STUDY ON TECHNOLOGY OF SLOPE/LANDSLIDE STABILITY ANALYSIS AND EARLY WARNING UNDER HEAVY RAINFALL
-
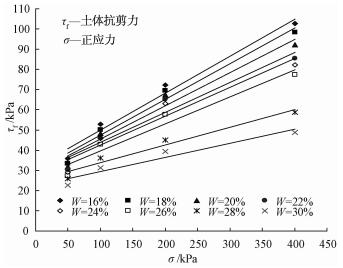
摘要: 以四川汉源二蛮山滑坡为例,根据现场滑坡情况勘查及室内试验确定土体参数;选择内置VBA为开发工具,开发基于ArcGIS的边(滑)坡稳定性分析插件,并据此得出研究区域危险区划评价图。研究结果表明,特殊地形条件、震后地质构造、连续强降雨以及坡体非饱和渗流等,使孔隙水压力增加和土基质吸力迅速减少,导致坡体滑移面处土的抗剪强度降低而发生滑坡;基于ArcGIS软件得出研究区域危险区划评价图,与滑坡的实际情况具有较高吻合度。研究成果为深入分析强降雨对边(滑)坡影响及边(滑)坡预警提供了新的途径。Abstract: Erman mountain landslide of Han Yuan County as the example, according to the exploration of landslide site conditions and indoor test of soil parameters; Choosing a built-in VBA for development tool to develop the side (slip) slope stability analysis plug-in based on ArcGIS, which makes the study regional risk zoning assessment diagram. Results show that the special topographical condition, geological structure after the earthquake, continuous heavy rains filled water load, slope unsaturated seepage flow, increasing the pore water pressure and rapidly reducing the soil matrix suction, leads to the shear strength decreased of the slope slip plane in the soil and finally landslides. Risk zoning evaluation chart of research area based on ArcGIS and the actual situation of slide have goodness of fit. Research result provides a new way for further analyzing the effect on side slope (slip) and warning under heavy rainfall condition.
-
Key words:
- earthquake slope /
- rainfall /
- landslide /
- stability assessment /
- intuitive forecasting
-
表 1 岩层物理力学参数
Table 1. Physical and mechanical parameters of rocks

表 1 模块数据库连接端口说明
Table 1. Module database

-
[1] 陶骞, 刘超, 朱志铭, 等.多工况下汉源二蛮山滑坡机理数值模拟[J].地质力学学报, 2012, 18(4):440~450. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20120410&journal_id=dzlxxbTAO Qian, LIU Chao, ZHU Zhi-ming, et al. Numerical simulation of landslide mechanism at Ermanshan in Hanyuan under different conditions[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2012, 18(4):440~450. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20120410&journal_id=dzlxxb [2] 王磊, 张春山, 杨为民, 等.基于GIS的甘肃省甘谷县地质灾害危险性评价[J].地质力学学报, 2011, 17(4):388~401. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20110409&journal_id=dzlxxbWANG Lei, ZHANG Chun-shan, YANG Wei-min, et al. Risk assessment of geo-hazards by using GIS in Gangu County, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2011, 17(4):388~401. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20110409&journal_id=dzlxxb [3] 魏丽, 单九生, 章毅之, 等.暴雨型滑坡灾害形成机理及预测方法研究思路[J].江西气象科技, 2005, 28(3):17~22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXQO200503002.htmWEI Li, SHAN Jiu-sheng, ZHANG Yi-zhi, et al. The formative mechanism and the research idea of prediction method about coast disaster of rainstorm model[J]. Jiangxi Meteorological Science and Technology, 2005, 28(3):17~22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXQO200503002.htm [4] 黄润秋, 邓荣贵, 张卓元.高边坡物质运动全过程模拟[M].成都:成都科技大学出版社, 1993:87~121.HUANG Run-qiu, DENG Rong-gui, ZHANG Zhuo-yuan. Full course numerical simulation of high slope material movement[M]. Chengdu:Press of Chengdu University of Science and Technology, 1993:87~121. [5] 唐芬, 郑颖人.基于双安全系数的边坡稳定性分析[J].公路交通科技, 2008, 25(11):39~44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2008.11.009TANG Fen, ZHENG Ying-ren. Slope stability analysis based on two safety factors[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2008, 25(11):39~44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2008.11.009 [6] 李兆平, 张弥.考虑降雨入渗影响的非饱和土边坡瞬态安全系数研究[J].土木工程学报, 2001, 34(5):57~61. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC200105012.htmLI Zhao-ping, ZHANG Mi. Effects of rain infiltration on transient safety of unsaturated soil slope[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2001, 34(5):57~61. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC200105012.htm [7] 谭春洪, 朱志铭, 周凯睿, 等.GIS在滑坡稳定性评价中的应用研究——以汉源县二蛮山为例[J].地质力学学报, 2013, 19(3):295~303. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20130306&journal_id=dzlxxbTAN Chun-hong, ZHU Zhi-ming, ZHOU Kai-rui, et al. Application of GIS in landslide stability evaluation:A case study for Ermanshan landslide[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2013, 19(3):295~303. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20130306&journal_id=dzlxxb [8] 陈丽霞, 殷坤龙, 刘长春.降雨重现期及其用于滑坡概率分析的探讨[J].工程地质学报, 2012, 20(5):745~750. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201205014.htmCHEN Li-xia, YAN Kun-Long, LIU Chang-chun. Return period statistics of extreme rainfall and application to landslide probability analysis[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2012, 20(5):745~750. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201205014.htm [9] 何专, 姚令侃.地震和暴雨工况下边(滑)坡稳定性分析方法评价[J].水土保持通报, 2009, 29(3):178~182. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB200903039.htmHE Zhuan, YAO Ling-kan. Assessment on the methods of analyzing slope (landslide) stability under earthquake and rainstorm conditions[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2009, 29(3):178~182. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB200903039.htm [10] 杜继稳.降雨型地质灾害预报预警——以黄土高原和秦巴山区为例[M].北京:科学出版社, 2010.DU Ji-wen. Forecasting and early warning for the geo-hazards caused by rainfall:Taking the geo-hazards in loess plateau and Qinling-Dabashan region as examples[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 2010. -





 下载:
下载: