STRUCTURAL FEATURES AND TECTONIC EVOLUTION OF THE WEI-ZI-LUO FAULT ZONE IN SOUTHWESTERN GUIZHOU PROVINCE
-
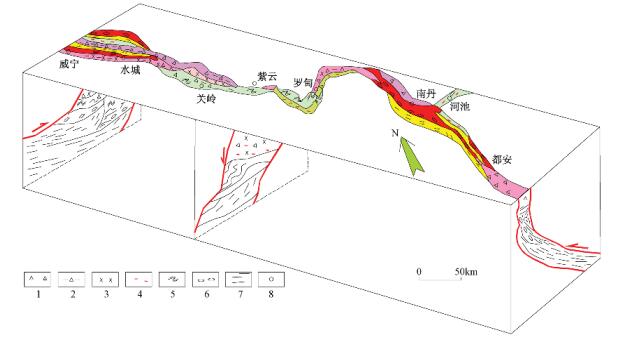
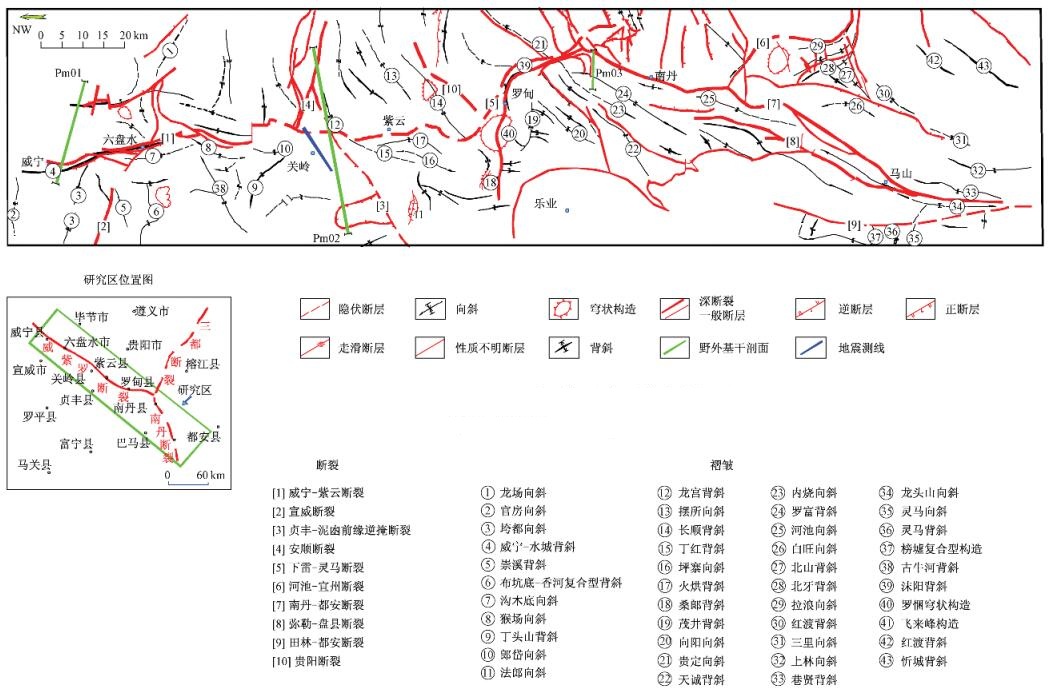
摘要: 威-紫-罗断裂带作为扬子板块南缘陆内较大的断裂, 控制着周围地区的盆地沉积及构造样式。本文通过野外地质勘查、平衡剖面技术及流体包裹体测温, 探讨了威-紫-罗断裂带的空间结构特征及构造演化历史。结果显示, NW-SE向威-紫-罗断裂带空间分段特征清楚, 运动性质以逆冲和左旋走滑活动为主。流体包裹体测温结果指示该断裂变形环境位于上地壳, 以脆性变形为主, 温度小于200 ℃。剖面复原结果显示, 断裂带在早泥盆世-中三叠世时期处于引张伸展构造背景下, 控制了断裂两侧沉积序列。断裂带挤压变形起始于中三叠世晚期的印支运动时期, 强烈变形发生在晚侏罗世早燕山运动时期, 与华南地块的向西挤压有关。Abstract: The Wei-Zi-Luo fault develops in southwestern margin of the Yangtze block. This is a deep crustal fault zone and controls the deposition and deformation styles of the region. Based on detailed field observations, fluid inclusion analysis and temperature measurements, and using cross section balance, this paper describes structural texture and segmentation feature of the fault zone and discusses its tectonic evolution. The results show that the Wei-Zi-Luo fault zone consists of several segments with kinematics dominated by reverse and sinistral strike-slip motion.Fluid inclusion analysis indicates brittle environment of deformation occurring in the upper crust, with temperature less than 200 ℃. Restoration of cross section shows that this fault zone was under extension during the Early Devonian to Middle Triassic, which controlled the depositional sequence of the region. It was deformed during the Indosinian orogen at the end of Triassic. The major deformation phase, related to westward push of the South China Block, occurred in Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous.
-
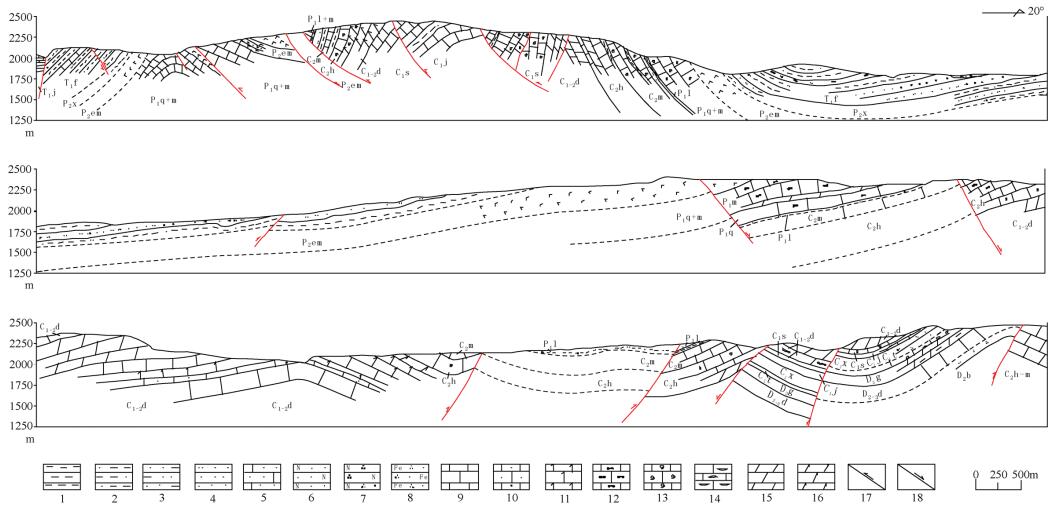
图 3 贵州威宁-垭都实测构造剖面图(PM01)(剖面位置见图 1)
1.泥岩;2.粉砂质泥岩;3.泥质粉砂岩;4.粉砂岩;5.钙质粉砂岩;6.长石砂岩;7.长石石英砂岩;8.含铁石英砂岩;9.石灰岩;10.砂质灰岩;11;白云质灰岩;12.条带状燧石灰岩;13.瘤状灰岩;14.泥灰岩;15.白云岩;16.灰质白云岩;17.逆断层;18.正断层
Figure 3. Structural section of Weining - Yadu, Guizhou Province (PM01) (see Fig.l for location)
图 4 贵州关岭实测构造剖面图(PM02)(剖面位置见图 1)
1.页岩;2.泥岩;3.粉砂质泥岩;4.泥质粉砂岩;5.粉砂岩;6.石灰岩;7.砂质灰岩;8.泥灰岩;9.白云岩;10.碎裂岩化带;11.角砾岩化带;12.节理化带;13.逆断层;14.正断层
Figure 4. Structural section of Guanling, Guizhou Province (PM02)
图 5 贵州罗甸沫阳实测构造基干剖面(PM03)(剖面位置见图 1)
1.泥岩; 2.粉砂质泥岩; 3.泥质粉砂岩; 4.粉砂岩; 5.石灰岩; 6.泥灰岩; 7.瘤状灰岩; 8.条带状燧石灰岩; 9.竹叶状灰岩; 10.硅质岩; 11.角砾岩化带; 12.逆断层; 13.正断层
Figure 5. Structural section of Luodian-Moyang, Guizhou Province (PM03)
表 1 威紫罗断裂带构造岩包裹体测试结果
Table 1. Result of fluid inclusion analysis in Wei-Zi-Luo fault zone

表 2 贞丰-镇宁剖面伸长量统计表
Table 2. I, e, β statistics of line Zhenfeng-Zhenning

-
[1] 戴传固, 张慧, 黄清华.黔东地区典型构造样式特征及其地质意义[J].地质力学学报, 2008, 14(4):339 ~ 345. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20080404&journal_id=dzlxxbDAI Chuan-gu, ZHANG Hui. Typical tectonic styles and their geological significance in eastern Guizhou Province[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 2008, 14(4):339~ 345. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20080404&journal_id=dzlxxb [2] 毛健全, 张启厚, 顾尚义.水城断陷的地质特征及构造演化[J].贵州工业大学学报, 1997, 26(2):1~ 6. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700163238MAO Jian-quan, ZHANG Qi-hou, GU Shang-yi. The geological characteristics and tectonic evolution of Shuicheng fault subsidence [J].Journal of Guizhou University of Technology, 1997, 26(2): 1~ 6. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700163238 [3] 郑荣才, 张锦泉.滇东-黔西南泥盆纪构造格局及岩相古地理演化[J].成都地质学院学报, 1989, 16(4):51~ 60. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000001169519ZHENG Rong-cai, ZHANG Jin-quan. The tectonic framework and the evolution of lithofacies and paleogeography of Devonian in eastern Yunnan and southwestern Guizhou[J].Journal of Chengdu College of Geology, 1989, 16(4): 51~ 60. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000001169519 [4] 王尚彦, 张慧, 王天华, 等.黔西水城一紫云地区晚古生代裂陷槽盆充填和演化[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(3): 402~ 407. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.03.010WANG Shang-yan, ZHANG Hui, WANG Tian-hua, et al. Filling and evolution of the Late Paleozoic Shuicheng-Ziyun aulacogen in western Guizhou, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(3): 402~ 407. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.03.010 [5] 程国繁, 徐安全.试论"威宁-紫云"北西向构造带变形特征[J].贵州地质, 1998, 15(4):311~ 320. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800170652CHENG Guo-fan, XU An-quan. An insight into the northwestern-trending tectonical deformation of the Weining-Ziyun belt, western Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 1998, 15(4):311~ 320. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800170652 [6] 赵孟军, 张水昌, 赵陵, 等.南盘江盆地油气成藏过程及天然气勘探前景分析[J].地质论评, 2006, 52 (5): 642~ 649. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2006.05.017ZHAO Meng-jun, ZHANG Shui-chang, ZHAO Ling, et al.Oil and gas accumulation and gas exploration potential in the Nanpanjiang Basin, China[J]. Geological Review, 2006, 52(5): 642~ 649. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2006.05.017 [7] 秦建华, 吴应林, 颜仰基, 等.南盘江盆地海西-印支期沉积构造演化[J].地质学报, 1996, 70(2):99~ 107. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1996.02.001QIN Jian-hua, WU Ying-lin, YAN Yang-ji, et al. Hercynian-Indosinian sedimentary-tectonic evolution of the Nanpanjiang Basin [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1996, 70(2): 99~ 107. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1996.02.001 [8] 周明辉.南盘江坳陷油气系统研究[J].云南地质, 1999, 18(3):248~ 265. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199900774700ZHOU M ing-hui. A study on the petroleum system of Nanpanjiang sag[J].Yunnan Geology, 1999, 18(3): 248~ 265. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199900774700 [9] 刘特民, 刘炳温, 陈国栋, 等.南盘江盆地构造演化与油气保存区划分[J].天然气工业, 2001, 21(1):18 ~ 23. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2001.01.004LIU Te-min, LIU Bing-wen, CHEN Guo-dong, et al.Tectonic evolution and hydrocarbon preservation region division in Nanpanjiang Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2001, 21(1): 18~ 23. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2001.01.004 [10] 周竞平.流体包裹体在断裂构造研究中的应用[J].地质力学学报, 1996, 2(4):90~ 91. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=19960484&journal_id=dzlxxbZHOU Jing-ping. Application of fluid inclusions in study on fault systems[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 1996, 2(4): 90~ 91. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=19960484&journal_id=dzlxxb [11] 殷秀兰, 周东生, 吕杰堂, 等.渤中坳陷液体包裹体特征及其对成藏研究的意义[J].地质力学学报, 2006, 12 (1):84~ 90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2006.01.013YIN Xiu-lan, ZHOU Dong-sheng, LU Jie-tang et al.Characteristics of fluid inclusions and their significance for research on oil accumulation in the Central Bohai depression[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2006, 12(1):84~ 90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2006.01.013 [12] 刘斌.脆韧性构造岩中矿物流体包裹体研究———以上海及其邻区为例[J].矿物学报, 1991, 11(4):377~ 385. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1991.04.012LIU Bin.A fluid inclusion study of minerals in brittle-ductile tectonites as exemplified by Shanghai and its adjacent areas[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 1991, 11(4):377~ 385. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1991.04.012 [13] 杨巍然, 张文淮.断裂性质与流体包裹体组合特征[J].地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 1996, 21(3):285~ 290. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.1996.03.002YANG Wei-ran, ZHANG Wen-huai.Character of fault property and combination of fluid inclusions[J].Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1996, 21(3): 285~ 290. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.1996.03.002 -





 下载:
下载: