CHARACTERISTICS OF POLLEN ASSEMBLAGES IN SURFACE SOILS IN THE MAQU-HONGYUAN AREA, ZOIGÊ PLATEAU, NORTHERN SICHUAN
-
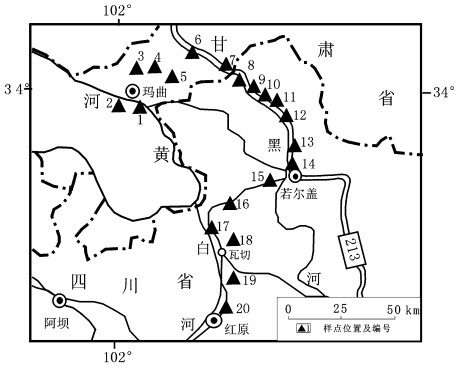
摘要: 通过对四川若尔盖高原玛曲-红原一带20个表土孢粉样的分析, 研究了该区域表土孢粉组合与现代植被的关系。结果显示, 玛曲-红原一带表土的孢粉组合基本反映了现代植被的整体特征, 与现代植被在植被类型、植被带的空间排列、主要建群种属和优势种属等方面基本一致。依据孢粉的百分含量, 可以划分为亚高山灌丛植被区, 亚高山灌丛、亚高山草甸植被区和高寒草甸、草原植被区3个植被带。表土花粉的代表性因种属的不同而各有差异, 松属和菊科花粉具超代表性, 云杉属花粉的代表性较好, 禾本科和莎草科具低代表性, 而桦木属则不具有超代表性, 可能与桦木属花粉不易搬运有关。3个植被区中的表土孢粉的种类、比例与现代植被均存在一定的差别, 这可能与植被退化有关。Abstract: In order to investigate the relationship between the surface pollen and modern vegetation, 20 surface soil samples collected from the Maqu-Hongyuan area on the Zoigê Plateau, Sichuan, were analyzed and the relationship between the surface pollen assemblages and modern vegetation in the study area were studied.The results show that the surface pollen assemblages in the area approximately reflect the whole features of the modern vegetation and are basically similar to the features of the modern vegetation in respect to vegetation types, spatial arrangement of vegetation zones and main assemblageestablished and dominant genera and species.Three vegetation zones may be distinguished by pollen percentages; they are the subalpine shrub, subalpine shrub and subalpine meadow, and alpine meadow and steppe vegetation zones.The representation of surface pollen varies with genera and species.Pinus and Compositae pollen are overrepresented and Picea pollen is moderately represented, while Gramineae and Cyperaceae pollen are underrepresented.Betula pollen is not overrepresented, which is possibly due to difficulty in transport.The genera and percentages of the surface pollen in the three vegetation zones show certain difference from those of the modern vegetation, which may be related to vegetation degeneration.
-
Key words:
- Zoigê Plateau /
- surface pollen assemblage /
- pollen analysis /
- vegetation /
-
-
[1] 李月丛, 许清海, 阳小兰, 等.内蒙古岱海表层沉积物中孢粉的分布及来源[J].古地理学报, 2004, 6(3):316~ 328. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2004.03.006 [2] 童国榜, 张俊牌, 严富华, 等.华北平原东部地区晚更新世以来的孢粉序列与气候分期[J].地震地质, 1991, 13 (3):259~ 268. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1991-DZDZ199103012.htm [3] 许清海, 李月丛, 阳小兰, 等.北方草原区主要群落类型表土花粉分析[J].地理研究, 2005, 24(3):394~ 402. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2005.03.008 [4] 张佳华, 孔昭宸, 杜乃秋.北京地区百花山东灵山表土花粉的特征分析[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1996, 16(3): 101~ 113. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDZ603.009.htm [5] Wright HE.The use of surface samples in Quaternary pollen analysis[J].Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 1967, 2:321 ~ 330. doi: 10.1016/0034-6667(67)90162-5 [6] Hjelld LK.Relationships between pollen and plants in human-influenced vegetation types using presence-absence data in western Norway[J].Rev.Palaeobot.Palynol, 1997, 99:1~ 16. doi: 10.1016/S0034-6667(97)00041-9 [7] 沈才明, 唐领余, 王苏民, 等.若尔盖盆地RM孔孢粉记录及其年代序列[J].科学通报, 2005, 50 (3):246~ 254. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2005.03.009 [8] 王富葆, 阎革, 林本海.若尔盖高原泥炭δ13C的初步研究[J].科学通报, 1993, 38(1):65~ 67. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1993.01.019 [9] 王苏民, 薛滨.中更新世以来若尔盖盆地环境演化与黄土高原比较研究[J].中国科学(D辑), 1996, 26 (4):323 ~ 328. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.1996.04.006 [10] 周卫建, 卢雪峰, 武振坤, 等.若尔盖高原全新世气候变化的泥炭记录与加速器放射性碳测年[J].科学通报, 2001, 46(12):1040~ 1044. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.12.018 [11] 王燕, 赵志中, 乔彦松, 等.川北若尔盖高原红原泥炭剖面孢粉记录的晚冰期以来古气候古环境的演变[J].地质通报, 2006, 25 (7):827~ 832. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.07.009 [12] 四川植被协作组.四川植被[M].成都:四川人民出版社, 1980:71~ 76, 324~ 329. [13] 黄大.甘肃植被[M].兰州:甘肃科学技术出版社, 1997:178~ 182. [14] 李文漪.中国第四纪植被与环境[M].北京:科学出版社, 1998:1~ 50. [15] 杨永兴.若尔盖高原生态环境恶化与沼泽退化及其形成机制[J].山地学报, 1999, 17 (4):318~ 322. [16] 王燕, 赵志中, 乔彦松, 等.若尔盖45年以来的气候变化特征及其对当地生态环境的影响[J].地质力学学报, 2005, 11(4):328~ 332. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2005.04.005 [17] 何池全, 赵魁义, 赵志春.若尔盖高原湿地草场退化成因分析及其保护利用[J].中国草地, 2000, 6:11~ 16. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgcd200006003 -





 下载:
下载: