GEOCHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND TECTONIC SETTING OF UPPER JURASSIC GRANITE FROM NORTHERN CHIFENG, INNER MONGOLIA
-
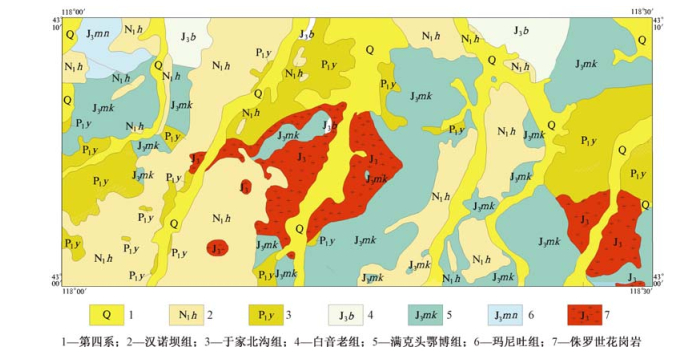
摘要: 通过内蒙古赤峰北部地区花岗岩地球化学数据与国内外各类型花岗岩资料的对比和判别, 认为内蒙古赤峰北部地区花岗岩以Ⅰ型为主, 少数具有A型花岗岩的特征。具有高钾和富碱的特点, 微量元素表现为富集Ba、Th、K等大离子亲石元素(LILE), 而高场强元素(HFSE)Nb、Ti等则相对亏损, 其中Sr和P出现强烈亏损。轻重稀土分馏明显, 重稀土未见明显分馏。Eu有明显的负异常(δ Eu值在0.30~0.88之间), 稀土模式呈现为明显的Eu异常右倾谱系。结合前人的研究资料, 初步认为在造山后的伸展减薄环境中, 压力的降低和软流圈的上涌对地壳的部分熔融起到了一定的作用, 从而为研究区花岗岩的形成提供了条件。Abstract: :Comparison geochemical characteristics of granite from northern Chifeng, Inner Mongolia with various type of granite at home and abroad and the discrimination show that most of the Chifeng granite belongs to Ⅰ-type granite, and a small number of A-type with.It is with the characteristic of high-K and alkali.The trace elements is rich in Ba, Th, K and other large ion lithophile elements (LILE), while the high field strength elements (HFSE) Nb, Ti, etc.are relatively depleted, which appear strongly depleted in Sr and P.LREE fractionation significantly, no significant fractionation of heavy rare earth.Significant negative Eu anomalies (δ Eu between the 0.3-0.843), REE patterns show significant Eu anomalies for the right-wing pedigree.Integrating the outcome of this paper and previous studies, we infer that the granite formed under the stretching and thinning environment.In this process, reducing the pressure and the upwelling of asthenosphere partial melting of the crust plays a role, so as to provide the conditions for the formation of granite.
-
Key words:
- Chifeng /
- granite /
- geochemical characteristics /
- tectonic environment
-
图 5 内蒙古赤峰北部晚侏罗世花岗岩微量元素蛛网图(原始地幔数据参见文献[11])
Figure 5. Primitive mantle-normalized trace element spidergrams of Upper Jurassic granite from northern Chifeng, Inner Mongolia
表 1 内蒙古赤峰北部晚侏罗世花岗岩主量元素分析结果
Table 1. Major element compositions of the upper Jurassic granite from Northern Chifeng, Inner Mongolia

表 2 内蒙古赤峰北部晚侏罗世花岗岩微量元素分析结果
Table 2. Trace element abundance of the upper Jurassic granite from Northern Chifeng, Inner Mongolia

-
[1] 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等.花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J].岩石学报, 2007, 023 (06):1217~1238.WU Fu-yuan, LI Xian-hua, YANG Jin-hui, et al. Discussions on the petrogenesis of granites[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23 (6):1217~1238. [2] 许文良, 王清海, 王冬艳, 等.华北克拉通东部中生代岩石圈减薄的过程与机制:中生代火成岩和深源捕虏体证据[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11 (3):309~317. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200403029XU Wen-liang, WANG Qing-hai, WANG Dong-yan, et al. Processes and mechanism of Mesozoic lithospheric thinning in eastern North China Craton: Evidence from Mesozoic igneous rocks and deep2seated xenoliths[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11 (3):309~317. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200403029 [3] 李锦轶, 高立明, 孙桂华, 等.内蒙古东部双井子中三叠世同碰撞壳源花岗岩的确定及其对西伯利亚与中朝古板块碰撞时限的约束[J].岩石学报, 2007, 023 (03):565~582. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200703004LI Jin-yi, GAO Li-ming, SUN Gui-hua, et al. Shuangjingzi middle Triassic syn-collisional crust-derived granite in the east Inner Mongolia and its constraint on the timing of collision between Siberian and Sino-Korean paleo-plants[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23 (3):565~582. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200703004 [4] 吴华英, 张连昌, 陈志广, 等.内蒙古西拉木伦成矿带库里吐钼_铜_矿区二长花岗岩地球化学、构造环境及含矿性分析[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24 (4):867~878. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ysxb200804026&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQWU Hua-ying, ZHANG Lian-chang, CHEN Zhi-guang, et al. Geochemistry, tectonic setting and mineralization potentiality of the ore-bearing monzogranite in the Kulitu molybdenum (copper) deposit of Xar Moron metallogetic belt, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24 (4):867~878. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ysxb200804026&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [5] 林强, 葛文春, 吴福元, 等.大兴安岭中生代花岗岩类的地球化学[J].岩石学报, 2004, 20 (3):403~412. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ysxb200403004&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQLIN Qiang, GE Wen-chun, WU Fu-yuan, et al. Geochemistry of Mesozoic granites in Da Hinggan Ling ranges[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2004, 20 (3):403~412. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ysxb200403004&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [6] 代军治, 毛景文, 杨富全, 等.华北地台北缘燕辽钼(铜)成矿带矿床地质特征及动力学背景[J].矿床地质, 2006, 5: 596~615. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=23232826Dai Jun-zhi, Mao Jing-wen, Yang Fu-quan, et al. Geological characteristics and geodynamic background of molybdenum (copper) deposits along Yanshan-Liaoning metallogenic belt on northern margin of North China block[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2006, 5: 596~615. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=23232826 [7] 肖庆辉, 邱瑞照, 邓晋福, 等.中国花岗岩与大陆地壳生长方式初步研究[J].中国地质, 2005, 32 (3):343~352. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dizi200503001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQXIAO Qing-hui, QIU Rui-zhao, DENG Jin-fu, et al. Granitoids and continental crustal growth modes in China[J]. Geology in China, 2005, 32 (3):343~352. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=dizi200503001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [8] 张旗, 王焰, 潘国强, 等.花岗岩源岩问题-关于花岗岩的研究思考之四[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24 (6):1193~1204. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ysxb200806004&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQZHANG Qi, WANG Yan, PAN Guo-qiang, et al. Sources of granites: Some crucial questions on granite study (4)[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24 (6):1193~1204. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ysxb200806004&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [9] 邵济安, 张履桥, 牟堡磊.大兴安岭中生代伸展造山过程中的岩浆作用[J].地学前缘, 1999, 6 (4):339~346. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy199904017SHAO Ji-an, ZHANG Lü-qiao, MU Bao-lei. Magmatism in the Mesozoic extending orogenic process of Da Hinggan Mountains[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 1999, 6 (4):339~364. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy199904017 [10] Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25: 956~983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956 [11] PitcherW S, Atherton M D, Cobbing E J, et al. Magmatism at a plate edge: The Pernvian Andes. Blackie, Glasgow [J]. 1985 [12] 战明国.花岗岩类分类与定位机制研究动向和进展[J].中国区域地质, 1998, 17 (2):182~188. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zqyd802.011&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQZHAN Ming-guo. Trend and progress in the study of the classification and emplacement mechism of granitoids[J]. Regional Geology of China, 1998, 17 (2):182~188. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=zqyd802.011&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [13] 刘伟, 潘小菲, 谢烈文, 等.大兴安岭南段林西地区花岗岩类的源岩:地壳生长的时代和方式[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23 (2):441~460. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-DZDQ200801003048.htmLIU Wei, PAN Xiao-fei, XIE Lie-wen, et al. Sources of material for the Linxi granitoids the southern segment of the Da Hinggan Mountains: When and how continental crust grew[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23 (2):441~460. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-DZDQ200801003048.htm [14] Gideon Rosenbauma, Weinberg, Roberto F et. al. The geodynamics of lithospheric extension[J]. Tectonophysics, 2008, 7 (16):1~8. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195108003454 [15] 马寅生, 崔盛芹, 赵越, 等.华北北部中新生代构造体制的转换过程[J].地质力学学报, 2002, 8 (1):15~25. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20020103&journal_id=dzlxxbMA Yin-sheng, CUI Sheng-qin, ZHAO Yue, et al. The transformation process of Mesozoic-Cenozoic tectonic regime in the north of North China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2002, 8 (1):15~25. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20020103&journal_id=dzlxxb [16] Collins W J. Upper-and middle-crustal response to delamination: An example from the Lachlan fold belt, eastern Australia [J]. Geology, 1994, 22: 143~146. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1994)022<0143:UAMCRT>2.3.CO;2 -





 下载:
下载: