The genesis and age of karst caves in Xinglong National Geopark, Hebei Province
-
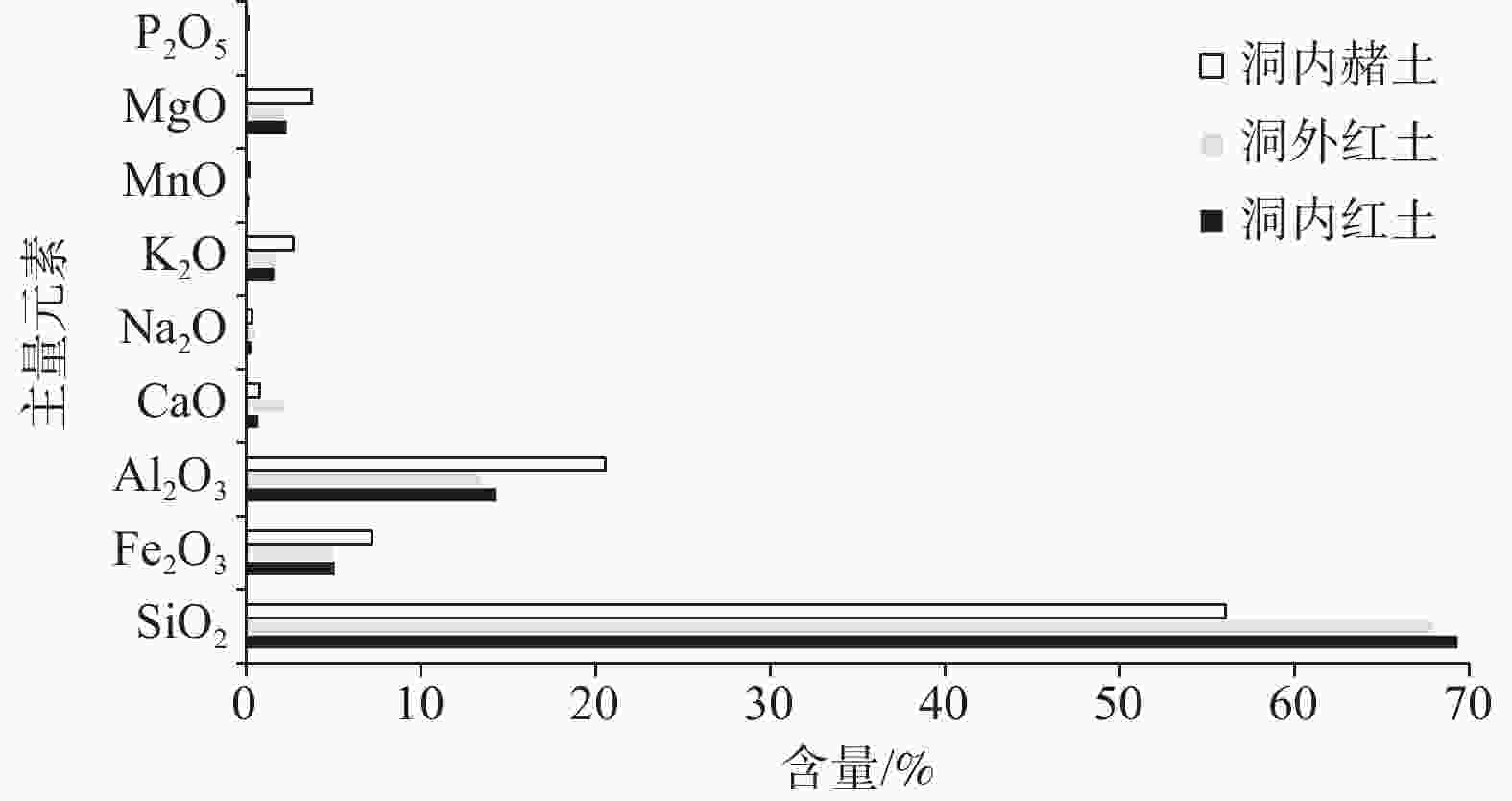
摘要: 岩溶洞穴作为地球关键带的重要组成部分,兼具景观和科学研究价值。已有研究对与溶洞形成密切相关的构造报道较少,对溶洞形成时代的定量分析更是缺乏。文章基于河北省兴隆县陶家台洞穴形态特征、组成洞穴的地层产状和构造的详细调查,结合沉积物矿物X射线衍射和地球化学元素分析,对兴隆溶洞成因及时代开展了研究。组成溶洞的中元古代含燧石团块白云质灰岩中发育2条断层,溶洞自上而下顺断层倾向发育,属断裂构造形成的差异溶蚀型溶洞。洞穴中上部灌入的红土堆积与洞外风化壳残积红土的地球化学特征基本一致,且洞穴中发育有经地表水溶滤而富铁的红色钟乳石,表明洞穴内堆积的红土来源于洞外,溶洞形成时代应在红土形成之后。通过区域对比,地表残积红土为唐县期(3.1~3.7 Ma)夷平面的产物,说明溶洞形成时代应在上新世早期。文章提出了兴隆溶洞发育受控于断层的新认识,并较好地约束了其形成时代,可为其他区域岩溶地貌的成因及时代研究提供参考。Abstract:
Objective Karst caves, as an essential part of the Earth's Critical Zone, hold significant scientific and scenic value. However, previous studies have largely overlooked the tectonic factors influencing cave formation, and quantitative constraints on the age of cave formation remain scarce. This study aims to investigate the genesis and chronology of the Xinglong Karst Cave in the Taojiatai area of Hebei Province, elucidating the controlling factors and temporal constraints of cave development. Methods A comprehensive investigation of cave morphology, stratigraphic attitude, and tectonic characteristics was conducted, supplemented by mineralogical analysis using X-ray diffraction and geochemical element analysis. The study analyzed the relationship between cave formation and fault activity, while the geochemical composition of red clay deposits inside the cave was compared with external weathering crusts to constrain the formation age of the cave. Results The cave developed within Middle Proterozoic dolomitic limestone containing flint nodules, influenced by two major faults that facilitated differential dissolution along fault planes. The red clay deposits inside the cave share geochemical characteristics with external weathering crusts, indicating an exogenous origin. The enrichment of iron in red stalactites suggests leaching from surface water, further confirming the post-weathering deposition of the red clay. Regional comparisons reveal that the residual red clay outside the cave corresponds to the Tangxian planation period (3.1–3.7 Ma), indicating that the cave must have formed after this period. Conclusion This study provides new insights into the fault-controlled genesis of the Xinglong Karst Cave and establishes a minimum formation age of 3.7 Ma, significantly younger than the Middle Proterozoic age of the host rock. The findings correct the previous misconception that the cave formed during the Proterozoic and highlight the crucial role of tectonic activity in cave development. [ Significance ] This research enhances our understanding of the tectonic control and chronological constraints of karst cave formation, providing valuable references for the study of karst landscapes in other regions. -
Key words:
- karst cave /
- tectonics /
- paleosoil /
- geochemistry /
- National Geopark /
- Xinglong County
-
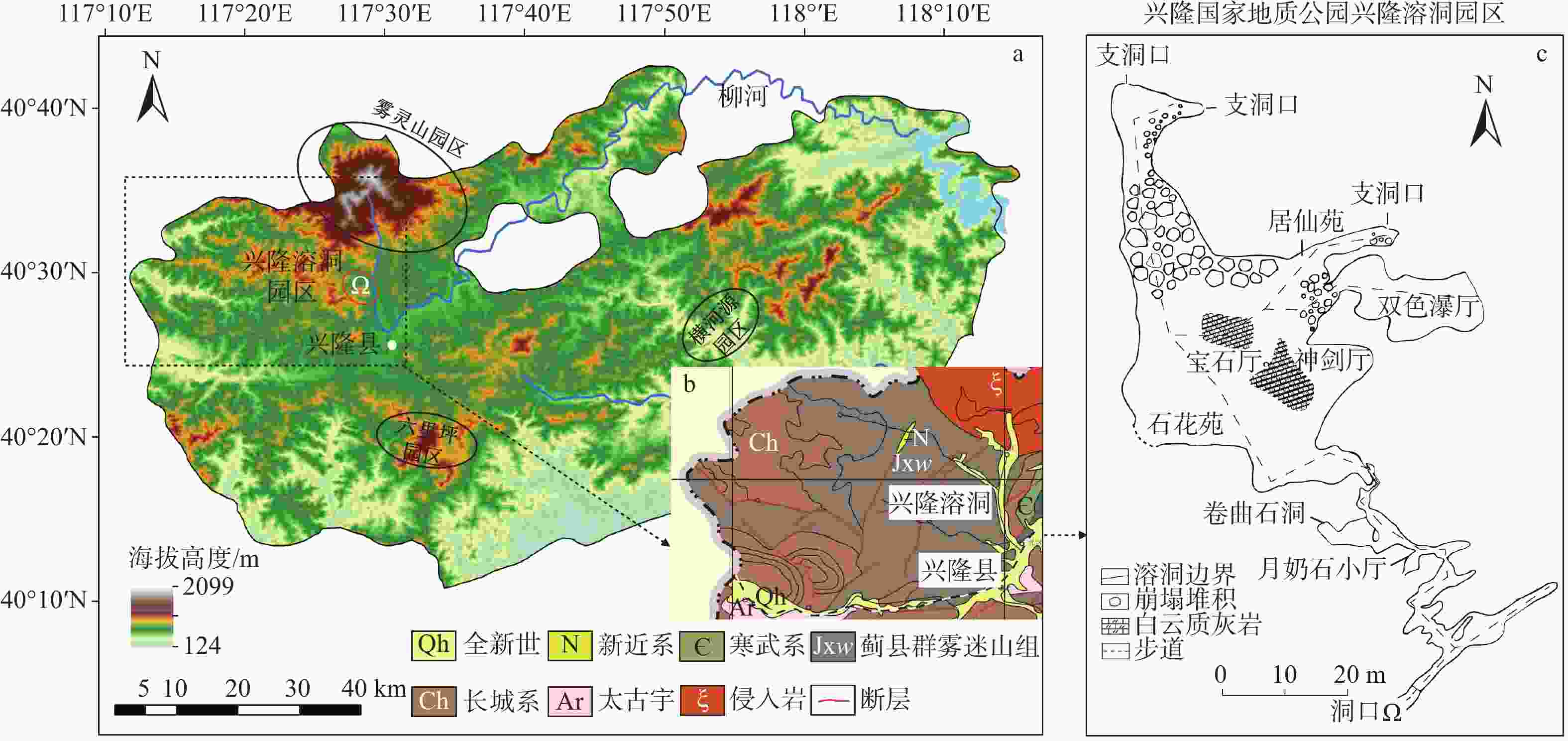
图 1 兴隆溶洞位置与洞穴平面图
a— 河北省兴隆县地形;b—研究区溶洞周边地质概况(据兴隆县2000年地质图编绘);c—洞穴特征
Figure 1. Location and plan of Xinglong Cave
(a) Topography of Xinglong County, Hebei Province; (b) Geological features of the area surrounding the cave (compiled from the 2000 geological map of Xinglong County); (c) Map with characteristics of the Xinglong Cave
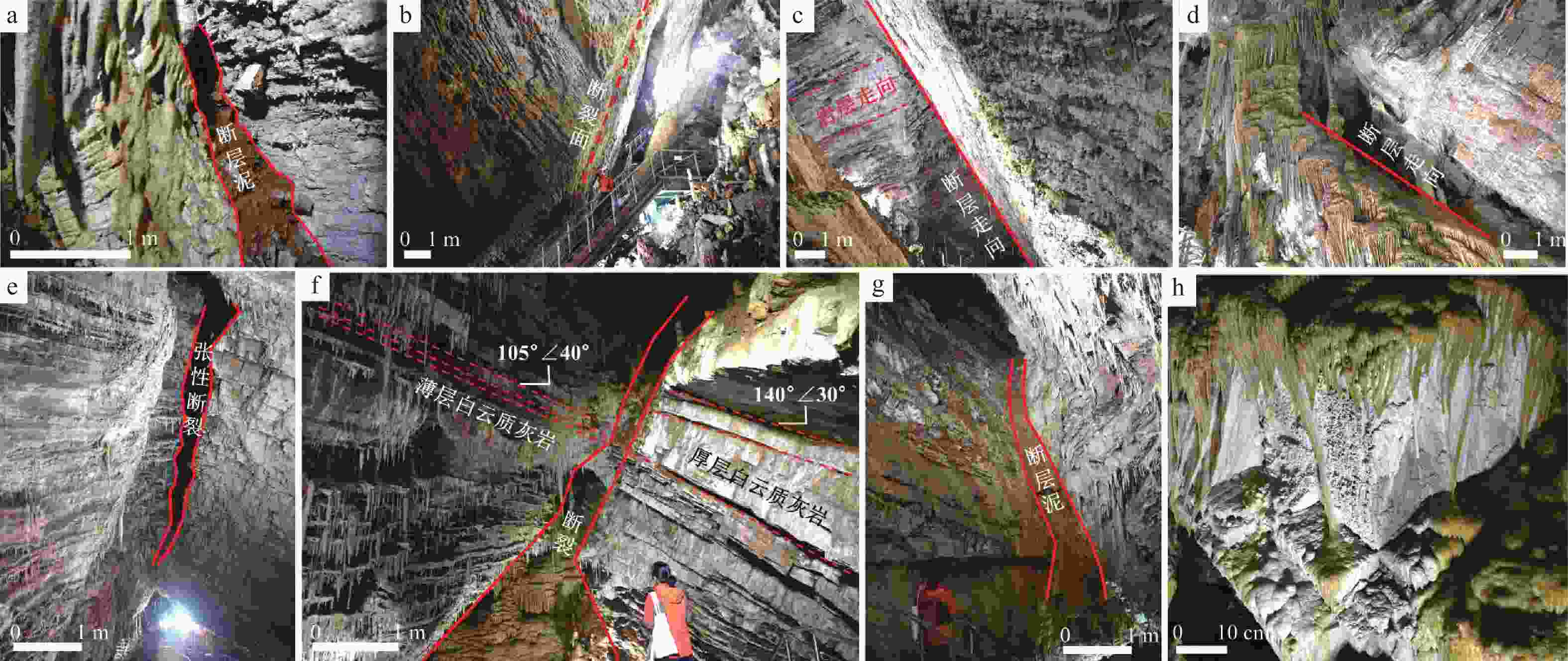
图 5 断层发育特征
a—断层破碎带;b—平直的断裂面;c—与岩层走向垂直的断裂面;d—沿断裂面发育的钟乳石;e—张性断裂;f—断层两侧的岩层厚度差异;g—高角度断层泥;h—豆腐块状岩石;a—d为第1条断层;e—h为第2条断层
Figure 5. Characteristics of the faults, including the first fault (a-d) and the second fault (e-h).
(a) Fault fracture zone; (b) Straight fracture surface; (c) Fracture surface perpendicular to the bedding orientation; (d) Stalactites developed along a fracture; (e) Tensional fault; (f) Thickness difference of rock layers on both sides of the fault; (g) High-angle fault gouge; (h) Blocky rock
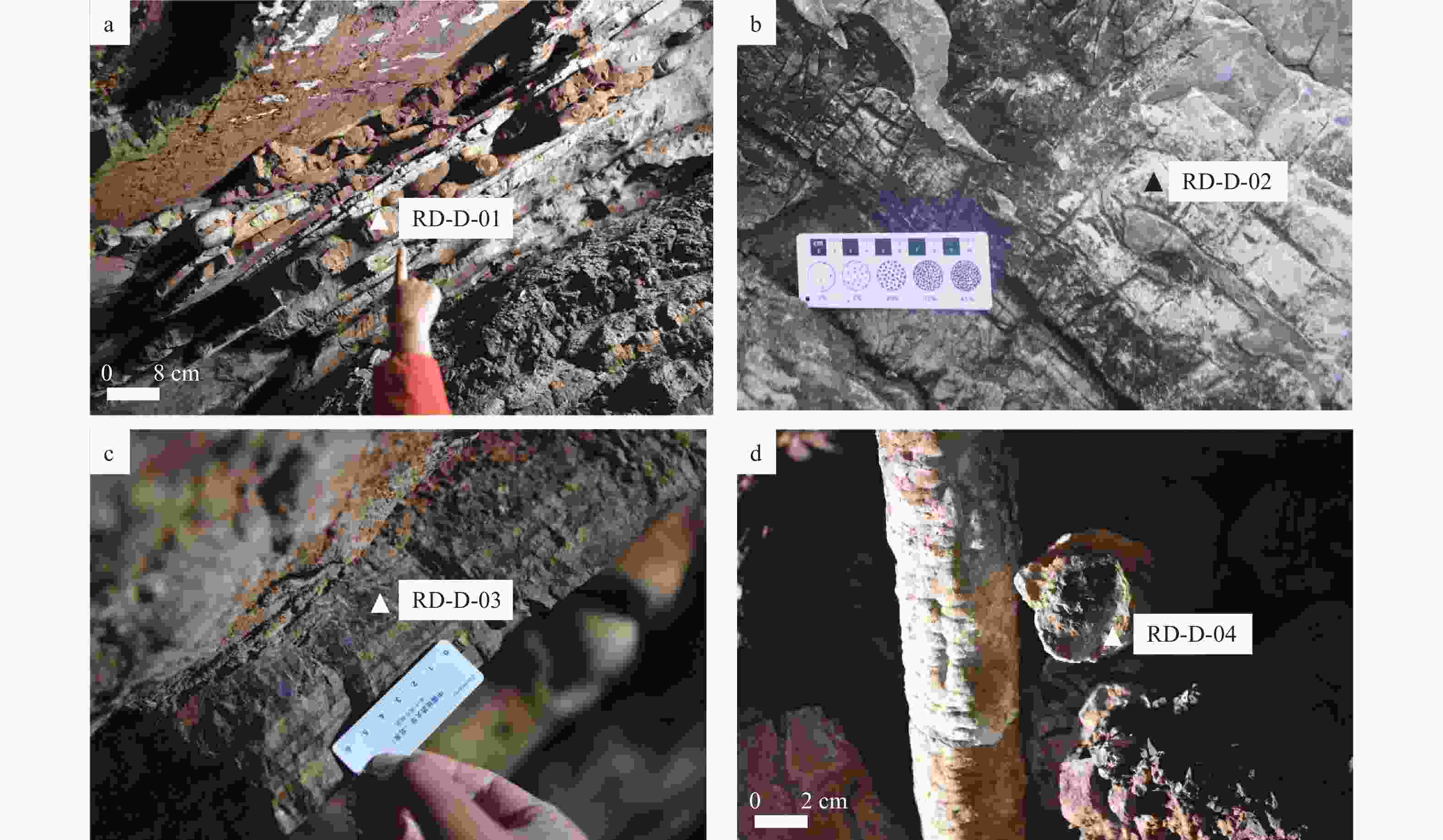
表 1 兴隆溶洞岩石的矿物X射线衍射结果(%)
Table 1. Mineral X-ray diffraction results of rocks in the Xinglong Cave (%)
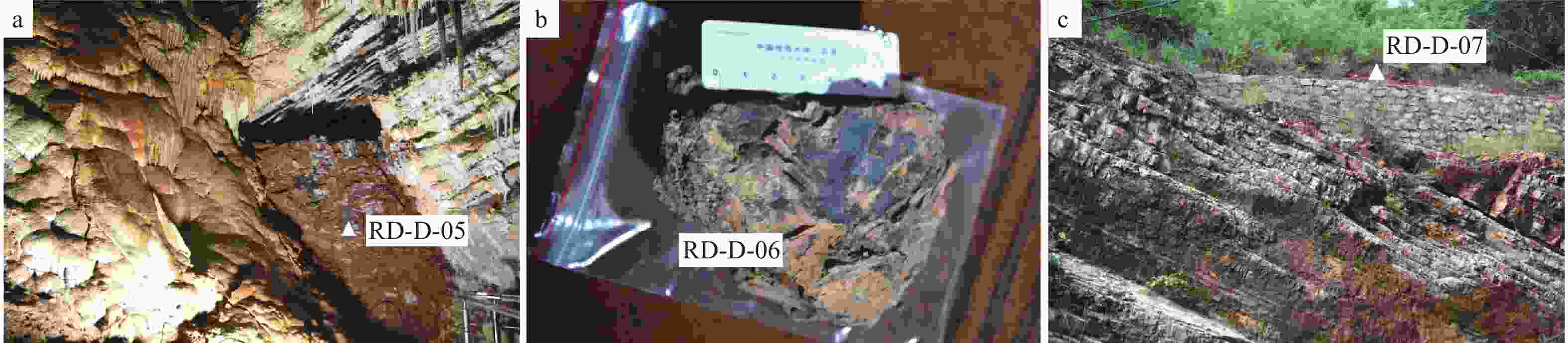
采样编号 RD-D-01 RD-D-02 RD-D-03 RD-D-04 样品属性 燧石团块 白云岩 灰岩 钟乳石 方解石 2 1 46 91 白云石 4 97 19 2 石英 92 2 33 4 其他矿物 2 0 2 3 -
[1] BAKER A, ASRAT A, FAIRCHILD I J, et al., 2007. Analysis of the climate signal contained within δ18O and growth rate parameters in two Ethiopian stalagmites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(12): 2975-2988. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.03.029 [2] BENEDETTO G, MADAU F A, CARZEDDA M, et al., 2022. Social economic benefits of an underground heritage: measuring willingness to pay for Karst caves in Italy[J]. Geoheritage, 14(2): 69. doi: 10.1007/s12371-022-00701-z [3] CHENG H, ZHANG H W, ZHAO J Y, et al., 2019. Chinese stalagmite paleoclimate researches: a review and perspective[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 62(10): 1489-1513. doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9478-3 [4] CUI S Q, WU Z H, MA Y S, et al., 2003. Meso-Cenozoic intracontinental orogenic process in the Beijing area: a case study based on geological observations from the Ming Tombs to Badaling Mountain[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 9(3): 201-219. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] FAN B X, ZHOU Z F, AN D, et al., 2021. The evolution process of atypical stalactites in Mahuang Cave, Suiyang County, Guizhou Province[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 41(6): 1565-1573. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] FORD D, WILLIAMS P, 2007. Karst Hydrogeology and Geomorphology[M]. Chichester, UK: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. [7] HE W, LI P, 2016. Evolution feature and scientific values of Zhijin cave[J]. Guizhou Science, 34(2): 31-36. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] WEI Y Y, SUN S L, HUANG J J, et al.,2018. A study on karst development characteristics and key control factors of collapse in Xuzhou, eastern China[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites,33(3):359-373. [9] HUANG B J, LI L L, LI C Z, et al., 2018. Feature of cave cloud and its origin in Jingua cave, Guizhou, China[J]. China Mining Magazine, 27(S2): 300-303. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] LI B, YU D L, WANG N, et al., 2024. Karst groundwater enrichment law in Laiwu Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 30(4): 691-702. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] LI B G, GAO R S, 2014. Characteristics and main controlling factors of karst caves in the southern margin of Kepingtage tectonic belt, Tarim Basin[J]. Geoscience, 28(1): 149-155. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] LIPAR M, BARHAM M, DANIŠÍK M, et al., 2024. Ironing out complexities in karst chronology: (U-Th)/He ferricrete ages reveal wet MIS 5c[J]. Science Advances, 10(40): eadp0414. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adp0414 [13] LÜ J B, LU Y R, ZHENG G S, et al., 2010. Formation of karst cave system and relationship with neotectonic movement in Beijing Western Hills, Bejing, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 29(4): 502-509. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] LÜ J B, LI T Y, ZHENG M C, et al., 2014. Progress of karst study in Beijing Shihua Cave[J]. Urban Geology, 9(2): 11-17. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] MA Y, YIN J J, YUAN D X, 2022. Research progress on response of elements and their ratios in cave drip water and speleothems to climate and environmental change[J]. Geological Review, 68(5): 1897-1911. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] MENG X P, 2001. Vertical distribution of vegetation in Wuling Mountain[J]. Journal of Hebei Forestry Science and Technology(1): 41-42. (in Chinese) [17] NEHME C, VERHEYDEN S, KLUGE T, et al., 2024. Climate variability in the northern levant from the highly resolved Qadisha record (Lebanon) during the Holocene optimum[J]. Quaternary Research, 118: 180-194. doi: 10.1017/qua.2023.24 [18] PENG B, ZHANG H, YANG S H, et al., 2020. Logging characterization of Carboniferous fractured-vuggy karst reservoirs in the eastern Qaidam Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(6): 923-931. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] PU J B, 2022. Earth’s critical zone and karst critical zone: structure, characteristic and bottom boundary[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 41(5): 230-241. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] SENDRA A, REBOLEIRA S P,2012. The world’s deepest subterranean community—Krubera-Voronja Cave (Western Caucasus)[J]. International Journal of Speleology,41(2):221-230 [21] SHI W Q, LIAO R S, LI C Z, et al., 2021. The karst characteristics and cultural transmission: Xiaya geological cultural village, Fengshan, Guangxi[J]. China Mining Magazine, 30(S1): 479-481. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] TANG B N, ZHU C Q, QIU N S, et al., 2020. Characteristics of the karst thermal reservoir in the Wumishan Formation in the Xiong’an New Area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(7): 2002-2012. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] WANG J, CHEN Z, ZHANG M P, et al., 2011. The genetic sorts of the typical karst caves in Tianguishan, Hebei Province[J]. Mountain Research, 29(2): 188-194. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] WEI Y L, JIANG Z C, CHEN W H, et al., 2020. An analysis of characteristics, formation and evolution of the karst landforms, Shandong Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 41(4): 561-574. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] WU C, 2008. Landform environment and its formation in North China[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) [26] WU C, ZHANG X Q, WANG R, et al. , 2017. The planarization surface of mountainous areas in North China[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 33(1): 124-126. (in Chinese) [27] XIONG J G, LI Y L, ZHANG P Z, 2020. New advances in planation surface research[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 35(4): 378-388. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] XIONG K N, ZHANG S R, FEI G Y, et al., 2023. Conservation and sustainable tourism development of the natural world heritage site based on aesthetic value identification: a case study of the Libo Karst[J]. Forests, 14(4): 755. doi: 10.3390/f14040755 [29] YANG H H, ZHOU Y M, ZHONG Y, et al., 2024. Variations and mechanisms of the Asian summer monsoon revealed by stalagmite δ18O records[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 44(1): 143-155. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] YANG Y, DUAN D, 2016. Influencing factors analysis of the ground stress distribution regularity of X-pattern normal fault[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 12(6): 1485-1490. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] ZHANG C, JIANG Z C, XIE Y Q, et al., 1995. Geological structure, neotectonic movement and the formation, evolution of regional karst geomorphology of West-Hill, Beijing[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 14(3): 231-240. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] ZHANG G Q, HE Q M, TIAN M Z, et al., 2009. Types, genesis and values of geological heritages in Xinglong County[J]. Resources & Industries, 11(2): 41-45. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] ZHANG L, 2013. Stratiform geomorphology’ development and significance of neotectonic movement in Wangmangling, Lingchuan, Shanxi Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing). (in Chinese with English abstract [34] ZHANG S Y, ZHOU Z F, XIONG K N, et al., 2016. Spatial pattern of the caves in Guizhou Province and their the influencing factors[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 71(11): 1998-2009. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] ZHANG Y, 2009. The type of geoheritages and comprehensive evaluation in Xinglong Geopark, Hebei[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing). (in Chinese with English abstract [36] ZHU X W, 2005. The classification scheme of speleothems[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 24(3): 169-174. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 崔盛芹,吴珍汉,马寅生,等,2003. 北京地区中新生代陆内造山过程:以十三陵—龙庆峡—八达岭路线观察为基础[J]. 地质力学学报,9(3):201-219. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2003.03.002 [38] 范宝祥,周忠发,安丹,等,2021. 贵州绥阳麻黄洞非典型钟乳石的演化过程[J]. 第四纪研究,41(6):1565-1573. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2021.06.05 [39] 贺卫,李坡,2016. 织金洞发育特征及其科学价值[J]. 贵州科学,34(2):31-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6563.2016.02.007 [40] 黄保健,李乐乐,李成展,等,2018. 贵州金瓜洞云朵石的特征及成因初探[J]. 中国矿业,27(S2):300-303. [41] 李宝刚,高日胜,2014. 塔里木盆地柯坪塔格构造带南缘古溶洞特征及主控因素分析[J]. 现代地质,28(1):149-155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2014.01.014 [42] 李波,于大潞,王楠,等,2024. 莱芜盆地岩溶地下水富集规律[J]. 地质力学学报,30(4):691-702. [43] 吕金波,卢耀如,郑桂森,等,2010. 北京西山岩溶洞系的形成及其与新构造运动的关系[J]. 地质通报,29(4):502-509. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.04.003 [44] 吕金波,李铁英,郑明存,等,2014. 北京石花洞岩溶学研究进展[J]. 城市地质,9(2):11-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2014.02.003 [45] 马源,殷建军,袁道先,2022. 洞穴滴水、石笋中元素及元素比值对气候环境变化响应的研究进展[J]. 地质论评,68(5):1897-1911. [46] 孟祥普,2001. 雾灵山植被垂直分布状况[J]. 河北林业科技(1):41-42. [47] 彭博,张浩,杨晟颢,等,2020. 柴达木盆地东部石炭系古岩溶缝洞单元测井响应[J]. 地质力学学报,26(6):923-931. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.06.073 [48] 蒲俊兵,2022. 地球关键带与岩溶关键带:结构、特征、底界[J]. 地质科技通报,41(5):230-241. [49] 史文强,廖如松,李成展,等,2021. 岩溶特色,文化传承:广西凤山下牙地质文化村[J]. 中国矿业,30(S1):479-481. doi: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2021.S1.094 [50] 唐博宁,朱传庆,邱楠生,等,2020. 雄安新区雾迷山组岩溶裂隙发育特征[J]. 地质学报,94(7):2002-2012. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.009 [51] 王健,陈琢,张梅平,等,2011. 河北省天桂山典型溶洞景观成因类型[J]. 山地学报,29(2):188-194. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2011.02.007 [52] 韦跃龙,蒋忠诚,陈伟海,等,2020. 山东岩溶地貌特征及其形成演化分析[J]. 地球学报,41(4):561-574. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2020.033001 [53] 吴忱,2008. 华北地貌环境及其形成演化[M]. 北京:科学出版社. [54] 吴忱,张秀清,王然,等,2017. 华北山地夷平面研究[J]. 地理与地理信息科学,33(1):124-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2017.01.021 [55] 熊建国,李有利,张培震,2020. 夷平面研究新进展[J]. 地球科学进展,35(4):378-388. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2020.032 [56] 杨会会,周祐民,仲义,等,2024. 石笋δ18O揭示的亚洲夏季风变化及机制综述[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质,44(1):143-155. [57] 杨瑶,段东,2016. X型正断层地应力分布规律影响因素分析[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,12(6):1485-1490. [58] 章程,蒋忠诚,谢运球,等,1995. 北京西山南部构造及新构造运动与区域岩溶地貌形成、演化[J]. 中国岩溶,14(3):231-240. [59] 张国庆,贺秋梅,田明中,等,2009. 河北兴隆地质遗迹类型、成因及其价值评价[J]. 资源与产业,11(2):41-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2464.2009.02.010 [60] 张蕾,2013. 山西陵川王莽岭地区层状地貌的发育及其新构造运动意义[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京). [61] 张绍云,周忠发,熊康宁,等,2016. 贵州洞穴空间格局及影响因素分析[J]. 地理学报,71(11):1998-2009. doi: 10.11821/dlxb201611010 [62] 张妍,2009. 河北兴隆地质公园地质遗迹类型及其综合评价[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京). [63] 朱学稳,2005. 洞穴钟乳石类的分类方案[J]. 中国岩溶,24(3):169-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2005.03.001 -




 下载:
下载: