-jie, et al. Three dimensional tectonic stress field and migration of oil and gas in Tanhai[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2002, 23 (2): 175~178. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200202015.htm [8] 周天伟, 周建勋, 董月霞, 等.渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷新生代断裂系统形成机制[J].中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2009, 33(1):12~17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200901003.htmZHOU Tian-wei, ZHOU Jian-xun, DONG Yue-xia, et al. Formation mechanism of Cenozoic fault system of Nanpu sag in Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Natural Science Edition, 2009, 33(1): 12~17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200901003.htm [9] 范柏江, 刘成林, 柳广弟, 等.南堡凹陷断裂系统形成机制及构造演化研究[J].西安石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 25(2):13~17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201002005.htmFAN Bai-jiang, LIU Cheng-lin, LIU Guang-di, et al. Forming mechanism of the fault system and structural evolution history of Nanpu Sag[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University: Natural Science Edition, 2010, 25(2): 13~17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201002005.htm [10] 董月霞, 周海民, 夏文臣.南堡凹陷火山活动与裂陷旋回[J].石油与天然气地质, 2000, 21(4):304~307. doi: 10.11743/ogg20000404DONG Yue-xia, ZHOU Hai-min, XIA Wen-chen. Volcanic activities and rift-subsidence cycles in nanpu sag[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2000, 21(4): 304~307. doi: 10.11743/ogg20000404 [11] 董月霞, 夏文臣, 周海民.南堡凹陷第三系火山岩演化序列研究[J].石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(2):24~26. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200302006.htmDONG Yue-xia, XIA Wen-chen, ZHOU Hai-min. Evolvement sequence of Tertiary volcanic rocks in the Nanpu sag, Eastern China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(2): 24~26. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200302006.htm [12] 张继标, 戴俊生, 王彤达, 等.高邮凹陷南断阶西部断裂特征及其成因机制[J].西安石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 27(3):29~34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201203007.htmZHANG Ji-biao, DAI Jun-sheng, WANG Tong-da, et al. Characteristics and genetic mechanism of the faults in the west of south fault terrace in Gaoyou Sag[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University: Natural Science Edition, 2012, 27(3): 29~34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201203007.htm [13] 戴俊生, 张继标, 冯建伟, 等.高邮凹陷真武断裂带西部低级序断层发育规律预测[J].地质力学学报, 2012, 18(1):11~21. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120102&flag=1DAI Jun-sheng, ZHANG Ji-biao, FENG Jian-wei, et al. Development law and prediction of the lower-order faults in the west of Zhenwu fault zone in Gaoyou sag[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2012, 18(1): 11~21. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120102&flag=1 [14] 中国石油冀东油田分公司. 南堡凹陷构造演化历史与裂缝发育分布[R]. 唐山: 中国石油冀东油田分公司, 2014. https://image.hanspub.org/xml/20462.xmlPetro China Jidong Oilfied Company. Tectonic evolution history and distribution of fractures in Nanpu Sag[R]. Tangshan: PetroChina Jidong Oilfied Company, 2014. https://image.hanspub.org/xml/20462.xml [15] 赵文.岩石力学[M].长沙:中南大学出版社, 2010:55~90.ZHAO Wen. Rock mechanics[M]. Changsha: Centra South University Press, 2010: 55~90. [16] 商琳, 戴俊生, 王彤达, 等.基于新钻井对柴达木盆地东部石炭系分布及控制因素的再认识[J].中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 38(2):25~31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201402004.htmSHANG Lin, DAI Jun-sheng, WANG Tong-da, et al. New study on Carboniferous stratigraphic distribution and controlling factors in the eastern Qaidam Basin based on new drilling data[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Natural Science Edition, 2014, 38(2): 25~31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201402004.htm [17] Santanu M. Deformation localization at the tips of shear fractures: An analytical approach[J]. Tectonophysics, 2011, 503(1): 182~187. http://www.academia.edu/8461103/Deformation_localization_at_the_tips_of_shear_fractures_An_analytical_approach [18] Kaus B J P. Factors that control the angle of shear bands in geodynamic numerical models of brittle deformation[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 484(1): 36~47. [19] 王正荣.应变椭球体平面投影及在构造分析中的应用[J].煤炭技术, 2006, 25(1):92~95. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTJS200601045.htmWANG Zheng-rong. Plane projection of strain ellipsoid and its application in geologic structure analysis[J]. Coal Technology, 2006, 25(1): 92~95. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTJS200601045.htm -





 下载:
下载: