GEOCHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF CLASTIC SEDIMENTARY ROCKS FROM LOWER PERMIAN YUJIABEIGOU FORMATION IN NORTHERN CHIFENG, INNER MONGOLIA
-
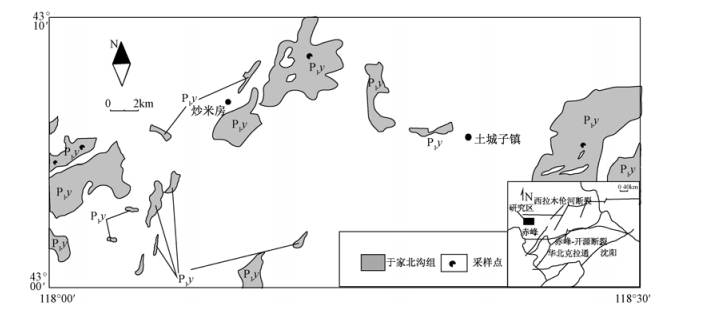
摘要: 内蒙古赤峰北部下二叠统于家北沟组碎屑沉积岩主要分布于华北克拉通北缘的内蒙古隆起。碎屑沉积岩主要以杂砂岩为主, 源区岩石没有经过充分的搬运、分选, 成熟度比较低。常量及稀土元素分析结果显示, 轻重稀土元素分异明显, 轻稀土元素富集, 重稀土元素含量稳定, δEu的值在0.72~0.99之间, 表现出一定的负Eu异常, 与NASC或PAAS配分模式相似, 说明物源来自于上地壳。结合前人的研究成果, 认为其母岩原岩可能以沉积岩和花岗岩为主, 或有少量的玄武岩; 物源区大地构造背景为活动大陆边缘或者大陆岛弧, 说明研究区在早二叠世或更早处于西伯利亚板块与华北克拉通缝合阶段。Abstract: Located in northern Chifeng, Inner Mongolia, the clastic sedimentary rocks of Lower Permian Yujiabeigou Formation is mainly distributed at the Inner Mongolia uplift in the northern margin of North China craton.These clastic sedimentary rocks are dominated by graywackes, and their source rocks have not been fully handling and sorting, with relatively low maturity.The studying results have shown that light and heavy rare earth elements differentiate distinctly, and that light rare earth elements are obvious enrichment while the heavy rare earth elements stay stable.The values of δEu vary from 0.72 to 0.99, show negative Eu anomalies particularly and are similar with NASC or PAAS distributing model, which suggest that these sediments are sourced from upper crust.Combining with the predecessors' achievements, it is obtained that the original rocks of these sediments' parent rocks mainly are consist of sedimentary rocks and granites, with a small amount of basalt; The geotectonic background of these sediments' source area is active continental margin or continent island arc, which may show that this studying area is in the suture stage between Siberia plate and North China craton in Lower Permian or earlier time.
-
表 1 内蒙古北部下二叠统于家北沟组碎屑沉积岩常量元素分析结果
Table 1. Constant elements values of clastic sedimentary rocks from Lower Permian Yujiabeigou formation in northern Chifeng, Inner Mongolia

表 2 内蒙古北部下二叠统于家北沟组碎屑沉积岩稀土元素测试结果
Table 2. Rare earth elements values of clastic sedimentary rocks from Lower Permian Yujiabeigou Formation in northern Chifeng, Inner Mongolia

表 3 内蒙古北部下二叠统于家北沟组碎屑沉积岩稀土元素统计分析
Table 3. Rare earth elements statistical values of clastic sedimentary rocks from Lower Permian Yujiabeigou Formation in northern Chifeng, Inner Mongolia

表 4 不同大地构造背景的沉积盆地中杂砂岩稀土元素特征[19]
Table 4. Characteristics of rare earth elements of greywacke in different sedimentary basins

-
[1] Roser B P, Korsch R J. Determination of tectonic setting of sandstone-mudstone suites using SiO2 content and K2O/Na2O ratio[J]. Journal of Geology, 1986, 94 (5):635~650. doi: 10.1086/629071 [2] Taylor S R, Mclennan S M. The continental crust: Its composition and evolution, An examination of the geochemical record preserved in sedimentary rocks[M]. London: Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1985: 1~301. [3] 王鸿祯.从活动论观点论中国大地构造分区[J].地球科学:武汉地质学院学报, 1981, (1):42~66. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqkx198101005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQWANG Hong-zhen. Geotectonic units of China from the viewpoint of mobilism[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1981, (1):42~66. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dqkx198101005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [4] 谢同伦.内蒙古古生代地槽的兴衰[J].内蒙古地质, 1980, (2):6~14.XIE Tong-lun. Inner Mongolia Paleozoic geosyncline vicissitude[J]. Geology of Inner Mongolia, 1980, (2):6~14. [5] 叶茂, 张世红, 吴福元.中国满洲里—绥芬河地学断面域古生代构造单位及其地质演化[J].长春地质学院学报, 1994, 24 (3):241~245. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ403.000.htmYE Mao, ZHANG Shi-hong, WU Fu-yuan. The classification of the Paleozoic tectonic units in the area crossed by M-S GGT[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Earth Sciences, 1994, 24 (3):241~245. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ403.000.htm [6] 李锦轶.内蒙古东部中朝板块与西伯利亚板块之间古缝合带的初步研究[J].科学通报, 1986, (14):1093~1096. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=kxtb198614014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQLI Jin-yi. The preliminary research of ancient suture zone between on Sino-Korean plate and Siberia plate from eastern Inner Mongolia[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1986, (14):1093~1096. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=kxtb198614014&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [7] 李益龙, 周汉文, 钟增球, 等.华北与西伯利亚板块的对接过程:来自西拉木伦缝合带变形花岗岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄证据[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2009, 34 (6):931~938. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx200906007LI Yi-long, ZHOU Han-wen, ZHONG Zeng-qiu, et al. Collision processes of North China and Siberian plates: Evidence from LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb age on deformed granite in Xar Moron suture zone[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2009, 34 (6):931~938. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx200906007 [8] 李鹏武, 高锐, 管烨, 等.华北与西伯利亚地块碰撞时代的古地磁分析———兼论苏鲁—大别超高压变质作用的构造起因[J].地球学报, 2007, 28 (3):234~252. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=24662724LI Peng-wu, GAO Rui, GUAN ye, et al. Paleomagnetic constraints on the collision of Siberian and North China Blocks: With a discussion on the tectonic origin of the ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism in the Sulu-Dabie region[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2007, 28 (3):234~252. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=24662724 [9] 王友, 宫玉亚.内蒙古赤峰北部二叠纪基性—中性次火山岩系地球化学特征[J].中国区域地质, 2000, 19 (2):131~136. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200002004WANG You, GONG Yu-ya. Geochemical features of the Permian basic-intermediate subvolcanics in northern Chifeng, Inner Mongolia[J]. Regional Geology of China, 2000, 19 (2):131~136. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200002004 [10] KuzminM L, Abramovich G Y A, Dril S L, et al. The Mongolian-Okhotsk suture as the evidence of late Paleozoic-Mesozoic collisional processes in central Asia[C]. Abstract of 30th IGC, 1996: 1~261. [11] 李文国.内蒙古自治区岩石地层[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 2008: 218~219.LI Wen-guo. The rock and stratum in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2008: 218~219. [12] Pettijohn F J, Potter P E, Siever R. Sand and sandstone[M]. New York: Springer Verlag, 1973. [13] Gromet L P, Dymek R F, Haskin L A, et al. The"North American shale composite": Its compilation, major and trace element characteristics[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48 (12):2469~2482. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90298-9 [14] Boynton W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies[C]//Henderson P. Rare earth element geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elservier, 1984: 63~114. [15] Mclenan S M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rock: Influence of provenance and sedimentary processes[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 1989, 21 (1):169~200. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/msa/rimg/article-abstract/21/1/169/87254/rare-earth-elements-in-sedimentary-rocks-influence?redirectedFrom=fulltext [16] 侯伟, 刘招君, 王伟涛, 等.黑龙江省东部绥滨坳陷下白垩统泥岩稀土元素地球化学特征[J].古地理学报, 2007, 9 (2):207~215. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2007.02.009HOU Wei, LIU Zhao-jun, WANG Wei-tao, et al. REE geochemical characteristics of the Lower Cretaceous mudstone in Suibin depression of eastern Heilongjiang Province[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2007, 9 (2):207~215. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2007.02.009 [17] 刘俊海, 杨香华, 于水, 等.东海盆地丽水凹陷古新统沉积岩的稀土元素地球化学特征[J].现代地质, 2003, 17 (4):421~427. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz200304010LIU Jun-hai, YANG Xiang-hua, YU Shui, et al. The REE geochemical characteristics of Paleocene-Eocene in the Lishui sag of the Donghai Basin[J]. Geosciences, 2003, 17 (4):421~427. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz200304010 [18] 包汉勇, 杨风丽, 王丹萍, 等.苏南地区中、古生界沉积岩地球化学特征:以圣科1井为例[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2011, 41 (1):29~38. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ccdz201101005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQBAO Han-yong, YANG Feng-li, WANG Dan-ping, et al. Geochemical characteristics of sedimentary rock in southern Jiangsu Province on Mesozoic and Paleozoic: A perspective from the Shengke-1 Well[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2011, 41 (1):29~38. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ccdz201101005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [19] Bhatia M R. Rare earth element geochemistry of Australian Paleozoic graywackes and mudrocks: Provence and tectonic control[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1985, 45 (1-2): 97~113 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0037073885900259 -





 下载:
下载: