DISTRIBUTION, ORIGIN AND MINERALIZATION OF TWO TYPES OF CENOZOIC ADAKITE AND ADAKITE-LIKE ROCKS IN SOUTHEASTERN ASIA
-
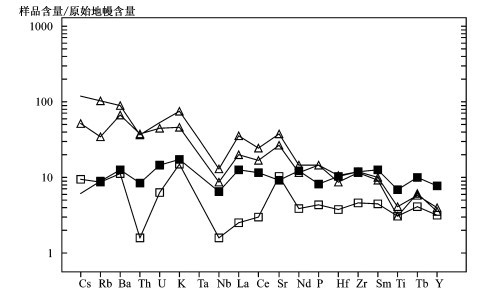
摘要: 东南亚的巽他群岛-巴布亚新几内亚是新生代埃达克岩和类埃达克岩发育的地区。这些中酸性岩浆岩广泛见于印度尼西亚几内亚岛、苏拉威西和巴布亚新几内亚, 零星见于苏门答腊、班达岛弧、西爪哇和中加里曼丹等地。本区埃达克岩和类埃达克岩岩石类型分别属于岛弧拉斑钙碱性系列和高钾钙碱性系列, 以重稀土元素Y, Yb含量低(分别为Y ≤19 ×10-6和Yb ≤1.8 ×10-6)和高Sr值(>355 × 10-6)为特征。微量元素蛛网图上有明显的Ba、K、Sr正异常峰和负的Th、Nb (Ta)异常谷。大离子亲石元素(LILE)和高场强元素(HFSE)相对富集。本区埃达克岩和类埃达克岩的构造位置为新生代缝合线附近的大洋岛弧和陆缘造山带, 可划分为两种成因类型:第一种为岛弧拉斑/钙碱性系列, 其REE配分模式属于大洋岛弧型, 见于现代大洋岛弧, 称为岛弧型(O-型)埃达克岩; 另一种为高钾钙碱性系列, 其REE配分模式属于大陆型, 产于大陆板块边缘造山带, 与弧-陆碰撞和后碰撞构造环境有成因联系, 见于大陆边缘, 称为大陆型(C-型)埃达克岩。 研究结果表明:大陆型(C-型)埃达克岩和类埃达克岩分布区域与世界级斑岩铜-金矿分布相一致, 而大洋岛弧型(O-型)主要与浅成热泉金矿和喷气型有成因联系。Abstract: The Sunda Islands of southeastern Asia is an area where Cenozoic adakite and adakite-like rocks are well developed.These intermediate-acid magmatic rocks are widespread in Guinea Island, Sulawesi (Indonesia), Papua New Guinea, and scattered in Sumatra western Java, Banda island arc and Central Kalimantan.The adakite and adakite-like rocks of the area belong respectively to island-arc tholeiitic /calc-alkaline series and high-potassium calc-alkaline series and are characterized by low HREE contents such as Y and Yb (Y ≤19 ×10-6 and Yb ≤1.8 ×10-6 respectively)and high Sr content (> 355 ×10-6).The spider diagrams show strongly positive anomalies of Ba, K and Sr and relatively negative anomalies of Th and Nb.The adakite and adakite-like rocks show enrichments in large-ion lithophitic element (LILE)and high-field strength elements (HFSE).The adakite and adakite-like rocks of Sunda Islands are tectonically distributed near the Cenozoic sutures, and can be divided into two types of origin.The first one, called oceanic type (O-type)of adakites, belongs to tholeiitic calcalk aline series with REE pattern of oceanic island arcs, and is seen at the oceanic island.The second type, named continental type (C-type)of adakites, belongs to high-potassium calc-alkaline series with REE patterns of continental type, often occurs in continental margin orogenic zone of continental plate and is originally related to arc-continent collision zone or post-collision.Our result reveals that the our research works reveals that the continental-type (C-type)adakite and adakite-like rocks have a similar distribution to the world-class porphyry copper-gold deposits, whereas the oceanic island arc type (Otyp e)adakite and adakite-like rocks are related in origin with epithermal hot-spring gold zones and ehalation ore deposits.
-
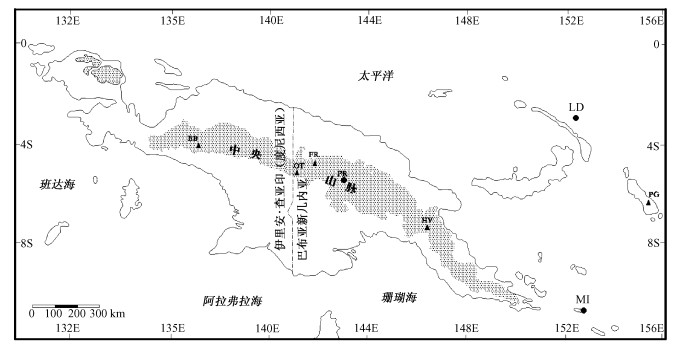
图 1 埃茨贝格矿区(Gunung Bijih矿床)位于伊里安查亚的中央山脉内[8], 细点区域表示高程大于1000米
矿床的符号:▲=斑岩Au±Cu系统, ●=Au矿床, EB =埃茨贝格, OT =奥克太迪, FR =费里达河, HV =海登谷, LD=拉多拉姆(利希岛), PG =潘古纳(布尔干维尔岛), MI =米西岛, PR=波格拉
Figure 1. Map showing the location of the Ertsberg mine (Gunung Bijih deposit) within the Central Ranges of Irian Java[8]. Stippled area shows elevations of more than 1000 m
Other deposits are shown for reference:▲=porphyry Au±Cu systems, ●=Au deposits, EB =Ertsberg, OT=Ok Tedi, FR= Freida River, HV=Hidden Valley, LD =Ladolam (Lihir Island), PG =Panguna (Bougainville Island), MI =Misima Island, PR=Porgera
表 1 埃茨贝格矿田和哈马黑拉岛弧代表性埃达克岩地球化学特征
Table 1. The geochemical characteristics of adakite and adakite-like rocks from Ertsberg area and Halmahera island arc

表 2 巴布亚新几内亚代表性埃达克岩和类埃达克岩的地球化学特征
Table 2. The geochemical characteristics of typical adakite and adakite-like rocks from Papua New Guinea

表 3 北新几内亚-新不列颠岛弧代表性O-型埃达克岩和类埃达克岩的地球化学特征
Table 3. The geochemical characteristics of O-type adakite and adakite-like rocks from North New Guinea-New Britain island arc

表 4 阿德默勒尔蒂群岛—所罗门群岛弧代表性O-型埃达克岩和类埃达克杂岩体的地球化学特征
Table 4. The geochemical characteristics of O-type adakite and adakite-like rocks from Admiralty-Solomon island arc

-
[1] Defant MJ, Drummond MS.Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J].Nature, 1990, 347 (18):662~665. http://www.mendeley.com/catalog/derivation-some-modern-arc-magmas-melting-young-subducted-lithosphere/ [2] Kay RW.Aleutian magnesian andesites:melts from subducted Pacific Ocean crust[J].Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 1978, 4 (1~2):117~132. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/037702737890032X [3] 朱章显, 杨振强, 姚华舟.巴布亚新几内亚新生代两类埃达克岩的构造环境意义[J].华南地质与矿产, 2007, (2):1~6, 13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2007.02.001 [4] 朱章显, 杨振强.巴布亚新几内亚新生代埃达克岩的地球化学证据[J].资源调查与环境, 2007, 28 (4):249~255. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4814.2007.04.003 [5] 朱章显, 杨振强.巴布亚新几内亚新生代埃达克岩及成矿意义[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2008, 38 (4): 618~623. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=CCDZ200804012&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [6] 朱章显, 杨振强.巴布亚新几内亚波格拉斑岩型铜-金矿床富Nb碱性火成岩成因新解[J].资源调查与环境, 2007, 28 (3):171~178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4814.2007.03.003 [7] 王强, 许继峰, 赵振华.强烈亏损重稀土元素的中酸性火成岩(或埃达克岩质岩)与Cu、Au成矿[J].地学前缘, 2003, 10 (4):561~572. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.04.022 [8] 王元龙, 张旗, 王强, 等.埃达克质岩与Cu-Au成矿作用关系的初步探讨[J].岩石学报, 2003, 19 (3):543~550. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=YSXB200303020&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [9] 刘红涛, 张旗, 刘建明, 等.埃达克质岩与Cu-Au成矿作用:有待深入研究的岩浆成矿关系[J].岩石学报, 2004, 20 (2):205~218. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200303021 [10] 侯增谦.斑岩Cu-Mo-Au矿床:新认识与新进展[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11 (1):131~144. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.01.010 [11] 芮宗瑶, 侯增谦, 李光明, 等.俯冲、碰撞、深断裂和埃达克岩与斑岩铜矿[J].地质与勘探, 2006, 42 (1): 1~6. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzykt200601001 [12] 侯增谦, 潘小菲, 杨志明, 等.初论大陆环境斑岩铜矿[J].现代地质, 2007, 21 (2):332~351. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.02.019 [13] Richards JP, Kerrich R.Special paper:adakite-like rocks:their diverse origins and questionable role in metallogenesis[J].Economic Geology, 2007, 102 (4):537~576. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.102.4.537 [14] Gow PA, Walshe JL.The role of preexisting geologic architecture in the formation of giant porphyry-related Cu +Au deposits: Examples from New Guinea and Chile[J].Economic Geology, 2005, 100 (5): 819~833. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.100.5.819 [15] Meinert LD, Hefton KK, Mayes D, et al.Geology, zonation, and fluid evolution of the Big Gossan Cu-Au skarn deposit, Ertsberg Distrit, Irian Jaya[J].Economic Geology, 1997, 92 (5): 509~534. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.92.5.509 [16] Morris JD, Jezek PA, Hart SR, et al. The Halmahera island arc, M olucca Sea collision zone, Indonesia: A Geochemical Survey [A]. In: Hayes DE (ed. ). The Tectonic and Geologic Evolution of South-east Asian Seas and Islands: Part 2[C]. Washington DC: American Geophysical Union, 1983. 373~387. doi: 10.1029/GM027p0373/summary [17] Mason DR, McDonald JA.Intrusive rocks and porphyry copper occurrences of the Papua New Guinea-Solomon Islands region:a reconnaissance study[J].Economic Geology, 1978, 73 (5):857~877. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.73.5.857 [18] Richards JP.Petrology and geochemistry of alkalic intrusives at the Porgera gold deposit, Papua New Guinea[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1990, 35 (1~3):141~199. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/037567429090038C [19] Johnson RW. Regional distribution and character of active andesite volcanism: Papua New Guinea[A]. In: Thorpe RS (Ed. ). Andesites: Orogenic andesites and related rocks[C]. New York: John Wiley &Sons, 1982. 225~244. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10003774230 [20] Vroon PZ.Subduction of continental material in the Banda Arc, Eastern Indonesia[M].Oost-Indonesia: Geologica Ultraiectina, 1992.1~205. [21] Thompson JFH, Abidin HZ, Both RA, et al.Alteration and epithermal mineralization in the Masupa Ria volcanic center, Central Kalimantan, Indonesia[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1994, 50 (1~3): 429~456. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0375674294900353 [22] van Leeuwen TM, Taylor R, Coote A, et al.Porphyry molybdenum mineralization in a continental collision setting at Malala, northwest Sulawesi, Indonesia[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1994, 50 (1~3): 279~315. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0375674294900280 [23] 张旗, 许继峰, 王焰, 等.埃达克岩的多样性[J].地质通报, 2004, 23 (9~10):959~965. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz200409020 [24] Hine R, Mason DR.Intrusive rocks associated with porphyry copper mineralization, New Britain, Papua New Guinea[J].Economic Geology, 1978, 73 (5): 749~760. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.73.5.749 [25] 朱弟成, 段丽萍, 廖忠礼, 等.两类埃达克岩(Adakite)的判别[J].矿物岩石, 2002, 22 (3):5~9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2002.03.002 [26] 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 段丽萍, 等.埃达克岩研究的几个问题[J].西北地质, 2003, 36 (2):13~19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2003.02.002 [27] 张旗, 王焰, 钱青, 等.中国东部燕山期埃达克岩的特征及其构造-成矿意义[J].岩石学报, 2001, 17 (2): 236~244. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200102008 [28] 孙书勤, 汪云亮, 张成江.玄武岩类岩石大地构造环境的Th、Nb、Zr判别[J].地质论评, 2003, 49 (1): 40~47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2003.01.006 [29] Chivas AR.Porphyry copper mineralization at the Koloula igneous complex, Guadalcanal, Solomon Islands[J].Economic Geology, 1978, 73 (5): 645~677. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.73.5.645 [30] Pollard PJ, Taylor KG.Ages of intrusion, alteration, and mineralization at the Grasberg Cu-Au deposit, Papua, Indonesia[J].Economic Geology, 2005, 100 (5):1005~1020. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.100.5.1005 [31] Rubin JN, Kyle JR.Precious Meta Mineralogy in porphyry, Skarn, and replacement-type ore deposits of the Estsberg (Gununy Bijih)district, Irian Jaya, Indonesia[J].Economic Geology, 1997, 92 (5):535~550. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.92.5.535 [32] Arnold GO, Griffin TJ.Intrusions and porphyry copper prospects of the Star Mountains, Papua New Guinea[J].Economic Geology, 1978, 73 (5):785~795. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.73.5.785 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 江晨轶,潘家伟,张丽军,李海兵,孙知明,Marie-Luce Chevalier,刘富财,苏强. UAV SfM技术在活动构造研究中的应用——以青藏高原西北部龙木错断裂为例. 地质力学学报. 2024(02): 332-347 .  本站查看
本站查看2. 杨勇忠,李占飞,任俊杰,徐锡伟,李康,程佳,康文君. 基岩地质差异对活动断层地表几何形态的控制作用——以祁连山北缘佛洞庙-红崖子断层为例. 地质力学学报. 2024(02): 348-362 .  本站查看
本站查看其他类型引用(0)
-





 下载:
下载: