ROCK COLLAPSE MECHANISM ON HIGH-STEEP SLOPE FAILURE IN SUB-HORIZONTAL THICK-BEDDED MOUNTAINS
-
摘要: 近水平厚层高陡斜坡岩层倾角小于10°,具有软硬相间或上硬下软的结构,常形成高陡斜坡或陡崖地形,主要以大型崩塌的形式发生破坏。在梳理国内外文献的基础上,从岩体破坏机制出发,对近水平厚层高陡斜坡崩塌的形成过程、破坏机制、失稳模式进行分析,总结归纳了6种地质力学模型,包括滑移-拉裂、塑流-拉裂、倾倒-拉裂、剪切-错断、剪切-滑移、劈裂-溃屈,并提出了相应的野外识别特征。Abstract: Sub-horizontal thick bedding slope shows a gentle dip of approximately 0~10°and strata structure of hard on soft, or hard interbedded with soft. It forms a high and steep terrain and is prone to rock collapse. Reviewing a lot of references, failure process and initiation mechanism, as well as failure modes of high-steep slope in sub-horizontal thick bedding mountains are analyzed in terms of rock mass failure mechanism. Six geomechanic models are summarized such as slipe-tensile, creep-tensile, slipe-shear, shear-rupture, shear-slipe and split-bulk. Corresponding to the reconginition features of geological structure are also presented.
-
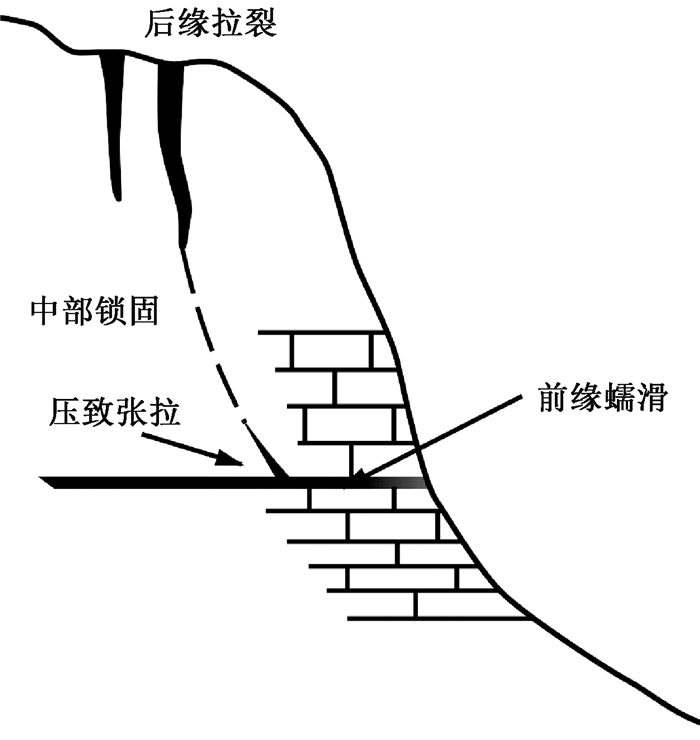
图 1 滑移-拉裂式崩塌模式(据文献[8]修改)
Figure 1. Creep-tensile failure mode
图 2 近水平厚层高陡山体塑流-拉裂破坏的地貌学演化过程[20]
Figure 2. Morphoevoltionary model of creep-tensile failure of sub-horizonatal thick bedding mountains
图 6 Katoomba剪切-错断式崩塌剖面图[22]
Figure 6. Shear-rupture failure in Katoomba escarpment
图 7 近水平厚层高陡斜坡平面滑移破坏[28]
Figure 7. Translational slide from shear-slide failure of rockmass
图 8 滑移-剪切破坏示意图[27]
Figure 8. Schematic model for slipe-shear failure
-
[1] 孙广忠.岩体结构力学[M].北京:科学出版社, 1988:61, 165.SUN Guang-zhong. Structural mechanics of rock mass[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1988: 61, 165. [2] 王玉川, 巨能攀, 赵建军, 等.缓倾煤层采空区上覆山体滑坡形成机制分析[J].工程地质学报, 2013, (1):61~68. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201301009.htmWANG Yu-chuan, JU Neng-pan, ZHAO Jian-jun, et al. Formation mechanism of landslide above the mined out area in gently inclined coal beds[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2013, 21(1): 61~63. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201301009.htm [3] 张倬元, 王世庆, 王兰生.工程地质分析原理[M].2版.北京:地质出版社, 1994:135, 335.ZHANG Zhuo-yuan, WANG Shi-qing, WANG Lan-sheng. Analysis principle of engineering geology[M]. 2th Edition. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1994: 135, 335. [4] 胡厚田.崩塌与落石[M].北京:中国铁道出版社, 1989.HU Hou-tian. Rock collapse and rock falls[M]. Beijing: China Railway Press, 1989. [5] Poisel R, Eppensteiner W. A contribution to the systematics of rock mass movements[C]//Bonnard C, ed. Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Landslides: Vol. 2. Lausanne, 1988: 1353~1357. [6] Poisel R, Angerer H, Pöllinger M, et al. Mechanics and velocity of the Lärchberg-Galgenwald Landslide(Austria)[J]. Engineering Geology, 2009, 109(1): 57~66. [7] Terzaghi K. Mechanism of landslides[M]. Harvard University, Department of Engineering, 1951. [8] 黄润秋. 中国西部地区典型岩质滑坡机理研究[J]. 地球科学进展, 2004, 19(3): 443~450.HUANG Run-qiu. Mechanism of large scale landslides in western China[M]. Advance in Earth Science, 2004, 19(3): 443~450. [9] Rohn J, Resch M, Schneider H, et al. Large-scale lateral spreading and related mass movements in the Northern Calcareous Alps[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2004, 63(1): 71~75. doi: 10.1007/s10064-003-0201-x [10] 殷跃平.三峡库区边坡结构及失稳模式研究[J].工程地质学报, 2005, 13(2):145~154. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200502000.htmYIN Yue-ping. Human-cutting slope structure and failure pattern at the Three Gorges Reservoip[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2005, 13(2): 145~154. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200502000.htm [11] 陈洪凯.三峡库区危岩链式规律的地貌学解译[J].重庆交通大学学报:自然科学版, 2008, 27(1):91~95. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CQJT200801022.htmCHEN Hong-kai. Geomophology research on chained regularity of perilous rock in the area of the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Journal of Chonqing Jiaotong University: Natural Science, 2008, 27(1):91~95. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CQJT200801022.htm [12] Dussauge-Peisser C, Helmstetter A, Grasso J R, et al. Probabilistic approach to rock fall hazard assessment: potential of historical data analysis[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Science, 2002, 2(1/2): 15~26. doi: 10.5194/nhess-2-15-2002 [13] 黄润秋.岩石高边坡发育的动力过程及其稳定性控制[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(8):1525~1544. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200808004.htmHuang Runqiu. Geodynamical process and stability control of high rock slope development[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(8): 1525~1544. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200808004.htm [14] Voight, B., 1973. The mechanism of retrogressive block-gliding with emphasis on the evolution of the Turnagain Heights Landslide, Anchorage, Alaska. In: De Jong, K.A., Scholten, R. (Eds.), Gravity and Tectonics. John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp. 97~121. [15] Hungr O, Evans S G. The occurrence and classification of massive rock slope failure[J]. Felsbau, 2004, 22(2): 16~23. [16] Zaruba Q. Landslides And Their Control: Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences[M]. Elsevier, 1969. [17] 黄波林, 陈小婷, 刘广宁, 等.巫山县望霞乡桐心村危岩体变形破坏机制分析[J].工程地质学报, 2008, 16(4):459~464. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200804003.htmHUANG Bo-lin, CHEN Xiao-ting, LIU Guang-ning, et al. Failure mode analysis of dangerous rockmass slope at Tongxin Village in Wangxia Town of Wushan County[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2008, 16(4): 459~464. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200804003.htm [18] Magri O, Mantovani M, Pasuto A, et al. Geomorphological investigation and monitoring of lateral spreading along the north-west coast of Malta[J]. Geografia Fisica e Dinamica Quaternaria, 2008, 31(2): 171~180. [19] Benedetti G, Bernardi M, Bonaga G, et al. San Leo: Centuries of Coexistence with Landslides[M]//Landslide Science and Practice. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2013: 529~537. [20] Di Maggio C, Madonia G, Vattano M. Deep-seated gravitational slope deformations in western Sicily: Controlling factors, triggering mechanisms, and morphoevolutionary models[J]. Geomorphology, 2014, 208(1): 173~189. [21] 乐琪浪, 王洪德, 薛星桥, 等.巫山县望霞危岩体变形监测及破坏机制分析[J].工程地质学报, 2011, (6):823~830. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201106004.htmLE Qi-lang, WANG Hong-de, XUE Xing-qiao, et al. Deformation monitoring and failure mechanism of Wangxia dangerous rock mass in Wushan County[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2011, (6): 823~830. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201106004.htm [22] Pells P J N. Assessing Parameters for Computations in Rock Mechanics[C]//Potvin Y, Carter J, Dyskin A, et al. SHIRMS 2008(1), Western Australia: Australian Centre for Geomechanics, 2008: 39~54. [23] Glastonbury J, Fell R. Report on the analysis of "rapid" natural rock slope failures[R]. Uniciv Reoprt No. R-390. Sydney:The University of New South Walws, 2000. [24] 谢全敏, 刘雄.危岩体柔性网络锁固治理研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2000, 19(5):640~642. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200005024.htmXIE Quan-min, LIU Xiong. Locking reinforcement of dangerous rocks with flexible network[J]. Chinses Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2000, 19(5): 640~642. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200005024.htm [25] Douglas K J. The shear strength of rock masses[D]. Sydney:The University of New South Wales, 2002. [26] Frayssines M, Hantz D. Failure mechanisms and triggering factors in calcareous cliffs of the Subalpine Ranges (French Alps)[J]. Engineering Geology, 2006, 86(4): 256~270. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2006.05.009 [27] Frayssines M, Hantz D. Modelling and back-analysing failures in steep limestone cliffs[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2009, 46(7): 1115~1123. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2009.06.003 [28] Deparis J, Garambois S, Hantz D. On the potential of Ground Penetrating Radar to help rock fall hazard assessment: A case study of a limestone slab, Gorges de la Bourne (French Alps)[J]. Engineering Geology, 2007, 94(1): 89~102. [29] 任幼蓉, 陈鹏, 张军, 等.重庆南川市甑子岩W12#危岩崩塌预警分析[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2005, 16(2):28~31, 37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200502006.htmREN You-rong, CHEN Peng, ZHANG Jun, et al. Early-warning analysis on the rockfall for Zengziyan W12# dangeous rock mass in Nanchuan City of Chongqing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hzard and Control, 2005, 16(2): 28~31, 37. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200502006.htm [30] 陈智强, 李渝生.重庆市南川甑子岩危岩形成演化机制分析及防治措施探讨[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2004, 15(2):78~81. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200401017.htmCHEN Zhi-qiang, LI Yu-sheng. Analysis on formation and development mechanism and discussion on prevention measures for Zengziyan dangerous rock mass in Chongqing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hzard and Control, 2004, 15(2): 78~81. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200401017.htm -





 下载:
下载: