THE CHARACTERISTICS AND TYPES OF THE NATURAL GAS IN THE WEIHE BASIN AND ITS PROSPECTING POTENTIAL
-
摘要: 根据渭河盆地地热井、油气调查井、氦气调查井气样分析成果,结合近年来地质、物探新成果分析,发现渭河盆地各类钻井中普遍存在含氦天然气,且这些天然气,按甲烷和氦气含量可分为富氦天然气和贫氦天然气两类。位于渭河盆地边部的地热井、区域地质和物化探成果均佐证了渭河盆地基底存在上古生界,未见隐伏的花岗岩体。区域构造演化佐证了渭河盆地周边断裂的形成与区域断裂同期,盆地的形成与演化是区域演化的一部分,其主沉降期是新生代。因此,前人对渭河盆地形成的最早时间为始新世以及不存在上古生界煤系地层基底以及氦气的主要气源岩是分布于基底的富铀花岗岩体和秦岭造山带富铀花岗岩体的认识有待进一步探究。对比邻区鄂尔多斯盆地,发现渭河盆地上古生界煤系地层可作为烃源岩,伽马异常层可作为氦源层,这为重新评价渭河盆地的氦气资源地质前景提供了依据。Abstract: According to the analysis results of gas samples from the geothermal well, the investigation well of oil and helium in the Weihe Basin, we find that all kinds of drills contain gas with helium prevalently, combining the results of geology and latest geophysical prospecting in recent years. And these gas could be divided into helium-rich gases and helium-poor gases based on the content of methane and helium. The results of geology, latest geophysical prospecting and geothermal well also support that the upper Paleozoic strata exits in the Weihe Bsain and insidious granite is not discovered. The regional tectonic evolution illustrates that the faults around the Weihe Basin and regional faults formed contemporaneously, and the formation of the Weihe Basin is the part of regional evolution, which settles mainly in Cenozoic era. Therefore, the former conclusions such as the Weihe Basin begins to form in the Eocene, there is no upper Paleozoic strata with coal in the basement, and the source rock of gas is bearing-uranium granite in the basement and the Qinling orogenic belt, should be further studied and explored. Compared with Ordos Basin, we find that the upper Paleozoic strata with coal in the basement could be the source rock of gas and the Gamma anomaly strata could be the source of helium, which provides evidence to reappraise the resource prospect of helium in the Weihe Basin.
-
Key words:
- the Weihe Basin /
- natural gas /
- helium /
- the upper Paleozoic /
- coal measure strata
-
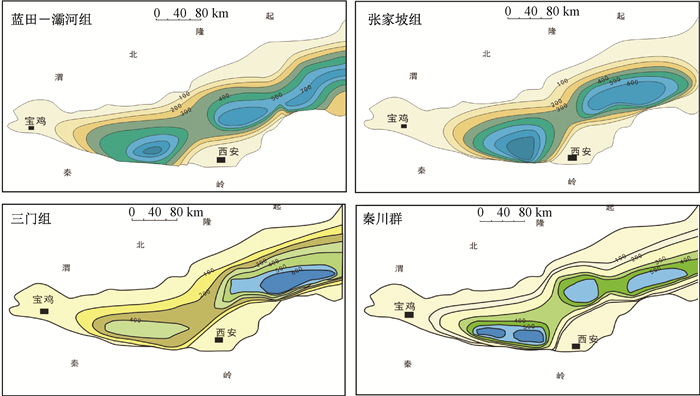
图 1 渭河盆地三门组、秦川群、蓝田—灞河组、张家坡组厚度等值线图[12]
Figure 1. The thickness isoline map of Sanmen, Qinchuan, Lantian-Bahe, Zhangjiapo group strata in the Weihe Basin
图 2 上地壳二维速度结构和构造解译及平面地质构造图[13]
Figure 2. 2-D velocity structure and tectonic interpretation in upper crust and geological structural map
图 5 鄂尔多斯盆地中生代沉积边界与沉积、堆积中心变迁分布图[14]
1—不同时代地层尖灭线;2—华北克拉通C—P沉积边界;3—盆地T2—3、J1—2古沉积边界;4—延长期堆积中心;5—延安期堆积中心;6—直罗—安定期堆积中心;7—早白垩世堆积中心;8—不同时期沉积中心;9—中生代残留盆地;10—侏罗纪残留含煤盆地
Figure 5. Distribution of sedimentary boundary, depocenters and accumulation centers of Mesozoic Ordos basin
表 1 渭河盆地不同构造单元天然气样品气体组分[3]
Table 1. The composition of nature gas from different tectonic units in the Weihe Basin
构造单元 井名 完井深度/m 气体组分含量% 甲烷 乙烷 丙烷 丁烷 戊烷 氮 二氧化碳 氢 氦 重烃 全烃 西安凹陷 秦宝 2150 2.237 0.024 0.003 0.000 0 96.531 0.024 0 0.754 0.027 2.264 三普2号 3553 12.800 0.051 0.006 0.002 0.002 73.800 8.180 0.200 2.240 0.061 12.861 渭深13井 3202 21.790 0.101 0.003 0.007 0 73.710 0.000 0.250 4.140 0.111 21.901 固市凹陷 华阴R1 3200 31.885 0.344 0.089 0.043 0.020 61.579 2.244 0.788 3.007 0.496 32.381 渭热1井 3200 72.200 2.700 0.500 0.206 0.059 4.301 19.832 0.029 0.106 3.465 75.670 渭热6井 2005 98.370 0.096 0.012 0.003 0 1.093 0.105 0.320 0 0.111 98.481 宝鸡凸起 眉县西汤峪 1400 0.873 0 0 0 0 98.132 0 0 0.528 0 0.873 宝鸡东方饭店 1450 0.165 0 0 0 0 98.715 0 0 0.968 0 0.165 表 2 渭河盆地天然气样品组分含量及碳同位素测试结果统计[4]
Table 2. The statistic results of composition and carbon isotope of nature gas in the Weihe Basin

表 3 渭河盆地与鄂尔多斯盆地天然气碳同位素特征对比
Table 3. Comparison between carbon isotopes of natural gas from the Weihe basin and Ordos basin
盆地 样品来源 δ13CH4/‰ 气源类型 样品数量 范围 平均值 渭河盆地 西安凹陷 -24.5~-43.1 -32.4 煤型气 42 -45.0~-48.5 -46.1 油型气 3 -19.8~-23.0 -21.4 幔源气 3 -48.5~-65.0 -58.9 生物气 8 固市凹陷 -23.8~-36.4 -33.3 煤型气 6 -52.2~-65.6 -61.8 生物气 4 鄂尔多斯盆地 下古生界(O) -30.6~-41.7 -34.2 煤型热解气 59 上古生界(C—P) -29.0~-38.5 -33.5 煤型热解气 85 中生界(T3y—J1y) -36.7~-59.7 -48.7 油型气 34 注:T3y—J1y为上三叠统延长组—下侏罗统延安组;C—P为石炭系—二叠系;O为奥陶系;据王建强资料修编 表 4 渭河盆地地热水水溶天然气中氦气地球化学分析结果[8]
Table 4. Geochemical analysis of soluble helium gas from geothermal water in the Weihe Basin
地热井井名/位置 取水深度/m 井口水温/℃ $\varphi $(He)/% R=3He/4He R/Ra 4He/20Ne 户县秦宝娱乐城 1646~2107 81 0.700 (4.70±0.24)×10-8 0.033 - 户县灵山寺 1035~1634 65 0.477 (6.50±0.38)×10-8 0.046 226 户县苗圃 1683~2453 71 0.410 (2.92±0.16)×10-7 0.209 439 临潼771所 1200~2971 91 1.076 (7.80±0.23)×10-7 0.557 1500 临潼临2井 1331~2692 79 0.840 - - - 蓝田峪后温泉 800~1832 65 3.395 (1.26±0.04)×10-7 0.090 132 蓝田东汤峪 670~1460 64 0.129 (5.02±0.31)×10-8 0.036 1011 西安电子科大 1216~1831 82 1.053 (3.61±0.29)×10-8 0.026 413 西安唐园小区 1690~2560 79 1.177 - - - 西安供销公司 975~1750 66 0.308 (5.56±0.25)10-8 0.040 163 西安武警医院 1889~2898 96 0.745 - - - 西安电缆厂 2349~3300 100 0.427 (5.17±0.27)×10-8 0.037 374 渭南中医学院 1766~2874 88 0.114 (1.49±0.07)×10-7 0.106 1985 兰山顶空气氦同位素标准取国际公认值Ra (1.40±0.03)×10-6 1.000 0.31 -
[1] 刘池洋, 赵红格, 桂小军, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地演化-改造的时空坐标及其成藏(矿)响应[J].地质学报, 2006, 80(5):617~638. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200605003.htmLIU Chi-yang, ZHAO Hong-ge, GUI Xiao-jun, et al. Space-time coordinate of the evolution and reformation and mineralization response in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2006, 80(5): 617~638. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200605003.htm [2] 王建强, 刘池洋, 高飞, 等.陕西渭河盆地前新生界地质特征及其油气意义[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(10):1981~1991. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.10.024WANG Jian-qiang, LIU Chi-yang, GAO Fei, et al. Pre-Cenozoic geological characteristics and oil-gas significance in Weihe Basin, Shaanxi Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015, 34(10): 1981~1991. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.10.024 [3] 张雪, 刘建朝, 李荣西, 等.渭河盆地水溶性天然气层类型研究[J].地质力学学报, 2014, 20(2):114~122. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20140202&journal_id=dzlxxbZHANG Xue, LIU Jian-chao, LI Rong-xi, et al. Research on classification of water-soluble gas in Weihe Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2014, 20(2): 114~122. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20140202&journal_id=dzlxxb [4] 张雪. 渭河盆地天然气及氦气成藏条件与资源量预测[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2015.ZHANG Xue, Accumulation conditions and resource prediction of natural gas and helium gas in Weihe Basin[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2015. [5] 矿产资源工业要求手册编委会.矿产资源工业要求手册(2012年修订本)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2012:854~856.Editorial committee of handbook of mineral resources industry requirements. Handbook of mineral resources industry requirements (revised edition in 2012)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2012: 854~856. [6] 宋岩, 徐永昌.天然气成因类型及其鉴别[J].石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(4):24~29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200504006.htmSONG Yan, XU Yong-chang. Origin and identification of natural gases[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(4): 24~29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200504006.htm [7] 李广之, 高伟, 江浩, 等.氦气的天然气地质意义[J].物探与化探, 2009, 33(2):154~156. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200902011.htmLI Guang-zhi, GAO Wei, JIANG Hao, et al. Geological implication of radon gas[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 33(2): 154~156. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200902011.htm [8] 刘建朝, 李荣西, 魏刚峰, 等.渭河盆地地热水水溶氦气成因与来源研究[J].地质科技情报, 2009, 28(6):84~88. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200906013.htmLIU Jian-chao, LI Rong-xi, WEI Gang-feng, et al. Origin and source of soluble helium gas in geothermal water, Weihe Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2009, 28(6): 84~88. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200906013.htm [9] 权新昌.渭河盆地断裂构造研究[J].中国煤田地质, 2005, 17(3):1~8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT200503001.htmQUAN Xin-chang. Study on the faulted structures in Weihe Basin[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2005, 17(3): 1~8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT200503001.htm [10] 薛华锋, 朱兴国, 王润三, 等.西安地热田伴生富氦天然气资源的发现及意义[J].西北大学学报:自然科学版, 2004, 34(6):751~754. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ200406031.htmXUE Hua-feng, ZHU Xing-guo, WANG Run-san, et al. The discovery and significance of rich helium natural gas resource in Xi'an geothermic field[J]. Journal of Northwest University: Natural Science Edition, 2004, 34(6): 751~754. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ200406031.htm [11] 王景明.渭河地堑断裂构造研究[J].地质论评, 1984, 30(3):217~223. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP198403002.htmWANG Jing-ming. A study on the tectonics of the Weihe river graben[J]. Geological Review, 1984, 30(3): 217~223. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP198403002.htm [12] 刘志武, 周立发.渭河盆地新生代构造-沉积格局与油气成藏潜力初探[J].福州大学学报:自然科学版, 2015, 43(5):708~714. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZDZ201505024.htmLIU Zhi-wu, ZHOU Li-fa. The Cenozoic tectonic and sedimentary framework and preliminary study on the hydrocarbon accumulation potential of the Weihe Basin[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University: Natural Science Edition, 2015, 43(5): 708~714. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZDZ201505024.htm [13] 任隽. 渭河盆地深部地壳结构探测与盆地构造研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2012.REN Jun. Probe on the deep crustal structure in Weihe Basin and tectonics research of basin[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2012. [14] 王存城.论渭河地堑[J].地质学报, 1965, 45(2):153~164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE196502002.htmWANG Cun-cheng. On the Weihe graben[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1965, 45(2): 153~164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE196502002.htm [15] 李俊建.华北陆块的构造格局及其演化[J].地质找矿论丛, 2011, 25(2):89~100. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201002001.htmLI Jun-jian. Structure framework and evolution of the North China Craton[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2011, 25(2): 89~100. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201002001.htm [16] 黎世美.小秦岭金矿地质与成矿预测[M].北京:地质出版社, 1996.LI Shi-mei. Geology of gold deposits and metallogenic prediction in Xiaoqinling area[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1996. [17] 罗镇宽, 苗来成, 关康, 等.冀东都山花岗岩基及相关花岗岩脉SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年及其意义[J].地球化学, 2003, 32(2):173~180. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200302010.htmLUO Zhen-kuan, MIAO Lai-cheng, GUAN Kang, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of the Dashan granitic batholith and related granite-porphyry dyke, eastern Hebei Province, China, and their geological significance[J]. Geochimica, 2003, 32(2): 173~180. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200302010.htm [18] 张灯堂, 冯建之, 李磊, 等.华北克拉通南缘后大陆碰撞背景下的岩石圈演化及金、钼成矿规律探讨[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2015, 39(2):300~314. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201502011.htmZHANG Deng-tang, FENG Jian-zhi, LI Lei, et al. Discussion on post-collision lithospheric evolution and Au-Mo mineralization in the southern margin of the North China Craton[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2015, 39(2): 300~314. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201502011.htm [19] Maruyama S, Isono T. Orogeny and relative plate motions: Example of the Japanese Islands[J]. Tectonophysics, 1986, 127: 306~329. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1986Tectp.127..305M [20] 吴奇, 许立青, 李三忠, 等.华北地台中部活动构造特征及汾渭地堑成因探讨[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(4):104~114.WU Qi, XU Li-qing, LI San-zhong, et al. Active tectonics in the Central North China Block and the cause of the formation of the Fenwei Graben[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(4): 104~114. [21] 任战利, 崔军平, 李进步, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地渭北隆起奥陶系构造-热演化史恢复[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(11):2044~2056. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201411003.htmREN Zhan-li, CUI Jun-ping, LI Jin-bu, et al. Tectonic-thermal history reconstruction of Ordovician in Weibei uplift of Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(11): 2044~2056. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201411003.htm [22] 朱夏.中国中、新生代盆地构造和演化[M].北京:科学出版杜, 1983:130~131.ZHU Xia. Tectonics and evolution of Mesozoic and Cenozoic Basins in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1983: 130~131. [23] 李钰, 符彩云.渭河盆地上新统沉积相研究[J].地下水, 2015, 37(1):185~187. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU201501074.htmLI Yu, FU Cai-yun. Study on Miocene sedimentary facies of the Weihe River Basin[J]. Ground Water, 2015, 37(1): 185~187. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU201501074.htm [24] 李钰. 渭河盆地地热井伴生气地球化学特征及生物气资源量评价[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2015.LI Yu. The geochemical characteristic of source rock and source rock potential evaluation of the Weihe Basin[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2015. [25] 李玉宏, 卢进才, 李金超, 等.渭河盆地富氦天然气井分布特征与氦气成因[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2011, (S1):47~53. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ2011S1008.htmLI Yu-hong, LU Jin-cai, LI Jin-chao, et al. Distribution of the helium-rich wells and helium derivation in Weihe Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2011, (S1): 47~53. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ2011S1008.htm [26] 谭成仟, 刘池阳, 赵军龙, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地高自然伽马值异常特征及主控因素研究[J].石油地球物理勘探, 2007, 42(1):50~58. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ200701009.htmTAN Cheng-qian, LIU Chi-yang, ZHAO Jun-long, et al. Study on feature of high natural gamma anomaly and main controlling factors in Ordos Basin[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2007, 42(1): 50~58. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ200701009.htm [27] 李卫红, 徐高中.鄂尔多斯盆地后期改造与砂岩型铀成矿关系[J].地球科学与环境学报, 2006, 28(3):19~23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX200603004.htmLI Wei-hong, XU Gao-zhong. Relationship between later reformation and formation of sandstone type uranium ore in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Earth Science and Environment, 2006, 28(3):19~23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX200603004.htm [28] 张明升. 渭河盆地氦气成藏特征初步研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2014.ZHANG Ming-sheng. The preliminary analysis of helium reservoir forming characteristic in Weihe Basin[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2014. [29] 陈岳龙.东天山北秦岭花岗岩类地球化学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1999.CHEN Yue-long. Geochemistry of granitoids from the eastern Tianshan Mountains and the northern Qinling belt[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1999. -





 下载:
下载: