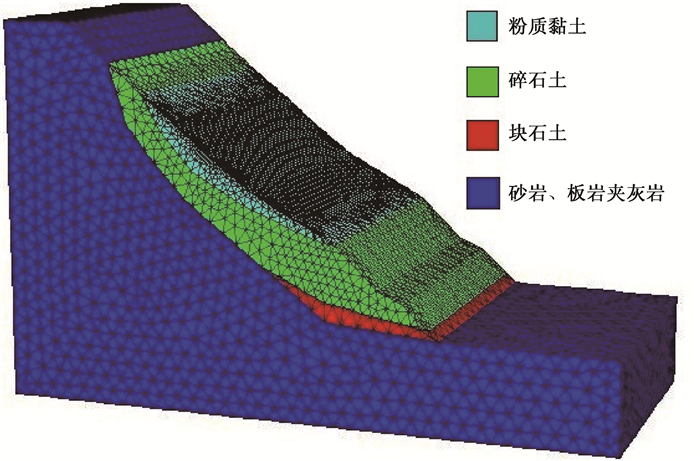
STUDY ON THE STABILITY OF HIGH SLOPE OF THE MINJIANG RIVER DOUBLE-TRACK BRIDGE
-
摘要: 成兰铁路岷江双线特大桥高边坡位于岷江地震带, 该区域属于高烈度地震强震频发区, 降雨量大且集中, 不良地质分布广, 在复杂环境因素的影响下, 极其容易引起边坡滑坡。在研究现场工程地质情况的基础上, 利用FLAC3D有限差分软件, 建立三维边坡模型, 进行天然、降雨、地震及降雨-地震耦合工况下的稳定性分析。研究结果表明, 天然工况下安全系数为1.318, 边坡处于稳定状态; 降雨工况下, 随降雨量的增加, 雨水入渗和加载作用增强, 位移高值区逐步扩大并逐渐向坡脚延伸, 25 mm/d、35 mm/d及45 mm/d降雨条件下的安全系数分别为1.001、0.932、0.912;地震工况下边坡不稳定, 坡腰中上部位移与加速度最大, 为易滑坡区域; 降雨-地震耦合工况下, 坡腰中上部极其不稳定, 且随降雨量增加, 滑体位移及加速度均增大。Abstract: The high slope of Double-track Bridge on Minjiang River of Chenglan Railway is located in Minjiang River seismic belt, which is a high and frequent seismic region, with substantial concentrated rainfall and widespread unfavorable geology. Under the impact of the complicated environmental factor, it may give rise to the slope slide easily. In this paper, 3D slope mode is established with FLAC3D finite difference software based on the study on the geology of field engineering, and stability analysis in such working conditions as the natural rainfall, earthquake and coupling of rainfall and earthquake. According to the results, the safety coefficient in natural working condition is 1.318, and the slope is in stable status. In rainfall working condition, with the increase of rainfall, the rainwater infiltration and loading function is enhanced, and the displacement high-value area expands gradually and extends to the slope toe. In 25 mm/d, 35 mm/d and 45 mm/d rainfall condition, the safety coefficient is 1.001, 0.932 and 0.912 respectively. The slope is quite unstable in earthquake working condition, and the upside displacement and accelerated speed of the mid-slope is the greatest, and it is easy-sliding area. In the coupling working condition of rainfall and earthquake, the upside of mid-slope is extremely unstable, and with the increase of rainfall, the displacement and accelerated speed would increase.
-
Key words:
- slopes /
- earthquake /
- rainfall /
- coupling /
- stability /
- numerical simulation
-
表 1 边坡岩石力学参数
Table 1. Natural and rainfall condition parameters
工况 岩土体类型 D/(kg·m-3) c/kPa $ \phi $/(°) E/GPa μ σt/MPa 安全系数 天然 砂岩、板岩夹灰岩 2400 3.30E+07 55.0 2.30E+10 0.26 5.00E+05 1.31875 块石土 2200 1.05E+04 40.0 8.20E+08 0.28 0.00E+00 碎石土 2100 1.11E+04 40.0 8.10E+08 0.23 0.00E+00 粉质黏土 1900 2.20E+04 20.0 1.00E+08 0.35 0.00E+00 25 mm/d(降雨量) 砂岩、板岩夹灰岩 2450 2.81E+07 46.7 2.30E+10 0.26 4.25E+05 1.00125 块石土 2320 8.93E+03 34.0 8.20E+08 0.28 0.00E+00 碎石土 2210 9.44E+03 34.0 8.10E+08 0.23 0.00E+00 粉质黏土 2030 1.87E+04 17.0 1.00E+08 0.35 0.00E+00 35 mm/d(降雨量) 砂岩、板岩夹灰岩 2470 2.60E+07 43.8 2.30E+10 0.26 3.93E+05 0.93245 块石土 2340 8.29E+03 31.4 8.20E+08 0.28 0.00E+00 碎石土 2230 8.62E+03 31.4 8.10E+08 0.23 0.00E+00 粉质黏土 2100 1.73E+04 15.7 1.00E+08 0.35 0.00E+00 45 mm/d(降雨量) 砂岩、板岩夹灰岩 2485 2.39E+07 39.9 2.30E+10 0.26 3.73E+05 0.91225 块石土 2357 7.58E+03 29.2 8.20E+08 0.28 0.00E+00 碎石土 2247 8.11E+03 29.2 8.10E+08 0.23 0.00E+00 粉质黏土 2148 1.62E+04 15.1 1.00E+08 0.35 0.00E+00 注:D-容重;c-粘聚力;$ \phi $-内摩擦角;E-弹性模量;μ-泊松比;σt-抗拉强度 表 2 耦合工况设置
Table 2. Multi load-case set
工况 降雨条件/(mm·d-1) 地震条件 耦合工况一 25 汶川地震波 耦合工况二 35 汶川地震波 耦合工况三 45 汶川地震波 -
[1] 蒋中明, 熊小虎, 曾铃.基于FLAC3D平台的边坡非饱和降雨入渗分析[J].岩土力学, 2014, 35(3):855~861. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201403041.htmJIANG Zhong-ming, XIONG Xiao-hu, ZENG Ling. Unsaturated seepage analysis of slope under rainfall condition based on FLAC3D[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(3): 855~861. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201403041.htm [2] 刘春玲, 祁生文, 童立强, 等.利用FLAC3D分析某边坡地震稳定性[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(16):2730~2736. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=10348267LIU Chun-ling, QI Sheng-wen, TONG Li-qiang, et al. Stability analysis of slope under earthquake with FLAC3D[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(16): 2730~2736. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=10348267 [3] 齐信, 唐川, 陈州丰, 等.汶川地震强震区地震诱发滑坡与后期降雨诱发滑坡控制因子耦合分析[J].工程地质学报, 2012, 20(4):522~531. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201204007.htmQI Xin, TANG Chuan, CHEN Zhou-feng, et al. Coupling analysis of control factors between earthquake-induced landslide and subsequent rainfall-induced landslide in epicenter area of Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2012, 20(4): 522~531. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201204007.htm [4] 龚文俊, 李明永, 吴志坚.降雨和地震耦合作用对滑坡稳定性的影响——以甘肃西和Ⅲ号滑坡为例[J].西北地震学报, 2012, 34(2):161~166. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ201202009.htmGONG Wen-jun, LI Ming-yong, WU Zhi-jian. Stability analysis of landslide under coupling action of earthquake and rainfall: Taking the No.Ⅲ landslide of Xihe County, Gansu Province as an example [J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 2012, 34(2): 161~166. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ201202009.htm [5] 杜宇本, 袁传宝, 王彦东.成兰铁路主要地质灾害与地质选线[J].铁道工程学报, 2012, (8):11~15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC201208003.htmDU Yu-ben, YUAN Chuan-bao, WANG Yan-dong, et al.Major geological hazard and geological alignment of chengdu-lanzhou Railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2012, 8(167):11~15. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC201208003.htm [6] 杨昌义, 李光辉, 杜宇本.汶川大地震灾区成兰铁路地质选线与工程对策[J].路基工程, 2010, (3):117~119. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJGC201003046.htmYANG Chang-yi, LI Guang-hui, DU Yu-ben. Geological route selection and engineering devices for Chengdu-Lanzhou railway in Wenchuan earthquake affected area[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2010, (3): 117~119. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJGC201003046.htm [7] 叶海林, 郑颖人, 李安洪, 等.成兰铁路茂县车站高边坡抗震设计研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2011, 30(S2):4117~4122. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2011S2101.htmYE Hai-lin, ZHANG Ying-ren, Li An-hong, et al. Seismic design study of high slope at Maoxian Station in Chengdu-Lanzhou railway[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 30(S2): 4117~4122. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2011S2101.htm [8] 陈育民, 徐鼎平.FLAC/FLAC3D基础与工程实例[M].北京:中国水利水电出版社, 2008:94~97.CHEN Yu-min, XU Ding-ping. The FLAC/FLAC3D foundation and engineering examples[M]. Beijing: Water Conservancy and Hydropower Press, 2008: 94~97. [9] 郑文棠.基于FLAC3D的强度折减法和点安全系数法对比[J].水利与建筑工程学报, 2010, 8(4):54~57. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSJS201004017.htmZHENG Wen-tang. Contrast on strength reduction method and point safety factor method with FLAC3D [J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering, 2010, 8(4): 54~57. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSJS201004017.htm [10] 杨明成, 康亚明.容重增加法在边坡稳定性分析中的应用[J].哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2009, 41(6):187~190. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBX200906043.htmYANG Ming-cheng, KANG Ya-ming. Application of gravity increase method in slope stability analysis[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2009, 41(6): 187~190. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBX200906043.htm -





 下载:
下载: