RESEARCH ON THE ENGINEERING GEOLOGY CONDITION AND RAILWAY ROUTES COMPARISON ALONG THE Mt. GAOLIGONG SECTION, DALI-RUILI RAILWAY
-
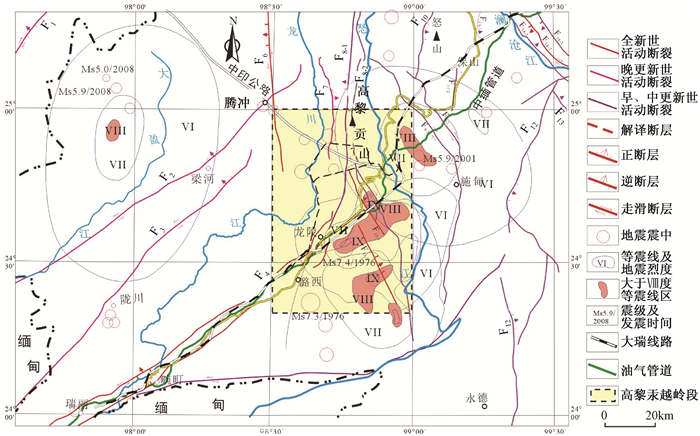
摘要: 在野外地质调查、钻探、地应力测量和室内测试分析的基础上, 对大瑞铁路高黎贡山越岭段规划设计中可能遇到的高地温、高地应力、活动断裂断错、岩爆、涌水突泥、软岩大变形和边坡稳定性等主要工程地质问题进行了论述, 认为高地温和热害是制约高黎贡山深埋隧道段建设的关键因素。根据地热钻探、测试资料分析, 该区的地热分布受断裂构造控制明显, 黄草坝断裂具有阻水隔热的工程地质特性。对比分析认为, C12K方案(34.5 km越岭长隧道方案)位于黄草坝阻水隔热断层之南, 通道内相对低温, 且在隧道口处避让了古滑坡等不利工程地质问题, 在众多比选方案中工程地质条件较好。调查研究结果对大瑞铁路全线贯通具有重要意义。Abstract: Based on the field geological investigation, drilling, in-situ stress measurement and lab test analysis, this paper illustrates the main engineering geological problems that could be encountered in the Mt. Gaoligong section railway planning and construction, such as high geo-temperature, high geo-stress, active fracture dislocation, rock burst, water pouring out and mud squirting, large deformation of the soft rock, landslide, and so on. The paper deems that the high geo-temperature and thermal harm are the key factors restricting the Mt. Gaoligong deep-buried tunnel section. According to geothermal drilling and lad test results analysis, the geothermal distribution is obviously controlled by the geology structure, and the Huangcaoba fault has the engineering geology of block water and heat insulation. Based on comprehensive comparative analysis, the C12K scheme (34.6 km long tunnel scheme) is a better scheme, located in the relatively low geothermal channel, south of the Huangcaoba fault, and this scheme has avoided some unfavorable engineering geological problems such as the ancient landslide at the tunnel entrance. The survey and research results have great importance for the landslide optimization and further design.
-
表 1 地温带划分、热害分析评估标准
Table 1. The temperate zone, heat damage evaluation standard table
地温带 温度界限T/℃ 热害分析评估标准 常温带 ≤28 无热害 低高温带(Ⅰ) 28<T≤37 热害轻微 中高温带(Ⅱ) 中高温带(Ⅱ1) 37<T≤50 热害中等 中高温带(Ⅱ2) 50<T≤60 热害较严重 超高温带(Ⅲ) >60 热害严重 表 2 高黎贡山比选方案隧道地质条件综合对比
Table 2. Comprehensive geological condition comparison for alternative schemes along Mt. Gaoligong deep-buried tunnel section
比选内容 C12K CK C4K C1K C10K C5K C22K 地热地质条件 隧道路肩面温度所占比例/% 常温带 63.90 36.90 39.60 27.60 近100 - 100 低高温带(Ⅰ) 34.10 61.10 32.10 23.80 无 - 无 中高温带(Ⅱ1) 2.0 2.0 20.45 39.02 无 - 无 中高温带(Ⅱ2) 无 无 7.10 6.75 无 - 无 高温带(Ⅲ) 无 无 0.75 2.83 无 - 无 地温梯度(℃/100 m) 1.68 1.78 3.66 3.91 - - - 热流值/(mW·m-2) 29.2~52.2 30.9~52.2 52.5~190 52.5~190 - - - 岩温产热率(10-2 J/m2·s) 2.4~4.3 3.0~3.5 3.0~6.4 6.5~12.0 - - - 隧道地热地质条件 位于相对低温通道 位于相对低温通道 穿越高地温地区,龙陵隧道进口地段高温热害严重 穿越高地温地区,龙陵隧道进口地段高温热害严重 线路多以路基、桥通过,避免了隧道高地温危害 穿越高地温地区,隧道热害严重 线路多以路基、桥通过,避免了隧道高地温危害 断裂构造 线路大角度与断裂构造大角度相交 线路大角度与断裂构造大角度相交 高黎贡山隧道位于断裂构造蜂腰部位,引线段与构造线平行 高黎贡山隧道位于断裂构造蜂腰部位,引线段与构造线平行 在断裂构造密集地区迂回展线 引线段与断裂构造平行 在断裂构造密集地区迂回展线 不良地质 绕避 引线段不良地质发育 引线段不良地质发育 不良地质发育 不良地质发育 不良地质发育 不良地质发育 工程地质条件评价 较好 好 差 差 差 -
[1] 张永双, 张加桂, 雷伟志, 等.中国西南泛亚大通道环境工程地质问题概论[J].地学前缘, 2007, 14(6):24~31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200706004.htmZHANG Yong-shuang, ZHANG Jia-gui, LEI Wei-zhi, et al. Discussion on environmental geological problems in the areas from southwest China to southeast Asia[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007, 14(6): 24~30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200706004.htm [2] 中铁二院工程集团有限责任公司. 新建铁路大理至瑞丽线高黎贡山越岭地段加深地质工作及专题地质研究工作工程地质勘察总报告[R]. 成都: 中铁二院工程集团有限责任公司, 2008.China Railway Eryuan Engineering Group Co. Ltd.. The engineering geological investigation general report of deepening geological work and special subject geological research of the Gaoligong Mt. Mountain-crossing Section, of Dali-Ruili newly built railway[R]. Chengdu: China Railway Eryuan Engineering Group Co. Ltd., 2008. [3] 郭长宝, 张永双, 杜宇本, 等.滇西南大通道主要地质灾害类型及发育规律研究[J].人民长江, 2011, 42(13):35~39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2011.13.009GUO Chang-bao, ZHANG Yong-shuang, DU Yu-ben, et al. Research on development pattern of typical geological disaster in Southwest Yunnan Channel[J]. Yangtze River, 2011, 42(13): 35~39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2011.13.009 [4] 郭长宝, 张永双, 屈科, 等.大瑞铁路保山至瑞丽段及邻区地壳稳定性定量评价[J].地质力学学报, 2014, 20(1):70~81. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20140107&journal_id=dzlxxbGUO Chang-bao, ZHANG Yong-shuang, QU Ke, et al. Quantitative zoning assessment of crustal stability assessment along the Dali-Ruili Railway[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2014, 20(1): 70~81. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20140107&journal_id=dzlxxb [5] 杜宇本, 郑光, 蒋良文, 等.大瑞铁路澜沧江大桥工程边坡稳定性三维数值模拟分析[J].地质力学学报, 2010, 16(1):108~114. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100113&journal_id=dzlxxbDU Yu-ben, ZHENG Guang, JIANG Liang-wen, et al. 3D numerical simulation of slope stability of Lancangjiang Bridge on Dali-Ruili Railway [J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2010, 16(1): 108~114. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20100113&journal_id=dzlxxb [6] 赵志明, 吴光, 寇川.大(理)瑞(丽)铁路高黎贡山越岭段地质灾害工程分区研究[J].西南交通大学学报, 2013, 48(2):310~316. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNJT201302020.htmZHAO Zhi-ming, WU Guang, KOU Chuan. Engineering geological division of geological hazards along Dali-Ruili Railway in Gaoligong Mountain section[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013, 48(2): 310~316. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNJT201302020.htm [7] 殷跃平.云南省腾冲县苏家河口电站小江平坝滑坡[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2008, (1):113. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200801026.htmYIN Yue-ping. Xiaopingba landslide at Sujiahekou Power Station, Tengchong Country, Yunnan Province [J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2008, (1): 113. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200801026.htm [8] 伍法权.中国21世纪若干重大工程地质与环境问题[J].工程地质学报, 2001, 9(2):115~121. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200102000.htmWU Faquan. Major engineering-geological and environmental problems in China in the 21st Century[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2001, 9(2): 115~121. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200102000.htm [9] 谷柏森.隧道高地温应对措施及通风设计——高黎贡山铁路特长隧道可行性研究[J].现代隧道技术, 2007, 44(2):66~71. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDSD200702013.htmGU Bai-sen. Countermeasures against high temperatures in a tunnel and the corresponding ventilation design: Feasibility study for the super-long Gaoligonshan tunnel[J]. Modern Tunneling Technology, 2007, 44(2): 66~71. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDSD200702013.htm [10] 杜宇本, 蒋良文, 邓宏科, 等.大瑞铁路高黎贡山越岭段水热活动特征及地质选线[J].铁道工程学报, 2010, (增刊):136~142.DU Yu-ben, JIANG Liang-wen, DENG Hong-ke, et al. Geological route selection of Dali-Ruili Railway through Gaoligong Mountain based on hydrothermal activity characteristics[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering, 2010, (Supp.): 136~142. [11] 杜宇本, 蒋良文.大瑞铁路大保段主要工程地质问题及地质选线[J].铁道工程学报, 2010, (4):23~28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC201004007.htmDU Yu-ben, JIANG Liang-wen. Main problems in engineering geology and alignment in Dali-Baoshan section of Dali-Ruili railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering, 2010, (4): 23~28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC201004007.htm [12] 侯新伟, 李向全, 蒋良文, 等.大瑞铁路高黎贡山隧道热害评估[J].铁道工程学报, 2011, (5):60~65. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC201105013.htmHOU Xin-wei, LI Xiang-quan, JIANG Liang-wen, et al. Heat damage evaluation of Gaoligong tunnel of Dali-Ruili Railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering, 2011, (5): 60~65. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC201105013.htm [13] 郭长宝, 张永双, 蒋良文, 等.褶皱构造体中深埋隧道岩爆机制与隧道断面适宜性研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(增1):2758~2766. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2012S1020.htmGUO Chang-bao, ZHANG Yong-shuang, JIANG Liang-wen, et al. Rock burst mechanism and feasible cross section for deep buried tunnel in the fold structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(Supp.1): 2758~2766. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2012S1020.htm [14] 张永双, 熊探宇, 杜宇本, 等.高黎贡山深埋隧道地应力特征及岩爆模拟试验[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(11):2286~2294. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.11.018ZHANG Yong-shuang, XIONG Tan-yu, DU Yu-ben, et al. Geostress characteristics and simulation experiment of rock burst of a deep-buried tunnel in Gaoligong Mountain[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(11): 2286~2294. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.11.018 [15] Zhang Y S, Xiong T Y, Guo C B, et al. On experimental simulation of rock burst processes of a deep-buried tunnel in Gaoligong Range, southwest China[C]//Proceedings of Conference of IAEG 2009. [16] 黄学猛, 杜义, 舒赛兵, 等.龙陵—瑞丽断裂(南支)北段晚第四纪活动性特征[J].震害防御技术, 2012, 7(3):215~226. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201002006.htmHUANG Xue-meng, DU Yi, SHU Sai-bing, et al. Late Quaternary activity characteristics of Longling-Ruili fault (south branch) north segment[J]. Earthquake Disaster Defense Technology, 2012, 7(3): 215~226. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201002006.htm [17] Zhang Y S, Guo C B, Qu Y X, et al. Engineering geological properties of altered rocks and implications for railway construction in the Sanjiang orogenic belt, southwest China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and Environment, 2010, 69: 10064~10073. doi: 10.1007/s10064-010-0294-y -





 下载:
下载: