GRAIN-SIZE DISTRIBUTION AND GENESIS OF LOESS IN THE QINGZHOU AREA, SHANDONG
-
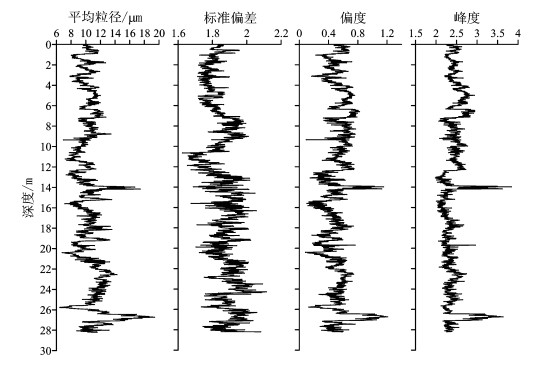
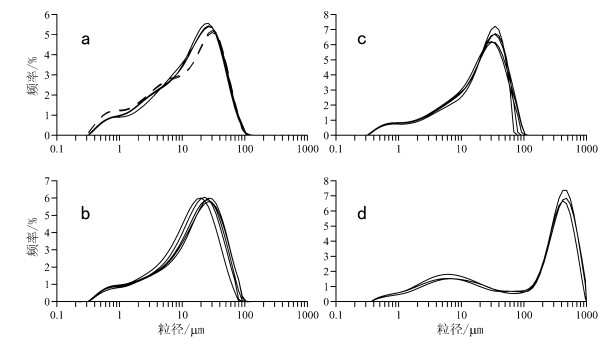
摘要: 在鲁中山地北侧的山间谷地及山麓地带广泛发育厚度不一的黄土堆积。对该区青州傅家庄黄土剖面进行了系统的粒度分析, 并与黄土高原的第四纪黄土-古土壤、北京现代降尘、剖面附近的河流相样品进行了对比。结果表明, 青州黄土的粒度分布特征与北京现代降尘、黄土高原黄土非常相似, 与河流相样品则有很大的不同; 在整个序列中, 青州黄土粒度变化与黄土高原典型的风成黄土、古土壤一致, 黄土层颗粒粗, 古土壤层颗粒细。上述结果从沉积学的角度为青州黄土风成成因提供了证据。青州黄土的粒度组成特征及前人的研究表明, 青州黄土主要来源于沉积区以北的黄泛平原和莱州弯等地出露的海相地层, 其次是高空气流携带的西北内陆的远缘粉尘。Abstract: Loess deposits with varying thicknesses are widely distributed on intermontane valleys and piedmont zones on the northern side of the central Shandong mountainous region.A systematic grain-size analysis was performed along the Fujiazhuang loess section of the Qingzhou area.The analytic results of the samples were correlated with those of the samples taken from Quaternary loess-paleosol of the Loess Plateau, modern dust fallouts in Beijing and fluvial deposits.The results show that the grain-size distribution of the Qingzhou loess is very similar to that of modern dust fallouts in Beijing and loess of the Loess Plateau but notably different from that of the fluvial samples.In the whole loess-paleosol sequence, the grain-size variation of the Qingzhou loess is consistent with the typical eolian loess and paleosol of the Loess Plateau.The loess is coarse in size, while the paleosol is fine in size.The above-mentioned results provide evidence for the eolian origin of the Qingzhou loess in the sedimentological context.The grain-size distribution of the Qingzhou loess combined with the previous studies indicates that the main provenances of the Qingzhou loess are the marine strata exposed in the flood plain of the Yellow River and Laizhou Bay north of the sedimentary region and less commonly distal silt and dust carried by high-layer circulation from northwest inland.
-
Key words:
- Qingzhou,Shandong /
-
/ - loess-paleosol /
- grain size /
- origin
-
表 1 西峰马兰黄土、北京现代降尘和河流相样品粒度特征参数
Table 1. Characteristic grain-size parameters of the Malan loess of Xifeng, modern dust fallouts of Beijing and fluvial sediments

-
[1] 刘东生, 等.中国的黄土堆积[M].北京:科学出版社, 1985:1~ 55. [2] 刘东生, 等.黄土与环境[M].北京:科学出版社, 1985:1~ 43. [3] 曹家欣, 李培英, 石宁.山东庙岛群岛的黄土[J].中国科学(B辑)1987, 10 (10):1117~ 1122. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx200812010 [4] 杨钟健.山东益都、临朐、昌乐地区新生代地质[J].中国地质学会志, 1936, 15 (2):16. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199600985015 [5] Skertchly SBL.Concerning about loess and other deposits of North China[J].The Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society of London, 1895, 51:11~ 20. [6] 蒋忠信, 林志介, 陈加光, 等.胶济铁路黄土堆积的化石地层材料[J].宁夏工程技术, 2004, 3 (3):214 ~ 220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7244.2004.03.004 [7] 郑洪汉, 朱照宇.山东半岛及苏皖北部黄土地层年代学研究[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1994, 14 (1):64~ 68. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400222303 [8] 刘乐军, 李培英, 王永吉.鲁中黄土粒度特征及其成因探讨[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 2 (20):81~ 86. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200001013 [9] 于洪军.中国东部陆架黄土成因的新探[J].第四纪研究, 1999, 7 (4):367~ 372. [10] 张祖陆.渤海莱州湾南岸平原黄土阜地貌及其古地理意义[J].地理学报, 1995, 9 (50):465~ 470. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500042471 [11] 张祖陆, 辛良杰, 聂晓红.山东黄土研究综述[J].地理科学, 2004, 24 (6):746~ 752. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2004.06.018 [12] 孙东怀, 鹿化煜.中国黄土粒度的双峰分布及其古气候意义[J].沉积学报, 2000, 18 (3):269~ 276. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cjxb200003001 [13] Friedman GM, Sanders JE.Principles of Sedimentology[M].New York:John Wiley & Sons, 1978.792. [14] Folk R, Ward WC.Brazos Rivervar.A study in significance of grain size parameters[J].Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1957.27 (1):3~ 26. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D [15] 李吉均, 方小敏.青藏高原隆起与环境变化研究[J].科学通报, 1998, 43 (15):1569~ 1574. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1998.15.001 [16] 刘东生, 郑绵平, 郭正堂.亚洲季风系统的起源和发展及其与两极冰盖和区域构造运动的时代耦合性[J].第四纪研究, 1998, (3):194~ 203. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1998.03.002 [17] 刘东生, 等.第四纪环境[M].北京:科学出版社, 1997:195~ 196. [18] Tsoar H, Pye K.Dust transport and the question of desert loess formation[J].Sedimentology, 1987, 34:139~ 154. doi: 10.1111/sed.1987.34.issue-1 -





 下载:
下载: