PETROGENESIS AND TECTONIC SIGNIFICANCE OF GRANITE IN THE HAOYAOERHUDONG GOLD DEPOSIT IN INNER MONGOLIA
-
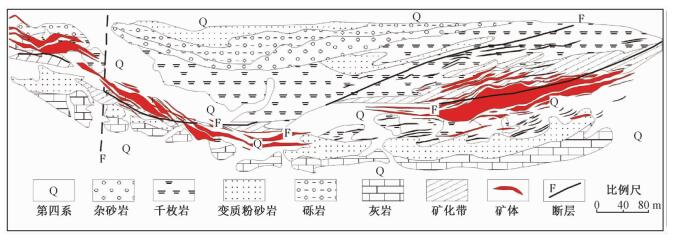
摘要: 内蒙古浩尧尔忽洞金矿为低品位超大型中低温热液型金矿,矿区内海西期花岗岩发育。在矿区内可见黑云花岗岩、花岗细晶岩、花岗伟晶岩和花岗斑岩。花岗岩中SiO2含量65.36%~74.29%,Na2O/K2O比值0.43~1.01,平均值为0.75,花岗脉岩类属于高钾钙碱性,黑云花岗岩属于钾玄岩系列。哈克图解上各元素含量随SiO2变化呈线性规律明显,具Ⅰ型花岗岩特征。∑REE值在64.86×10-6~164.80×10-6范围内变化,总体上稀土含量较低。(La/Yb)N值为6.59~16.98,显示轻重稀土有明显的分馏。稀土元素蛛网图表现为右倾。黑云母花岗岩δEu平均值0.30,具低Sr低Y的特点。花岗脉岩类δEu平均值为0.65,表现出高Sr低Y的特点。花岗岩类具有中等到强的铕亏损。根据其地球化学特征,认为该岩体为同碰撞—后碰撞期形成的高钾钙碱性Ⅰ型花岗岩。Abstract: The Haoyaoerhudong gold deposit is a mesothermal-epithermal deposit with ultra-large reserves and low grade. Hercynian granite was developed in the gold deposit. Granitite, granite aplite, granite pegmatite and granite-porphyry could be found in the Haoyaoerhudong gold deposit. The content of SiO2 is from 65.36 to 73.07, and Na2O/K2O is 0.43 to 1.01, with average value of 0.75. The granite dikes belong to high potassium calcium alkaline. The biotite granitization belongs to shoshonitic series. The variation tendency of other elements with following the content of SiO2 is obviously linear, and then it expresses the characters of Ⅰ-type granite. The content of ∑REE ranges from 64.86×10-6 to 164.80×10-6, which means low content of REE. The ratio of (La/Yb)N ranges from 6.59 to 16.98, revealing apparent fractionation between LREE and HREE. The distribution curve of REE is right deviation. The δEu average value of biotite granitization is 0.30. The δEu average value of granite dikes is 0.65, indicating high and medium negative anomaly of Eu elememt. The biotite granitization showed low Sr and low Y characteristics. The granite dikes showed high Sr and low Y characteristics. According to the geochemical characteristics, the granitoids belong to collision-post collision environment Ⅰ-type granite.
-
图 3 浩尧尔忽洞岩体SiO2-K2O和A/NK-A/CNK岩浆系列判别图[7]
Figure 3. SiO2-K2O and A/NK-A/CNK magma discrimination diagram of the Haoyaoerhudong rock
图 7 208Pb/204Pb-206Pb/204Pb和207Pb/204Pb-206Pb/204Pb投影图解(底图据文献[22])
Figure 7. 208Pb/204Pb-206Pb/204Pb and 207Pb/204Pb-206Pb/204Pb projective diagrams
表 1 浩尧尔忽洞岩体主量元素分析结果
Table 1. The analytical results of major elements of the Haoyaoerhudong granitoids

表 2 浩尧尔忽洞岩体微量及稀土元素分析结果
Table 2. Analytical results of trace elements and rare earth elements in the Haoyaoerhudong granitoids

表 3 浩尧尔忽洞岩体Pb同位素分析结果
Table 3. Pb isotopic compositions for the Haoyaoerhudong granitoids

-
[1] 郭书胜.浩尧尔忽洞金矿床成因-控矿因素浅析[J].中国科技博览, 2008, (16):22~23.GUO Shu-sheng. Analysis on ore genesis and ore-controlling factors in Haoyaoerhudong gold deposit[J]. China Science and Technology Review, 2008, (16):22~23. [2] 赵百胜, 刘家军, 王建平, 等.内蒙古长山壕金矿矿床地球化学特征与成因研究[J].现代地质, 2012, 25(6):1077~1086. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201106006.htmZHAO Bai-sheng, LIU Jia-jun, WANG Jian-ping, et al. Geological-geochemical characteristics and genesis of Changshanhao gold deposit in Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 25(6):1077~1086. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201106006.htm [3] 王玉峰. 内蒙古浩尧尔忽洞金矿区岩体地球化学特征及其成矿意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学地球科学与资源学院, 2012: 30~40. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1012365086.htmWANG Yu-feng. The geochemical characteristics of the pluton in the Haoyaoerhudong gold deposit in Inner Mongolia and its ore-forming significance[D]. Beijing:School of Earth Science and Resources, China University of Geosciences, 2012:30~40. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1012365086.htm [4] 王建平, 刘家军, 江向东, 等.内蒙古浩尧尔忽洞金矿床黑云母氩-氩年龄及其地质意义[J].矿物学报, 2011, (增刊):643~644. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2011S1335.htmWANG Jian-ping, LIU Jia-jun, JIANG Xiang-dong, et al. Argon-argon age of the black mica in the Haoyaoerhudong gold deposit in Inner Mongolia and its geological significance[J]. Acta Minalogica Sinica, 2011, (Supp.):643~644. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2011S1335.htm [5] 肖伟, 聂凤军, 刘翼飞, 等.内蒙古长山壕金矿区花岗岩同位素年代学研究及地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(2):535~543. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201202016.htmXIAO Wei, NIE Feng-jun, LIU Yi-fei, et al. Isotope geochronology study of the granitoid intrusions in the Changshanhao gold deposit and its geological implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(2):535~543. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201202016.htm [6] ZHONG Hong, ZHU Wei-guang, HU Rui-zhong, et al. Zircon U-Pb age and Sr-Nd-Hf isotope geochemistry of the Panzhihua A-type syenitic intrusion in the Emeishan large igneous province, southwest China and implication for growth of iuvenile crust[J]. Lithos, 2009, 110(1-4):109~128. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2008.12.006 [7] Rick P C. Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and minor elements lithos. 1989, 22:247~263. [8] Chappell B W. Aluminium saturation in I-and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3):535~551. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00086-3 [9] WU Fu-yuan, Jahn Bor-ming, Wilde S A, et al. Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China (Ⅰ):Geochronology and petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 2003, 66(3-4):241~273. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00222-0 [10] LI Xian-hua, LI Zheng-xiang, LI Wu-xian, et al. U-Pb zircon, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on age and origin of Jurassic I-and A-type granites from central Guangdong, SE China:A major igneous event in response to foundering of a subducted flat-slab?[J]. Lithos, 2007, 96(1-2):186~204. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.09.018 [11] 杨理华, 李钦祖.华北地区地壳应力场[M].北京:地震出版社, 1980:39~41.YANG Li-hua, LI Qin-zu. Crustal stress field in North China[M]. Beijing:Seismological Publishing House, 1980:39~41. [12] 崔盛芹.华北陆块北缘构造运动序列及区域构造格局[M].北京:地质出版社, 2000:179~183.CUI Sheng-qin. Tectonic movement sequence in the northern margin of North China Landmass and regional structure pattern[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2000:179~183. [13] 胡桂明, 王守伦.华北陆台北缘地体构造与铁金矿产[M].北京:地质出版社, 1998:50~56.HU Gui-ming, WANG Shou-lun. Terrane tectonics and gold minerals in the northern margin of North China Landmass[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1998:50~56. [14] Dirk Küster, Ulrich Harms. Post-collisional potassic granitoids from the southern and northwestern parts of the late Neoproterozoic East African Orogen:A review[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45(1-4):177~195. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00031-0 [15] 翁望飞, 曹诚, 支利赓, 等.皖南燕山期高钾钙碱性埃达克岩厘定及岩石成因[J].地质与勘探, 2001, 47(6):967~981. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201106005.htmWENG Wang-fei, CAO Cheng, ZHI Li-geng, et al. Geochemical characteristics and petrogenesis of high-K calc-alkaline adakite of the Yanshanianepoch in South Anhui[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2011, 47(6):967~981. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201106005.htm [16] 张成立, 刘良, 张国伟, 等.北秦岭新元古代后碰撞花岗岩的确定及其构造意义[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(3):33~42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200403005.htmZHANG Cheng-li, LIU Liang, ZHANG Guo-wei, et al. Determination of Neoproterozoic post-collisional granites in the north Qinling Mountains and its tectonic significance[J]. Earth Science Frontier, 2004, 11(3):33~42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200403005.htm [17] 韩宝福.后碰撞花岗岩类的多样性及其构造环境判别的复杂性[J].地学前缘, 2007, 14(3):64~72. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200703007.htmHAN Bao-fu. Diverse post-collisional granitoids and their tectonic setting discrimination[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007, 14(3):64~72. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200703007.htm [18] 刘昊, 杨欣德, 郝彬, 等.内蒙古赤峰北部晚侏罗世花岗岩地球化学特征及构造背景[J].地质力学学报, 2011, 17(3):286~294. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20110308&journal_id=dzlxxbLIU Hao, YANG Xin-de, HAO Bin, et al. Geochemical characteristics and tectonic setting of Upper Jurassic granite from northern Chifeng, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2011, 17(3):286~294. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20110308&journal_id=dzlxxb [19] Defant M J, Drummond M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 374:662~665. [20] Castillo P R. An overview of adakite petrogenesis[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(3):257~268. doi: 10.1007/s11434-006-0257-7 [21] 李承东, 张旗, 苗来成, 等.冀北中生代高Sr低Y和低Sr低Y型花岗岩:地球化学、成因及其与成矿作用的关系[J].岩石学报, 2004, 20(2):269~284. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200402008.htmLI Cheng-dong, ZHANG Qi, MIAO Lai-cheng, et al. Mesozoic high-Sr, low-Y and low-Sr, low-Y types granitoids in the northern Hebei province:Geochemistry and petrogenesis and its relation to mineralization of gold deposites[J]. Acte Petrologica Sinica, 2004, 20(2):269~284. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200402008.htm [22] Zartman R E, Doe B R.Plumbotectonics:the model[J].Tectonophysics, 1981, 75(1/2):135~162. -





 下载:
下载: