A STUDY ON FAULT STRESS CHARACTERISTICS AND THE LAW OF OIL AND GAS CONTROLLING BY FAULT DEFLECTING: A CASE STUDY OF THE NANPU DEPRESSION
-
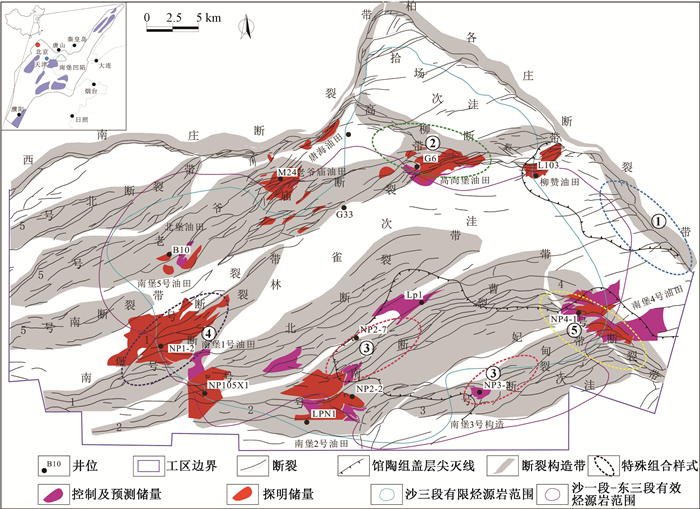
摘要: 为了分析断裂对油气宏观分布规律的控制作用,寻找有勘探潜力的油气富集带,文中以地质力学理论为指导,对南堡凹陷断裂组合应力特征、断裂转折及成因进行解析,并结合砂体分布和古今构造应力场分布特征,对南堡凹陷东营组油气分布规律和有利勘探区带做了研究。结果表明:断裂转折部位对油气分布有着控制作用,东营组已探明的油气主要在帚状断裂系、入字形断裂系、交织式断裂系转折轴部高曲率附近呈环带状分布;断裂转折凹面一侧控油性明显,从宏观上来看,油气具有沿沉积相带由细到粗的构造脊高点以及弧形断裂转折凹面一侧的选择性运移的特征,断裂转折轴部高曲率高孔、高渗域与高孔、高渗砂体沉积相带的有利对置决定了油气的主流向;综合研究指出,南堡凹陷北堡构造带是今后优势勘探的首要区带,其次是南堡构造带和南堡4号蛤坨构造带南部。Abstract: In order to find out the control effects of faults on the macroscopic distribution of oil and gas and look for the oil and gas accumulation zones with exploration potential, taking the geomechanics theory as a guide, the combined stress characteristics of faults, the fault deflecting and the causes in the Nanpu Depression are analyzed, and the oil and gas distribution law and favorable exploration zones in Dongying formation of the Nanpu Depression are studied combined with the characteristics of sand body distribution and ancient and modern tectonic stress field distribution. The results show that the fault deflecting controls the distribution of oil and gas, and the proven oil and gas in Dongying formation mainly shows a circular band distribution near the high curvature of the deflecting shaft of the broom-shaped fault system, the λ-type fault system and the interlaced-type fault system. The oil-controlling property on the concave side of the fault deflecting is obvious. Macroscopically, the oil and gas has the characteristics of selective migration along the sedimentary facies belt from fine to thick tectonic ridge highs and on the concave side of arc fault deflecting. The main direction of the oil and gas is determined by the favorable alignment of high curvature and high porosity, high permeability domain and high porosity, and high permeability sand body sedimentary facies zone in the fault deflecting shaft. The comprehensive study indicates that the Beibu structural belt in the Nanpu Depression is the primary zone for superior exploration in the future, followed by the Nanpu structural belt and the south of the Nanpu No.4 Getuo structural belt.
-
表 1 南堡凹陷断裂平面组合模式
Table 1. Composite pattern of fault planes in the Nanpu Depression

表 2 部分已知油藏周围有利井位位置
Table 2. Favorable location of well around part of the known oil reservoirs
已知油藏 有利位置 已知油藏 有利位置 已知油藏 有利位置 NP4-2 南部 NP1-88 北东部 M10x1 北部 NP4-57 北西部 NP1-90 北东部 M10 西南部 NP401x3 北西部 NP1 北东部 G5 北部 NP4-55 西部 NP1-4 西南部 G10 西部 NP3-2 西部 NP5-10 北部 G29-6 西部 NP3-19CZ 西部 NP503 西北部 L10 东部 NP286 南部 M2 南部 L68-1 东北部 NP288 东部 M36 南部 B22x1 北部 NP2-82 西南部 G23 西部 M16x1 西北部 -
[1] 丛良滋, 周海民.南堡凹陷主动裂谷多幕拉张与油气关系[J].石油天然气地质, 1998, 19(4):296~301. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=3324401CONG Liangzi, ZHOU Haiming. Polyphase pulls and aparts of active rift in Nanpu depression and their relationship with oil and gas[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1998, 19(4):296~301. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=3324401 [2] 李海丽.南堡凹陷断裂系统及对中浅层油气控藏作用研究[D].大庆: 东北石油大学, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10220-1013290078.htmLI Haili. Study of fault system and their control effects on hydrocarbon accumulation in the shallow Nanpu Sag[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10220-1013290078.htm [3] 李宏义, 姜振学, 董月霞, 等.渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷断层对油气运聚的控制作用[J].现代地质, 2010, 24(8):755~761. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xddz201004015LI Hongyi, JIANG Zhengxue, DONG Yuexia, et al. Control of faults on hydrocarbon migration and accumulation in Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2010, 24(8):755~761. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xddz201004015 [4] 万涛, 蒋有录, 董月霞, 等.南堡凹陷断层活动与油气成藏和富集的关系[J].中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 36(2):60~67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2012.02.010WAN Tao, JIANG Youlu, DONG Yuexia, et al. Relationship between fault activity and hydrocarbon accumulation and enrichment in Nanpu depression[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2012, 36(2):60~67. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2012.02.010 [5] 张华文, 周江羽, 刘德志, 等.南堡凹陷4号构造带蛤坨断层特征与油气成藏关系[J].海洋石油, 2010, 30(2):14~18, 22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2010.02.014ZHANG Huawen, ZHOU Jiangyu, LIU Dezhi. The relationship between Getuo fault and hydrocarbon accumulation in the 4th structural belt of Nanpu Depression[J]. Offshore Oil, 2010, 30(2):14~18, 22. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2010.02.014 [6] 吕延防, 韦丹宁, 孙永河, 等.南堡凹陷断层对中、上部含油组合油气成藏的控制作用[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015, 45(4):971~982. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201504001LÜ Yanfang, WEI Danning, SUN Yonghe, et al. Control action of faults on hydrocarbon migration and accumulation in the middle and upper oil-bearing group in Nanpu Sag[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2015, 45(4):971~982. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201504001 [7] 孙永河, 赵博, 董月霞, 等.南堡凹陷断裂对油气运聚成藏的控制作用[J].石油与天然气地质, 2013, 34(4):540~549. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syytrqdz201304018SUN Yonghe, ZHAO Bo, DONG Yuexia, et al. Control of faults on hydrocarbon migration and accumulation in the Nanpu Sag[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2013, 34(4):540~549. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syytrqdz201304018 [8] 李琦, 田景春, 何建军, 等.河流相砂体的沉积微相特征——以济阳坳陷埕东北坡馆陶组砂体为例[J].岩相古地理, 1999, 19(1):25~31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.1999.01.004LI Qi, TIAN Jingchun, HE Jianjun, et al. Sedimentary microfacies of the fluvial sandstones:an example from the sandstones in the Guantao formation on the northern slope of the Chengdong oilfield in the Jiyang depression, Eastern China[J]. Sedimentary Facies and Palaeogeography, 1999, 19(1):25~31. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.1999.01.004 [9] 罗群, 黄捍东, 王保华, 等.低序级断层的成因类型特征与地质意义[J].油气地质与采收率, 2007, 14(3):19~21, 25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2007.03.006LUO Qun, HUANG Handong, WANG Baohua, et al. Genetic types of low-grade faults and their geologic significance[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2007, 14(3):19~21, 25. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2007.03.006 [10] 熊永旭, 张福礼.入字型构造与油气[J].石油与天然气地质, 1981, 2(1):11~17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT198101001.htmXIONG Yongxu, ZHANG Fuli. On the relation of λ-type structure to oil and gas migration and accumlation[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1981, 2(1):11~17. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT198101001.htm [11] 刘泽容, 王孝陵, 吴乃苓, 等.帚状构造体系形成机制及其控油规律[J].华东石油学院学报, 1982, (3):1~13. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=SYDX198203000&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQLIU Zerong, WANG Xiaoling, WU Nailing, et al. Formation of brush structure system and its control upon hydrocarbon habitat[J]. Journal of East China Petroleum Institute, 1982, (3):1~13. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=SYDX198203000&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [12] 周海民, 魏忠文, 曹中宏, 等.南堡凹陷的形成演化与油气的关系[J].石油与天然气地质, 2000, 21(4):345~349. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2000.04.015ZHOU Haimin, WEI Zhongwen, CAO Zhonghong, et al. Relationship between formation, evolution and hydrocarbon in Nanpu sag[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2000, 21(4):345~349. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2000.04.015 [13] 周海民, 从良滋.浅析断陷盆地多幕拉张与油气的关系——以南堡凹陷的多幕裂陷作用为例[J].地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 1999, 24(6):625~629. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.1999.06.014ZHOU Haimin, CONG Liangzi. Polyphase extension and its impact on hydrocarbon accumulation in fault basin-case analysis of polyphase rifting in Nanpu depression[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1999, 24(6):625~629. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.1999.06.014 [14] 马乾, 张军勇, 李建林, 等.南堡凹陷扭动构造特征及其对油气成藏的控制作用[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2001, 35(2):183~189. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201102002MA Qian, ZHANG Junyong, LI Jianlin, et al. Characteristics of the shear structures in nanpu sag and their controls on hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2001, 35(2):183~189. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201102002 [15] Despaigne-Díaz A I, Casco A G, Govea D C, et al. Structure and tectonic evolution of the southwestern Trinidad dome, Escambray complex, Central Cuba:Insights into deformation in an accretionary wedge[J]. Tectonophysics, 2017, 717:139~161. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2017.07.024 [16] Vannoli P, Bernardi F, Palombo B, et al. New constraints shed light on strike-slip faulting beneath the southern Apennines (Italy):The 21 August 1962 Irpinia multiple earthquake[J]. Tectonophysics, 2016, 691:375~384. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.10.032 [17] Lekkas E L, Mavroulis S D. Fault zones ruptured during the early 2014 Cephalonia Island (Ionian Sea, Western Greece) earthquakes (January 26 and February 3, Mw 6. 0) based on the associated co-seismic surface ruptures[J]. Journal of Seismology, 2016, 20(1):63~78. doi: 10.1007/s10950-015-9510-3 [18] Arfaoui A, Soumaya A, Ben Ayed N, et al. Role of N-S strike-slip faulting in structuring of north-eastern Tunisia; geodynamic implications[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2017, 129:403~416. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.01.013 [19] Doǧan B, Tüysüz O, Şanlı F B. Tectonostratigraphic evolution of the basins on the southern branch of the North Anatolian fault system in the SE Marmara region, Turkey[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2015, 104(2):389~418. doi: 10.1007/s00531-014-1083-9 [20] Aşcı M, Doǧanan B, Yas T, et al. Determination of the deep fault geometry along the southern branch of the North Anatolian Fault System by using resistivity and magnetic methods[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 125:117~137. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.05.020 [21] Biegel R L, Sammis C G, Rosakis A J. Interaction of a dynamic rupture on a fault plane with short frictionless fault branches[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 2007, 164(10):1881~1904. doi: 10.1007/s00024-007-0251-2 [22] 李四光.地质力学概论[M].北京:科学出版社, 1973:6~84.LI Siguang. Geological mechanics theory[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1973. (in Chinese) [23] 刘泽容, 李德同.浅谈覆盖区结构面的鉴定[M].地质力学文集, 1979.LIU Zerong, LI Detong. Discussion on the identification of the structural surface of the cover area[M]. Anthology of Geomechanics, 1979. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] 王连捷, 范雪玲.旋卷构造应力场之有限元分析[M].地质力学文集, 1979.WANG Lianjie, FAN Xueling. Finite element analysis of the stress field of spiral structure[M]. Anthology of Geomechanics, 1979. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] 陈子光.岩石力学性质与构造应力场[M].北京:地质出版社, 1986:108~137.CHEN Ziguang. Rock mechanical properties and tectonic stress field[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1986:108~137. (in Chinese) [26] 张寿庭, 李忠权.断裂转折及其控矿特征[J].矿物岩石, 1998, 18(2):85~89. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS802.015.htmZHANG Shouting, LI Zhongquan. Fault deflecting and its ore-controlling characteristics[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 1998, 18(2):85~89. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS802.015.htm [27] 叶洪, 马瑾, 汪一鹏, 等.从破裂模拟实验探讨破坏性地震发震条件的一些初步成果[J].地质科学, 1973, (1):48~55. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=DZKX197301003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQYE Hong, MA Jin, WANG Yipeng, et al. from fracture modeling test study destructive earthquake conditions of some features[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1973, (1):48~55. (in Chinese) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=DZKX197301003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [28] 徐安娜, 郑红菊, 董月霞, 等.南堡凹陷东营组层序地层格架及沉积相预测[J].石油勘探与开发, 2006, 33(4):437~443. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.04.009XU Anna, ZHENG Hongju, DONG Yuexia, et al. Sequence stratigraphic framework and sedimentary facies prediction in Dongying Formation of Nanpu Sag[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2006, 33(4):437~443. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.04.009 [29] 刘德志, 周江羽, 马良, 等.渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷断裂控藏特征研究[J].海洋石油, 2009, 29(4):19~25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2009.04.019LIU Dezhi, ZHOU Jiangyu, MA Liang, et al. Study on the features of fault controlling pool in Nanpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Offshore Oil, 2009, 29(4):19~25. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2009.04.019 [30] 李振宏, 贾建恒.浅析断裂活动与油气运聚的时空配置关系[J].特种油气藏, 2004, 11(3):9~11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2004.03.003LI Zhenghong, JIA Jianheng. Time-space relation of faulting movement and hydrocarbon migration[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2004, 11(3):9~11. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2004.03.003 [31] 晋香兰.南堡凹陷构造应力场模拟与油气运聚分析[A].中国地质学会、中国煤炭学会煤田地质专业委员会暨中国煤炭工业劳动保护科学技术学会水害防治专业委员会学术年会论文汇编[C].北京: 中国地质学会, 中国煤炭学会, 中国煤炭工业劳动保护科学技术学会, 2007: 84~88.JIN Xianglan. Nanpu sag tectonic should force field s84imulation and analysis of petroleum migration and accumulation[A]. Safe and efficient mine geological guarantee technologies and applications, 2007: 84~88. [32] 邓俊国, 王贤.南堡凹陷构造应力场演化史与油气聚集[J].保定师专学报, 1999, 12(2):72~77. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BDSZ199902017.htmDENG Junguo, WANG Xian. The Evolution history on the tectonic stress field and the oil-gas accumulation[J]. Journal of Baoding Teachers College, 1999, 12(2):72~77. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BDSZ199902017.htm -





 下载:
下载: