EAST ASIAN MONSOON CHANGES DURING THE HOLOCENE———RECORDS FROM THE SOUTHEASTERN LOESS PLATEAU
-
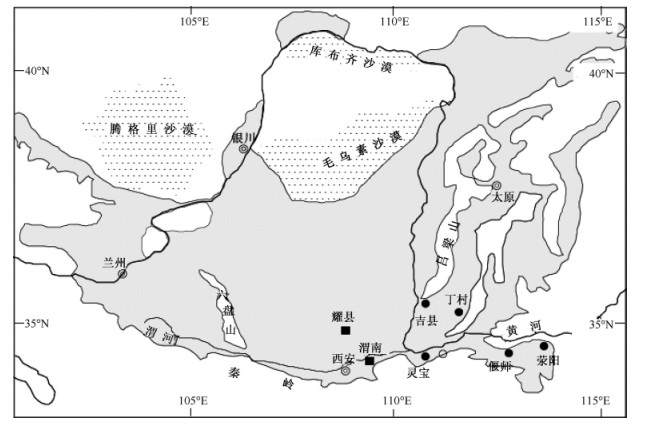
摘要: 在全球变暖背景下,未来东亚季风的变化一直备受关注,而东亚季风演化规律的研究能够为未来的预测提供重要基础。黄土-古土壤序列几乎连续地记录了古东亚季风变化的信息,本文选取黄土高原东南部的荥阳、偃师、灵宝、吉县、丁村五个剖面进行磁化率和古风化强度分析,重建了黄土高原东南部两万年以来的东亚夏季风演化历史: 18~12 ka B. P.,季风强度较弱; 12~10 ka B. P.,季风强度显著增强; 10~6 ka B. P.,季风强度最强; 6 ka B. P.以后季风强度逐渐减弱。对比发现黄土高原东南缘全新世东亚夏季风的演化与东亚季风区不同纬度代表性记录基本同步,没有显著的区域性差别; 东亚夏季风变化主要受控于北半球低纬太阳辐射,但存在明显滞后。同时发现全新世古土壤磁化率与古风化强度峰值在地层中的位置往往不一致,在风化较强的地区,古风化强度最大值位置偏下,两个指标相比,古风化强度能够更客观地反映东亚夏季风强度。Abstract: The influence of global warming on East Asian Monsoon (EAM) has received intensive concern, and studies on history of EAM could provide important climate analogue in the warmer temperature context.Five loess-paleosol sequences in the southeastern Loess Plateau were sampled to address the history of EAM during the last 20 ka.The intensity of EAM was weak from 18 to 12 ka B.P., increased rapidly in the interval of 12-10 ka B.P, and reached highest points during 10-6 ka B.P., and declined after 6 ka B.P.The proxies of summer monsoon, magnetic susceptibility and paleo-weathering intensity in this study is basically timely consistent with the geological records in different part of EAM region.The insolation of low-latitude northern hemisphere is main control factor of EAM, although changes of EAM lagged variations of insolation of low-latitude northern hemisphere.The lag may be induced by several important boundary conditions (e.g., scales of polar ice sheet in northern high latitudes, sea level changes, interaction between sea and atmosphere in low latitudes) of EAM to insolation and interaction between components of climate system.Additionally, our studies showed that magnetic susceptibility (MS) and maximum FeD/FeT values in same section were not in same position of soil profiles, with lower position of maximum FeD/FeT value than that of MS in relatively strong weathering area.Compared with MS, FeD/FeT ratio can better reflect the intensity of EAM.
-
Key words:
- loess /
- magnetic susceptibility /
- paleo-weathering intensity /
- East Asian summer monsoon
-
图 3 黄土高原东南部黄土古风化强度与东亚夏季风指标、冰芯记录的对比
a. GISP2冰芯中氧同位素[29]; b.三宝洞石笋氧同位素[30]; c.北纬30°太阳辐射[31]; d.黄土高原东南部古风化强度(虚线为5个剖面FeD/FeT值,实线为5个剖面平均的FeD/FeT值); e.东亚季风有效湿度指数[32]; f.渭南黄土剖面的植硅体组合重建过去20 ka的降雨量[33]; g.岱海钻孔中10 ka以来的木本花粉浓度的变化[34]; h.巴彦查干湖钻孔中10 ka以来盘星藻浓度的变化[35]
Figure 3. Comparison of paleo-weathering intensity in southeastern Loess Plateau and several proxies such as EAM and oxygen isotope record of ice core
-
[1] Zhang J C, Liu Z G.Climate of China[M].New York: Wiley, 1992.1~376. [2] 刘东生, 等.黄土与环境[M].北京:科学出版社, 1985.1~481.LIU Dong-sheng, et al.Loess and the Environment[M].Beijing: Science Press, 1985.1~481. [3] An Z S, Liu T S, Lu Y C, et al.The long-term paleomonsoon variation recorded by the loess-paleosol sequence in central China[J].Quaternary International, 1990, 7 (8): 91~95. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=be070a18bbcb29bbd49ac2da8e92eb62&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [4] Guo Z T, Biscaye P, Wei L, et al.Summer monsoon variations over the last 1.2 Ma from the weathering of loess-soil sequences in China[J].Geophysical Research Letters, 2000, 27 (12): 1751~1754. doi: 10.1029/1999GL008419 [5] 吴文祥, 刘东生.丁村旧石器文化遗址的黄土地层研究[J].地震地质, 2002, 24 (2): 241~248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.02.012WU Wen-xiang, LIU Dong-sheng.Study on the Loess-Paleosols sequence of the Dingcun Paleolithic sites[J].Seismology and Geology, 2002, 24 (2): 241~248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.02.012 [6] Jiang F C, Fu J, Wang S, et al.Formation of the Yellow River, inferred from loess – palaeosol sequence in Mangshan and lacustrine sediments in Sanmen Gorge, China[J].Quaternary International, 2007, 175 (1): 62~70. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2007.03.022 [7] 蒋复初, 傅建利, 王书兵, 等.关于黄河贯通三门峡的时代[J].地质力学学报, 2005, (4): 293~301. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2005.04.001JIANG Fu-chu, FU Jian-li, WANG Shu-bing, et al.The age of the Yellow River passing through the Sanmen Gorge[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 2005, (4): 293~301. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2005.04.001 [8] Guo Z T, Liu D S, Fedoroff N, et al.Shift of monsoon intensity on the Loess Plateau at ca.0.85 Ma BP[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 1993, 38: 586~586. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5b6e40f94615f565b199ca96f0ff5e0e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [9] Chen J, An Z S, Head J.Variation of Rb/Sr ratios in the loess-paleosol sequences of central China during the last 130, 000 years and their implications for monsoon paleoclimatology[J].Quaternary Research, 1999, 51 (3): 215~219. doi: 10.1006/qres.1999.2038 [10] Chen J, An Z S, Liu L, W, et al.Variations in chemical compositions of the eolian dust in Chinese Loess Plateau over the past 2.5 Ma and chemical weathering in the Asian inland[J].Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2001, 44 (5): 403~413. doi: 10.1007/BF02909779 [11] Yang S L, Ding Z L.Color reflectance of Chinese loess and its implications for climate gradient changes during the last two glacial-interglacial cycles[J].Geophysical Research Letters, 2003, 30 (20): 2058~2061. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ027379148 [12] Guo Z T, Liu T S, Guiot J et al.High frequency pulses of East Asian monsoon climate in the last two glaciations: Link with the North Atlantic[J].Climate Dynamics, 1996, 12 (10): 701~709. doi: 10.1007/s003820050137 [13] Ding Z L, Yang S L, Sun J M, et al.Iron geochemistry of loess and red clay deposits in the Chinese Loess Plateau and implications for long-term Asian monsoon evolution in the last 7.0 Ma[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 185 (1): 99~109. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ023669033 [14] 刘青松, 邓成龙.磁化率及其环境意义[J].地球物理学报, 2009, 52 (4): 1041~1048. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.04.021LIU Qingsong, DENG Chenglong.Magnetic susceptibility and its environmental significances[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52 (4): 1041~1048. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.04.021 [15] Guo Z T, Liu T S, Fedoroff N, et al.Climate extremes in loess of China coupled with the strength of deep-water formation in the North Atlantic[J].Global and Planetary Change, 1998, 18 (3): 113~128. doi: 10.1016-S0921-8181(98)00010-1/ [16] 刘嘉麒, 陈铁梅, 聂高众, 等.渭南黄土剖面的年龄测定及十五万年来高分辨时间序列的建立[J].第四纪研究: 1994, 3: 193~200. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1994.03.001LIU Jia-qi, CHEN Tie-mei, NIE Gao-zong, et al.Dating and reconstruction of the high resolution time series in Weinan Loess section of the last 150000 years[J].Quaternary Sciences, 1994, 3: 193~200. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1994.03.001 [17] Zhao H, Chen F H, Li S H, et al.A record of Holocene climate change in the Guanzhong Basin, China, based on optical dating of a loess-palaeosol sequence[J].The Holocene, 2007, 17 (7), 1015~1022. doi: 10.1177/0959683607080530 [18] Kukla G, Heller F, Ming L X, et al.Pleistocene climates in China dated by magnetic susceptibility[J].Geology, 1988, 16 (9): 811~814. [19] Mehra O P, Jackson M L.Iron oxide removal from soils and clays by a dithionite-citrate system buffered with sodium bicarbonate[J].Clays and Clay Minerals, 1960, 7: 317~327. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=577b1f2cca893595cbbd7ed156e81967&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [20] McKeague J A.Manual on soil sampling and methods of analysis[M].Toroto: Canadian Society of Soil Science, 1981.1~491. [21] Hunt C P, Singer M J, Kletetschka G, et al.Effect of citrate-bicarbonate-dithionite treatment on fine-grained magnetite and maghemite[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1995, 130 (1): 87~94. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a80aa86482190ba14f503950bab99118&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [22] Torrent J, Liu Q S, Bloemendal J, et al.Magnetic enhancement and iron oxides in the Upper Luochuan Loess Paleosol Sequence, Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2007, 71 (5): 1570. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2006.0328 [23] Singer M J, Fine P.Pedogenic factors affecting magnetic susceptibility of northern California soils[J].Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1989, 53 (4): 1119. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1989.03615995005300040023x [24] Singer M J, Fine P, Verosub K L, et al.Time dependence of magnetic susceptibility of soil chronosequences on the California coast[J].Quaternary research, 1992. doi: 10.1016-0033-5894(92)90070-Y/ [25] Torrent J, Barrón V, Liu Q S.Magnetic enhancement is linked to and precedes hematite formation in aerobic soil[J].Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33 (2): L02401. doi: 10.1029-2005GL024818/ [26] Hao Q Z, Oldfield F, Bloemendal J, et al.The record of changing Hematite and Goethite deposition over the last 22Ma on the Chinese Loess Plateau from magnetic measurements and Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy[J].Journal of Geophysical Research, 2009, 114 (B12101), doi: 10.1029/2009JB006604. [27] 孙东怀, 周杰.全新世气候适宜期黄土高原及黄土/沙漠过渡区年降水量的初步恢复[J].中国沙漠, 1995, 15 (004): 339~344. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500624436SUN Dong-huai, ZHOU Jie.Preliminary reconstruction of annual rainfall in Loess Plateau and loess-desert transitional regions in suitable climatic period of Holocene[J].Journal of Desert Research, 1995, 15 (004): 339~344. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500624436 [28] Hao Q Z, Guo Z T.Spatial variations of magnetic susceptibility of Chinese loess for the last 600 kyr: Implications for monsoon evolution[J].Journal of Geophysical Research, 2005, 110 (B12101), doi: 10.1029/2005JB003765. [29] Grootes P M, Stuiver M.Oxygen 18/16 variability in Greenland snow and ice with 103 to 105-year time resolution[J].Journal of Geophysical Research, 1997, 102: 26455~26470. doi: 10.1029/97JC00880 [30] Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al.Millennial- and orbital-scale changes in the East Asian monsoon over the past 224, 000 years[J].Nature, 2008, 451 (7182): 1090~1093. doi: 10.1038/nature06692 [31] Berger A, Loutre M F.Insolation values for the climate of the last 10 million years[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 1991, 10 (4): 297~317. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(91)90033-Q [32] Herzschuh U.Palaeo-moisture evolution in monsoonal Central Asia during the last 50, 000 years[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25 (1): 163~178. [33] Lu H Y, Wu N Q, Liu K B, et al.Phytoliths as quantitative indicators for the reconstruction of past environmental conditions in China Ⅱ: palaeoenvironmental reconstruction in the Loess Plateau[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 2007, 26 (5~6): 759~772. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2006.10.006 [34] Li X Q, Zhou J, Ji S, et al.Vegetation history and climatic variations during the last 14 ka BP inferred from a pollen record at Daihai Lake, north-central China[J].Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 2004, 132 (3~4): 195~205. doi: 10.1016/j.revpalbo.2004.06.002 [35] Jiang W Y, Guo Z T, Sun X, et al.Reconstruction of climate and vegetation changes of Lake Bayanchagan (Inner Mongolia): Holocene variability of the East Asian monsoon[J].Quaternary Research, 2006, 65 (3): 411~420. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2005.10.007 [36] Hao Q Z, Guo Z T.Magnetostratigraphy of a late Miocene-Pliocene loess-soil sequence in the western Loess Plateau in China [J].Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31: L092099, doi: 10.1029/2003GL019392. [37] 乔彦松, 刘冬雁, 李朝柱, 等.川西甘孜地区黄土的磁性地层学研究[J].地质力学学报, 2007, (4): 289~296. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2007.04.001QIAO Yan-song, LIU Dong-yan, LI Chao-zhu, et al.Magnetostratigraphy of a Loess-soil sequence in the Garze area, western Sichuan[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 2007, (4): 289~296. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2007.04.001 [38] 施炜, 马寅生, 吴满路, 等.青藏高原东北缘共和盆地第四纪磁性地层学研究[J].地质力学学报, 2006, (3): 317~323. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2006.03.005SHI Wei, MA Yan-sheng, WU Man-lu, et al.Quaternary magnetostratigraphy of the Gonghe Basin on the northeastern of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 2006, (3): 317~323. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2006.03.005 [39] Guo Z T, Liu T S, Guiot J, et al.High frequency pulses of East Asian monsoon climate in the last two glaciations: link with the North Atlantic[J].Climate Dynamics, 1996, 12: 701-709. doi: 10.1007/s003820050137 [40] Kutzbach J E.Monsoon climate of the early Holocene: climate experiment with the earth's orbital parameters for 9000 years ago[J].Science, 1981, 214 (4516): 59~61. doi: 10.1126/science.214.4516.59 [41] Porter S C, An Z S.Correlation between climate events in the North Atlantic and China during the last glaciation[J].Nature, 1995, 375: 305~308. doi: 10.1038/375305a0 [42] Fleitmann D, Burns S J, Mudelsee M, et al.Holocene forcing of the Indian monsoon recorded in a stalagmite from Southern Oman[J].Science, 2003, 300 (5626): 1737~1739. doi: 10.1126/science.1083130 [43] Clemens S, Prell W, Murray D, et al.Forcing mechanisms of the Indian Ocean monsoon[J].Nature, 1991, 353: 720~725. doi: 10.1038/353720a0 [44] Clemens S C, Prell W L.The timing of orbital-scale Indian monsoon changes[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 2007, 26 (3~4): 275~278. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2006.11.010 [45] Xiao J L, Si B, Zhai D Y, et al.Hydrology of Dali Lake in central-eastern Inner Mongolia and Holocene East Asian monsoon variability[J].Journal of Paleolimnology, 2008, 40 (1): 519~528. doi: 10.1007/s10933-007-9179-x [46] Yu K F, Zhao J X, Liu T S, et al.High-frequency winter cooling and reef coral mortality during the Holocene climatic optimum[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 224 (1~2): 143~155. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2004.04.036 [47] 聂宝符.五千年来南海海平面变化的研究[J].第四纪研究, 1996, (001): 80~87. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600050682NIE Bao-fu.Sea-Level changes of the South Sea in the past 5000 years[J].Quaternary Sciences, 1996, (001): 80~87. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600050682 [48] 黄镇国, 张伟强.南海地区全新世高海平面遗迹高程的区域差异问题[J].台湾海峡, 2005, 24 (002): 228~235. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/twhx200502016HUANG Zhen-guo, ZHANG Wei-qiang.On elevation differentiation of the Holocene high sea level relics in the South China Sea area[J].Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2005, 24 (002): 228~235. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/twhx200502016 [49] 丁仲礼, 余志伟.第四纪时期东亚季风变化的动力机制[J].第四纪研究, 1995, 1: 63~74. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1995.01.007DING Zhong-li, YU Zhi-wei.Forcing mechanisms of paleomonsoons over East Asia[J].Quaternary Sciences, 1995, 1: 63~74. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1995.01.007 -





 下载:
下载: