STUDY ON PRESERVED-ORE FACTOR IN XIAZHUANG URANIUM ORE FIELD
-
摘要: 下庄矿田是我国落实的第一个花岗岩型铀矿田,矿床和矿点分布在贵东岩体的东部,受构造、岩性联合控制,矿化类型有硅化带型(群脉型)、交点型、蚀变碎裂岩型和花岗岩外接触带变质砂岩型,矿床形成后经历了华南地壳的新生代特别是晚新生代的隆升和剥露。成矿后的构造活动研究表明,上洞断裂和马屎山断裂是矿田的保矿构造,它们形成时代较新,联合控制了下庄断块的下陷,保护了之前形成的铀矿免受或少受侵蚀破坏,这也是贵东岩体东部有矿西部无矿的根本所在。Abstract: Xiazhuang ore field is the first granite-type uranium ore field found in China, where the deposits and occurrences located in the eastern part of Guidong grante, controlled by structure and lithology. About uranium mineralization type, there are silicified zone type (group vein), intersection type, altered cataclastic rock type and metamorphic sandstone of the outer contact zone of granite. It had experienced the uplifting and exhumating of the crust in the South China during the Cenozoic, specially the late Cenozoic Era after the ore deposits formed. Data integration and field investigation shows that the Shangdong and horse feces Mountain fault are the protection-ore ones. The forming time is newer. The two faults which have together controlled Xiazhuang fault block undercutting, protect the uranium mine not or less being corroded and exhausted. This is why there is ore existing in the east part but not in west of Guidong granite.
-
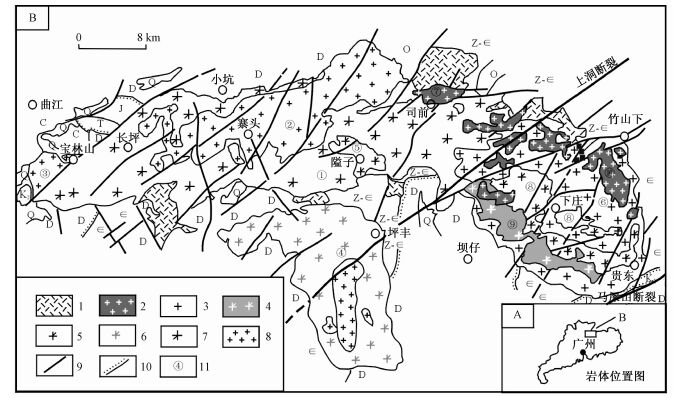
图 1 贵东复式花岗岩体位置及地质略图[7]
1—英安斑岩;2—细粒二云母花岗岩;3—中粗粒黑云母花岗岩;4—粗粒似斑状黑云母花岗岩;5—中粒似斑状二云母花岗岩;6—中粒似斑状黑云母花岗岩;7—中粗粒似斑状黑云母花岗岩;8—中细粒黑云母花岗岩;9—断层;10—不整合界线;11—岩体名称及编号(① 长坪岩体,② 寨头岩体,③ 宝林山岩体,④ 热水岩体,⑤ 隘子岩体,⑥ 下庄岩体,⑦ 司前岩体,⑧ 高栋岩体,⑨ 鲁溪岩体,⑩ 帽峰岩体)
Figure 1. Asketch geological map of the Guidong composite granite bodies
图 4 马屎山断裂剖面示意图[18]
1—上白垩统紫红色砂砾岩;2—马屎山断裂及运动方向;3—印支期片麻状花岗闪长岩
Figure 4. Section sketch map of Horse Feces Mountain fault
-
[1] 陈永坤. 花岗岩型铀矿床是怎样突破的——301矿田发现和发展概况[R]. 南昌: 核工业270研究所, 1985.CHEN Yong-kun. How did the breakthrough for granite-type uranium deposit be made:Summary of discovery and development of the 301 Ore Field[R]. Nanchang:No. 270 Research Institute of Nuclear Industry, 1985. [2] 邓平, 舒良树, 谭正中.诸广-贵东大型铀矿聚集区富铀矿成矿地质条件[J].地质论评, 2003, 49(5):486~494. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200305005.htmDENG Ping, SHU Liang-shu, TAN Zheng-zhong. The geological setting for the formation of rich uranium ores in Zhuguang-Guidong large-scale uranium metallogenetic area[J]. Geological Review, 2003, 49(5):486~494. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200305005.htm [3] 丁瑞钦, 梁天锡.下庄矿田构造岩浆演化与富铀成矿作用初探[J].铀矿地质, 2003, 19(1):21~27. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ200301003.htmDING Rui-qin, LIANG Tian-xi. Preliminary discussion on tectonic-magmatic evolution with respect to metalloginesis of rich uranium deposits in Xiazhuang ore-field[J]. Uranium Geology, 2003, 19(1):21~27. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ200301003.htm [4] 中国核工业地质局. 华南铀矿地质志[R]. 北京: 中国核工业地质局, 2005.China Nuclear Geology. Uranium ore geology in south China[R]. Beijing:China Nuclear Geology, 2005. [5] 李建红, 夏宗强. 贵东岩体及下庄铀矿田成岩成矿序列模式[C]//陈毓川, 薛春纪, 张长青. 第九届全国矿床会议论文集. 北京: 地质出版社, 2008: 203~204.LI Jian-hong, XIA Zong-qiang. Formation of the host rock and mineralization sequence pattern of Guidong granite massif and Xiazhuang uranium ore field[C]//CHEN Yu-chuan, XUE Chun-ji, ZHANG Chang-qing. Proceedings of the 9th National Mineral Deposit Conference. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2008:203~204. [6] 吴烈勤, 谭正中, 刘汝洲, 等.粤北下庄矿田铀矿成矿时代探讨[J].铀矿地质, 2003, 19(1):28~33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ200301004.htmWU Lie-qin, TAN Zheng-zhong, LIU Ru-zhou, et al. Discussion on uranium ore-formation age in Xiazhuang ore-field, northern Guandong[J]. Uranium Geology, 2003, 19(1):28~33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ200301004.htm [7] 沈渭洲, 凌洪飞, 邓平, 等. 贵东岩体(含热水岩体)[C]//周新民. 南岭地区晚中生代花岗岩成因与岩石圈动力学演化. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007: 394~435.SHEN Wei-zhou, LING Hong-fei, DENG Ping, et al. The Guidong granite massif (hydrothermal rock mass)[C]//ZHOU Xin-min. The Late Mesozoic granite genesis and lithosphere dynamic evolvement in the Nanling Region. Beijing:Science Press, 2007:394~435. [8] 林锦荣.论贵东岩体东西部花岗岩岩石学特征和铀成矿条件差异性[J].铀矿地质, 1992, 8(2):93~99. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ199202005.htmLIN Jin-rong. On the differences of the lithological features of granite and uranium ore-formation conditions between east and west parts of Guidong granite massif[J]. Uranium Geology, 1992, 8(2):93~99. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ199202005.htm [9] 核工业290研究所. 下庄矿田滑脱构造系控矿特征及深部突破口的选择[R]. 韶关: 核工业290研究所, 1995.No. 290 Research Institute of Nuclear Industry. Ore-control features of the decollement structure system and selection of the deep breakthrough in Xiazhuang ore field[R]. Shaoguan:No. 290 Research Institute of Nuclear Industry, 1995. [10] 地质矿产部地质辞典办公室.地质大辞典[M].北京:地质出版社, 2005.Geological dictionary office of Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources. Great geological dictionary[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2005. [11] 叶定衡, 王新政, 李增悦.中国及毗邻海区新构造图(1:5000000) 说明书[M].北京:地质出版社, 1995.YE Ding-heng, WANG Xin-zheng, LI Zeng-yue. The meotectonic map of China and adjacent sea areas (1:5000000)[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1995. [12] 陈庆宣, 王维襄, 孙叶, 等.岩石力学与构造应力场分析[M].北京:地质出版社, 1998:159~186.CHEN Qing-xuan, WANG Wei-xiang, SUN Ye, et al. Rock mechanics and analysis of tectonic stress field[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1998:159~186. [13] 赖锡安, 黄立人, 徐菊生.中国大陆现今地壳运动[M].北京:地震出版社, 2004.LAI Xi-an, HUANG Li-ren, XU Ju-sheng. Current crustal movement in Chinese mainland[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 2004. [14] 周友华, 胡奉湘, 燕为民, 等.地壳构造运动·地震·地震预报的新探索[M].北京:地质出版社, 2009.ZHOU You-hua, HU Feng-xiang, YAN Wei-min, et al. Research on geotectonic movement, earthquake and earthquake prediction[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2009. [15] 广东省地震局.广东省地震构造概论[M].北京:地震出版社, 2000:44~117.Earthquake Administration of Guangdong Province. Introduction of earthquake structures in Guangdong Province[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 2000:44~117. [16] 柏道远, 李长安, 王先辉, 等.第四纪洞庭盆地澧县凹陷构造活动特征及动力学机制探讨[J].地球学报, 2010, 31(1):43~55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201001008.htmBAI Dao-yuan, LI Chang-an, WANG Xian-hui, et al. Tectonic activities and dynamic mechanisms of the Quaternary Lixian sag of Dongting Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2010, 31(1):43~55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201001008.htm [17] 张万良.华南红盆与铀矿保存[J].矿产与地质, 2007, 21(2):118~121. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD200702001.htmZHANG Wan-liang. Red basin in south China and uranium ore conservation[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2007, 21(2):118~121. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD200702001.htm [18] 广东省核工业地质局296大队. 广东省下庄矿田及两翼铀矿地质填图总结报告(比例尺1: 10000)[R]. 广州: 广东省核工业地质局296大队, 1994.Guangdong Province Nuclear Industry Geological Bureau 296 Brigade. Summary report of uranium ore geologic mapping in Xiazhuang ore field and its both flanks in Guangdong Province (1:10000)[R]. Guangzhou:Guangdong Province Nuclear Industry Geological Bureau 296 Brigade, 1994. [19] 王军, 赖中信, 张辉仁, 等.粤北下庄矿田新生代构造演化及其对铀成矿的影响[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2011, 35(3):355~363. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201103004.htmWANG Jun, LAI Zhong-xin, ZHANG Hui-ren, et al. Cenozoic tectonic evolution and its influence on uranium ore-forming processes in the Xiazhuang ore field, northern Guangdong Province[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2011, 35(3):355~363. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201103004.htm [20] 张万良.桃山铀矿田桃山断裂及其保矿作用[J].地质论评, 2008, 54(6):768~774. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200806008.htmZHANG Wan-liang. Taoshan fault and its ore-conservation in Taoshan uranium orefield[J]. Geological Review, 2008, 54(6):768~774. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200806008.htm [21] 张万良, 吕川, 韦金文.鹿井铀矿田成矿地质特征及成因[J].矿床地质, 2010, 29(增刊):162~164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2010S1086.htmZHANG Wan-liang, LÜ Chuan, WEI Jin-wen. Metallogenic geologic feature and genesis of Lujing uranium ore field[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2010, 29(Supp.):162~164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2010S1086.htm [22] 张万良, 刘德长, 李子颖, 等.相山铀矿田多源地学信息示范应用[M].北京:地质出版社, 2009.ZHANG Wan-liang, LIU De-chang, LI Zi-ying, et al. Demonstrational application of the multi-source geoscience information in Xiangshan uranium ore field[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2009. [23] 曹小兵, 吕古贤, 胡宝群, 等.相山矿田沙洲铀矿床围岩蚀变地球化学特征[J].地质力学学报, 2012, 18(4):389~400. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20120404&journal_id=dzlxxbCAO Xiao-bing, LÜ Gu-xian, HU Bao-qun, et al. The wall rock alteration and its geochemical characteristics of the Shazhou deposit in Xiangshan uranium ore-field[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2012, 18(4):389~400. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20120404&journal_id=dzlxxb [24] 张万良.赣南河草坑铀矿田成矿地质特征及找矿目标类型[J].地质找矿论丛, 2005, 20(3):192~194, 214. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK200503008.htmZHANG Wan-liang. Ore-forming geological features and prospecting target types of Hecaokeng ore field in southern Jiangxi Province[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2005, 20(3):192~194, 214. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK200503008.htm -





 下载:
下载: