NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF STRUCTURAL STRESS FIELD IN THE LATE SEDIMENTARY PERIOD OF Es4 AND PREDICTION OF THE LOWER-ORDER FAULTS IN LANGGU SAG
-
摘要: 在了解区域构造背景、分析断层活动特征及构造演化特征的基础上, 对廊固凹陷沙四晚期构造应力场进行数值模拟, 并对低级序断层发育进行预测。研究结果表明, 研究区在沙四晚期活动的主要断层包括大兴断层、半截河断层等6条, 牛北斜坡构造带与河西务构造带在该时期隆起明显, 综合分析可知该时期最小主应力方向为SE144°—NW324°;低级序断层发育受最小主应力、剪应力等的影响, 最小主应力和最大主应力与最小主应力的差值控制断层的优势发育区, 平面剪应力控制断层走向, 该区主要发育北北东—北东走向的断层; 剖面剪应力在大部分区域为左旋, 表明断层视倾向以北西向为主。Abstract: On the basis of the research of structural background, fault activity and structural evolution, the method of numerical simulation of structural stress was applied to simulate the stress distribution in the late sedimentary period of Es4 in Langgu sag, and the development of the lower-order faults could be predicted. The research showed that the active faults in the late sedimentary period of Es4 were Daxing fault, Banjiehe fault and so on. Niubei slope belt and Hexiwu structural belt were uplift obviously during this period. The comprehensive analysis indicated that the direction of the minimum principal stress was SE144°-NW324°, the development of the lower-order faults were mainly influenced by the minimum principal stress and the shear stress, et al. The minimum principal stress and the difference between principal stresses (the maximum and minimum principal stress) controlled the advantage area of the fault development. The plane shear stress controlled the fault strike, and its most faults in this area were NNE-NE. The profile shear stress controlled the dip direction, in the main part of this area the profile shear stress was sinistral shear stress, which showed that the dip direction of the most faults was NW.
-
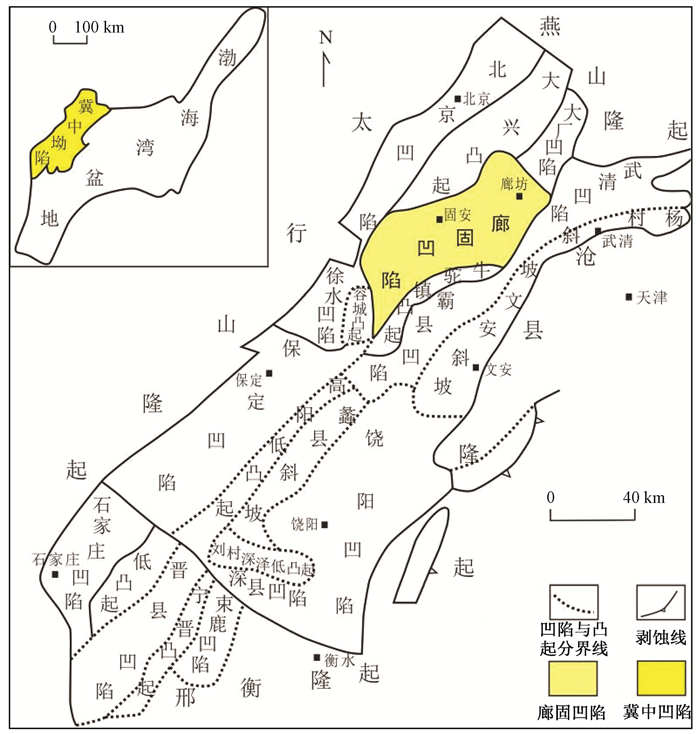
图 2 廊固凹陷构造带分布及地震测线位置(据文献[14]修改)
Figure 2. The distribution of the structural belts and the position of seismic lines in Langgu Sag
表 1 廊固凹陷沙四晚期应力场模拟力学参数
Table 1. Mechanical parameters in stress field simulation in the late sedimentary period of Es4 of Langgu Sag
地质单元 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 密度/(kg·m-3) 地层 2.6 0.15 2350 断层 2.2 0.20 2320 -
[1] 孙晓庆.古构造应力场有限元数值模拟的应用及展望[J].断块油气田, 2008, 15(3):31-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT200803012.htmSUN Xiao-qing. Present situation and prospect of application for finite element numerical simulation of palaeotectonic stress fields[J]. Fault Block Oil & Gas Field, 2008, 15(3): 31~33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT200803012.htm [2] 张胜利.构造应力场模拟-有限元理论、方法和研究进展[J].西北地震学报, 2010, 32(4):405~409. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201101007.htmZHANG Sheng-li. Modeling of tectonic stress field -the theory, method and related research progress of the finite element method[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 2010, 32(4) : 405~409. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201101007.htm [3] 王延欣, 侯贵廷, 李江海, 等.塔北隆起中西部新近纪末构造应力场数值模拟[J].北京大学学报:自然科学版, 2008, 44(6):902~907. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BDXP200801010.htmWANG Yan-xin, HOU Gui-ting, LI Jiang-hai, et al. Numercial simulation of tenconic stress field at the end of Neocene in the midwest of Tabei Uplift[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2008, 44(6): 902~907. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BDXP200801010.htm [4] Hou G T, Wang C C, Li J H, et al. Late Paleoproterozoic extension and a paleostress field reconstruction of the North China Craton[J]. Tectonophysics, 2006, 422: 89~98. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2006.05.008 [5] Martin A M, Cloeginch S, Vicente G D, et al. Finite-element modeling of Tertiary paleostress field in the eastern part of the Tajo Basin (central Spain) [J]. Tectonophysics, 1998, 300: 47~62. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(98)00233-9 [6] 宋荣彩, 张哨楠, 李弢.廊固凹陷大兴断层对油气分布的控制研究[J].天然气工业, 2006, 26(8):30~33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200608010.htmSONG Rong-cai, ZHANG Shao-nan, LI-Tao. Research on the hydrocarbon distribution controlled by Daxing fault in Langgu Sag[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2006, 26(8): 30~33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200608010.htm [7] 戴俊生, 陆克政, 漆家福, 等.渤海湾盆地早第三纪构造样式的演化[J].石油学报, 1998, 19(4):16~19. doi: 10.7623/syxb199804003DAI Jun-sheng, LU Ke-zheng, QI-Jiafu, et al. The evolution of the Paleogene structural styles in Bohai Gulf Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1998, 19(4):16~19. doi: 10.7623/syxb199804003 [8] 漆家福, 张一伟, 陆克政, 等.渤海湾盆地新生代构造演化[J].石油大学学报:自然科学版, 1995, 19(增):1~6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ200106016.htmQI Jia-fu, ZHANG Yi-wei, LU Ke-zheng, et al. Cenozoic tectonic evolution in Bohai Bay Basin Province[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China, 1995, 19(Suppl.): 1~6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ200106016.htm [9] 杨明慧, 刘池阳, 杨斌谊, 等.冀中坳陷古近纪的伸展构造[J].地质论评, 2002, 48(1):58~65. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200201012.htmYANG Ming-hui, LIU Chi-yang, YANG Bin-yi, et al. Extensional structures of the Paleogene in the central Hebei Basin, China[J]. Geological Review, 2002, 48(1): 58~65. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200201012.htm [10] 赵红格, 刘池洋.廊固凹陷的拆离滑脱构造[J].西北大学学报:自然科学版, 2003, 33(3):315~318. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ200303018.htmZHAO Hong-he, LIU Chi-yang. Detachment gliding structures of Langgu Sag[J]. Journal of Northwest University: Natural Science Edition, 2003, 33(3): 315~318. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ200303018.htm [11] 宋荣彩, 周文, 董树义, 等.渤海湾盆地廊固凹陷油气分布特征研究[J].石油实验地质, 2008, 30(1):64~68. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200801064SONG Rong-cai, ZHOU Wen, DONG Shu-yi, et al. The research of oil-gas distribution characteristics in the Langgu Sag of Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2008, 30(1): 64~68. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200801064 [12] 孙宏斌, 陈汉林, 程晓敢, 等.辽河盆地葵花岛构造裂隙发育的有限元模拟[J].地质科学, 2004, 39(2):199~200. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200402005.htmSUN Hong-bin, CHEN Han-lin, CHENG Xiao-gan, et al. Finite element simulation of fracture development in the Kuihuadao structure, Liaohe Basin [J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2004, 39 (2):199~200. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200402005.htm [13] 张丹丹, 戴俊生, 邹娟, 等.冀中坳陷廊固凹陷古近纪断层活动特征[J].地质力学学报, 2014, 20(1):25~33. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20140103&journal_id=dzlxxbZHANG Dan-dan, DAI Jun-sheng, ZOU Juan, et al. Research on fault activity in Paleogene of Langgu Sag, Jizhong Depression[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2014, 20 (1):25~33. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20140103&journal_id=dzlxxb [14] 田建章, 苏建杰, 辛玮江, 等.廊固凹陷潜山成藏模拟及油气勘探潜力[J].中国石油勘探, 2012, 17(6):53~57. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201206012.htmTIAN Jian-zhang, SU Jian-jie, XIN Wei-jiang, et al. Buried hill accumulation model and oil and gas exploration potential in Langgu Depression[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2012, 17(6): 53~57. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201206012.htm [15] 戴俊生, 张继标, 冯建伟, 等.高邮凹陷真武断裂带西部低级序断层发育规律预测[J].地质力学学报, 2012, 18(1):11~19. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20120102&journal_id=dzlxxbDAI Jun-sheng, ZHANG Ji-biao, FENG Jian-wei, et al. Development law and prediction of the lower-order faults in the west of Zhenwu fault zone in Gaoyou Sag[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2012, 18(1) :11~19. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20120102&journal_id=dzlxxb [16] 付晓龙, 戴俊生, 张宏国.汊涧斜坡带阜宁期应力场数值模拟及低级序断层发育规律预测[J].地质力学学报, 2013, 19(2):125~130. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20130202&journal_id=dzlxxbFU Xiao-long, DAI Jun-sheng, ZHANG Hong-guo. Numerical simulation of structural stress field of Funing sedimentary period and prediction of the development law of lower-order faults in Chajian Slope Zone[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2013, 19(2) :125~130. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20130202&journal_id=dzlxxb -





 下载:
下载: