STUDY ON LATE CENOZOIC CRUSTAL TECTONISM
-
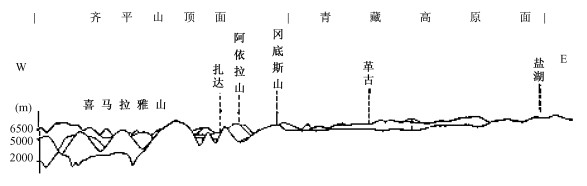
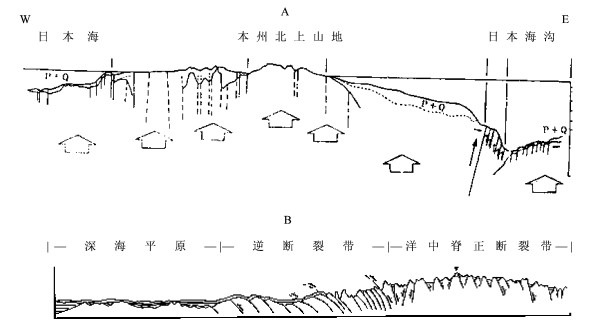
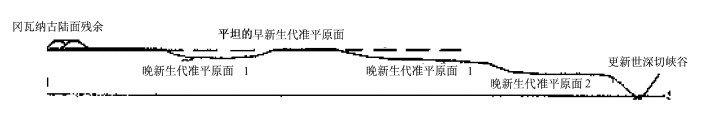
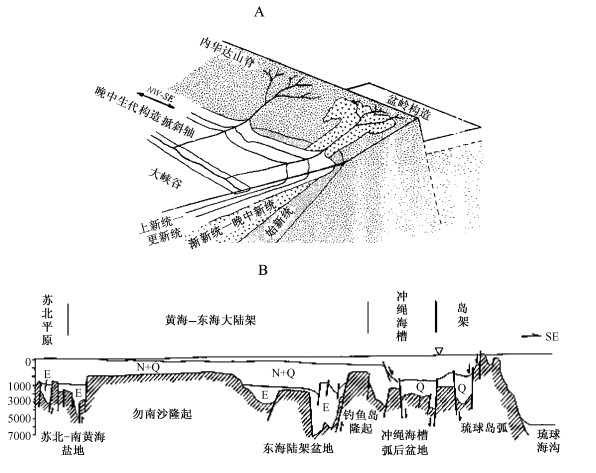
摘要: 通过地球表面清、新的构造地貌与现代水文网记录, 研究晚新生代年轻地壳构造运动。研究发现高原-山带-盆地排列有序形影相依的定式, 与现代水文网的演化相辅相成, 揭示高原边缘山带本质上就是高原边缘流水深切割的产物。论证了于晚中新世时期全球曾准平原化, 发育了全球统一的准平原, 散布全球不同高度的高原面、齐平山顶面与盆地底面时代相当可广泛对比。现代构造地貌演化始于导致晚中新世准平原面分裂解体的上新世以来, 同时证明晚新生代地壳构造运动属垂直拱曲块断差异升降构造运动, 仅在某些特定部位局部派生次级不同规模的引张构造变形和层间滑动薄皮挤压构造变形。现代水文网发育经历了上新世-早更新世属盆地向心水系伴以河湖相沉积, 以及中更新世以来串珠状水系与相关的河流相沉积, 两套地层呈假整合或不整合, 明确记录了晚新生代地壳构造运动进程的两个主要阶段。约近70~80万年的中更新世以来, 新一轮强烈的地壳的差异升降构造运动, 显著的改造了已有的格局。自俄罗斯远东山地, 经蒙古高原和青藏高原至印度西北阿拉瓦利山, 地球表面规模最雄伟的、分开太平洋水系与北冰洋水系的亚洲巨型分水岭的出现, 标志新兴的全球现代构造地貌与水文网的形成, 奠定了今日构造地貌与水文网的景观。研究表明, 大陆与大洋晚中新世全球统一准平原面一脉相承, 晚新生代地壳构造运动完全可以对比。深入系统研究年轻的晚新生代地壳构造运动不仅有实用价值, 同时也有重要的科学意义, 特别是为探究全球构造运动本质和地球动力学提供了一个新的视角。
-
关键词:
- 晚新生代地壳构造运动 /
- 构造地貌 /
- 准平原面 /
- 高原-山带-盆地(平原)组合 /
- 拱曲隆升 /
- 块断差异升降运动
Abstract: This paper deals with late Cenozoic crustal tectonism by studying morphostructure and associated water system in a global scope.As young mountain belt is caused by deep dissection at the edge of a plateau, the keynote of complex morphostructure on Earth surface is actually made up of sequentially fixing arrangement of plateau-mountain-basin (P-M-B), with horst-like assemblage of B-M-P =P-M-B and step-like assemblage of P-M-B =P-M-B =P-M-B in different scales.It is found that the late Miocene planation surface preserved on the plateaus is comparable in age with the unconformity at the base of the Pliocene-early Pleistocene basins.Both imply the existence of a unified peneplain on the Earth surface until the latest Miocene.So the late Miocene peneplain substantially constrains the framework of the late Cenozoic crustal tectonism, and it is the late Cenozoic crustal tectonism that led to the breaking-up of the unified peneplain and brought about today' s morphostructure.From sedimentation, unconformity, and evolution of the water system, two evolutionary stages can be recognized for the late Cenozoic crustal tectonism, namely the Pliocene-early Pleistocene and middle Pleistocene-present.The paper also demonstrated the Asian mega-dividing.It extends from the mountain area of East Siberia in the northeast, passing through the Mongolian and Tibetan Plateaus, to the Aravalli Range in northwestern India to the southwest, and that divides water systems into the Pacific and Indian Oceans and the Arctic Ocean, respectively.It has emerged since middle Pleistocene (0.78 Ma), indicating the forming time of the global morphostructure.Geological records related to deformation of broken peneplain fragments indicate that vertical arching movement with block faulting at differential elevation and subsidence is predominant.It is debated that extensional and compressive crustal tectonism can be induced only from vertical movements at some specific areas.Except local compression deformation, no any geological records show that the Pleistocene sediments experienced any processes related with regionally horizontal compression on a global scope.Recent crustal tectonism follows the same keynote. -
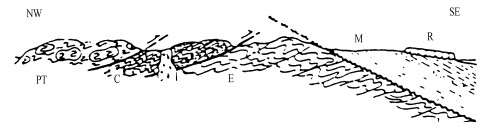
图 9 拱曲隆升伴以逆断块断抬升。美国怀俄明州落基山脉构造
Owl Creek山隆升, 伴以山前风河盆地边缘古近系—新近系逆断变形[16]。
Figure 9. Plateau uplift with reverse faulting on flank of the arching uplift
-
[1] Suvorov AI.Recent global kinematics of the lithosphere (on the basis of regional tectonic pairs)[J].Geotectonics English Translation, 1978, 12:79~89. [2] Gao Ming-xiu. Late Cenozoic vertical movement either a specific case or a universal law[C]. New Concepts in Global Tectonics. Colorado: Otero Junior College La Junta, 2002. [3] 高名修.东亚北东向块断构造与现代地裂运动[M].北京:地震出版社, 1995. [4] King LC.The Morphology of the Earth:A Study and Synthesis of World Scenery[M].London: Oliver And Boyd, 1962. [5] Wadia DN. Geology of India[M]. London: Macmillan & Co. LTD. Third Edition(Revised), 1975. [6] Embleton C.Geomorphology of Europe[M].London: Macmillan Publishers, 1984. [7] Bridges EM.World Geomorphology[M].Combridge: Cambridge University Press, 1991. [8] 杨逸畴, 李炳元, 尹泽生, 等.西藏地貌[M].北京:科学出版社, 1983. [9] Seeber L, Gornitz V.River profiles along the Himalayan arc as indicators of active tectonics[J].Tectonophysics, 1983, 92 (4): 335~367. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(83)90201-9 [10] 任美锷, 包浩生.中国自然地理、地貌[M].北京:科学出版社, 1980. [11] 张荣祖, 郑度, 杨勤业.西藏自然地理[M].北京:科学出版社, 1982. [12] Oller C, Pain C.The origin of mountains[M].Routledge, Taylor & Francis Group, London and New York.1998. [13] 藤田至则. 岛弧变动について. 地团研专报第24号别刷, 1982. [14] Antipov MP, Zharkov SM, Kozhenov V Ya, et al.Structure of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and adjacent parts of the abyssal plain at Lat.13° N[J].International Geology Review, 1990, 32: 468~478. doi: 10.1080/00206819009465791 [15] Meyerhoff AA, Taner I, Morris AEL, et al. Surge Tectonics: a new hypothesis of Earth dynamics[A]. In: Chatterjee S, Hotton N Ⅲ (Eds). New Concepts in Global Tectonics. Lubbock: Texas Tech University Press, 1992. 309~409. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10025417756 [16] Eardley AJ.Structural Geology of North America[M].New York: Harper & Brothers Publishers, 1951. [17] De Sitter LU.Pliocene uplift of Tertiary mountain chains[J].American Journal of Science, 1952, 250 (4):297~307. doi: 10.2475/ajs.250.4.297 [18] 李祥根.中国新构造运动概论[M].北京:地震出版社, 2002. [19] 施雅风, 李吉均, 李炳元.青藏高原晚新生代隆升与环境变化[M].广州:广东科技出版社, 1998. [20] 中国科学院内蒙古宁夏综合考察队.内蒙古自治区及东北西部地区地貌[M].北京:科学出版社, 1980. [21] Shackleton R M, Chang Chengfa.Cenozoic uplift and deformation of the Tibet Plateau:the geomorphologic evidence[J].Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 1988, A 327: 365~378. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1988RSPTA.327..365S [22] 黄培华.论云南之地貌发育问题[J].中国第四纪研究, 1960, 3:39~55. [23] Sengor AMC, Kidd WSF.Post-collisional tectonics of the Turkish-Iranian Plateau and a comparison with Tibet[J].Tectonophysics, 1979, 55 (3~4): 361~376. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(79)90184-7 [24] Verma PK, Singh KK. Evidence, motive forces and the time frame of neotectonism in the Aravalli mountain range, India[C]. In: Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology. Seminar On Himalayan Geology &Geophysics (New Data And New Approaches). Dehra Dun: Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology, 1993. [25] Nalivkin DV, Richey JE, Cloud Preston E Jr.The geology of the U S S R: A short outline[M].London: Pergamon Press, 1960. [26] Ufimtsev GF.Morphotectonics of the Mongolia-Siberian mountain belt[J].Journal of Geodynamics, 1990, 11 (4): 309~325. doi: 10.1016/0264-3707(90)90014-L [27] McQuarrie N, Chase CG.Raising the Colorado plateau[J].Geology, 2000, 28 (1):91~94. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)028<0091:RTCP>2.0.CO;2 [28] Morrison RB. Quaternary geology of the southern Basin and Range province[A]. In: Morrison RB. Quaternary Nonglacial Geology: Conterminous US. Colorado: Geological Society of America, 1991. [29] 李春芬.南美洲地理环境的结构[M].北京:科学出版社, 1962. [30] Gonzá lez-Fsrrán O.Volcanic and tectonic evolution of the northern Antarctic peninsula-late Cenozoic to recent[J].Tectonophysics, 1991, 114:389~409. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/004019518590023X [31] Lamb S, Hoke L.Origin of the high plateau in the Central Andes, Bolivia, South Ameica[J].Tectonics, 1997, 16 (4): 623~649. doi: 10.1029/97TC00495 [32] Ferran OG.International Symposium On Andean and Antarctic Volcanology Problems[M].Santiago: Universidad de Chile, 1974. [33] Sevon WD, Potter N, Crowl GH.Appalachian peneplains:An historical review[J].Earth Sciences History, 1983, 2:156 ~164. doi: 10.17704/eshi.2.2.068421x54v1r7826 [34] 日本第四纪学会.日本第四纪研究[M].北京:海洋出版社, 1984. [35] Matenco L, Bertotti G, Dinu C, et al.Tertiary tectonic evolution of the external South Carpathians and the adjacent Moesian platform (Romania)[J].Tectonics, 1997, 16 (6):896~911. doi: 10.1029/97TC01238 [36] Rouchy JM, Martin JPS.Late Miocene events in the Mediterranean as recorded by carbonate-evaportions[J].Geology, 1992, 20 (7): 269~632. [37] Unruh JR.The uplift of the Sierra Nevada and implications for late Cenozoic epeirogeny in the western Cordillera[J].Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1991, 103 (11):1395~1404. http://www.mendeley.com/research/uplift-sierranevada-implications-late-cenozoic-epeirogeny-western-cordillera/ [38] Yeats RS, Rockwell TK. Quayernary geology of the Ventura and Los Angeles Basins, California[A]. In: Morrison R B. Quaternary Nonglacial Geology: Conterminous US. Colorado: Geological Society of America, 1991. [39] Dupre WR, M orrison RB, Clifton HE, et al. Quaternary geology of the pacific margin[A]. Morrison RB. Quaterrary Nonglacial Geology: Conterminous US. Colorado: Geological Society of America, 1991. [40] McNeill LC, Goldfinger C, Kulm LD, et al.Tectonics of the Neogene Cascadian forearc basin: Investigations of a deformed late Miocene unconformity[J].Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2000, 112 (8):1209~1224. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2000)112<1209:TOTNCF>2.0.CO;2 [41] 石和田靖章.东中国海的区域不整合[J].海洋地质译丛, 1982, 1: 35~39. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000001538393 [42] Krishna KS, Bull JM, Scrutton RA.Evidence for multiphase folding of the central Indian Ocean lithosphere[J].Geology, 2001, 29 (8): 715~718. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0715:EFMFOT>2.0.CO;2 [43] Keller G, Barron JA.Paleodepth distribution of Neogene deep-sea hiatuses[J].Paleoceanography, 1987, 2 (6): 697~713. doi: 10.1029/PA002i006p00697 [44] 郑绵平, 向军, 等.青藏高原盐湖[M].北京:科学出版社, 1989. [45] 陈克造.中国盐湖的基本特征[J].第四纪研究, 1992, 3:193~201. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1992.03.001 [46] 谢明.长江三峡地区第四纪以来新构造上升速度和形式[J].第四纪研究, 1990, 4:308~315. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1990.04.003 [47] 唐贵智, 陶明.长江三峡地区新构造运动及其对工程建设影响的研究[J].中国地质科学院宜昌地质矿产研究所所刊, 1991, 第十七号:1~68. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HY000002738100 [48] 吴继远.羚羊峡的形成与西江改道[J].广西地质, 1993, 6 (总29):45~51. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000891554 [49] Clifton HE, Leithold EL. Quaternary costal and shallow-marine facies Sequences, Northern California and the Pacific Northwest [A]. In: Morrison RB. Quaterrary Nonglacial Geology: Conterminous US. Colorado: Geological Society of America, 1991. [50] Aseev AA, Blagovolin NS, Serebryannyi LR. Exogenic landforms of Europe[A]. In: Geomorphology of Europe. London: Macmillan Publishers, 1984. doi: 10.1007/978-1-349-17346-4_3 [51] 新野弘.探索中国东海宝库—钓鱼岛等岛屿周围的海底地质调查[J].Ocean Age, 1970.11. [52] Gladenkov Yu B. Neogene biotic events[A]. In: Tsuchi R, Ingle J C Jr. Pacific Neogene Environment, Evolution and Events [M]. Tokyo: University of Tokyo Press, 1992. [53] Michihel H.The expanding earth: evidence, causes and effects[M].Tokyo: University of Tokyo Press, 1998. [54] 姚庆元.福建沿海第四纪地层划分的若干问题与区域地层表[J].福建地震, 1982, 3: 66~75. [55] 潘桂棠, 王培生, 徐耀荣, 等.青藏高原新生代构造演化[M].北京:地质出版社, 1990. [56] 葛肖虹, 段吉业, 刘先文, 等. 中国西北的大地构造[R]. 岩石圈构造与动力学开放研究实验室年报. 北京: 中国科技出版社, 1992. [57] 崔之久, 五永秋, 刘耕年, 等. 青藏公路昆仑山垭口天然剖面记录[C]. 青藏高原晚新生代隆升与环境变化[M]. 广州: 广东科技出版社, 1998. [58] 金小赤, 王军, 任留东, 等. 西昆仑地质构造的几个问题[C]. 构造地质学—岩石圈动力学研究进展(马杏垣纪念册). 1999. [59] Valdiya KS. Newtectonics of Himalayan Belt[A]. In: International Symposium on Newtectonics in South Asia[C]. Dehra Dun, India, 1986. [60] 黄汲清. 中国新构造运动的几个类型[C]. 中国科学院. 第一次新构造运动座谈会发言记录. 北京: 科学出版社, 1957. [61] 刘东生, 黄万波, 王挺梅. 三门系地层的新构造运动[C]. 中国科学院. 第一次新构造运动座谈会发言记录. 北京: 科学出版社, 1957. [62] 方鸿琪.长江中下游的新构造运动[J].地质学报, 1959, 39 (3). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000377239 [63] Letouzey J, Kimura M.Okinawa trough genesis:structure and evolution of a backarc basin developed in a continent[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1985, 2 (2): 111~130. doi: 10.1016/0264-8172(85)90002-9 [64] 何春荪. 台湾地质概况(台湾地质图说明书)[M]. 经济部中央地质调查所, 1994. [65] 颜沧波.台湾的地质和地史[J].海洋科学, 1977, 9 (8). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000001494515 [66] Ruddiman WF, Kutzbach JE.Forcing of late Cenozoic northern hemisphere climate by plateau uplift in southeast Asia and the American Southwest[J].Journal of Geophysical Research, 1989, 94 (D15): 18409~18427. doi: 10.1029/JD094iD15p18409 [67] Raymo M E. Late Cenozoic evolution of global climate[A]. In: Tsuchi R, Ingle J C Jr. Pacific Neogene Environment, Evolution and Events. Tokyo: University of Tokyo Press, 1992. [68] Raymo M E, Ruddiman WF.Tectonic forcing of the late Cenozoic climate[J].Nature, 1992, 359: 117~122. doi: 10.1038/359117a0 [69] DeMenocal PB.Plio-Pleistocene African Climate[J].Science, 1995, 270: 53~59. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5233.53 [70] 潘保田, 方小敏, 李吉均, 等. 晚新生代青藏高原隆升与环境变化[A]. 施风, 李吉均, 李炳元. 青藏高原晚新生代隆升与环境变化[M]. 广州: 广东科学技术出版社, 1998. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=LDZK201302005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [71] Dupont LM, Donner B, Schneider R, et al.Mid-Pleistocene environment change in tropical Africa began as early as 1.05 Ma[J].Geology, 2001, 29 (3): 195~198. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0195:MPECIT>2.0.CO;2 [72] Montgomery DR, Balco G, Willett SD.Climate, tectonics, and morphology of the Andes[J].Geology, 2001, 29 (7):579~582. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0579:CTATMO>2.0.CO;2 [73] 刘东生, 施雅风, 王汝建, 等.以气候变化为标志的中国第四纪对比表[J].第四纪研究, 2000, 20 (2):108~128. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2000.02.002 [74] 的场保望.从底栖和浮游有孔虫看日本海的古环境变迁[J].海洋地质, 1982, 2: 65~71. [75] Molnar P, England P.Late Cenozoic uplift of mountain ranges and global climate change:chicken or egg?[J].Nature, 1990, 346:29~34. doi: 10.1038/346029a0 [76] Nakata T. Active faults of the Himalaya of India and Nepal[C]. In: Malinconico Jr LL, Lillie RJ. Tectonics of the western Himalaya. Geological Society of America Special Paper 232, 1989. 243~264. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10026535722 [77] GAO Ming-xiu. Geodynamic significance of NE-SW transected fault system in Himalaya[C]. In: Seminar On Himalayan Geology &Geophysics(New Data And New Approaches), Abstracts. Dehra Dun: Wadia Institute Of Himalayan Geology, 1993. [78] 高名修.青藏高原南缘现今地球动力学研究[J].地震地质, 1996, 18:143~155. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600061825 [79] Gao Ming-xiu. Seismotectonics of the Kumaun Himalaya[C]. In: Jain AK, Manickavasagam RM. Geodynamics of the NW Himalaya. Gondwana Research Group Memoir, 1999. [80] Jain AK, Manickavasagam RM, Patel RC, et al. Extensional tectonics in the collisonal NW-Himalayan belt[C]. In: Seminar On Himalayan Geology &Geophysics (New Data And New Approaches), Abstracts. Dehra Dun: Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology, 1993. [81] Mugnier JL, Chalaron E, Huughe P, et al. The active normal faults close to the Main Boundary Fault in western Nepal: a peculiar feature of a fold and thrust compressional wedge[C]. In: Seminar On Himalayan Geology &Geophysics (New Data And New Approaches), Abstracts. Dehra Dun: Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology, 1993. [82] Blisniuk PM, Sonder LJ, Lillie RJ.Foreland normal fault control on northwest Himalayan thrust from development[J].Tectonics, 1998, 17 (5): 766~779. doi: 10.1029/98TC01870 [83] Jackson JA, Fitch TJ, M cKenzie DP. Active thrusting and the evolution of the Zagros fold belt[C]. In: McClay K, Price N. Special Publication(No. 9). London: Geological Society of London, 1981. 371~379. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1981GSLSP...9..371J [84] Kashfi MS. Geological evidence for a simple horizontal compression of the crust in the Zagros Crush Zone[C]. In: Chatterjee S, Hotton N Ⅲ, (eds. ). New Concepts in Global Tectonics. Lubbock: Texas Tech University Press, 1992. 119~130. [85] Ratschbacher L, Frisch W, Neubauer F, et al.Extension in compressional orogenic belts: The eastern Alps[J].Geology, 1989, 17 (5): 404~407. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1989)017<0404:EICOBT>2.3.CO;2 [86] Janoschek WR, Matura A.Geology of the European countries Austria, Federal Republic of Germany, Ireland, The Netherlands, Switzerland, United Kingdom[M].the Comite National Fran ais de Géologie, 1980. [87] 高名修, 唐荣昌. 鲜水河断裂带新构造特征与地震关系的初步研究[C]. 鲜水河断裂带地震学术讨论会文集. 北京: 地震出版社, 1985. [88] 四川省地震局.鲜水河活动断裂带[M].成都:四川科学出版社, 1989. [89] Martin BD. Constraints to major right-lateral movements, San Andreas fault system, central and northern California, USA[A]. In: Chatterjee S, Hotton N Ⅲ, (eds. ). New Concepts in Global Tectonics. Lubbock: Texas Tech University Press, 1992. [90] Hancock PL, Barka AA.Plio-Pleistocene reversal of displacement on the North Anatonian fault zone[J].Nature, 1980, 286: 591 ~594. doi: 10.1038/286591a0 [91] Sibson RH, White SH, Atkinson BK. Structure and distribution of foultrocks in the Alpine Fault Zone, New Zealand[A]. In: McCley KR, Price NJ. (eds. ). Thrust and Nappe Tectonics. Published for The Geological Society of London by Blackwell Scientific Publishations Oxford London Ediuburgh Bost M elboune. Ocean lithosphere, Geological Society of America, 1981, 29: 715~718. [92] 藤田至则.隆起と陷没———环太平洋变动の问题, シンポジウム[隆起と陷没], 1986, 1~32.(日文) [93] Damon P.Continental uplift at convergent boundaries[J].Tectonophysics, 1979, 61 (1~3): 307~319. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(79)90303-2 [94] Dupre WR, Worrison RB. Quaternary geology of the Pacific margin[A]. In: Morrison RB. (ed. ). Quaternary Nonglacial Geology: Conterminous US. Colorado: Geological Society of America, 1991. 141~214. [95] Gao Ming-xiu. Late Cenozoic taphrogeny and related earth dynamics in East Asia[A]. In: Proceedings of International Symposium on New Concepts in Global Tectonics, 1998. [96] Zorin Yu A.Florensov NA.On Geodynamics of Cenozoic uplifts in Central Asia[J].Tectonophysics, 1979, 61: 271~283. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(79)90301-9 [97] 平山次郎, 浅野周三.中央复活山脉-帕米尔, 喜马拉雅山山脉[J].科学, 1972, 42 (6).(日文) [98] Carminati E, Giunchi C, Argnani A, et al.Plio-Quaternary vertical motion of the Northern Apennines:Insight from dynamic mode ling[J].Tectonics, 1999, 18 (4): 703~718. doi: 10.1029/1999TC900015 [99] Unruh JR.The uplift of the Sierra Nevada and implications for late Cenozoic epeirogeny in the western Cordillera[J].Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1991, 103 (11): 1395~1404. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1991)103<1395:TUOTSN>2.3.CO;2 [100] Morgan P, Swanberg CA.On the Cenozoic uplift and tectonic stability of the Colorado Plateau[J].Journal of Geodynamics, 1985, 3 (1):39~63. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0264370785900213 [101] Smith AG.Late Cenozoic uplift of stable continents in a reference frame fixed to South America[J].Nature, 1982, 296:400~404. doi: 10.1038/296400a0 [102] Cunningham WD.Cenozoic normal faulting and regional doming in the southern Hangay region, Central Mongolia: implications for the origin of the Baikal rift province[J].Tectonophysics, 2001, 331 (4):389~411. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00228-6 [103] Yano T, Matsumoto Y, Wu G.Pacific genesis induced from Phanerozoic reheating of upper mantle[J].Himalayan Geology, 2001, 22:51~64. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10025417595 [104] Bertotti GR, Picotti CV.Extension controls Quaternary tectonics, geomorphology and sedimentation of the N-Apennines foothills and adjacent Po Plain[J].Tectonophysics, 1997, 282: 291~301. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(97)00229-1 [105] Carminati E, Giunchi Co, Argnani A, et al.Plio-Quaternary vertical motion of the Northern Apennines:Insights from dynamic mo deling[J].Tectonics, 1999, 18: 703~718. http://www.mendeley.com/catalog/plioquaternary-vertical-motion-northern-apennines-insights-dynamic-modeling/ [106] Scisciani V, Calamita F, Tavarnelli E, et al.Foreland-dipping normal faults in the inner edges of syn-orogenic basins: a case from the Central Apennines, Italy[J].Tectonophysics, 2001, 330:211~224. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00229-8 [107] Hussong DM, Uyeda S.Tectonic processes and the history of the Mariana Arc: a synthesis of the results of deep sea drilling project Leg 60[J].Intitial Reports of the Dreep Sea Drilling Project, 1981, 60:909~929. http://www.jstor.org/stable/info/20077684 [108] Wise DU.Keystone faulting and gravity sliding driven by basement uplift of Ow l Creek Rocky Mountains of Montana and Wyoming [J].GSA Bulletin, 1963, 75: 287~306. http://www.mendeley.com/research/keystone-faulting-gravity-sliding-driven-basement-uplift-owl-creek-mountains-wyoming/ [109] Lin A, Ouchi T, Cen A, et al.Co-seismic displacements, folding and shortening structures along the Chelungpu surface rupture zone occurred during the Chi-Chi (Taiwan)earthquake[J].Tectonophysics, 2001, 330: 225~244. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00230-4 [110] Murdock JN.Unrecognized failure of a critical test of strict plate tectonics, the trench region offshore of Guatemala, and a comparison with the Aleutians:Part Ⅳ[J].New Concept In Global Tectonics, 1999, 12:2~9. [111] Michihel H. Ocean trenches[A]. In: Proceedings of International Symposium on New Concepts in Global Tectonics. Tsukuba: . 1998. http://www.mysciencework.com/publication/show/tectonics-ocean-trenches-97b97a17 [112] Choi DR.Subduction does not exist-from seismic data interepretation[J].New Concepts in Global Tectonics, 2000, 15. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10016973232 [113] Choi DR.Deep earthquakes and deep-seated tectonic zones[J].New Concepts in Global Tectonics, 2003, 27. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ029085/ [114] Smoot NC, Choi DR, Bhat MI.Mareing geomirpho-logy[M].Xyibrie corporation, 2001. [115] White RS. Deformation of the Makran Continental Margin[A]. In: Farah A, GeJong K (eds. ). Geodynamics of Pakistan. Quetta: Geological Survey of Pakistan, 1979. [116] Chanier F, Ferrière J.Extensional deformation across an active margin, relations with subsidence, uplift, and rotations:the Hikurangi subduction, New Zealand[J].Tectonics, 1999, 18: 962~976. doi: 10.1029/1999TC900028/full [117] 叶·达包尼叶, 普鲁斯特, 等. 印度-欧亚碰撞带的西藏一侧[A]. 中国地质科学院法国科学研究中心编, 中法喜马拉雅考察成果(1980). 北京: 地质出版社, 1984. [118] Fielding E, Isaqchs B, Barazangi M, et al.How flat is Tibet?[J].Geology, 1994, 22: 163~167. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1994)022<0163:HFIT>2.3.CO;2 [119] Chai BHT.Structure and tectonics evolution of Taiwan[J].American Journal of Science, 1972, 272: 389~422. doi: 10.2475/ajs.272.5.389 [120] Sissingh W.Tectonostratigraphy of the North Alpine foreland basin: correlation of Tertiary depositional cycles and orogenic phases [J].Tectonophysics, 1997, 282: 223~256. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(97)00221-7 [121] 刘嘉麒.中国火山[M].北京:科学出版社, 1999. [122] 汪成民, 张洪波.地震前地下水的短期与临震变化异常[J].地震学报, 1982, 4 (4). [123] 高名修. 中国大陆内的一条重要地质灾害带[A]. 天地生综合研究进展———第二届天地生相互关系学术讨论会论文集. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 1989. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=XKJY404.016&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [124] GAO Ming-xiu. Effect of the processes of continental dynamics for environmental engineering geology in China[A]. In: Msrinos PG, Koukis GC, Tsiambaos GC, et al. Proceedings International Symposium on Engineering Geology and the Environment. Athens: Greek National Group of Iaeg, 1997. [125] Dasgupta S, Mukhopadhyay M, Nandy DR.Active transverse features in the central portion of the Himalaya[J].Tectonophysics, 1987, 136:255~264. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(87)90028-X [126] 王富葆, 曹琼英, 刘福涛.西昆仑山南麓湖泊和水系的近期变化[J].第四纪研究, 1990, 4: 316~325. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1990.04.004 [127] Plafker G, Savage JC.Mechanism of the Chilean earthquakes of the May 21 and 22, 1960[J].GSA Bulletin, 1970, 81 (4): 1001~1030. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1970)81[1001:MOTCEO]2.0.CO;2 [128] Plafker G.Tectonic deformation associated with the 1964 Alaskan earthquake[J].Science, 1965, 148 (3678):1675~1687. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3678.1675 [129] 高名修.华北块断区的现代引张应力场[J].地震地质, 1979, 1 (1). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000348327 -





 下载:
下载: