GEOCHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF BEIYI AND NANLIU OREBODIES IN THE SHILU IRON DEPOSIT IN HAINAN PROVINCE
-
摘要: 北一、南六矿体是海南石碌铁矿床最主要的2个铁矿体,赋矿围岩同为二透岩,铁矿石主要为赤铁矿加少量磁铁矿。研究两矿体赋矿围岩和富铁矿石的地球化学特征,比较其物质组成差异性,可以为本矿床深部和外围找矿提供有用信息。研究表明,北一、南六2个矿体二透岩、富铁矿的主量元素、微量元素及稀土元素配分曲线差异明显;北一矿体二透岩除CaO和Co含量低于南六矿体样品外,其余氧化物及微量元素含量均高于南六矿体样品;北一矿体二透岩及富铁矿有Eu弱负异常,南六矿体二透岩及富铁矿Eu正异常;所有样品均表现Ce的弱负异常和轻稀土相对亏损、重稀土相对富集的特征。研究结果表明两矿体成矿环境或受后期热液影响不同。Abstract: Beiyi orebody and Nanliu orebody are the two main orebodies of Shilu iron deposit in Hainan Province, with high research value, ore-bearing wall rocks being the diopside-tremolite rocks and iron ores being mainly composed of hematite and tiny magnetite. By studying geochemical characteristics of wall rocks and ores of two orebodies and comparing their material composition differences, we hope that it could provide some useful information for prospecting in depth and periphery of deposit. Two orebodies have pronounced differences. The distribution patterns of main elements and trace elements of Beiyi's and Nanliu's high-grade Fe ore samples of two orebodies are pronounced; except that CaO and Co of Beiyi orebody's diopside-tremolite rocks are less than Nanliu orebody's, the remaining oxides and trace elements are more than Nanliu samples'. Beiyi orebody's diopside-tremolite rocks and high-grade Fe ores have weak Eu negative anomaly, and Nanliu orebody's iopside-tremolite rocks and high-grade Fe ores have Eu positive anomaly, and all samples have the characteristic of weak Ce negative anomaly and LREE depleted and HREE enriched relatively. It reflected that metallogenic environments or late hydrothermal fluid affected of two ore bodies are different.
-
Key words:
- main elements /
- trace elements /
- diopside-tremolite rocks /
- high-grade Fe ores /
- Shilu iron deposit
-
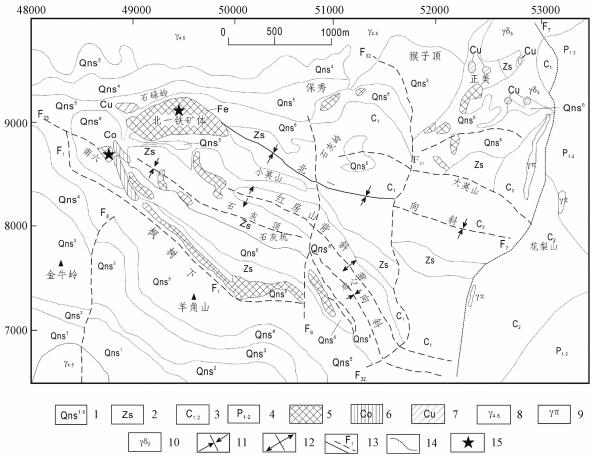
图 1 石碌矿区地质简图[14]
1—石碌群第一至第六层;2—原震旦系石灰顶组;3—中—下石炭统;4—中—下二叠统;5—铁矿体;6—钴矿体;7—铜矿体;8—海西—印支期花岗岩;9—燕山晚期花岗斑岩;10—印支期粗中粒斑状黑云母花岗闪长岩;11—向斜;12—背斜;13—实测及推测断裂;14—地质界线;15—采样位置
Figure 1. Simplified geological map of the Shilu iron mining area
表 1 石碌矿区二透岩、富铁矿主量元素含量
Table 1. Main elements content in diopside-tremolite rock and high-grade Fe ore in Shilu mining area

表 2 石碌矿区二透岩、富铁矿稀土元素含量
Table 2. REE contents in diopside-tremolite rock and high-grade Fe ore in Shilu mining area

表 3 石碌矿区二透岩、富铁矿稀土元素特征值
Table 3. REE characteristic values of diopside-tremolite rock and high-grade Fe ore in Shilu mining area

表 4 石碌矿区二透岩、富铁矿微量元素含量
Table 4. Trace elements contents in diopside-tremolite rock and high-grade Fe ore in Shilu mining area

-
[1] 陈国达, 关尹文, 邓景, 等.海南岛石碌式铁矿的大地构造成矿条件初探[J].中南矿冶学院学报, 1977, (3):1~12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD197703000.htmCHEN Gu-da, GUAN Yin-wen, DENG Jing, et al. The preliminary exploration of tectonic metallogenic conditions of the "Shilu-type" ore deposit in Hainan Province[J]. Journal of Central South University, 1977, (3):1~12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD197703000.htm [2] 冷盛强, 李佩兰.海南岛石碌矿区富铁矿形成的物理化学条件实验研究[J].中南矿冶学院学报, 1979, (3):116~128. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD197903012.htmLENG Sheng-qiang, LI Pei-lan. The experimental investigation of the physico-chemical condition of the rich iron formation in Shilu ore district, Hainan[J]. Journal of Central South University, 1979, (3):116~128. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD197903012.htm [3] 刘成湛, 胡腊英, 刘汉元, 等.海南石碌铁矿成矿过程的地球化学[J].中南矿冶学院学报, 1979, (3):45~55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD197903005.htmLIU Cheng-zhan, HU La-ying, LIU Han-yuan, et al. Geochemistry of the mineralization of Shilu iron deposit, Hainan island[J]. Journal of Central South University, 1979, (3):45~55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD197903005.htm [4] 冯建良, 王静纯, 何双梅.石碌铁矿成因矿物学研究[J].矿物学报, 1981, (3):145~181. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB198103002.htmFENG Jian-liang, WANG Jing-chun, HE Shuang-mei. Mineralogical genesis of Shilu iron ores[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 1981, (3):145~181. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB198103002.htm [5] 中国科学院华南富铁科学研究队.海南岛地质与石碌铁矿地球化学[M].北京:科学出版社, 1986.South China Iron-rich Research Team of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Geology of Hainan Island and geochemistry of iron ore deposits in Shilu[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1986. [6] 张仁杰, 马国干, 冯少南, 等.海南石碌铁矿的Sm-Nd法年龄及其意义[J].地质科学, 1992, (1):38~43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX199201005.htmZHANG Ren-jie, MA Guo-gan, FENG Shao-nan, et al. Sm-Nd age of the Shilu rion ore deposits on Hainan island and its significance[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 1992, (1):38~43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX199201005.htm [7] 许德如, 肖勇, 夏斌, 等.海南石碌铁矿床成矿模式与找矿预测[M].北京:地质出版社, 2009.XU De-ru, XIAO Yong, XIA Bin, et al. Metallogenic mode and prospecting prediction of Shilu iron deposit in Hainan Province[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2009. [8] Xu Deru, Wang Zhilin, Cai Jianxin, et al. Geological characteristics and metallogenesis of the shilu Fe-ore deposit in Hainan Province, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013, 52:318~342. [9] 刘宏英.海南石碌铁矿硫、氧同位素组成特征及矿床成因分析[J].矿产与地质, 1982, (1):133~138. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD198200024.htmLIU Hong-ying. S and O isotopic composition and Genesis analysis of Shilu iron ore, Hainan[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 1982, (1):133~138. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD198200024.htm [10] 许德如, 吴俊, 肖勇, 等.海南石碌铁矿床构造变形特征及其与铁多金属成矿富集的关系[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(4):553~564. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201104013.htmXU De-ru, WU Jun, XIAO Yong, et al. Structural deformation of the Shilu iron ore deposit in Hainan, southern China, and its relationship with the formation and enrichment of iron-polymetallic metals[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2011, 30(4):553~564. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201104013.htm [11] 肖勇, 蔡仁杰, 符启基, 等.海南岛石碌铁、钴、铜多金属矿集区地质特征及找矿方向[J].矿产与地质, 2010, 24(3):251~255. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD201003012.htmXIAO Yong, CAI Ren-jie, FU Qi-ji, et al. Geological characteristics and prospecting orientation of Shilu iron, cobalt and copper polymetallic ore accumulation zone[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2010, 24(3):251~255. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD201003012.htm [12] 许德如, 陈广浩, 黄智龙, 等.海南岛中元古代花岗岩地球化学及成因研究[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2001, 25(4):420~433. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200104008.htmXU De-ru, CHEN Guang-hao, HUANG Zhi-long, et al. Research on the geochemistry and genesis of mesoproterozoic granites on Hainan Island[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2001, 25(4):420~433. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200104008.htm [13] 葛小月. 海南岛中生代岩浆作用及其构造意义——年代学、地球化学及Sr-Nd同位素证据[D]. 广州: 中国科学院广州地球化学研究所, 2003. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y540859GE Xiao-yue. Mesozoic magmatism in Hainan Island (southeastern China) and its tectonic significance:Geochronology, geochemistry and Sr-Nd isotope evidences[D]. Guangzhou:Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2003. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y540859 [14] 许德如, 王力, 肖勇, 等."石碌式"铁氧化物-铜(金)-钴矿床成矿模式初探[J].矿床地质, 2008, 27(6):681~694. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200806003.htmXU De-ru, WANG Li, XIAO Rong, et al. A preliminary discussion on metallogenic model for Shilu-type iron oxide-copper-gold-cobalt ore deposit[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2008, 27(6):681~694. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200806003.htm [15] 喻茨玫, 卢焕章.包裹体研究与石碌铁矿成因的探讨[J].地球化学, 1980, (4):356~367. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX198004003.htmYU Ci-mei, LU Huan-zhang. An investigation into the genesis of Shilu iron deposit in special reference to its fluid inclusions[J]. Geochimica, 1980, (4):356~367. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX198004003.htm [16] 易建. 海南石碌铁矿床碧玉岩地质特征及铁沉积成矿模式研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2012. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y2189331YI Jian. Jasperite geological characteristics and iron sedimentation-mineralization model of Shilu iron deposit in Hainan[D]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences, 2012. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y2189331 [17] Kato Y, Kawakami T, Kano T, et al. Rare-earth element geochemistry of banded iron formations and associated amphibolite from the Sargur belts, south India[J]. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 1996, 14:161~164. doi: 10.1016/S0743-9547(96)00054-2 [18] 沈其韩, 宋会侠, 赵子然.山东韩旺新太古代条带状铁矿的稀土和微量元素特征[J].地球学报, 2009, 30(6):693~699. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200906004.htmSHEN Qi-han, SONG Hui-xia, ZHAO Zi-ran. Characteristics of rare earth elements trace elemensts in Hanwang neo-archaean banded iron formations, Shandong Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2009, 30(6):693~699. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200906004.htm [19] 沈其韩, 宋会侠, 杨崇辉, 等.山西五台山和冀东迁安地区条带状铁矿的岩石化学特征及其地质意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2011, 30(2):161~171. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201102003.htmSHEN Qi-han, SONG Hui-xia, YANG Chong-hui, et al. Petrochemical characteristics and geological significations of banded iron formations in the Wutai Mountain of Shanxi and Qian'an of eastern Hebei[J]. Acta Petrologica ET Mineralogica, 2011, 30(2):161~171. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201102003.htm -





 下载:
下载: