D-INSAR OBSERVATION OF EARTH SURFACE DEFORMATION IN THE MS7.1 YUSHU EARTHQUAKE
-
摘要: 采用玉树MS7.1级地震前后两期PALSAR雷达数据(震前2010年1月15日, 震后4月17日)进行了“两轨+DEM”的InSAR处理, 获得了高质量的差分干涉雷达条纹图像和同震变形场。参考该区的基本构造格局, 根据干涉图像的变形范围、变形量和变形梯度可以初步判断:(1)玉树地震诱发了总体上NWW走向, 全长约70km地表陡变带, 陡变带南段位错及陡变梯度较大, 会在地表产生地表破裂;而西北部4段位错及陡变梯度较小, 不易在地表诱发破裂, 但可能在地下一定层位产生了隐伏破裂带;(2)陡变带两侧的雷达视线向运动方向预示发震断裂以左旋走滑运动为主;(3)宏观震中位于玉树县城西北约16km的地表陡变带上。D-InSAR解译结果与中国地震台网中心震源机制解、野外发震断裂调查结果及地貌特征吻合较好, 证明了干涉雷达解译成果的可靠性, 可以为准确定位玉树地震发震断裂地表行迹和快速评定震害损失提供有力的技术支持。Abstract: A "Two Paths+DEM" interferometric process was made for the PALSAR SAR data before (Jan. 15, 2010) and after (Apr. 17, 2010) the Yushu MS7.1 Earthquake, which yielded a high-quality co-seismic InSAR strip image and absolutely surface deformation. Based on the deformation scale, deformation magnitude and deformation gradient, in combination with tectonic setting of the area, the following conclusions can be drawn: (1) Yushu earthquake triggered a 70-km NWW-extending mutation belt, with a southern section Showing greater dislocation and deformation gradient, which will induce surface raptures, and No. 4 segment in northwestern part showing weaker deformation and no ruptures on the ground surface. (2) The SAR motive directions from both sides of mutation belt indicate a dominant sinistral movement of seisgenic faults. (3) The macro-epicenter is located on the mutation belt 16km northwest of Yushu County. The present InSAR interpretations match well with the seismic mechanics, field investigations and geomorphology features from the China Earthquake Networks Center, and can provide better support for rapid evaluation to earthquake hazard and accurately ing surface track of seismogenic fault.
-
Key words:
- Yushu Earthquake /
- InSAR /
- Surface Rupture /
- Coseismal seismic Deformation
-
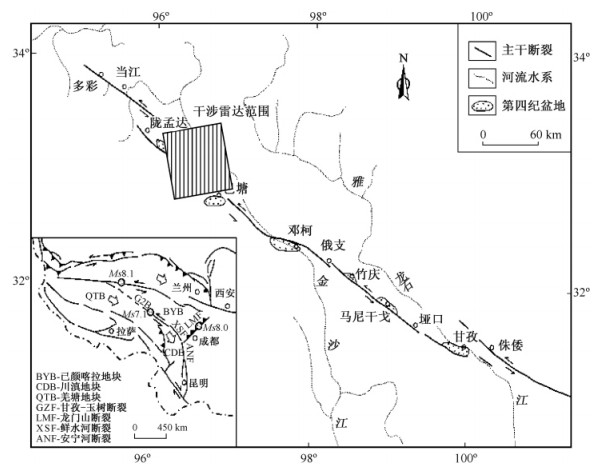
图 1 甘孜-玉树断裂带地表活动形迹图(据周荣军等[14], 1997年修改)及干涉雷达覆盖范围
Figure 1. A map showing the distribution map of Gznai-Yushu active fault zone (after Zhou Rongjun, 1997) and InSAR covering area
-
[1] 张永双, 石菊松, 孙萍, 等.汶川地震内外动力耦合及灾害实例[J].地质力学学报, 2009, 15(2):131~141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.02.003ZHANG Yong-shuang, SHI Ju-song, SUN Ping, et al.Coupling between endogenic and exogenic geological processes in the Wenchuan earthquake and example analysis of geo-hazards[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 2009, 15(2):131~141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.02.003 [2] 张永双, 雷伟志, 石菊松, 等.四川5.12地震次生地质灾害的基本特征初析[J].地质力学学报, 2008, 14(2):109~116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2008.02.002ZHANG Yong-shuang, LEI Wei-zhi, SHI Ju-song, et al.General characteristics of 5.12 earthquake-induced geo-hazards in Sichuan[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 2008, 14(2):109~116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2008.02.002 [3] 谭成轩, 孙叶, 吴树仁, 等.5.12汶川MS 8.0大地震后关于我国区域地壳稳定性评价的思考[J].地质力学学报, 2009, 15(2):142~150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.02.004TAN Cheng-xuan, SUN Ye, WU Shu-ren, et al.A consideration on regional crustal stability assessment after MS 8.0 Wenchuan strong earthquake in China[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 2009, 15(2):142~150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.02.004 [4] 王连捷, 周春景, 孙东生, 等.汶川5.12地震引起的库仑应力变化及其对周边地震活动的影响[J].地质力学学报, 2008, 14(3):193~200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2008.03.001WANG Lian-jie, ZHOU Chun-jing, SUN Dong-sheng, et al.Coulomb stress changes caused by Wenchuan earthquake and its influence on seismic activity in the adjacent area[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 2008, 14(3):193~200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2008.03.001 [5] 王连捷, 崔军文, 周春景, 等.汶川5.12地震发震机理的数值模拟[J].地质力学学报, 2009, 15(2):105~113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.02.001WANG Lian-jie, CUI Jun-wen, ZHOU Chun-jing, et al.Numerical modeling for Wenchuan earthquake mechanism[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 2009, 15(2):105~113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.02.001 [6] 彭华, 马秀敏, 姜景捷.龙门山北端青川断层附近应力测量与断层稳定性[J].地质力学学报, 2009, 15(2):114~130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.02.002PENG Hua, MA Xiu-min, JIANG Jing-jie.Stability and stress measurement near the Qingchuan fault in the northern Longmen Mountains[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 2009, 15(2):114~130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.02.002 [7] 彭华, 马秀敏, 姜景捷.山丹地应力监测站体应变仪的地震效应[J].地质力学学报, 2008, 14(2):97~108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2008.02.001PENG Hua, MA Xiu-min, JIANG Jing-jie.Analysis of the volume strain data from the Shandan in-situ stress Monitoring Station[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 2008, 14(2):97~108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2008.02.001 [8] 姚鑫, 张永双.基于差分干涉雷达的汶川地震同震形变特点[J].地质力学学报, 2009, 15(2):151~161. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.02.005YAO Xin, ZHANG Yong-shuang.Co-seismic deformation of 5.12 Wenchuan earthquake based on D-INSAR[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 2009, 15(2):151~161. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.02.005 [9] 马寅生, 张永双, 胡道功, 等.玉树地震地表破裂与宏观震中[J].地质力学学报, 2010, 16(2):115~124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2010.02.002MA Yin-sheng, ZHANG Yong-shuang, HU Dao-gong.et al.The surface ruptures and the macroscopical epicenter of Yushu MS 7.1 Earthquake[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 2010, 16(2):115~124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2010.02.002 [10] 姚鑫, 张永双, 杨农, 等.玉树地震地表变形InSAR观测及初步分析[J].地质力学学报, 2010, 16(2):129~136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2010.02.003YAO Xin, ZHANG Yong-shuang, YANG Nong, et al.D-InSAR Deformation Observation and Preliminary Analysis of the MS 7.1 Yushu Earthquake[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 2010, 16(2):129~136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2010.02.003 [11] 王连捷, 崔军文, 王薇, 等.青海玉树MS 7.1地震发震过程的数值模拟[J].地质力学学报, 2010, 16(2):137~145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2010.02.004WANG Lian-jie, CUI Jun-wen, WANG Wei, et al.Numercal modeling of Yushu MS 7.1 earthquake mechanism[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 2010, 16(2):137~145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2010.02.004 [12] 张岳桥, 杨农, 施炜, 等.青藏高原东缘新构造及其对汶川地震的控制作用[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(12):1668~1678. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.12.004ZHANG Yue-qiao, YANG Nong, SHI Wei, et al.Neotectonics of Eastern Tibet and Its Control on the Wenchuan Earthquake[J].ACTA GEOLOGICA SINICA, 2008, 82(12):1668~1678. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.12.004 [13] 嵇少丞, 王茜, 孙圣思, 等.亚洲大陆逃逸构造与现今中国地震活动[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(12):1644~1667. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.12.003JI Shao-cheng, WANG Qian, SUN Sheng-si, et al.Continental Extrusion and Seismicity in China[J].ACTA GEOLOGICA SINICA, 2008, 82(12):1644~1667. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.12.003 [14] 周荣军, 闻学泽, 蔡长星, 等.甘孜-玉树断裂带的近代地震与未来地震趋势估计[J].地震地质, 1997, 19(2):115~124. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700063315ZHOU Rong-jun, WEN Xue-ze, CHAI Chang-xing, et al.Recent Earthquakes and Assessment of Seismic Tendency on The Ganzi Yushu Fault Zone Seismology and Geology[J].SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 1997, 19(2):115~124. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700063315 [15] 都昌庭, 李文巧, 卢宁, 等.2006年青海玉树5.0、5.6、5.4级地震灾害损失及震害特点[J].震灾防御技术, 2006, 1(4):371~377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2006.04.012DU Chang-ting, LI Wen-qiao, LU Ning, et al.Characteristics of Loss and Hazards of Yushu Earthquakes with MS=5.0, 5.6 and 5.4 in Qinghai Province, 2006[J].Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 2006, 1(4):371~377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2006.04.012 -





 下载:
下载: