ANISOTROPY OF MAGNETIC SUSCEPTIBILITY:THEORY AND CASE STUDIES
-
摘要: 磁化率各向异性(AMS)在地质领域中的应用极为广泛,可以用来研究古流向造成的磁性矿物的定向排列,以及构造应力作用引起的岩石内磁性矿物的定向重结晶、定向排列及韧性变形。本文介绍了AMS的基本原理和参数,并并介绍了前人及作者应用AMS详细分析研究了二个实例:(1)以假多畴(MD)高钛磁铁矿为主要载磁矿物的玄武岩样品的AMS变化及其对构造运动的响应;(2)以MD磁铁矿为主要载磁矿物的湖泊沉积物样品在沉积过程中AMS变化。AMS可以灵敏地检测样品中磁性矿物的定向排列,因此在在地质领域中具有很好的应用前景。Abstract: Anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility (AMS) has been widely utilized to study orientation of magnetic minerals due to the paleo-flow, and direction of magnetic minerals or their recrystallization caused by tectonic stress. We presented the AMS principle and parameters, and studied AMS changes in:(1) two basalt samples (unheated and heated) that have experienced tectonic deformation, with multidomain (MD) titanomagnetite as dominant magnetic minerals, and this is from a previous study; (2) lake sediments that are majorly characterized by MD magnetite. The results show that AMS can sensitively investigate orientation of magnetic minerals.
-
Key words:
- anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility (AMS) /
- magnetite /
- basalt /
- lake sediment /
- rock magnetism
-
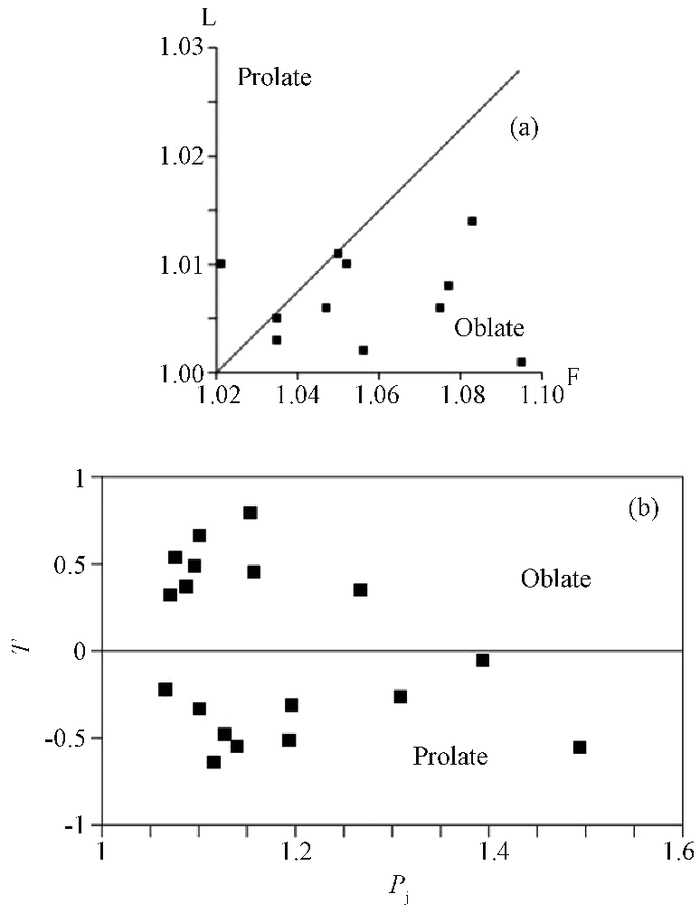
图 1 费林图(a)和磁化率各向异性-椭球形状参数图(b)[15]
Figure 1. Flinn (L-F) and Pj-T diagrams
图 2 磁化率各向异性图[15]
K1—方框;K2—三角;K3—实心圆;F—片理面;B—层面;红箭头—挤压应力方向
A-D—未加热和加热(580 ℃)石灰岩样品的等面积投影图和费林图;E-H—未加热和加热(580 ℃)玄武岩样品的等面积投影图和费林图;Ⅰ, J—受南北向挤压构造应力的玄武岩样品磁化率各向异性最小轴的等密度曲线(Ⅰ)和这些玄武岩体的层面法线等密度曲线(J)Figure 2. Anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility Map
-
[1] CAÑÓN-TAPIA E. Factors affecting the relative importance of shape and distribution anisotropy in rocks:theory and experiments[J]. Tectonophysics, 1997, 340:117-131. doi: 10.1007/s11200-015-0675-6 [2] 张拴宏, 周显强.磁化率各向异性地学应用综述[J].地质论评, 1999, 45(6):613-620. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP199906010.htm [3] BORRADAILE G J, JACKSON M. Anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility (AMS):Magnetic petrofabrics of deformed rocks[J]. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ., 2004, 238:299-360. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2004.238.01.18 [4] JACKSON M. Anisotropy of magnetic remanence:a brief review of mineralogical sources, physical origins, and geological applications, and comparison with susceptibility anisotropy[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 1991, 136(1):1-28. doi: 10.1007/BF00878885 [5] RAPOSO M I B, BERQUÓ T S. Tectonic fabric revealed by AARM of the proterozoic mafic dike swarm in the Salvador city (Bahia State):São Francisco Craton, NE Brazil[J]. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter., 2008, 167:179-194. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2008.03.012 [6] CAÑÓN-TAPIA E, WALKER G P L, HERRERO-BERVERA E. The internal structure of lava flows-insights from AMS measurements (Ⅰ):Near-vent a'a.[J]. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res., 1996, 70:21-36. doi: 10.1016/0377-0273(95)00050-X [7] HARGRAVES R B, JOHNSON D, CHAN C Y. Distribution anisotropy:The cause of AMS in igneous rocks?[J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 1991, 18:2193-2196. doi: 10.1029/91GL01777 [8] GAILLOT P, DE SAINT-BLANQUAT M, BOUCHEZ J L. Effects of magnetic interactions in anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility:Models, experiments and implications for igneous rock fabrics quantification[J]. Tectonophysics, 2006, 418:3-19. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2005.12.010 [9] GRÉGOIRE V, DARROZES P, GAILLOT P, et al. Magnetite grain shape fabric and distribution anisotropy vs rock magnetic fabric:A three-dimensional case study[J]. J. Struct. Geol., 1998, 20(7):937-944. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(98)00022-4 [10] TARLING D H, HROUDA F. The magnetic anisotropy of rocks[M]. London:Chapman & Hall, 1993:1-217. [11] ELLWOOD B B. Flow and emplacement direction determined for selected basaltic bodies using magnetic susceptibility anisotropy measurements[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1978, 41:254-264. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(78)90182-6 [12] JELINEK V. Characterization of the magnetic fabric of rocks[J]. Tectonophysics, 1981, 79:63-67. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(81)90110-4 [13] HROUDA F. Magnetic anisotropy of rocks and its application in geology and geophysics[J]. Geophys. Surv., 1982, 5:37-82. doi: 10.1007/BF01450244 [14] CAÑÓN-TAPIA E. AMS parameters:Guidelines for their rational selection[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 1994, 142:365-382. doi: 10.1007/BF00879310 [15] ZHANG S W. Magnetic anisotropy of igneous rocks from the Taimyr peninsula, Arctic Russia. Unpublished M.Sc Thesis, University of Bergen. 132 pp. [16] INGER S, SCOTT R A, GOLIONKO B G. Tectonic evolution of the Taimyr Peninsula, northern Russia:Implications for Arctic continental assembly[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1999, 156:1069-1072. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.156.6.1069 [17] WALDERHAUG H J, EIDE E A, SCOTT R A, et al. Palaeomagnetism and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology from the South Taimyr igneous complex, Arctic Russia:A Middle-Late Triassic magmatic pulse after Siberian flood-basalt volcanism[J]. Geophys. J. Int., 2005, 163:1-17. doi: 10.1111/gji.2005.163.issue-1 [18] 张淑伟, WALDERHAUG H J, 杨跃俊, 等.俄罗斯北部泰米尔半岛褶皱带岩床和玄武岩岩石磁学及磁各向异性[J].科学通报, 2008, 53(2):229-237. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200802016.htmZHANG Shu-wei, WALDERHAUG H J, YANG Yue-jun, et al. Rock magnetism and magnetic anisotropy in folded sills and basaltic flows:A case study of volcanics from the Taimyr Peninsula, Northern Russia[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53:759-767. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200802016.htm [19] ZHANG S W, CAÑÓN-TAPIA E, WALDERHAUG H J. Magnetic fabric and its significance in the sills and lava flows from Taimyr fold-belt, Arctic Siberia[J]. Tectonophysics, 2011, 505:68-85. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2011.04.004 [20] ROBERT D, HATCHER J R. Structural geology:Principles, concepts, and problems. Merrill Publishing Company and A Bell & Howell Information Company, Columbus Toronto London Melbourne. [21] DE WALL H, WARR L N. Oblique magnetic fabric in siderite-bearing pelitic rocks of the Upper Carboniferous Culm Basin, SW England:An indicator for paleo-fluid migration?[J]. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ., 2004, 238:493-507. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2004.238.01.25 [22] HENRY B, PLENIER G, CAMPS P. Post-emplacement tilting of lava flows inferred from magnetic fabric study:the example of Oligocene lavas in the Jeanne d'Arc Peninsula (Kerguelen Islands)[J]. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res., 2003, 127:153-164. doi: 10.1016/S0377-0273(03)00198-7 [23] REES A I. The use of anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility in the estimation of sedimentary fabric[J]. Sedimentology, 1965, 4(4):257-271. doi: 10.1111/sed.1965.4.issue-4 [24] ELLWOOD B B. Sample shape and magnetic grain sizes:two possible controls on the anisotropy of the magnetic susceptibility variability in deep-sea sediments[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1979, 43:309-314. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(79)90216-4 [25] LAKSHMI B.V., SATYANARAYANA K.V.V., BASAVAIAH N., GAWALI P. Anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility of earthquake-affected soft sediments:example from Ther village, Latur, Maharashtra, India[J]. Current Science, 2015, 108(4):708-712. http://www.currentscience.ac.in/php/toc.php?vol=108&issue=04 -





 下载:
下载: