THE TIME SPACE DISTRIBUTION CHARACTERISTICS AND MIGRATION LAW OF LARGE EARTHQUAKES IN THE INDIAM-EURASIAN PLATE COLLISION DEFORMATION AREA
-
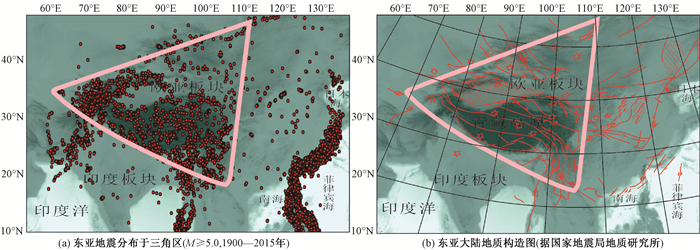
摘要: 印度板块与欧亚板块在新生代期间的持续碰撞和挤压过程导致亚洲大陆发生了强烈的弥散式板内变形,并形成了一个以贝加尔湖为顶点,以喜马拉雅带为底边的近似三角形的变形区与强震活动区,即新-藏三角区。基于固体刚塑性变形平面结构,结合滑移线场网络模型,对该区历史强震活动的大范围离散式空间分布特点进行了分析解释。结合1505-1976年以来历史强震空间迁移的实例,归纳了该区历史强震活动与地震应变释放从印度板块边界→新-藏地块→两侧大陆的顺序性及定向性迁移特征,并根据对地震空间迁移规律的认识,进一步探讨了区域未来强震危险性问题。结果显示,从2000-2018年间,印度板块边界和新-藏三角区已多次发生M7.9~9.1大地震,但其东、西两侧的区域大陆地区却异常平静,没发生过7级以上大地震。依照区域强震活动的顺序性迁移特点,推测在未来几到几十年,亚洲大陆东部与中部以及喜马拉雅带东段等区域的大地震危险性较大。Abstract: The continuous collision and compression between the Indian plate and the Eurasian plate during the Cenozoic period led to a strong intraplate deformation of the Asian continent, which resulted in the formation of a triangle deformation area and strong earthquake activity area, namely the Xinjiang-Tibet Triangle Area, with Lake Baikal as the apex and the Himalayan belt as the bottom. Based on the plane structure of solid rigid-plastic deformation and the network model of slip line field, the characteristics of large-scale discrete spatial distribution of historical strong earthquakes in this region are explained. Combined with the examples of the spatial migration of historical strong earthquakes from 1505 to 1976, the sequential and directional migration characteristics of the historical strong earthquakes and the seismic strain release from the boundary of the Indian plate-the Xinjiang-Tibet block-the two sides of the continents are summarized, and potential risks of regional strong earthquakes on the basis of the understanding of the law of seismic spatial migration are discussed. The results show that from 2000 to 2018, the boundary of the Indian plate and the Xinjiang-Tibet Triangle Area have been hit by M7.9~9.1 earthquakes for many times; however, the east and west sides of the continent are the contrary with few earthquakes larger than M7.0. According to the sequential migration characteristics of strong seismic activities in the above seismic regions, it is believed that in the next few to decades, the east and central parts of the Asian continent and the eastern part of the Himalayan belt are at greater risk of major earthquakes.
-
表 1 新藏三角区主要地震纵向迁移带及其特征一览表
Table 1. Main seismic longitudinal migration zones and their characteristics in the Xinjiang-Tibet Triangle Area
地震迁移带名称 迁移方式 出现时段/a 持续时间/a 迁移速率km/a 统计震级 帕米尔—贝加尔带 由西南向东北往复式迁移 1669—1761 92 50 M≥7.8 1902—1957 55 喜马拉雅带 东西向往复迁移 1803—1897 94 30 M≥7.8 1905—1950 45 2005—2015 10 南北带 由南向北迁移 1500—1561 61 50 M≥7.0 1713—1742 29 1789—1932 143 1913—1957 44 1988—2008 20 昆仑带 从西向东迁移 1956—2001 45 53 M≥7.0 祁连山带 从东南向西北 1920—1932 12 83 M≥7.5 -
[1] GUTENBERG B, RICHTER C F. Seismicity of the earth and associated phenomena[M]. Princeton:Princeton University Press, 1954, 16-20, 64-73. [2] TAPPONNIER P, MOLNAR P. Active faulting and cenozoic tectonics of the Tien Shan, Mongolia, and Baykal Regions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 1979, 84(B7):3425-3459. doi: 10.1029/JB084iB07p03425 [3] 许忠淮.东亚地区现今构造应力图的编制[J].地震学报, 2001, 23(5):492-501. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2001.05.005XU Zhonghuai. A present-day tectonic stress map for eastern Asia region[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 2001, 23(5):492-501. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2001.05.005 [4] 傅征祥, 吕晓健, 郝平, 等.东亚大陆大三角地震区地震活动性概要[M].北京:地震出版社, 2012.FU Zhengxiang, LV Xiaojian, HAO Ping, et al. Seismicity of Large triangular area of East Asia continent[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 2012. (in Chinese) [5] MOLNAR P, TAPPONNIER P. Cenozoic tectonics of Asia:effects of a continental collision:Features of recent continental tectonics in Asia can be interpreted as results of the India-Eurasia collision[J]. Science, 1975, 189(4201):419-426. doi: 10.1126/science.189.4201.419 [6] 李建国, 周永胜, 王绳祖.中东亚大陆塑性流动网络控制下构造变形的物理模拟[J].地震地质, 1998, 20(1):63-72. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ801.007.htmLI Jianguo, ZHOU Yongsheng, WANG Shengzu. Physical modelling of plastic flow network controlled tectonic deformation in the central eastern Asian continent[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1998, 20(1):63-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ801.007.htm [7] BILHAM R, GAUR V K, MOLNAR P. Himalayan seismic hazard[J]. Science, 2001, 293(5534):1442-1444. doi: 10.1126/science.1062584 [8] 马宗晋, 汪一鹏, 张燕平.青藏高原岩石圈现今变动与动力学[M].北京:地震出版社, 2001.MA Zongjin, WANG Yipeng, ZHANG Yanping. Study on the recent deformation and dynamics of the lithosphere of Qinghai-Xizang plateau[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 2001. (in Chinese) [9] 王绳祖, 张四昌, 田勤俭, 等.大陆动力学:网状塑性流动与多级构造变形[M].北京:地震出版社, 2000.WANG Shengzu, ZHANG Sichang, TIAN Qinjian, et al. Continental dynamics-netlike plastic-flow and hierarchical tectonic deformation[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 2000. (in Chinese) [10] 朱元清, 宋治平, 等.中国西部及邻区百年尺度周期的地震活动及其和太阳活动之间的负相关性[J].地球物理学报, 2011, 54(9):2263-2271.YIN Jiyao, ZHU Yuanqing, SONG Zhiping, et al. Hundred-year-scale cycle of seismic activities in western China and its negative correlativity with sunspot activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(9):226-2271. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] YIN A, ZUZA A V, PAPPALARDO R T. Mechanics of evenly spaced strike-slip faults and its implications for the formation of tiger-stripe fractures on Saturn's moon Enceladus[J]. Icarus, 2016, 266:204-216. doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2015.10.027 [12] YIN A, XIE Z M, MENG L S. A viscoplastic shear-zone model for deep (15-50 km) slow-slip events at plate convergent margins[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2018, 491:81-84. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2018.02.042 [13] 李三忠, 李涛, 赵淑娟, 等.东亚原特提斯洋(Ⅴ):北界西段陆缘属性及微陆块拼合[J].岩石学报, 2017, 33(6):1633-1652.LI Sanzhong, LI Tao, ZHAO Shujuan, et al. Proto-Tethys Ocean in East Asia (Ⅴ):Attribute of contientnal margin and microcontinental assembly in the west segment of the northern Proto-Tethys Tectonic Domain[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(6):1633-1652. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] HILL R. The mathematical theory of plasticity (E. Ullrich)[J]. Zeitschrift Naturforschung Teil A, 1950, 6:171. [15] 杨桂通, 熊祝华.塑性动力学[M].北京:清华大学出版社, 1984.YANG Guitong, XIONG Zhuhua. Plastic dynamics[M]. Beijing:Tsinghua University Press, 1984. (in Chinese) [16] 尚福林, 王子昆.塑性力学基础[M].西安:西安交通大学出版社, 2011.SHANG Fulin, WANG Zikun. Plasticity mechanics basis[M]. Xi'an:Xi'an Jiaotong University Press, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] 《2006年-2020年中国大陆地震危险区与地震灾害损失预测研究》项目组. 2006-2020年中国大陆地震危险区与地震灾害损失预测研究[M].北京:地震出版社, 2006.Research group of "Researches on Earthquake Risk Regions and Losses Prediction of China Continent During from 2006 to 2002". Researches on earthquake risk regions and losses prediction of China continent[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 袁道阳, 雷中生, 王爱国.1654年甘肃天水南8级地震补充考证[J].地震工程学报, 2017, 39(3):509-520. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ201703016.htmYUAN Daoyang, LEI Zhongsheng, WANG Aiguo.Additional Textual Criticism of Southern TianshuiM8 Earthquake in Gansu Province in 1654[J].China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2017, 39(3):509-520. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ201703016.htm [19] 刘艳辉, 赵根模, 吴中海, 等.青藏高原东南缘及邻区近年来地震b值特征[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(1):58-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.01.005LIU Yanhui, ZHAO Genmo, WU Zhonghai, et al. An analysis of b-value characteristics of earthquake on the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau and its neighboring areas[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015, 34(1):58-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.01.005 [20] 陈昊, 王琼, 苏金波, 魏芸芸.2015年尼泊尔MS8.1地震在喀什-乌恰交汇区的动态触发活动[J].地震工程学报, 2017, 39(2):253-261. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2017.02.0253CHEN Hao, WANG Qiong, SU Jin-bo, WEI Yun-yun.Remotely Triggered Seismicity around Kashi-Wuqia Area Following the 2015 MS8.1 Nepal Earthquake[J].China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2017, 39(2):253-261. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2017.02.0253 [21] 赵根模, 刘杰, 吴中海, 等. 2015尼泊尔大地震及喜马拉雅造山带未来地震趋势[J].地质力学学报, 2015, 21(3):351-358. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2015.03.005ZHAO Genmo, LIU Jie, WU Zhonghai, et al. 2015 Nepal earthquake and the future seismic trend of Himalaya orogenic belt[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2015, 21(3):351-358. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2015.03.005 [22] 吴中海, 赵根模, 刘杰. 2015年尼泊尔Ms8.1地震构造成因及对青藏高原及邻区未来强震趋势的影响[J].地质学报, 2016, 90(6):1062-1085. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.06.002WU Zhonghai, ZHAO Genmo, LIU Jie. Tectonic genesis of the 2015Ms8.1 nepal great earthquake and its influence on future strong earthquake tendency of Tibetan Plateau and its adjacent region[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(6):1062-1085. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.06.002 [23] 刘杰, 赵根模, 吴中海. 2015年尼泊尔8.1级大地震前后喜马拉雅带地震活动图像演变[J].地质力学学报, 2017, 23(1):173-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.01.013LIU Jie, ZHAO Genmo, WU Zhonghai. The evolution of seismic activity image in the Himalaya Belt before and after 2015 Nepal M8.1 great earthquake[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 23(1):173-181. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.01.013 [24] MOGI K. Migration of seismic activity[J]. Bulletin of the Earthquake Research Institute University of Tokyo, 1968, 46:53-74. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_fa7516a18875cf4d67ba984855a49139 [25] 赵根模, 王大宏, 赵明.板块地震迁移链与汶川地震[J].国际地震动态, 2010, (5):34-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4975.2010.05.009ZHAO Genmo, WANG Dahong, ZHAO Ming. Relationship between migration chains of seismic activity along plate boundaries and Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Recent Developments in World Seismology, 2010, (5):34-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4975.2010.05.009 [26] 赵根模, 姚兰予.东亚大陆的地震迁移(一)——从西太平洋海沟到中国大陆内部的巨震及火山活动迁移[J].地震学报, 1995, 7(4):440-447. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500063445ZHAO Genmo, YAO Lanyu. Seismic migration from the East Asia continent (a)——the migration of giant earthquakes and volcanic activity from the western Pacific trench to Chinese mainland[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 1995, 7(4):440-447. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500063445 [27] KASAHARA R. Migration of Crustal ditformation[J]. Tectonophysics, 1979, 52(1-4):329-341. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(79)90240-3 [28] 見野和夫.日本列島の海溝に沿う巨大地震の移動[J].地震, 1988, 41(2):375-380. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=J-STAGE_38971Mino K. Migration of great earthquakes along the subduction zone of the Japan arc[J]. Earthquake, 1988, 41(2):375-380. (in Japanese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=J-STAGE_38971 [29] NI J, BARAZANGI M. Seismotectonics of the Himalayan collision zone:Geometry of the underthrusting Indian Plate beneath the Himalaya[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 1984, 89(B2):1147-1163. doi: 10.1029/JB089iB02p01147 [30] 秦向辉, 陈群策, 孟文, 等.大地震前后实测地应力状态变化及其意义——以龙门山断裂带为例[J].地质力学学报, 2018, 24(3):309-320. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180303&journal_id=dzlxxbQIN Xianghui, CHEN Qunce, MENG Wen, et al. Evaluating measured in-situ stress state changes associated with earthquakes and its implications:a case study in the Longmenshan fault zone[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2008, 24(3):309-320. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180303&journal_id=dzlxxb -





 下载:
下载: