TRANSMAGMATIC FLUID THEORY AND OREFIELD STRUCTURE
-
摘要: 从透岩浆流体成矿理论的角度对矿田构造进行了重新认识, 提出矿田构造系统是一种复杂性动力系统的观点。根据这个模型, 矿田构造是近场应力场与远场应力场强烈相互作用的产物。近场应力场由岩浆成矿系统而不是远场应力场派生, 因而不能由矿田构造反演区域构造, 但可以从区域构造限定矿田构造。矿田构造常有岩脉和热液脉充填, 因而是可识别的。利用构造统计学方法, 可以根据岩脉和/或热液脉的分布密度图(或等值线图)预测找矿靶区。Abstract: A new understanding of the ore-field structure is proposed. According to the theory of metallogeny by transmagmatic fluid (TMF), it is emphasized that the ore-field structure system is a complexity dynamic system. Based on this model, the ore-field structure deformation is resulted by strong interactions between the near-field and the far-field stress fields. The near-field stress field is induced by the magmatic mineral system instead of the far-field stress field. Accordingly, the regional structure can not be inversed by the ore-field structures, but it could constrain them. The ore-field fractures are often filled by magmatic and/or hydrothermal veins or veinlets, and hence can be recognized. Using the statistic method described in the structure geology, the density map (or contour map) of the magmatic and/or hydrothermal dikes can be used for prognosis of the prospecting targets.
-
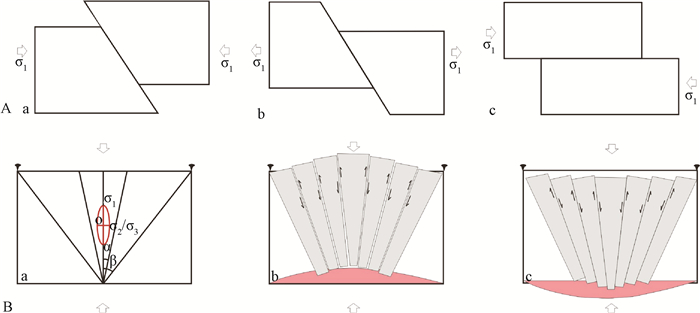
图 3 透岩浆流体成矿系统中屏蔽介质的变形机制[22]
a-挤压逆冲断层、伸展正断层和走滑断层裂隙网络活化的流体压力条件(基于孔隙流体因子-深度图解,限定条件为(σ1-σ3)<4T,T为抗拉强度,4T=40 MPa[21]);b-地震震群的Hill网模型(由三轴应力场中发育的相互联系的剪切、伸展和伸展-剪切裂隙构成),表示的是伸展正断层应力体制(竖直看)、挤压逆冲断层体制(侧面看)和走滑体制(平面看)
Figure 3. Deformation mechanism of the shielding material of transmagmatic fluid metallogenic system
-
[1] 陈宣华, 陈正乐, 杨农.区域成矿与矿田构造研究——构建成矿构造体系[J].地质力学学报, 2009, 15(1):1~19. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20090101&journal_id=dzlxxbCHEN Xuan-hua, CHEN Zheng-le, YANG Nong. Study on regional mineralizations and ore-field structures: Building of mineralizing tectonic systems[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2009, 15(1): 1~19. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20090101&journal_id=dzlxxb [2] 翟裕生, 吕古贤.构造动力体制转换与成矿作用[J].地球学报, 2002, 23(2):97~102. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200202000.htmZHAI Yu-sheng, LÜ Gu-xian. Transition of tectonic and dynamic regime and mineralization[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2002, 23(2): 97~102. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200202000.htm [3] 於崇文.地质系统的复杂性(上、下册)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2003.YU Chong-wen. The complexity of geological systems [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2003. [4] 罗照华, 莫宣学, 卢欣祥, 等.透岩浆流体成矿作用——理论分析与野外证据[J].地学前缘, 2007, 14(3):165~183. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200703021.htmLUO Zhao-hua, MO Xuan-xue, LU Xin-xiang, et al. Metallogeny by trans-magmatic fluids: Theoretical analysis and field evidence[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007, 14(3): 165~183. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200703021.htm [5] 罗照华, 卢欣祥, 陈必河, 等.透岩浆流体成矿作用导论[M].北京:地质出版社, 2009:1~177.LUO Zhao-hua, LU Xin-xiang, CHEN Bi-he, et al. Introduction to the metallogenic theory on the transmagmatic fluids[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2009. [6] 刘瑞珣, 吕古贤.地质作用深度测算中的问题[J].地质力学学报, 2000, 6(3):45~49. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20000335&journal_id=dzlxxbLIU Rui-xun, LÜ Gu-xian. Considerations on determination of the depth of geological processes[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2000, 6(3): 45~49. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20000335&journal_id=dzlxxb [7] 翟裕生.论成矿系统[J].地学前缘, 1999, 6(1):14~28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201104004.htmZHAI Yu-sheng. On the metallogenic system[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 1999, 6(1): 14~28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201104004.htm [8] 翟裕生, 邓军, 彭润民, 等.成矿系统论[M].北京:地质出版社, 2010.ZHAI Yu-sheng, DENG Jun, PENG Run-min, et al. Metallogenic system theory[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2010. [9] 汤中立.中国的小岩体岩浆矿床[J].中国工程科学, 2002, 4(6):9~12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKX200206002.htmTANG Zhong-li. Magmatic ore deposits in small rockbody in China[J]. Engineering Sciences, 2002, 4(6): 9~12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKX200206002.htm [10] 罗照华, 卢欣祥, 刘翠, 等.岩浆热液成矿理论的失败:原因和出路[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2011, 41(1):1~11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201101002.htmLUO Zhao-hua, LU Xin-xiang, LIU Cui. On failing of the magmatic hydrothermal metallogenic theory: The causes and the new departure[J]. Journal of Jinlin University: Earth Science Edition, 2011, 41(1): 1~11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201101002.htm [11] Candela P A. A review of shallow, ore-related granites: textures, volatiles, and ore metals[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997, 38(12): 1619~1633. doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.12.1619 [12] Campbell I. Glossary of geology [M]. New York: American Geological Institute, 1973. [13] Bachmann O, Bergantz G W. Deciphering magma chamber dynamics from styles of compositional zoning in large silicic ash flow sheets[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2008, 69: 651~674. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2008.69.17 [14] 罗照华.流体-熔体强相互作用的成矿功能[J].矿物学报, 2011, (增刊):503~504. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2011S1255.htmLUO Zhao-hua. The mineralization function of fluid-melt strong interaction[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2011, (Supp.): 503~504. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2011S1255.htm [15] Miller C F, Wark D A. Supervolcanoes and their explosive supereruptions[J]. Elements, 2008, 4: 11~16. doi: 10.2113/GSELEMENTS.4.1.11 [16] Bachmann O, Bergantz G W. Gas percolation in upper-crustal silicic crystal mushes as a mechanism for upward heat advection and rejuvenation of near-solidus magma bodies[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2006, 149: 85~102. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2005.06.002 [17] 罗照华, 卢欣祥, 许俊玉, 等.成矿侵入体的岩石学标志[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(8):2247~2254. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201008003.htmLUO Zhao-hua, LU Xin-xiang, XU Jun-yu, et al. Petrographic indicators of the ore-bearing intrusions[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(8): 2247~2254. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201008003.htm [18] Baker D R. Granitic melt viscosity and dike formation[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1998, 20(9/10): 1395~1404. http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=10675730 [19] Zotov I A.Transmagmatic magmatizme fluids and ore formation[M]. Moscow: Nauka, 1989: 1~214. [20] Korzhinskii D S. Granitization as magmatic replacement[J]. Izvestiya Akademii Nauk Kazakhskoi SSR, Seriya Geologicheskaya, 1952, 2: 56~69. doi: 10.1134/S1819714009010059 [21] Etheridge M A. Differential stress magnitudes during regional deformation and metamorphism: Upper bound imposed by tensile fracturing[J]. Geology, 1983, 11: 231~234. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1983)11<231:DSMDRD>2.0.CO;2 [22] 张永北.龙陵—瑞丽走滑体系中段自相似结构与热液成矿定位[J].地质学报, 1999, 73(4):334~341. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE199904004.htmZHANG Yong-bei. Self-similar texture of the Mid-Longling-Ruili strike-slip system and the location of hydrothermal deposits[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1999, 73(4): 334~341. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE199904004.htm [23] Simmons S F, Brown K L. Gold in magmatic hydrothermal solutions and the rapid formation of a giant ore deposit[J]. Science, 2006, 314: 288~291. doi: 10.1126/science.1132866 [24] Annen C, Blundy J D, Sparks R S J. The genesis of intermediate and silicic magmas in deep crustal hot zones[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2006, 47(3): 505~539. https://academic.oup.com/petrology/article/47/3/505/1536924/The-Genesis-of-Intermediate-and-Silicic-Magmas-in [25] Campbell I H. Large igneous provinces and the mantle plume hypothesis[J]. Elements, 2005, 1: 265~269. doi: 10.2113/gselements.1.5.265 [26] 郭晶, 罗照华, 刘晓, 等.利用宽谱系岩墙群进行靶区定位的数值化方法:以新疆南阿拉套山为例[J].中国地质, 2013, 40(2):423~429. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201302007.htmGUO Jing, LUO Zhao-hua, LIU Xiao, et al. A quantitative method for target prediction using the wide composition-spectrum dike swarms: A case study of the South Alataw Mountain in Xinjiang[J]. Geology in China, 2013, 40(2): 423~429. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201302007.htm [27] 罗照华, 卢欣祥, 王秉璋, 等.造山后脉岩组合与内生成矿作用[J].地学前缘, 2008, 15(4):1~12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200804002.htmLUO Zhao-hua, LU Xin-xiang, WANG Bing-zhang, et al. Post orogenic dike complexes and implications for metallogenesis[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2008, 15(4): 1~12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200804002.htm [28] 罗照华, 陈必河, 江秀敏, 等.利用宽谱系岩墙群进行勘查靶区预测的初步尝试:以南阿拉套山为例[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(7):1949~1965. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201207002.htmLUO Zhao-hua, CHEN Bi-he, JIANG Xiu-min, et al. A preliminary attempt for targeting prospecting districts using the wide composition-spectrum dike swarms: An example of the South Alatao Mountains, Xinjiang, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(7): 1949~1965. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201207002.htm -





 下载:
下载: