Structural analysis and ore-controlling model of the Xiaohe lead-zinc deposit in ore-concentrated area, northeastern Yunnan, China
-
摘要: 小河铅锌矿是滇东北铅锌矿集区内少数几个由北西向主断裂控制的典型铅锌矿床之一,矿化蚀变的空间展布严格受构造控制。为查明其区内构造对矿化蚀变的控制作用特征,通过不同中段大比例尺构造-蚀变岩相学填图,对不同方向构造进行筛分,并对不同中段不同矿(化)体特征和蚀变特征开展了系统的剖析,结果表明:小河铅锌矿床矿化蚀变的岩石组成、类型及结构等相对简单,围岩蚀变以热液白云石化、方解石化、硅化和黄铁矿化为主;矿化主要为闪锌矿化、方铅矿化;该区构造组合形迹反映矿区内存在6期构造体系,分别为加里东期-海西期、印支早-中期、印支晚期-燕山早期、燕山中期、燕山晚期和喜马拉雅期;印支晚期-燕山早期成矿流体沿区内北西向张性-张扭性构造发生大规模运移,在断裂上盘及与之配套的次级断裂、构造破碎带、节理裂隙等构造有利部位成矿,并依次形成以断裂为中心且平面上呈带状展布的矿化蚀变分带:矿化边缘带(Ⅰ)→矿化过渡带(Ⅱ)→矿化中心带(Ⅲ)。最终建立了小河铅锌矿床构造控矿模式。研究成果对同类矿床及川滇黔接壤区的找矿预测具有重要指导意义。Abstract: The Xiaohe lead-zinc deposit is one of the few typical lead-zinc deposits controlled by NW-trending major faults in the ore-concentrated area in northeastern Yunnan,China. The spatial distribution of mineralization and alteration is strictly controlled by structures. In order to ascertain the characteristics of the controlling effect of the structures on mineralization and alteration in this area,the large-scale tectonic-altered lithofacies mapping method in different level adits is adopted. The faults in different directions were screened and the characteristics of different mineralization and alteration in different level adits were systematically analyzed. The results show that:the composition,type and structure of mineralization and alteration of the Xiaohe lead-zinc deposit are relatively simple. Wall rock alteration is dominated by hydrothermal dolomitization,calcilization,silicification and pyritization. The mineralization mainly occurs to sphalerite and galena. Tectonic assemblages reflect the existence of a 6-phase tectonic system in the mining area:Caledonian-Haixi period,Early-Mid-Indosinian period,Late-Indosinian period to Early-Yanshan period,Middle Yanshan period,Late Yanshan period and Himalayan period. Large scale migration of ore-forming fluid occurred along the NW direction of tensile or torsional faults in the late Late-Indosinian and Early-Yanshan. Meneralization occurs in favorable structural parts such as the upper wall of the faults and its supporting secondary faults,structural fracture zones,joint fractures,etc. The mineralization-alteration zone was formed with the fault as the center and was distributed with zone. The sequence is mineralized marginal zone (Ⅰ),mineralized transition zone (Ⅱ) to mineralized central zone (Ⅲ). Finally,the structure-controlling model of the Xiaohe lead-zinc deposit was established. This understanding has important guiding significance for the prospecting prediction of similar deposits and the border area between Sichuan,Yunnan and Guizhou province.
-
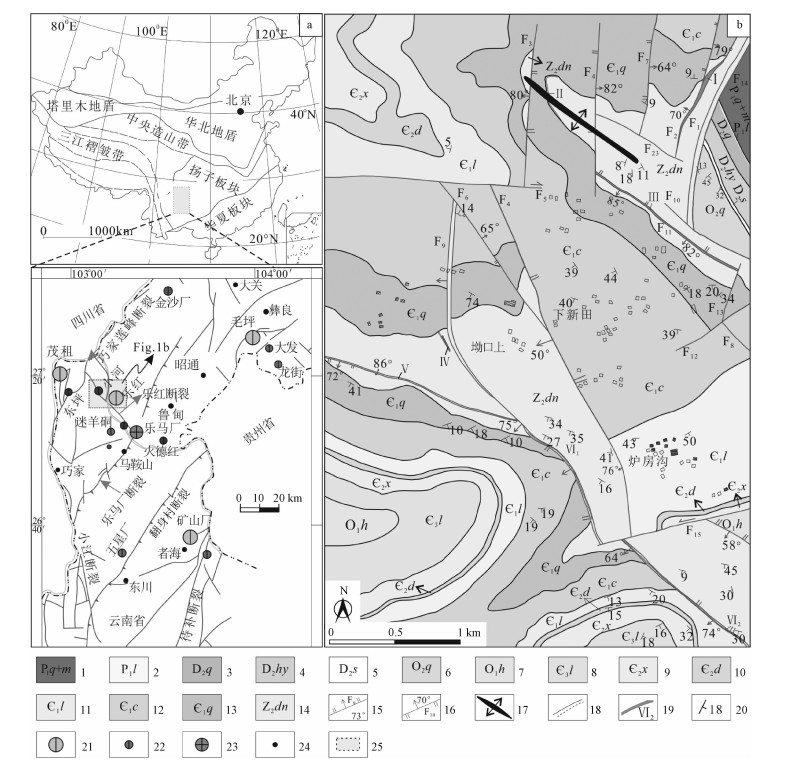
图 1 滇东北小河铅锌矿区地质简图
1-下二叠统栖霞茅口组;2-下二叠统梁山组;3-中泥盆统曲靖组;4-中泥盆统红石崖组;5-上奥陶统缩头山组;6-中奥陶统上巧家组;7-下奥陶统红石崖组;8-上寒武统龙头山组;9-中寒武统西王庙组;10-中寒武统陡坡寺组;11-下寒武统龙王庙组;12-下寒武统沧浪铺组;13-下寒武统筇竹寺组;14-上震旦统灯影组;15-逆断层;16-正断层;17-背斜;18-地质界线;19-矿体及编号;20-地层产状;21-大型铅锌矿床;22-中小型铅锌矿床;23-大型银矿床;24-市县;25-研究区a-区域构造和矿集区位置(据韩润生等,2014修改);b-小河铅锌矿区地质简况(据云南省煤田地质局昆明工程勘察公司,2010修改)
Figure 1. Geological sketch map of the Xiaohe Pb-Zn deposit
图 9 小河铅锌矿床近南北向断裂素描及力学性质分析图
Py-黄铁矿;Gn-方铅矿;Sp-闪锌矿a-F4断裂素描图及照片:①-灰色白云质碎裂岩;②-白云质构造角砾岩,被灰色、黄褐色泥质物胶结;③-黄褐色构造角砾岩;④-第四系堆积物b-f5与f6断裂素描图及照片:①-灰黑色细晶白云岩,具黄铁矿化、铅锌矿化;②-片理化带; σ1-压应力;σ2-剪应力;σ3-张应力
Figure 9. Profile sketch mapping and mechanical properties analysis of the near SN-trending faults in the Xiaohe Pb-Zn deposit
图 11 小河铅锌矿床构造体系及其演化图解(据崔俊豪等,2018修改)
1-压性断层;2-张性断层;3-扭性断层;4-压扭性断层;5-扭压性断层;6-张扭性断层;7-褶皱
Figure 11. Plots showing the tectonic system and evolution of the Xiaohe Pb-Zn deposit (modified after Cui et al, 2018)
表 1 小河铅锌矿床成矿阶段划分及矿物生成顺序
Table 1. Paragenetic sequence of minerals in the Xiaohe Pb-Zn deposit

-
CHEN X H, CHEN Z L, YANG N, 2009. Study on regional mineralizations and ore-field structures:building of mineralizing tectonic systems[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 15(1):1-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN Z L, YANG N, WANG P A, et al., 2011. Analysis of the tectonic stress field in the Xiangshan uranium ore field, Linchuan area, Jiangxi, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(4):514-531. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201104008 CUI J H, HAN R S, WANG J S, et al., 2018. Generation and Development of Structures and Their Controls on Ore Mineralization in the Lehong Zinc-lead Deposit, Northeastern Yunnan[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 42(4):664-680. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201804007 DENG J, WANG C M, LI W C, et al., 2014. The situation and enlightenment of the research of the tectonic evolution and metallogenesis in the Sanjiang Tethys[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(1):52-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201401006 HAN K, 2019. Application of the structure-alteration lithofacies mapping method in ore prospecting:An example of the Huanglong gold deposit in Hanyin, South Qinling[J]. Geology and Exploration, 55(4):939-954. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZKT201904005.htm HAN R S, CHEN J, HUANG Z L, et al., 2006. Dynamics of tectonic ore-forming processes and localization-prognosis of concealed orebodies:As exemplified by the Huize super-large Zn-Pb-(Ag-Ge) district, Yunnan[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) HAN R S, LIU C Q, HUANG Z L, et al., 2007. Geological features and origin of the Huize carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb-(Ag) district, Yunnan, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 31(1-4):360-383. doi: 10.1016-j.oregeorev.2006.03.003/ HAN R S, ZOU H J, HU B, et al., 2007. Features of fluid inclusions and sources of ore-forming fluid in the Maoping carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb-(Ag-Ge) deposit, Yunnan, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(9):2109-2118. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200709010 HAN R S, LIU C Q, CARRANZA E J M, et al., 2012. REE geochemistry of altered tectonites in the huize base-metal district, Yunnan, China[J]. Geochemistry:Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 12(2):127-146. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c74383dd02ccde1c345cf4661a279afe HAN R S, HU Y Z, WANG X K, et al., 2012. Mineralization model of rich Ge-Ag-bearing Zn-Pb polymetallic deposit concentrated district in northeastern Yunnan, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(2):280-294. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201202007 HAN R S, WANG F, HU Y Z, et al., 2014. Metallogenic tectonic dynamics and chronology constrains on the Huize-type (HZT) Germanium-rich silver-zinc-lead deposits[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 38(4):758-768. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201404003 HAN R S, LI B, NI P, et al., 2016. Infrared micro-thermometry of fluid inclusion in sphalerite and geological sigificance of Huize super-large Zn-Pb-(Ge-Ag) deposit, Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition). 38(4):758-768. (in Chinese with English abstract) He S H, Rong H F, Shang W, et al., 2006. Geological characterisitcs and genesis of Maozu lead and zinc deposit, Yunnan[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology. 20(4-5):397-402. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcydz200604013 HU Y G, 2000. Occurrence of silver, sources of mineralized substances and ore-forming mechanism of Yinchangpo silver polymetallic deposit, Guizhou Province, China[D]. Guiyang: Institute of Geochemistry Chinese Academy of Sciences: 1-88. (in Chinese) HUANG Z L, CHEN J, LIU C Q, et al., 2001. A preliminary discussion on the genetic relationship between Emeishan basalts and Pb-Zn deposits as exemplified by the Huize Pb-Zn deposit, Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 21(4):681-688. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwxb200104019 Kunming Engineering Survey Company of Yunnan Coalfield Geology Bureau, 2010. Verification Report of Mineral Reserves of Xiaohe Lead-Zinc Mine in Ludian County, Yunnan Province[R]. 5-75. (in Chinese) LI B, HAN R S, WEN S M, et al., 2014. Structural characteristics and fault tectono-geochemistry of the Songliang lead-zinc deposit in Northeast Yunnan, China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 38(4):855-865. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201404011 LI W B, HUANG Z L, ZHANG G, 2006. Sources of the ore metals of the Huize ore field in Yunnan Province:Constraints from Pb, S, C, H, O and Sr isotope geochemistry[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(10):2567-2580. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB200610017.htm LIU H C, LIN W D, 1999. Regularity research of Ag-Zn-Pb ore deposits North-East Yunnan Province[M]. Kunming:Yunnan University Press, 1-468. (in Chinese with English abstract) L? G X, 2019. Research on tectonic dynamo-petrogenesis and metallogenesis and tectonophysicochemistry[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(5):962-980. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlxxb201905024 MAO J W, ZHOU Z H, FENG C Y, et al., 2012. A preliminary study of the Triassic large-scale mineralization in China and its geodynamic setting[J]. Geology in China, 39(6):1437-1471. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201206001 REN T, ZHOU J X, WANG D, et al., 2019. Trace elemental and S-Pb isotopic geochemistry of the Fule Pb-Zn deposit, NE Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(11):3493-3505. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201911015 SHI Y B, YAN C M, CHEN S H, et al., 2019. Geology of mineral resources of Yunnan Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-515. (in Chinese) TANG Z, LI W C, WANG C B, et al., 2016. Geochemical characteristics of primary halo and prospecting of Lehong Pb-Zn deposit in northeastern Yunnan[J]. Mineral Exploration, 7(4):657-666. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ytgcj201604020 WANG J Z, LI Z Q, NI S J, 2003. Origin of ore-forming fluids of Mississippi Valley-Type (MVT) Pb-Zn deposits in Kangdian area, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 22(4):369-376. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdqhx-e200304010 WU Y T, HAN R S, REN T, et al., 2017. REE geochemistry of fluorite from Maozu Pb-Zn deposit and its geological implications, Northeastern Yunnan, China[J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 35(3):403-412. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgxtxb201703013 YU J, 2012. Progress and prospect in the study of ore field structure based on geomechanics theroy[J]. Geology and Exploration, 48(1):102-109. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzykt201201012 ZHANG C Q, MAO J W, WU S P, et al., 2005. Distribution, characteristics and genesis of Mississippi Valley-Type lead-zinc deposits in Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou area[J]. Mineral Deposits, 24(3):336-350. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcdz200503013 ZHANG C Q, WU Y, HOU L, et al., 2015. Geodynamic setting of mineralization of Mississippi Valley-type deposits in world-class Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou Zn-Pb triangle, southwest China:Implications from age-dating studies in the past decade and the Sm-Nd age of Jinshachang deposit[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 103:103-114. ZHANG Y X, WU Y, TIAN G, et al., 2014. Mineralization age and the source of ore-forming material at Lehong Pb-Zn deposit, Yunnan Province:Constraints from Rb-Sr and S isotopes system[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 34(3):305-311. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwxb201403002 ZHAO D, HAN R S, REN T, et al., 2016. The mineralization and alteration zoning of the Le-hong lead zinc deposit, the large deposit concentration area in the Northeast of Yunnan Province, China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 35(6):1258-1269. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwysdqhxtb201606017 ZHAO D, HAN R S, WANG J S, et al., 2017. REE Geochemical Characteristics in Lehong Large Lead-Zinc Deposit, Northeastern Yunnan Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 37(5):588-595. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201705009.htm ZHOU J X, HUANG Z L, GAO J G, et al., 2012. Sources of ore-forming metals and fluids, and mechanism of mineralization, Maozu large carbonate-hosted lead-zinc deposit, northeast Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Mineralogy & Petrology, 32(3):62-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/288131531_Sources_of_Ore-forming_metals_and_fluids_and_mechanism_of_mineralizationmaozu_large_carbonare-hosted_Lead-znic_deposit_Northeast_Yunnan_Province ZHOU J X, HUANG Z L, YAN Z F, 2013. The origin of the Maozu carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit, southwest China:Constrained by C-O-S-Pb isotopic compositions and Sm-Nd isotopic age[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 73:39-47. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912013002411 ZHOU Y M, 2001. Characteristics and ore-controlling role of the thrusting nappe structure in the Lemachang silver deposit[J]. Mineral Deposits, 20(3):271-278. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcdz200103011 ZHOU Y M, 2003. Geological characteristics of the Lehong lead-zinc deposit in Northeastern Yunnan and its orr-search prospects[J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 31(4):16-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200304003.htm 陈宣华, 陈正乐, 杨农, 2009.区域成矿与矿田构造研究:构建成矿构造体系[J].地质力学学报, 15(1):1-19. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20090101&journal_id=dzlxxb 陈正乐, 杨农, 王平安, 等, 2011.江西临川地区相山铀矿田构造应力场分析[J].地质通报, 30(4):514-531. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz201104008 崔峻豪, 韩润生, 王加昇, 等, 2018.滇东北乐红铅锌矿床构造成生发展及其控矿作用[J].大地构造与成矿学, 42(4):664-680. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201804007 邓军, 王长明, 李文昌, 等, 2014.三江特提斯复合造山与成矿作用研究态势及启示[J].地学前缘, 21(1):52-64. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201401006 韩珂, 2019.构造-蚀变岩相填图方法在南秦岭汉阴黄龙金矿中的应用[J].地质与勘探, 55(4):939-954. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzykt201904005 韩润生, 陈进, 黄智龙, 等, 2006.构造成矿动力学及隐伏矿定位预测:以云南会泽超大型铅锌(银、锗)矿床为例[M].北京:科学出版社, 1-79. 韩润生, 邹海俊, 胡彬, 等, 2007.云南毛坪铅锌(银、锗)矿床流体包裹体特征及成矿流体来源[J].岩石学报, 23(9):2109-2118. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200709010 韩润生, 胡煜昭, 王学琨, 等, 2012.滇东北富锗银铅锌多金属矿集区矿床模型[J].地质学报, 86(2):280-294. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201202007 韩润生, 王峰, 胡煜昭, 等, 2014.会泽型(HZT)富锗银铅锌矿床成矿构造动力学研究及年代学约束[J].大地构造与成矿学, 38(4):758-771. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201404003 韩润生, 李波, 倪培, 等. 2016.闪锌矿流体包裹体显微红外测温及其矿床成因意义:以云南会泽超大型富锗银铅锌矿床为例[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 46(1):91-104. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201601010 贺胜辉, 荣惠锋, 尚卫, 等. 2006.云南茂租铅-锌矿床地质特征及成因研究[J].矿产与地质, 20(4-5):397-402. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcydz200604013 胡耀国, 2000.贵州银厂坡银多金属矿床银的赋存状态、成矿物质来源与成矿机制[D].贵阳: 中国科学院地球化学研究所: 1-88. 黄智龙, 陈进, 刘丛强, 等, 2001.峨眉山玄武岩与铅锌矿床成矿关系初探:以云南会泽铅锌矿床为例[J].矿物学报, 21(4):681-688. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwxb200104019 云南省煤田地质局昆明工程勘察公司, 2010.云南省鲁甸县小河铅锌矿核查矿区资源储量核查报告[R]. 5-75. 李波, 韩润生, 文书明, 等, 2014.滇东北巧家松梁铅锌矿床构造特征及构造地球化学[J].大地构造与成矿学, 38(4):855-865. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201404011 柳贺昌, 林文达, 1999.滇东北铅锌银矿床规律研究[M].昆明:云南大学出版社, 1-468. 吕古贤, 2019.构造动力成岩成矿和构造物理化学研究[J].地质力学学报, 25(5):962-980. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190523&journal_id=dzlxxb 李文博, 黄智龙, 张光, 等. 2006.云南会泽铅锌矿田成矿物质来源:Pb、S、C、H、O、Sr同位素制约[J].岩石学报, 22(10):2567-2580. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200610018 毛景文, 周振华, 丰成友, 等, 2012.初论中国三叠纪大规模成矿作用及其动力学背景[J].中国地质, 39(6):1437-1471. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201206001 任涛, 周家喜, 王蝶, 等, 2019.滇东北富乐铅锌矿床微量元素和S-Pb同位素地球化学研究[J].岩石学报, 35(11):3493-3505. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201911015 唐忠, 李文昌, 王长兵, 等, 2016.滇东北乐红铅锌矿原生晕特征及深部找矿预测[J].矿产勘查, 7(4):657-666. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcj201604020 吴永涛, 韩润生, 任涛, 等, 2017.滇东北矿集区茂租铅锌矿床萤石的稀土元素特征及其指示意义[J].中国稀土学报, 35(3):403-412. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgxtxb201703013 余佳. 2012.地质力学矿田构造的进展与前景[J].地质与勘探, 48(1):102-109. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzykt201201012 张长青, 毛景文, 吴锁平, 等, 2005.川滇黔地区MVT铅锌矿床分布、特征及成因[J].矿床地质, 24(3):336-350. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz200503013 张云新, 吴越, 田广, 等, 2014.云南乐红铅锌矿床成矿时代与成矿物质来源:Rb-Sr和S同位素制约[J].矿物学报, 34(3):305-311. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwxb201403002 赵冻, 韩润生, 任涛, 等, 2016.滇东北大型矿集区乐红大型铅锌矿床矿化蚀变分带模式[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 35(6):1258-1269. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwysdqhxtb201606017 赵冻, 韩润生, 王加昇, 等, 2017.滇东北乐红大型铅锌矿床稀土元素地球化学特征[J].矿物学报, 37(5):588-595. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95783X/20175/673768038.html 周家喜, 黄智龙, 高建国, 等, 2012.滇东北茂租大型铅锌矿床成矿物质来源及成矿机制[J].矿物岩石, 32(3):62-69. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwys201203009 周云满, 2001.乐马厂银矿逆冲推覆构造特征及控矿作用[J].矿床地质, 20(3):271-278. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz200103011 周云满, 2003.滇东北乐红铅锌矿床地质特征及找矿远景[J].地质地球化学, 31(4):16-21. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzdqhx200304003 -





 下载:
下载: